Questões Militares
Comentadas para fundep (gestão de concursos)
Foram encontradas 318 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Nesse caso, a melhor ferramenta disponibilizada pelo sistema é o(a):
Nesse caso, a fibra óptica utilizada é do tipo:
• Equipamento utilizado para interligar segmentos de redes locais, permitindo a comunicação entre eles. • Os dados de um barramento ficam restritos a esse segmento e só passam a outro se forem endereçados. • Evita congestionamento e colisões: uma rede local não interfere nas outras redes locais conectadas a esse componente. • A comutação de frames Ethernet é baseada em hardware, em que a execução da comutação é feita por chips e não por programas armazenados.
Nesse quadro, apresentam-se algumas características de um:
International Civil Defence Organisation
1. Introduction
Fires are the accidents which occur most frequently, whose causes are the most diverse and which require intervention methods and techniques adapted to the conditions and needs of each incident. Depending on the type of fire (nature of the material ablaze), meteorological conditions (wind) and the effectiveness of the intervention, material damage can be limited (a single car, building or production or storage warehouse installation), or affect wide areas (forest or agricultural fires, hydrocarbons, gas or other highly flammable products, storage or piping installations, harbour installations and rail or marine transport equipment). […]
2. Preventive and protective measures
Fires can spread more or less rapidly depending on their causes, the nature of the material and goods alight, the fire prevention installations (automatic sprinklers), meteorological conditions, the ways the population is informed and the initiative it shows, as well as the speed and efficiency of the intervening services and of their fire-fighting equipment. In the light of experience, prevention is seen to be most important and consists of two distinct components. On the one hand, the primary responsibility falling upon the political authorities empowered to implement the legal prescriptions concerning fire protection, to forecast accidents and to inform the population, as well as to set up measures and means for fighting fires and explosions. On the other hand, the responsible behaviour of each individual based upon an education geared towards caution and the respect of instructions in case of fire. Defining, and controlling the implementation of, the particular rules of protection against fires, specific to each enterprise presenting a potential danger, including the training of security personnel, is also relevant in this context. The many types of fire and the preventive and protective measures which relate to them, make it advisable to limit the present study to the specific measures falling to the political authorities in one area only, namely that of “forest fires”. This type of fire is of particular interest to developing countries and the preventive measures to be applied have a general representative value, that is:
– organising an observation service, prevention and alarm (security) service at local and regional levels;
– implementing legislation regulating the use of fire by all the population present in or at the edge of forests, and more particularly by owners and individuals exercising a professional activity in sensitive areas;
– planning and concrete preparation (periodic maintenance) for fire-fighting through adequate landscaping of the territory and appropriate forest cultivation limiting fire propagation (alternating vegetation, clearance, trimming), creating and maintaining access paths (extinction) and fire-break areas as well as fire-fighting equipment such as water supplies (conduits, cisterns), watch towers and meteorological posts, and the construction of helicopter landing pads;
– surveillance and detection of fires as soon as the danger of fires is forecast by the ad hoc meteorological service (which comprises automatic or mobile statistics posts observing the winds and the vegetation: dryness, force, direction, evolution);
– as soon as the danger of fire increases, activating an alarm plan (basic intervention plan) requiring the engagement of preventive intervention squads (firemen), and their wide positioning as near as possible to the threatened zones, and making available water bombers and specialised aerial machines ready for action;
– preparation and concretisation (organisation) of an intervention mechanism: this requires the setting up of specialised management programmes ensuring the coordination of powerful and efficient equipment and means for fighting forest fires (instruction);
– preparedness management and the coordination of the use of the means of intervention of the authorities and the information and alarm services for the population require a secure transmission network (radio network);
– planning the evacuation of the population possibly under threat in the various sensitive areas, particularly if there are risks of explosion (reservoirs and gas conduits explosives or ammunition dumps, hydrocarbon production, handling or transport installations, other dangerous material, etc.).
[...]
Available at: <http://www.icdo.org/en/disasters/man-made-disasters/industrial-accidents/fire>
International Civil Defence Organisation
1. Introduction
Fires are the accidents which occur most frequently, whose causes are the most diverse and which require intervention methods and techniques adapted to the conditions and needs of each incident. Depending on the type of fire (nature of the material ablaze), meteorological conditions (wind) and the effectiveness of the intervention, material damage can be limited (a single car, building or production or storage warehouse installation), or affect wide areas (forest or agricultural fires, hydrocarbons, gas or other highly flammable products, storage or piping installations, harbour installations and rail or marine transport equipment). […]
2. Preventive and protective measures
Fires can spread more or less rapidly depending on their causes, the nature of the material and goods alight, the fire prevention installations (automatic sprinklers), meteorological conditions, the ways the population is informed and the initiative it shows, as well as the speed and efficiency of the intervening services and of their fire-fighting equipment. In the light of experience, prevention is seen to be most important and consists of two distinct components. On the one hand, the primary responsibility falling upon the political authorities empowered to implement the legal prescriptions concerning fire protection, to forecast accidents and to inform the population, as well as to set up measures and means for fighting fires and explosions. On the other hand, the responsible behaviour of each individual based upon an education geared towards caution and the respect of instructions in case of fire. Defining, and controlling the implementation of, the particular rules of protection against fires, specific to each enterprise presenting a potential danger, including the training of security personnel, is also relevant in this context. The many types of fire and the preventive and protective measures which relate to them, make it advisable to limit the present study to the specific measures falling to the political authorities in one area only, namely that of “forest fires”. This type of fire is of particular interest to developing countries and the preventive measures to be applied have a general representative value, that is:
– organising an observation service, prevention and alarm (security) service at local and regional levels;
– implementing legislation regulating the use of fire by all the population present in or at the edge of forests, and more particularly by owners and individuals exercising a professional activity in sensitive areas;
– planning and concrete preparation (periodic maintenance) for fire-fighting through adequate landscaping of the territory and appropriate forest cultivation limiting fire propagation (alternating vegetation, clearance, trimming), creating and maintaining access paths (extinction) and fire-break areas as well as fire-fighting equipment such as water supplies (conduits, cisterns), watch towers and meteorological posts, and the construction of helicopter landing pads;
– surveillance and detection of fires as soon as the danger of fires is forecast by the ad hoc meteorological service (which comprises automatic or mobile statistics posts observing the winds and the vegetation: dryness, force, direction, evolution);
– as soon as the danger of fire increases, activating an alarm plan (basic intervention plan) requiring the engagement of preventive intervention squads (firemen), and their wide positioning as near as possible to the threatened zones, and making available water bombers and specialised aerial machines ready for action;
– preparation and concretisation (organisation) of an intervention mechanism: this requires the setting up of specialised management programmes ensuring the coordination of powerful and efficient equipment and means for fighting forest fires (instruction);
– preparedness management and the coordination of the use of the means of intervention of the authorities and the information and alarm services for the population require a secure transmission network (radio network);
– planning the evacuation of the population possibly under threat in the various sensitive areas, particularly if there are risks of explosion (reservoirs and gas conduits explosives or ammunition dumps, hydrocarbon production, handling or transport installations, other dangerous material, etc.).
[...]
Available at: <http://www.icdo.org/en/disasters/man-made-disasters/industrial-accidents/fire>
International Civil Defence Organisation
1. Introduction
Fires are the accidents which occur most frequently, whose causes are the most diverse and which require intervention methods and techniques adapted to the conditions and needs of each incident. Depending on the type of fire (nature of the material ablaze), meteorological conditions (wind) and the effectiveness of the intervention, material damage can be limited (a single car, building or production or storage warehouse installation), or affect wide areas (forest or agricultural fires, hydrocarbons, gas or other highly flammable products, storage or piping installations, harbour installations and rail or marine transport equipment). […]
2. Preventive and protective measures
Fires can spread more or less rapidly depending on their causes, the nature of the material and goods alight, the fire prevention installations (automatic sprinklers), meteorological conditions, the ways the population is informed and the initiative it shows, as well as the speed and efficiency of the intervening services and of their fire-fighting equipment. In the light of experience, prevention is seen to be most important and consists of two distinct components. On the one hand, the primary responsibility falling upon the political authorities empowered to implement the legal prescriptions concerning fire protection, to forecast accidents and to inform the population, as well as to set up measures and means for fighting fires and explosions. On the other hand, the responsible behaviour of each individual based upon an education geared towards caution and the respect of instructions in case of fire. Defining, and controlling the implementation of, the particular rules of protection against fires, specific to each enterprise presenting a potential danger, including the training of security personnel, is also relevant in this context. The many types of fire and the preventive and protective measures which relate to them, make it advisable to limit the present study to the specific measures falling to the political authorities in one area only, namely that of “forest fires”. This type of fire is of particular interest to developing countries and the preventive measures to be applied have a general representative value, that is:
– organising an observation service, prevention and alarm (security) service at local and regional levels;
– implementing legislation regulating the use of fire by all the population present in or at the edge of forests, and more particularly by owners and individuals exercising a professional activity in sensitive areas;
– planning and concrete preparation (periodic maintenance) for fire-fighting through adequate landscaping of the territory and appropriate forest cultivation limiting fire propagation (alternating vegetation, clearance, trimming), creating and maintaining access paths (extinction) and fire-break areas as well as fire-fighting equipment such as water supplies (conduits, cisterns), watch towers and meteorological posts, and the construction of helicopter landing pads;
– surveillance and detection of fires as soon as the danger of fires is forecast by the ad hoc meteorological service (which comprises automatic or mobile statistics posts observing the winds and the vegetation: dryness, force, direction, evolution);
– as soon as the danger of fire increases, activating an alarm plan (basic intervention plan) requiring the engagement of preventive intervention squads (firemen), and their wide positioning as near as possible to the threatened zones, and making available water bombers and specialised aerial machines ready for action;
– preparation and concretisation (organisation) of an intervention mechanism: this requires the setting up of specialised management programmes ensuring the coordination of powerful and efficient equipment and means for fighting forest fires (instruction);
– preparedness management and the coordination of the use of the means of intervention of the authorities and the information and alarm services for the population require a secure transmission network (radio network);
– planning the evacuation of the population possibly under threat in the various sensitive areas, particularly if there are risks of explosion (reservoirs and gas conduits explosives or ammunition dumps, hydrocarbon production, handling or transport installations, other dangerous material, etc.).
[...]
Available at: <http://www.icdo.org/en/disasters/man-made-disasters/industrial-accidents/fire>
International Civil Defence Organisation
1. Introduction
Fires are the accidents which occur most frequently, whose causes are the most diverse and which require intervention methods and techniques adapted to the conditions and needs of each incident. Depending on the type of fire (nature of the material ablaze), meteorological conditions (wind) and the effectiveness of the intervention, material damage can be limited (a single car, building or production or storage warehouse installation), or affect wide areas (forest or agricultural fires, hydrocarbons, gas or other highly flammable products, storage or piping installations, harbour installations and rail or marine transport equipment). […]
2. Preventive and protective measures
Fires can spread more or less rapidly depending on their causes, the nature of the material and goods alight, the fire prevention installations (automatic sprinklers), meteorological conditions, the ways the population is informed and the initiative it shows, as well as the speed and efficiency of the intervening services and of their fire-fighting equipment. In the light of experience, prevention is seen to be most important and consists of two distinct components. On the one hand, the primary responsibility falling upon the political authorities empowered to implement the legal prescriptions concerning fire protection, to forecast accidents and to inform the population, as well as to set up measures and means for fighting fires and explosions. On the other hand, the responsible behaviour of each individual based upon an education geared towards caution and the respect of instructions in case of fire. Defining, and controlling the implementation of, the particular rules of protection against fires, specific to each enterprise presenting a potential danger, including the training of security personnel, is also relevant in this context. The many types of fire and the preventive and protective measures which relate to them, make it advisable to limit the present study to the specific measures falling to the political authorities in one area only, namely that of “forest fires”. This type of fire is of particular interest to developing countries and the preventive measures to be applied have a general representative value, that is:
– organising an observation service, prevention and alarm (security) service at local and regional levels;
– implementing legislation regulating the use of fire by all the population present in or at the edge of forests, and more particularly by owners and individuals exercising a professional activity in sensitive areas;
– planning and concrete preparation (periodic maintenance) for fire-fighting through adequate landscaping of the territory and appropriate forest cultivation limiting fire propagation (alternating vegetation, clearance, trimming), creating and maintaining access paths (extinction) and fire-break areas as well as fire-fighting equipment such as water supplies (conduits, cisterns), watch towers and meteorological posts, and the construction of helicopter landing pads;
– surveillance and detection of fires as soon as the danger of fires is forecast by the ad hoc meteorological service (which comprises automatic or mobile statistics posts observing the winds and the vegetation: dryness, force, direction, evolution);
– as soon as the danger of fire increases, activating an alarm plan (basic intervention plan) requiring the engagement of preventive intervention squads (firemen), and their wide positioning as near as possible to the threatened zones, and making available water bombers and specialised aerial machines ready for action;
– preparation and concretisation (organisation) of an intervention mechanism: this requires the setting up of specialised management programmes ensuring the coordination of powerful and efficient equipment and means for fighting forest fires (instruction);
– preparedness management and the coordination of the use of the means of intervention of the authorities and the information and alarm services for the population require a secure transmission network (radio network);
– planning the evacuation of the population possibly under threat in the various sensitive areas, particularly if there are risks of explosion (reservoirs and gas conduits explosives or ammunition dumps, hydrocarbon production, handling or transport installations, other dangerous material, etc.).
[...]
Available at: <http://www.icdo.org/en/disasters/man-made-disasters/industrial-accidents/fire>
International Civil Defence Organisation
1. Introduction
Fires are the accidents which occur most frequently, whose causes are the most diverse and which require intervention methods and techniques adapted to the conditions and needs of each incident. Depending on the type of fire (nature of the material ablaze), meteorological conditions (wind) and the effectiveness of the intervention, material damage can be limited (a single car, building or production or storage warehouse installation), or affect wide areas (forest or agricultural fires, hydrocarbons, gas or other highly flammable products, storage or piping installations, harbour installations and rail or marine transport equipment). […]
2. Preventive and protective measures
Fires can spread more or less rapidly depending on their causes, the nature of the material and goods alight, the fire prevention installations (automatic sprinklers), meteorological conditions, the ways the population is informed and the initiative it shows, as well as the speed and efficiency of the intervening services and of their fire-fighting equipment. In the light of experience, prevention is seen to be most important and consists of two distinct components. On the one hand, the primary responsibility falling upon the political authorities empowered to implement the legal prescriptions concerning fire protection, to forecast accidents and to inform the population, as well as to set up measures and means for fighting fires and explosions. On the other hand, the responsible behaviour of each individual based upon an education geared towards caution and the respect of instructions in case of fire. Defining, and controlling the implementation of, the particular rules of protection against fires, specific to each enterprise presenting a potential danger, including the training of security personnel, is also relevant in this context. The many types of fire and the preventive and protective measures which relate to them, make it advisable to limit the present study to the specific measures falling to the political authorities in one area only, namely that of “forest fires”. This type of fire is of particular interest to developing countries and the preventive measures to be applied have a general representative value, that is:
– organising an observation service, prevention and alarm (security) service at local and regional levels;
– implementing legislation regulating the use of fire by all the population present in or at the edge of forests, and more particularly by owners and individuals exercising a professional activity in sensitive areas;
– planning and concrete preparation (periodic maintenance) for fire-fighting through adequate landscaping of the territory and appropriate forest cultivation limiting fire propagation (alternating vegetation, clearance, trimming), creating and maintaining access paths (extinction) and fire-break areas as well as fire-fighting equipment such as water supplies (conduits, cisterns), watch towers and meteorological posts, and the construction of helicopter landing pads;
– surveillance and detection of fires as soon as the danger of fires is forecast by the ad hoc meteorological service (which comprises automatic or mobile statistics posts observing the winds and the vegetation: dryness, force, direction, evolution);
– as soon as the danger of fire increases, activating an alarm plan (basic intervention plan) requiring the engagement of preventive intervention squads (firemen), and their wide positioning as near as possible to the threatened zones, and making available water bombers and specialised aerial machines ready for action;
– preparation and concretisation (organisation) of an intervention mechanism: this requires the setting up of specialised management programmes ensuring the coordination of powerful and efficient equipment and means for fighting forest fires (instruction);
– preparedness management and the coordination of the use of the means of intervention of the authorities and the information and alarm services for the population require a secure transmission network (radio network);
– planning the evacuation of the population possibly under threat in the various sensitive areas, particularly if there are risks of explosion (reservoirs and gas conduits explosives or ammunition dumps, hydrocarbon production, handling or transport installations, other dangerous material, etc.).
[...]
Available at: <http://www.icdo.org/en/disasters/man-made-disasters/industrial-accidents/fire>
O diagrama Volume versus Temperatura, a seguir, representa uma transformação gasosa, I → II → III, sofrida por um mol de gás ideal.
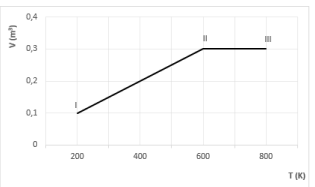
Considerando R = 2,0 cal/mol.K, qual é o trabalho realizado pelo gás nesse processo?
A chave automática é um dispositivo muito útil na prevenção de incêndios elétricos, uma vez que “desarma” (abre o circuito) quando a corrente elétrica que a atravessa é superior a um dado valor nominal.
Considere que, em uma residência, um chuveiro que era ligado à tensão de 110 V será agora ligado em uma tensão de 220 V. A potência desse chuveiro quando ligado em 110 V em uma dada posição de temperatura é de 4,4 kW.
Sendo a resistência constante para qualquer tensão aplicada e a chave automática ligada a esse chuveiro tendo um valor nominal de 50 A, ao ser ligada a essa nova tensão elétrica, a chave automática
Quando ocorrem variações exageradas de temperatura, um fenômeno comum que se pode observar é a dilatação dos corpos. Tal fenômeno é observado, por exemplo, em um local em que ocorre um incêndio.
Analisando a dilatação de dois objetos distintos, essa dilatação dependerá apenas da(o)
Uma antena parabólica desativada de 120 cm de raio de curvatura e sem o receptor de sinal foi coberta com papel alumínio, de modo a se tornar um espelho côncavo. Essa antena foi deixada no quintal de uma casa e, em um dia quente de verão, acabou por incendiar uma pequena caixa de papelão situada a uma certa distância d do centro dessa antena.
Sabendo que os raios do Sol chegam à parte côncava do espelho paralelos ao eixo principal, a distância d ideal para que ocorra o incêndio é de
“Assim como os animais, as plantas também tiveram dificuldades para se fixar em terra firme. Os desafios eram muitos e as plantas precisavam enfrentar problemas, tais como: dessecação, trocas gasosas na atmosfera, sustentar-se fora da água e reprodução. Esses problemas foram os mesmos enfrentados pelos animais ao tentarem conquistar esse novo ambiente.”
Disponível em: <http://mundoeducacao.bol.uol.com.br/biologia/plantas-meio-terrestre.htm> . Acesso em: 9 abr. 2018.
São processos que permitiram essa adaptação, exceto:
Observe a figura, a seguir, que evidencia determinadas organelas celulares vegetais.
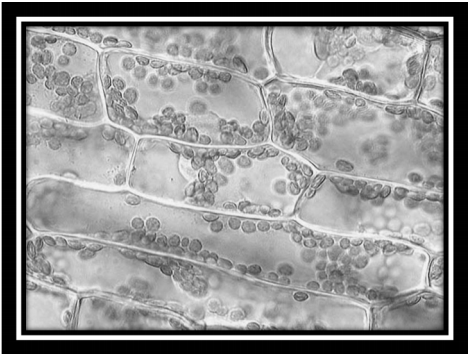
Disponível em:<https://www.thinglink.com/scene/734036539838824449> . Acesso em: 8 abr. 2018
O uso de preservativos masculinos é uma eficiente profilaxia para as chamadas doenças sexuais transmissíveis. Entretanto, nem todas DSTs podem ser evitadas com o uso das camisinhas.
A patologia para a qual essa medida profilática é de baixa eficiência é
O Ibama deu sinal verde para os trabalhos de esterilização das capivaras que vivem no entorno da Lagoa da Pampulha, um dos principais cartões-postais de Belo Horizonte. No início da semana, técnicos da Secretaria Municipal de Meio Ambiente começaram a fazer o trabalho de dedetização da área externa, capina e limpeza de contêineres onde serão realizadas as cirurgias nos animais. As medidas estão sendo tomadas depois da morte de um homem de 42 anos, vítima de febre maculosa – doença transmitida pelo carrapato-estrela. Moradores comemoram o início dos trabalhos após ficarem apreensivos com a volta da doença.
Disponível em: <https://www.em.com.br/app/noticia/gerais/2017/11/01/interna_gerais,913265/ibama-libera-manejo-decapivaras-da-pampulha.shtml>
O Ibama deu sinal verde para os trabalhos de esterilização das capivaras que vivem no entorno da Lagoa da Pampulha, um dos principais cartões-postais de Belo Horizonte. No início da semana, técnicos da Secretaria Municipal de Meio Ambiente começaram a fazer o trabalho de dedetização da área externa, capina e limpeza de contêineres onde serão realizadas as cirurgias nos animais. As medidas estão sendo tomadas depois da morte de um homem de 42 anos, vítima de febre maculosa – doença transmitida pelo carrapato-estrela. Moradores comemoram o início dos trabalhos após ficarem apreensivos com a volta da doença.
Disponível em: <https://www.em.com.br/app/noticia/gerais/2017/11/01/interna_gerais,913265/ibama-libera-manejo-decapivaras-da-pampulha.shtml>
Em condições ideais, pequenas quantidades de gás cloro podem ser geradas em laboratório pela reação do óxido de manganês (MnO2 ) com ácido clorídrico (HCl), conforme a equação química a seguir não balanceada.
HCl(aq) + MnO2 (s) → H2O(L) + MnCl2(s) + Cl2(g)
A partir dessas informações, quantas moléculas de gás cloro, aproximadamente, podem ser produzidas quando 10 g de óxido de manganês com grau de pureza de 87% são colocados para reagir completamente com excesso de ácido clorídrico?
Dado: Número de Avogadro (N) = 6 x 1023
Segundo o que dispõe o seu Estatuto, a criança e o adolescente têm direito de serem educados sem o uso de castigo físico ou de tratamento cruel ou degradante como formas de correção, disciplina, educação ou qualquer outro pretexto por parte dos pais, integrantes da família ampliada, pelos responsáveis, pelos agentes executores de medidas socioeducativas ou por qualquer pessoa encarregada de cuidar deles, tratá-los, educá-los ou protegê-los.
Considerando os termos do citado Estatuto, é correto afirmar que