Questões de Concurso Público SME do Recife - PE 2023 para Professor II - Disciplina: Língua Inglesa
Foram encontradas 45 questões
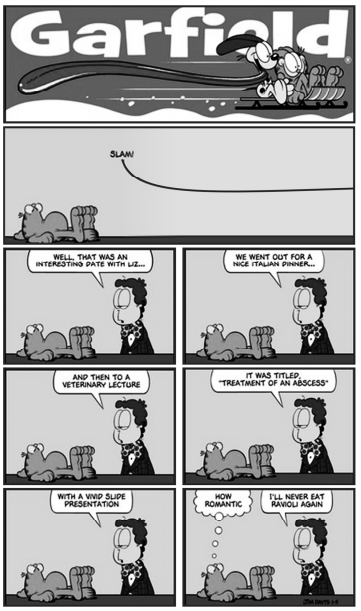
Based on the precedent comic strip, judge the following item.
The man wished he had not eaten ravioli.
Based on the precedent comic strip, judge the following item.
The cat’s only comment is very sarcastic.
Judge the following item, related to text 7A2 and its subject.
It is correct to infer that languages in general work the same
way because they are structures.
Judge the following item, related to text 7A2 and its subject.
Differences among languages do not allow them to be
hierarchically classified according to decontextualized
criteria.
Judge the following item, related to text 7A2 and its subject.
It would be correct to infer from the text that fishing and
beer production are of great concern both for the Agta people
and for the inhabitants of Munich.
Judge the following item concerning text 7A2.
Because of the complex structures of the first sentence of the
text, it would be enough to replace the question mark with a
full stop at the end of such sentence to make it into a
statement.
Judge the following item concerning text 7A2.
The conjunction “though”, in the third sentence of the
second paragraph, indicates that the fact that languages are
potentially equal is somewhat surprising or unexpected when
compared to the information that only certain languages have
adapted to the needs of a ‘complex industrial civilization’.
Judge the following item concerning text 7A2.
In “play no part in their culture?”, the word “part” could be
replaced by role or act without any change in the meaning of
the sentence.
Judge the following item concerning text 7A2.
In the last sentence of the first paragraph, using “are
reported”, the author means that the Agta people themselves
have studied their vocabulary on fishing.
Judge the following item concerning text 7A2.
In the beginning of the second paragraph, the word “this”
stands for the information given immediately before about
no language spoken today being primitive.

Judge the following item considering the comic strip.
Cultural differences may lead to problems even between
people coming from the same continent.

Judge the following item considering the comic strip.
One of the characters needs to go back to learn how to read
the time on a watch.

Judge the following item considering the comic strip.
Speaking the same language does not guarantee a cultural
conflict-free encounter between people from different
communities.
Judge the following item, about the vocabulary and the grammatical features of the text.
In the first paragraph, if the authors qualified “native
language” as Asian, primaeval, guttural and beautiful, the
correct order of such adjectives would be: beautiful Asian
guttural primaeval native language.
Judge the following item, about the vocabulary and the grammatical features of the text.
Because the expression “concerted efforts” is used in the last
sentence of the text, it can be said that initiatives or measures
that were once ineffective, went through improvement, and
are presently adequate and successful.
Judge the following item, about the vocabulary and the grammatical features of the text.
In the second sentence of the second paragraph, “who are
capable of speaking their native language” restrains the
meaning of “Aboriginal youth” and cannot be omitted
without this changing the meaning of the sentence.
Judge the following item, about the vocabulary and the grammatical features of the text.
The excerpt “a decrease in youth suicide by 50% a year”
(end of the second paragraph) can be correctly replaced by a
50-per-cent-a-year decrease in suicide among youth.
Judge the following item, about the vocabulary and the grammatical features of the text.
In “Separate indigenous language educational institutions”
(last paragraph), the use of “Separate” indicates that the
educational institutions should be independent and
autonomous educational units.
Judge the following item, related to the vocabulary and to the grammar in the precedent text.
In the first paragraph, the word “humanlike” can be correctly
replaced by humane without this changing the meaning
relations in the paragraph.
Judge the following item, related to the vocabulary and to the grammar in the precedent text.
With the passage “unveiled a gender-neutral option”, in the
first paragraph, the author informs that Apple’s Siri had such
an option already, but it was difficult for users to find it.