Questões de Concurso Público CAPES 2008 para Comunicação Social (Bacharelado)
Foram encontradas 70 questões
Majority of workers feel overwhelmed by deluge of data,
survey finds
By Eve Tahmincioglu
updated 8:18 p.m. ET March 16, 2008
Don't expect Shaun Osher, the CEO of Core Group
Marketing in New York, to answer your e-mail right away.
He has stopped responding to e-mails every minute and
only checks his e-mail account twice a day. He also started
turning off his BlackBerry during meetings.
This tactic has made him so much more productive
that earlier this year he held a meeting with his staff of 50
and "strongly suggested" that they stop relying so heavily
on e-mail and actually start calling clients on the phone.
And, he requested his employees put cell phones and
PDAs on silent mode during meetings, as well as curtail
the common practice of cc-ing everybody when sending
out an e-mail. "There was so much redundancy, so much
unnecessary work," he explains. "One person could handle
an issue that should take two minutes, but when an email
goes out and five people get cc-ed, then everybody
responds to it and there's a snowball effect."
It's not that Osher has anything against technology. In
fact, he loves it. The problem is, last year he realized he
was inundated with so many e-mails and so much
information in general that he began to experience data
overload. "In the beginning, e-mail and all this data was a
great phenomenon, revolutionizing what we do. But the
pendulum has swung way too much to the other side," he
maintains. "We're less productive."
Osher isn't the only one out there under a data
avalanche. Thanks to technological innovations, you can
be talking to a customer on your cell phone, answering a
LinkedIn invitation on your laptop, and responding to email
on your PDA all at the same time. Besides, during
tough economic times, who will want to miss any
information when your job could be on the line if you indulge
in the luxury of being offline? Turns out, seven out of 10
office workers in the United States feel overwhelmed by
information in the workplace, and more than two in five
say they are headed for a data "breaking point," according
to a recently released Workplace Productivity Survey.
Mike Walsh, CEO of LexisNexis U.S. Legal Markets,
says there are a host of reasons we're all on the information
brink: "exponential growth of the size of the information
'haystack,' the immensity and immediacy of digital
communications, and the fact that professionals are not
being provided with sufficient tools and training to help
them keep pace with the growing information burden."
Ellen Kossek, a professor from Michigan State, believes
we are less productive in this age of 24-7 technology, and
our multitasking mentality has spawned a "not-mentallypresent"
society. "We're becoming an attention-deficit
disorder society switching back and forth like crazy,"
Kossek says. "We're connected all the time. We're
working on planes, in coffee shops, working on the
weekends. Work is very seductive, but yet we're actually
less effective."
The key to getting your head above the data flood,
according to workplace experts, is managing and reducing
the information you're bombarded with.
© 2008 MSNBC Interactive - (slightly adapted)
http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/23636252/
Majority of workers feel overwhelmed by deluge of data,
survey finds
By Eve Tahmincioglu
updated 8:18 p.m. ET March 16, 2008
Don't expect Shaun Osher, the CEO of Core Group
Marketing in New York, to answer your e-mail right away.
He has stopped responding to e-mails every minute and
only checks his e-mail account twice a day. He also started
turning off his BlackBerry during meetings.
This tactic has made him so much more productive
that earlier this year he held a meeting with his staff of 50
and "strongly suggested" that they stop relying so heavily
on e-mail and actually start calling clients on the phone.
And, he requested his employees put cell phones and
PDAs on silent mode during meetings, as well as curtail
the common practice of cc-ing everybody when sending
out an e-mail. "There was so much redundancy, so much
unnecessary work," he explains. "One person could handle
an issue that should take two minutes, but when an email
goes out and five people get cc-ed, then everybody
responds to it and there's a snowball effect."
It's not that Osher has anything against technology. In
fact, he loves it. The problem is, last year he realized he
was inundated with so many e-mails and so much
information in general that he began to experience data
overload. "In the beginning, e-mail and all this data was a
great phenomenon, revolutionizing what we do. But the
pendulum has swung way too much to the other side," he
maintains. "We're less productive."
Osher isn't the only one out there under a data
avalanche. Thanks to technological innovations, you can
be talking to a customer on your cell phone, answering a
LinkedIn invitation on your laptop, and responding to email
on your PDA all at the same time. Besides, during
tough economic times, who will want to miss any
information when your job could be on the line if you indulge
in the luxury of being offline? Turns out, seven out of 10
office workers in the United States feel overwhelmed by
information in the workplace, and more than two in five
say they are headed for a data "breaking point," according
to a recently released Workplace Productivity Survey.
Mike Walsh, CEO of LexisNexis U.S. Legal Markets,
says there are a host of reasons we're all on the information
brink: "exponential growth of the size of the information
'haystack,' the immensity and immediacy of digital
communications, and the fact that professionals are not
being provided with sufficient tools and training to help
them keep pace with the growing information burden."
Ellen Kossek, a professor from Michigan State, believes
we are less productive in this age of 24-7 technology, and
our multitasking mentality has spawned a "not-mentallypresent"
society. "We're becoming an attention-deficit
disorder society switching back and forth like crazy,"
Kossek says. "We're connected all the time. We're
working on planes, in coffee shops, working on the
weekends. Work is very seductive, but yet we're actually
less effective."
The key to getting your head above the data flood,
according to workplace experts, is managing and reducing
the information you're bombarded with.
© 2008 MSNBC Interactive - (slightly adapted)
http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/23636252/
Majority of workers feel overwhelmed by deluge of data,
survey finds
By Eve Tahmincioglu
updated 8:18 p.m. ET March 16, 2008
Don't expect Shaun Osher, the CEO of Core Group
Marketing in New York, to answer your e-mail right away.
He has stopped responding to e-mails every minute and
only checks his e-mail account twice a day. He also started
turning off his BlackBerry during meetings.
This tactic has made him so much more productive
that earlier this year he held a meeting with his staff of 50
and "strongly suggested" that they stop relying so heavily
on e-mail and actually start calling clients on the phone.
And, he requested his employees put cell phones and
PDAs on silent mode during meetings, as well as curtail
the common practice of cc-ing everybody when sending
out an e-mail. "There was so much redundancy, so much
unnecessary work," he explains. "One person could handle
an issue that should take two minutes, but when an email
goes out and five people get cc-ed, then everybody
responds to it and there's a snowball effect."
It's not that Osher has anything against technology. In
fact, he loves it. The problem is, last year he realized he
was inundated with so many e-mails and so much
information in general that he began to experience data
overload. "In the beginning, e-mail and all this data was a
great phenomenon, revolutionizing what we do. But the
pendulum has swung way too much to the other side," he
maintains. "We're less productive."
Osher isn't the only one out there under a data
avalanche. Thanks to technological innovations, you can
be talking to a customer on your cell phone, answering a
LinkedIn invitation on your laptop, and responding to email
on your PDA all at the same time. Besides, during
tough economic times, who will want to miss any
information when your job could be on the line if you indulge
in the luxury of being offline? Turns out, seven out of 10
office workers in the United States feel overwhelmed by
information in the workplace, and more than two in five
say they are headed for a data "breaking point," according
to a recently released Workplace Productivity Survey.
Mike Walsh, CEO of LexisNexis U.S. Legal Markets,
says there are a host of reasons we're all on the information
brink: "exponential growth of the size of the information
'haystack,' the immensity and immediacy of digital
communications, and the fact that professionals are not
being provided with sufficient tools and training to help
them keep pace with the growing information burden."
Ellen Kossek, a professor from Michigan State, believes
we are less productive in this age of 24-7 technology, and
our multitasking mentality has spawned a "not-mentallypresent"
society. "We're becoming an attention-deficit
disorder society switching back and forth like crazy,"
Kossek says. "We're connected all the time. We're
working on planes, in coffee shops, working on the
weekends. Work is very seductive, but yet we're actually
less effective."
The key to getting your head above the data flood,
according to workplace experts, is managing and reducing
the information you're bombarded with.
© 2008 MSNBC Interactive - (slightly adapted)
http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/23636252/
Majority of workers feel overwhelmed by deluge of data,
survey finds
By Eve Tahmincioglu
updated 8:18 p.m. ET March 16, 2008
Don't expect Shaun Osher, the CEO of Core Group
Marketing in New York, to answer your e-mail right away.
He has stopped responding to e-mails every minute and
only checks his e-mail account twice a day. He also started
turning off his BlackBerry during meetings.
This tactic has made him so much more productive
that earlier this year he held a meeting with his staff of 50
and "strongly suggested" that they stop relying so heavily
on e-mail and actually start calling clients on the phone.
And, he requested his employees put cell phones and
PDAs on silent mode during meetings, as well as curtail
the common practice of cc-ing everybody when sending
out an e-mail. "There was so much redundancy, so much
unnecessary work," he explains. "One person could handle
an issue that should take two minutes, but when an email
goes out and five people get cc-ed, then everybody
responds to it and there's a snowball effect."
It's not that Osher has anything against technology. In
fact, he loves it. The problem is, last year he realized he
was inundated with so many e-mails and so much
information in general that he began to experience data
overload. "In the beginning, e-mail and all this data was a
great phenomenon, revolutionizing what we do. But the
pendulum has swung way too much to the other side," he
maintains. "We're less productive."
Osher isn't the only one out there under a data
avalanche. Thanks to technological innovations, you can
be talking to a customer on your cell phone, answering a
LinkedIn invitation on your laptop, and responding to email
on your PDA all at the same time. Besides, during
tough economic times, who will want to miss any
information when your job could be on the line if you indulge
in the luxury of being offline? Turns out, seven out of 10
office workers in the United States feel overwhelmed by
information in the workplace, and more than two in five
say they are headed for a data "breaking point," according
to a recently released Workplace Productivity Survey.
Mike Walsh, CEO of LexisNexis U.S. Legal Markets,
says there are a host of reasons we're all on the information
brink: "exponential growth of the size of the information
'haystack,' the immensity and immediacy of digital
communications, and the fact that professionals are not
being provided with sufficient tools and training to help
them keep pace with the growing information burden."
Ellen Kossek, a professor from Michigan State, believes
we are less productive in this age of 24-7 technology, and
our multitasking mentality has spawned a "not-mentallypresent"
society. "We're becoming an attention-deficit
disorder society switching back and forth like crazy,"
Kossek says. "We're connected all the time. We're
working on planes, in coffee shops, working on the
weekends. Work is very seductive, but yet we're actually
less effective."
The key to getting your head above the data flood,
according to workplace experts, is managing and reducing
the information you're bombarded with.
© 2008 MSNBC Interactive - (slightly adapted)
http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/23636252/
Majority of workers feel overwhelmed by deluge of data,
survey finds
By Eve Tahmincioglu
updated 8:18 p.m. ET March 16, 2008
Don't expect Shaun Osher, the CEO of Core Group
Marketing in New York, to answer your e-mail right away.
He has stopped responding to e-mails every minute and
only checks his e-mail account twice a day. He also started
turning off his BlackBerry during meetings.
This tactic has made him so much more productive
that earlier this year he held a meeting with his staff of 50
and "strongly suggested" that they stop relying so heavily
on e-mail and actually start calling clients on the phone.
And, he requested his employees put cell phones and
PDAs on silent mode during meetings, as well as curtail
the common practice of cc-ing everybody when sending
out an e-mail. "There was so much redundancy, so much
unnecessary work," he explains. "One person could handle
an issue that should take two minutes, but when an email
goes out and five people get cc-ed, then everybody
responds to it and there's a snowball effect."
It's not that Osher has anything against technology. In
fact, he loves it. The problem is, last year he realized he
was inundated with so many e-mails and so much
information in general that he began to experience data
overload. "In the beginning, e-mail and all this data was a
great phenomenon, revolutionizing what we do. But the
pendulum has swung way too much to the other side," he
maintains. "We're less productive."
Osher isn't the only one out there under a data
avalanche. Thanks to technological innovations, you can
be talking to a customer on your cell phone, answering a
LinkedIn invitation on your laptop, and responding to email
on your PDA all at the same time. Besides, during
tough economic times, who will want to miss any
information when your job could be on the line if you indulge
in the luxury of being offline? Turns out, seven out of 10
office workers in the United States feel overwhelmed by
information in the workplace, and more than two in five
say they are headed for a data "breaking point," according
to a recently released Workplace Productivity Survey.
Mike Walsh, CEO of LexisNexis U.S. Legal Markets,
says there are a host of reasons we're all on the information
brink: "exponential growth of the size of the information
'haystack,' the immensity and immediacy of digital
communications, and the fact that professionals are not
being provided with sufficient tools and training to help
them keep pace with the growing information burden."
Ellen Kossek, a professor from Michigan State, believes
we are less productive in this age of 24-7 technology, and
our multitasking mentality has spawned a "not-mentallypresent"
society. "We're becoming an attention-deficit
disorder society switching back and forth like crazy,"
Kossek says. "We're connected all the time. We're
working on planes, in coffee shops, working on the
weekends. Work is very seductive, but yet we're actually
less effective."
The key to getting your head above the data flood,
according to workplace experts, is managing and reducing
the information you're bombarded with.
© 2008 MSNBC Interactive - (slightly adapted)
http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/23636252/
Majority of workers feel overwhelmed by deluge of data,
survey finds
By Eve Tahmincioglu
updated 8:18 p.m. ET March 16, 2008
Don't expect Shaun Osher, the CEO of Core Group
Marketing in New York, to answer your e-mail right away.
He has stopped responding to e-mails every minute and
only checks his e-mail account twice a day. He also started
turning off his BlackBerry during meetings.
This tactic has made him so much more productive
that earlier this year he held a meeting with his staff of 50
and "strongly suggested" that they stop relying so heavily
on e-mail and actually start calling clients on the phone.
And, he requested his employees put cell phones and
PDAs on silent mode during meetings, as well as curtail
the common practice of cc-ing everybody when sending
out an e-mail. "There was so much redundancy, so much
unnecessary work," he explains. "One person could handle
an issue that should take two minutes, but when an email
goes out and five people get cc-ed, then everybody
responds to it and there's a snowball effect."
It's not that Osher has anything against technology. In
fact, he loves it. The problem is, last year he realized he
was inundated with so many e-mails and so much
information in general that he began to experience data
overload. "In the beginning, e-mail and all this data was a
great phenomenon, revolutionizing what we do. But the
pendulum has swung way too much to the other side," he
maintains. "We're less productive."
Osher isn't the only one out there under a data
avalanche. Thanks to technological innovations, you can
be talking to a customer on your cell phone, answering a
LinkedIn invitation on your laptop, and responding to email
on your PDA all at the same time. Besides, during
tough economic times, who will want to miss any
information when your job could be on the line if you indulge
in the luxury of being offline? Turns out, seven out of 10
office workers in the United States feel overwhelmed by
information in the workplace, and more than two in five
say they are headed for a data "breaking point," according
to a recently released Workplace Productivity Survey.
Mike Walsh, CEO of LexisNexis U.S. Legal Markets,
says there are a host of reasons we're all on the information
brink: "exponential growth of the size of the information
'haystack,' the immensity and immediacy of digital
communications, and the fact that professionals are not
being provided with sufficient tools and training to help
them keep pace with the growing information burden."
Ellen Kossek, a professor from Michigan State, believes
we are less productive in this age of 24-7 technology, and
our multitasking mentality has spawned a "not-mentallypresent"
society. "We're becoming an attention-deficit
disorder society switching back and forth like crazy,"
Kossek says. "We're connected all the time. We're
working on planes, in coffee shops, working on the
weekends. Work is very seductive, but yet we're actually
less effective."
The key to getting your head above the data flood,
according to workplace experts, is managing and reducing
the information you're bombarded with.
© 2008 MSNBC Interactive - (slightly adapted)
http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/23636252/
Majority of workers feel overwhelmed by deluge of data,
survey finds
By Eve Tahmincioglu
updated 8:18 p.m. ET March 16, 2008
Don't expect Shaun Osher, the CEO of Core Group
Marketing in New York, to answer your e-mail right away.
He has stopped responding to e-mails every minute and
only checks his e-mail account twice a day. He also started
turning off his BlackBerry during meetings.
This tactic has made him so much more productive
that earlier this year he held a meeting with his staff of 50
and "strongly suggested" that they stop relying so heavily
on e-mail and actually start calling clients on the phone.
And, he requested his employees put cell phones and
PDAs on silent mode during meetings, as well as curtail
the common practice of cc-ing everybody when sending
out an e-mail. "There was so much redundancy, so much
unnecessary work," he explains. "One person could handle
an issue that should take two minutes, but when an email
goes out and five people get cc-ed, then everybody
responds to it and there's a snowball effect."
It's not that Osher has anything against technology. In
fact, he loves it. The problem is, last year he realized he
was inundated with so many e-mails and so much
information in general that he began to experience data
overload. "In the beginning, e-mail and all this data was a
great phenomenon, revolutionizing what we do. But the
pendulum has swung way too much to the other side," he
maintains. "We're less productive."
Osher isn't the only one out there under a data
avalanche. Thanks to technological innovations, you can
be talking to a customer on your cell phone, answering a
LinkedIn invitation on your laptop, and responding to email
on your PDA all at the same time. Besides, during
tough economic times, who will want to miss any
information when your job could be on the line if you indulge
in the luxury of being offline? Turns out, seven out of 10
office workers in the United States feel overwhelmed by
information in the workplace, and more than two in five
say they are headed for a data "breaking point," according
to a recently released Workplace Productivity Survey.
Mike Walsh, CEO of LexisNexis U.S. Legal Markets,
says there are a host of reasons we're all on the information
brink: "exponential growth of the size of the information
'haystack,' the immensity and immediacy of digital
communications, and the fact that professionals are not
being provided with sufficient tools and training to help
them keep pace with the growing information burden."
Ellen Kossek, a professor from Michigan State, believes
we are less productive in this age of 24-7 technology, and
our multitasking mentality has spawned a "not-mentallypresent"
society. "We're becoming an attention-deficit
disorder society switching back and forth like crazy,"
Kossek says. "We're connected all the time. We're
working on planes, in coffee shops, working on the
weekends. Work is very seductive, but yet we're actually
less effective."
The key to getting your head above the data flood,
according to workplace experts, is managing and reducing
the information you're bombarded with.
© 2008 MSNBC Interactive - (slightly adapted)
http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/23636252/
Majority of workers feel overwhelmed by deluge of data,
survey finds
By Eve Tahmincioglu
updated 8:18 p.m. ET March 16, 2008
Don't expect Shaun Osher, the CEO of Core Group
Marketing in New York, to answer your e-mail right away.
He has stopped responding to e-mails every minute and
only checks his e-mail account twice a day. He also started
turning off his BlackBerry during meetings.
This tactic has made him so much more productive
that earlier this year he held a meeting with his staff of 50
and "strongly suggested" that they stop relying so heavily
on e-mail and actually start calling clients on the phone.
And, he requested his employees put cell phones and
PDAs on silent mode during meetings, as well as curtail
the common practice of cc-ing everybody when sending
out an e-mail. "There was so much redundancy, so much
unnecessary work," he explains. "One person could handle
an issue that should take two minutes, but when an email
goes out and five people get cc-ed, then everybody
responds to it and there's a snowball effect."
It's not that Osher has anything against technology. In
fact, he loves it. The problem is, last year he realized he
was inundated with so many e-mails and so much
information in general that he began to experience data
overload. "In the beginning, e-mail and all this data was a
great phenomenon, revolutionizing what we do. But the
pendulum has swung way too much to the other side," he
maintains. "We're less productive."
Osher isn't the only one out there under a data
avalanche. Thanks to technological innovations, you can
be talking to a customer on your cell phone, answering a
LinkedIn invitation on your laptop, and responding to email
on your PDA all at the same time. Besides, during
tough economic times, who will want to miss any
information when your job could be on the line if you indulge
in the luxury of being offline? Turns out, seven out of 10
office workers in the United States feel overwhelmed by
information in the workplace, and more than two in five
say they are headed for a data "breaking point," according
to a recently released Workplace Productivity Survey.
Mike Walsh, CEO of LexisNexis U.S. Legal Markets,
says there are a host of reasons we're all on the information
brink: "exponential growth of the size of the information
'haystack,' the immensity and immediacy of digital
communications, and the fact that professionals are not
being provided with sufficient tools and training to help
them keep pace with the growing information burden."
Ellen Kossek, a professor from Michigan State, believes
we are less productive in this age of 24-7 technology, and
our multitasking mentality has spawned a "not-mentallypresent"
society. "We're becoming an attention-deficit
disorder society switching back and forth like crazy,"
Kossek says. "We're connected all the time. We're
working on planes, in coffee shops, working on the
weekends. Work is very seductive, but yet we're actually
less effective."
The key to getting your head above the data flood,
according to workplace experts, is managing and reducing
the information you're bombarded with.
© 2008 MSNBC Interactive - (slightly adapted)
http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/23636252/
Majority of workers feel overwhelmed by deluge of data,
survey finds
By Eve Tahmincioglu
updated 8:18 p.m. ET March 16, 2008
Don't expect Shaun Osher, the CEO of Core Group
Marketing in New York, to answer your e-mail right away.
He has stopped responding to e-mails every minute and
only checks his e-mail account twice a day. He also started
turning off his BlackBerry during meetings.
This tactic has made him so much more productive
that earlier this year he held a meeting with his staff of 50
and "strongly suggested" that they stop relying so heavily
on e-mail and actually start calling clients on the phone.
And, he requested his employees put cell phones and
PDAs on silent mode during meetings, as well as curtail
the common practice of cc-ing everybody when sending
out an e-mail. "There was so much redundancy, so much
unnecessary work," he explains. "One person could handle
an issue that should take two minutes, but when an email
goes out and five people get cc-ed, then everybody
responds to it and there's a snowball effect."
It's not that Osher has anything against technology. In
fact, he loves it. The problem is, last year he realized he
was inundated with so many e-mails and so much
information in general that he began to experience data
overload. "In the beginning, e-mail and all this data was a
great phenomenon, revolutionizing what we do. But the
pendulum has swung way too much to the other side," he
maintains. "We're less productive."
Osher isn't the only one out there under a data
avalanche. Thanks to technological innovations, you can
be talking to a customer on your cell phone, answering a
LinkedIn invitation on your laptop, and responding to email
on your PDA all at the same time. Besides, during
tough economic times, who will want to miss any
information when your job could be on the line if you indulge
in the luxury of being offline? Turns out, seven out of 10
office workers in the United States feel overwhelmed by
information in the workplace, and more than two in five
say they are headed for a data "breaking point," according
to a recently released Workplace Productivity Survey.
Mike Walsh, CEO of LexisNexis U.S. Legal Markets,
says there are a host of reasons we're all on the information
brink: "exponential growth of the size of the information
'haystack,' the immensity and immediacy of digital
communications, and the fact that professionals are not
being provided with sufficient tools and training to help
them keep pace with the growing information burden."
Ellen Kossek, a professor from Michigan State, believes
we are less productive in this age of 24-7 technology, and
our multitasking mentality has spawned a "not-mentallypresent"
society. "We're becoming an attention-deficit
disorder society switching back and forth like crazy,"
Kossek says. "We're connected all the time. We're
working on planes, in coffee shops, working on the
weekends. Work is very seductive, but yet we're actually
less effective."
The key to getting your head above the data flood,
according to workplace experts, is managing and reducing
the information you're bombarded with.
© 2008 MSNBC Interactive - (slightly adapted)
http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/23636252/
Majority of workers feel overwhelmed by deluge of data,
survey finds
By Eve Tahmincioglu
updated 8:18 p.m. ET March 16, 2008
Don't expect Shaun Osher, the CEO of Core Group
Marketing in New York, to answer your e-mail right away.
He has stopped responding to e-mails every minute and
only checks his e-mail account twice a day. He also started
turning off his BlackBerry during meetings.
This tactic has made him so much more productive
that earlier this year he held a meeting with his staff of 50
and "strongly suggested" that they stop relying so heavily
on e-mail and actually start calling clients on the phone.
And, he requested his employees put cell phones and
PDAs on silent mode during meetings, as well as curtail
the common practice of cc-ing everybody when sending
out an e-mail. "There was so much redundancy, so much
unnecessary work," he explains. "One person could handle
an issue that should take two minutes, but when an email
goes out and five people get cc-ed, then everybody
responds to it and there's a snowball effect."
It's not that Osher has anything against technology. In
fact, he loves it. The problem is, last year he realized he
was inundated with so many e-mails and so much
information in general that he began to experience data
overload. "In the beginning, e-mail and all this data was a
great phenomenon, revolutionizing what we do. But the
pendulum has swung way too much to the other side," he
maintains. "We're less productive."
Osher isn't the only one out there under a data
avalanche. Thanks to technological innovations, you can
be talking to a customer on your cell phone, answering a
LinkedIn invitation on your laptop, and responding to email
on your PDA all at the same time. Besides, during
tough economic times, who will want to miss any
information when your job could be on the line if you indulge
in the luxury of being offline? Turns out, seven out of 10
office workers in the United States feel overwhelmed by
information in the workplace, and more than two in five
say they are headed for a data "breaking point," according
to a recently released Workplace Productivity Survey.
Mike Walsh, CEO of LexisNexis U.S. Legal Markets,
says there are a host of reasons we're all on the information
brink: "exponential growth of the size of the information
'haystack,' the immensity and immediacy of digital
communications, and the fact that professionals are not
being provided with sufficient tools and training to help
them keep pace with the growing information burden."
Ellen Kossek, a professor from Michigan State, believes
we are less productive in this age of 24-7 technology, and
our multitasking mentality has spawned a "not-mentallypresent"
society. "We're becoming an attention-deficit
disorder society switching back and forth like crazy,"
Kossek says. "We're connected all the time. We're
working on planes, in coffee shops, working on the
weekends. Work is very seductive, but yet we're actually
less effective."
The key to getting your head above the data flood,
according to workplace experts, is managing and reducing
the information you're bombarded with.
© 2008 MSNBC Interactive - (slightly adapted)
http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/23636252/
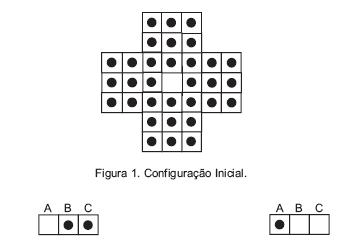
Nesse jogo, a única jogada possível consiste em: dadas três casas consecutivas em linha, na horizontal ou na vertical, se uma das casas, que não a central, estiver vazia e as outras duas, ocupadas, uma das peças salta a outra, adjacente, retirando-se do jogo a que foi pulada. Se não for possível realizar a jogada, o jogo acaba.
Na Figura 2, vê-se a casa A vazia e as casas B e C ocupadas. A peça que está em C pula a que está em B e passa a ocupar a casa A. A peça da casa B, que foi pulada, é retirada do jogo (Figura 3).
Abaixo, está representada uma situação de jogo no Resta Um.
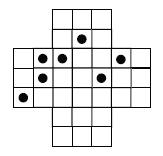
Na situação apresentada, o jogo acaba com, no mínimo, um número de peças igual a
