Questões de Vestibular de Inglês
Foram encontradas 5.955 questões









Read the graph below and answer the following question.
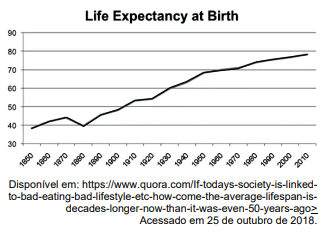
According to the graph above we can assert that
Read the graph below and answer the following question.
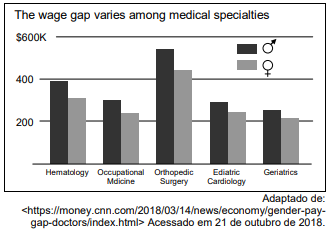
According to the graph above it is true to assert that
Read the text below and answer the following question.
Can Cellular Agriculture Feed the World?
Within 20 years, there will be 2 billion more people than today — over 9 billion people in total. The impact to the environment could be severe. Just feeding that population using current methods is problematic.
On average, cattle ranchers need 100 times more land than corn growers to produce a gram of food. So, if that hungry world continues to eat meat like we do, the demand for land — and fresh water — will be alarming, not to mention the environmental impact of raising so many animals. Meat production aside, the large-scale monoculture of crops like corn usually results in damaging terrestrial pollution from pesticides and soil depletion. The impact to the oceans is equally perilous.
Instead of farming animals, fish and plants, cellular agriculture grows the proteins and nutrients we consume from a culture, cell by cell. With this alternative approach, the consumable meat and plant tissues produced don’t need to be harvested from animals or plants. It’s food production on an industrial scale.
The technology to do this is not new. Growing meat from a scaffold embedded in growth culture is no different in theory than making bread from yeast. The vast majority of insulin for diabetics is already manufactured by genetically engineered bacteria, as is the rennet used to culture cheese. In the past 10 years, this approach has been pioneered with a variety of foodstuffs: milk, eggs, beef, chicken, fish — even coffee.
To succeed, cellular agriculture must overcome 6,000 years of established dependence on traditional agriculture, and it has to do so via one of the most finicky human senses: taste. No one will eat manufactured meat or fish if it doesn’t have the same sensual satisfaction generated by the grown version. So, in addition to all the technical challenges in creating edible tissues from cultures, the startups pioneering this approach are working diligently to make their products tasty.
The possibilities for cellular agriculture are seemingly limitless; it may be possible to grow human organs for transplant using the method. But it is still early days.
Adaptado de: <https://earth911.com/business-policy/cellular-agriculture/>
Read the text below and answer the following question.
Can Cellular Agriculture Feed the World?
Within 20 years, there will be 2 billion more people than today — over 9 billion people in total. The impact to the environment could be severe. Just feeding that population using current methods is problematic.
On average, cattle ranchers need 100 times more land than corn growers to produce a gram of food. So, if that hungry world continues to eat meat like we do, the demand for land — and fresh water — will be alarming, not to mention the environmental impact of raising so many animals. Meat production aside, the large-scale monoculture of crops like corn usually results in damaging terrestrial pollution from pesticides and soil depletion. The impact to the oceans is equally perilous.
Instead of farming animals, fish and plants, cellular agriculture grows the proteins and nutrients we consume from a culture, cell by cell. With this alternative approach, the consumable meat and plant tissues produced don’t need to be harvested from animals or plants. It’s food production on an industrial scale.
The technology to do this is not new. Growing meat from a scaffold embedded in growth culture is no different in theory than making bread from yeast. The vast majority of insulin for diabetics is already manufactured by genetically engineered bacteria, as is the rennet used to culture cheese. In the past 10 years, this approach has been pioneered with a variety of foodstuffs: milk, eggs, beef, chicken, fish — even coffee.
To succeed, cellular agriculture must overcome 6,000 years of established dependence on traditional agriculture, and it has to do so via one of the most finicky human senses: taste. No one will eat manufactured meat or fish if it doesn’t have the same sensual satisfaction generated by the grown version. So, in addition to all the technical challenges in creating edible tissues from cultures, the startups pioneering this approach are working diligently to make their products tasty.
The possibilities for cellular agriculture are seemingly limitless; it may be possible to grow human organs for transplant using the method. But it is still early days.
Adaptado de: <https://earth911.com/business-policy/cellular-agriculture/>
Read the text below and answer the following question.
Can Cellular Agriculture Feed the World?
Within 20 years, there will be 2 billion more people than today — over 9 billion people in total. The impact to the environment could be severe. Just feeding that population using current methods is problematic.
On average, cattle ranchers need 100 times more land than corn growers to produce a gram of food. So, if that hungry world continues to eat meat like we do, the demand for land — and fresh water — will be alarming, not to mention the environmental impact of raising so many animals. Meat production aside, the large-scale monoculture of crops like corn usually results in damaging terrestrial pollution from pesticides and soil depletion. The impact to the oceans is equally perilous.
Instead of farming animals, fish and plants, cellular agriculture grows the proteins and nutrients we consume from a culture, cell by cell. With this alternative approach, the consumable meat and plant tissues produced don’t need to be harvested from animals or plants. It’s food production on an industrial scale.
The technology to do this is not new. Growing meat from a scaffold embedded in growth culture is no different in theory than making bread from yeast. The vast majority of insulin for diabetics is already manufactured by genetically engineered bacteria, as is the rennet used to culture cheese. In the past 10 years, this approach has been pioneered with a variety of foodstuffs: milk, eggs, beef, chicken, fish — even coffee.
To succeed, cellular agriculture must overcome 6,000 years of established dependence on traditional agriculture, and it has to do so via one of the most finicky human senses: taste. No one will eat manufactured meat or fish if it doesn’t have the same sensual satisfaction generated by the grown version. So, in addition to all the technical challenges in creating edible tissues from cultures, the startups pioneering this approach are working diligently to make their products tasty.
The possibilities for cellular agriculture are seemingly limitless; it may be possible to grow human organs for transplant using the method. But it is still early days.
Adaptado de: <https://earth911.com/business-policy/cellular-agriculture/>

(nytimes.com)
Shimmering white and gracefully statuesque, the Mount Washington Hotel is a granite fortress, a manmade anomaly among the raw wilderness of the surrounding White Mountains in remote northern New Hampshire, U.S. Even to this day, the hotel is geographically secured by 800,000 acres of the White Mountain National Forest around it. This was the main reason why the Hotel was chosen for a World War Two meeting – a meeting that shaped present-day global economic policies.
(Linda Laban. www.bbc.com, 26.08.2020. Adapted.)
The term “this”, which introduces the last sentence in the text, refers to the fact that the Mount Washington Hotel