Questões de Concurso Público IBGE 2016 para Analista - Engenharia Civil
Foram encontradas 70 questões
TEXT II
The backlash against big data
[…]
Big data refers to the idea that society can do things with a large body of data that weren’t possible when working with smaller amounts. The term was originally applied a decade ago to massive datasets from astrophysics, genomics and internet search engines, and to machine-learning systems (for voice-recognition and translation, for example) that work well only when given lots of data to chew on. Now it refers to the application of data-analysis and statistics in new areas, from retailing to human resources. The backlash began in mid-March, prompted by an article in Science by David Lazer and others at Harvard and Northeastern University. It showed that a big-data poster-child—Google Flu Trends, a 2009 project which identified flu outbreaks from search queries alone—had overestimated the number of cases for four years running, compared with reported data from the Centres for Disease Control (CDC). This led to a wider attack on the idea of big data.
The criticisms fall into three areas that are not intrinsic to big data per se, but endemic to data analysis, and have some merit. First, there are biases inherent to data that must not be ignored. That is undeniably the case. Second, some proponents of big data have claimed that theory (ie, generalisable models about how the world works) is obsolete. In fact, subject-area knowledge remains necessary even when dealing with large data sets. Third, the risk of spurious correlations—associations that are statistically robust but happen only by chance—increases with more data. Although there are new statistical techniques to identify and banish spurious correlations, such as running many tests against subsets of the data, this will always be a problem.
There is some merit to the naysayers' case, in other words. But these criticisms do not mean that big-data analysis has no merit whatsoever. Even the Harvard researchers who decried big data "hubris" admitted in Science that melding Google Flu Trends analysis with CDC’s data improved the overall forecast—showing that big data can in fact be a useful tool. And research published in PLOS Computational Biology on April 17th shows it is possible to estimate the prevalence of the flu based on visits to Wikipedia articles related to the illness. Behind the big data backlash is the classic hype cycle, in which a technology’s early proponents make overly grandiose claims, people sling arrows when those promises fall flat, but the technology eventually transforms the world, though not necessarily in ways the pundits expected. It happened with the web, and television, radio, motion pictures and the telegraph before it. Now it is simply big data’s turn to face the grumblers.
(From http://www.economist.com/blogs/economist explains/201 4/04/economist-explains-10)
TEXT II
The backlash against big data
[…]
Big data refers to the idea that society can do things with a large body of data that weren’t possible when working with smaller amounts. The term was originally applied a decade ago to massive datasets from astrophysics, genomics and internet search engines, and to machine-learning systems (for voice-recognition and translation, for example) that work well only when given lots of data to chew on. Now it refers to the application of data-analysis and statistics in new areas, from retailing to human resources. The backlash began in mid-March, prompted by an article in Science by David Lazer and others at Harvard and Northeastern University. It showed that a big-data poster-child—Google Flu Trends, a 2009 project which identified flu outbreaks from search queries alone—had overestimated the number of cases for four years running, compared with reported data from the Centres for Disease Control (CDC). This led to a wider attack on the idea of big data.
The criticisms fall into three areas that are not intrinsic to big data per se, but endemic to data analysis, and have some merit. First, there are biases inherent to data that must not be ignored. That is undeniably the case. Second, some proponents of big data have claimed that theory (ie, generalisable models about how the world works) is obsolete. In fact, subject-area knowledge remains necessary even when dealing with large data sets. Third, the risk of spurious correlations—associations that are statistically robust but happen only by chance—increases with more data. Although there are new statistical techniques to identify and banish spurious correlations, such as running many tests against subsets of the data, this will always be a problem.
There is some merit to the naysayers' case, in other words. But these criticisms do not mean that big-data analysis has no merit whatsoever. Even the Harvard researchers who decried big data "hubris" admitted in Science that melding Google Flu Trends analysis with CDC’s data improved the overall forecast—showing that big data can in fact be a useful tool. And research published in PLOS Computational Biology on April 17th shows it is possible to estimate the prevalence of the flu based on visits to Wikipedia articles related to the illness. Behind the big data backlash is the classic hype cycle, in which a technology’s early proponents make overly grandiose claims, people sling arrows when those promises fall flat, but the technology eventually transforms the world, though not necessarily in ways the pundits expected. It happened with the web, and television, radio, motion pictures and the telegraph before it. Now it is simply big data’s turn to face the grumblers.
(From http://www.economist.com/blogs/economist explains/201 4/04/economist-explains-10)
TEXT II
The backlash against big data
[…]
Big data refers to the idea that society can do things with a large body of data that weren’t possible when working with smaller amounts. The term was originally applied a decade ago to massive datasets from astrophysics, genomics and internet search engines, and to machine-learning systems (for voice-recognition and translation, for example) that work well only when given lots of data to chew on. Now it refers to the application of data-analysis and statistics in new areas, from retailing to human resources. The backlash began in mid-March, prompted by an article in Science by David Lazer and others at Harvard and Northeastern University. It showed that a big-data poster-child—Google Flu Trends, a 2009 project which identified flu outbreaks from search queries alone—had overestimated the number of cases for four years running, compared with reported data from the Centres for Disease Control (CDC). This led to a wider attack on the idea of big data.
The criticisms fall into three areas that are not intrinsic to big data per se, but endemic to data analysis, and have some merit. First, there are biases inherent to data that must not be ignored. That is undeniably the case. Second, some proponents of big data have claimed that theory (ie, generalisable models about how the world works) is obsolete. In fact, subject-area knowledge remains necessary even when dealing with large data sets. Third, the risk of spurious correlations—associations that are statistically robust but happen only by chance—increases with more data. Although there are new statistical techniques to identify and banish spurious correlations, such as running many tests against subsets of the data, this will always be a problem.
There is some merit to the naysayers' case, in other words. But these criticisms do not mean that big-data analysis has no merit whatsoever. Even the Harvard researchers who decried big data "hubris" admitted in Science that melding Google Flu Trends analysis with CDC’s data improved the overall forecast—showing that big data can in fact be a useful tool. And research published in PLOS Computational Biology on April 17th shows it is possible to estimate the prevalence of the flu based on visits to Wikipedia articles related to the illness. Behind the big data backlash is the classic hype cycle, in which a technology’s early proponents make overly grandiose claims, people sling arrows when those promises fall flat, but the technology eventually transforms the world, though not necessarily in ways the pundits expected. It happened with the web, and television, radio, motion pictures and the telegraph before it. Now it is simply big data’s turn to face the grumblers.
(From http://www.economist.com/blogs/economist explains/201 4/04/economist-explains-10)
TEXT II
The backlash against big data
[…]
Big data refers to the idea that society can do things with a large body of data that weren’t possible when working with smaller amounts. The term was originally applied a decade ago to massive datasets from astrophysics, genomics and internet search engines, and to machine-learning systems (for voice-recognition and translation, for example) that work well only when given lots of data to chew on. Now it refers to the application of data-analysis and statistics in new areas, from retailing to human resources. The backlash began in mid-March, prompted by an article in Science by David Lazer and others at Harvard and Northeastern University. It showed that a big-data poster-child—Google Flu Trends, a 2009 project which identified flu outbreaks from search queries alone—had overestimated the number of cases for four years running, compared with reported data from the Centres for Disease Control (CDC). This led to a wider attack on the idea of big data.
The criticisms fall into three areas that are not intrinsic to big data per se, but endemic to data analysis, and have some merit. First, there are biases inherent to data that must not be ignored. That is undeniably the case. Second, some proponents of big data have claimed that theory (ie, generalisable models about how the world works) is obsolete. In fact, subject-area knowledge remains necessary even when dealing with large data sets. Third, the risk of spurious correlations—associations that are statistically robust but happen only by chance—increases with more data. Although there are new statistical techniques to identify and banish spurious correlations, such as running many tests against subsets of the data, this will always be a problem.
There is some merit to the naysayers' case, in other words. But these criticisms do not mean that big-data analysis has no merit whatsoever. Even the Harvard researchers who decried big data "hubris" admitted in Science that melding Google Flu Trends analysis with CDC’s data improved the overall forecast—showing that big data can in fact be a useful tool. And research published in PLOS Computational Biology on April 17th shows it is possible to estimate the prevalence of the flu based on visits to Wikipedia articles related to the illness. Behind the big data backlash is the classic hype cycle, in which a technology’s early proponents make overly grandiose claims, people sling arrows when those promises fall flat, but the technology eventually transforms the world, though not necessarily in ways the pundits expected. It happened with the web, and television, radio, motion pictures and the telegraph before it. Now it is simply big data’s turn to face the grumblers.
(From http://www.economist.com/blogs/economist explains/201 4/04/economist-explains-10)
TEXT II
The backlash against big data
[…]
Big data refers to the idea that society can do things with a large body of data that weren’t possible when working with smaller amounts. The term was originally applied a decade ago to massive datasets from astrophysics, genomics and internet search engines, and to machine-learning systems (for voice-recognition and translation, for example) that work well only when given lots of data to chew on. Now it refers to the application of data-analysis and statistics in new areas, from retailing to human resources. The backlash began in mid-March, prompted by an article in Science by David Lazer and others at Harvard and Northeastern University. It showed that a big-data poster-child—Google Flu Trends, a 2009 project which identified flu outbreaks from search queries alone—had overestimated the number of cases for four years running, compared with reported data from the Centres for Disease Control (CDC). This led to a wider attack on the idea of big data.
The criticisms fall into three areas that are not intrinsic to big data per se, but endemic to data analysis, and have some merit. First, there are biases inherent to data that must not be ignored. That is undeniably the case. Second, some proponents of big data have claimed that theory (ie, generalisable models about how the world works) is obsolete. In fact, subject-area knowledge remains necessary even when dealing with large data sets. Third, the risk of spurious correlations—associations that are statistically robust but happen only by chance—increases with more data. Although there are new statistical techniques to identify and banish spurious correlations, such as running many tests against subsets of the data, this will always be a problem.
There is some merit to the naysayers' case, in other words. But these criticisms do not mean that big-data analysis has no merit whatsoever. Even the Harvard researchers who decried big data "hubris" admitted in Science that melding Google Flu Trends analysis with CDC’s data improved the overall forecast—showing that big data can in fact be a useful tool. And research published in PLOS Computational Biology on April 17th shows it is possible to estimate the prevalence of the flu based on visits to Wikipedia articles related to the illness. Behind the big data backlash is the classic hype cycle, in which a technology’s early proponents make overly grandiose claims, people sling arrows when those promises fall flat, but the technology eventually transforms the world, though not necessarily in ways the pundits expected. It happened with the web, and television, radio, motion pictures and the telegraph before it. Now it is simply big data’s turn to face the grumblers.
(From http://www.economist.com/blogs/economist explains/201 4/04/economist-explains-10)
Em uma caixa há doze dúzias de laranjas, sobre as quais sabe-se que:
I - há pelo menos duas laranjas estragadas;
II - dadas seis quaisquer dessas laranjas, há pelo menos duas não estragadas.
Sobre essas doze dúzias de laranjas, deduz-se que:
De um grupo de controle para o acompanhamento de uma determinada doença, 4% realmente têm a doença. A tabela a seguir mostra as porcentagens das pessoas que têm e das que não têm a doença e que apresentaram resultado positivo em um determinado teste.
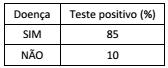
Entre as pessoas desse grupo que apresentaram resultado
positivo no teste, a porcentagem daquelas que realmente têm a
doença é aproximadamente:
Sem A, não se tem B.
Sem B, não se tem C.
Assim, conclui-se que:
Sobre os amigos Marcos, Renato e Waldo, sabe-se que:
I - Se Waldo é flamenguista, então Marcos não é tricolor;
II - Se Renato não é vascaíno, então Marcos é tricolor;
III - Se Renato é vascaíno, então Waldo não é flamenguista.
Logo, deduz-se que:
Após a extração de uma amostra, as observações obtidas são tabuladas, gerando a seguinte distribuição de frequências:
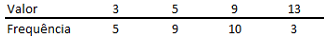
Considerando que E(X) = Média de X, Mo(X) = Moda de X e Me(X)
= Mediana de X, é correto afirmar que:
Sejam Y, X, Z e W variáveis aleatórias tais que Z = 2.Y - 3.X, sendo E(X2 ) = 25, E(X) = 4, Var (Y) =16, Cov(X,Y)= 6.
Então a variância de Z é:
Com relação à execução de estacas de fundação na construção, analise as afirmativas a seguir.
I. A estaca tipo hélice contínua é executada por meio de trado contínuo e injeção de concreto, sob pressão controlada, através da haste central do trado simultaneamente a sua retirada do terreno.
II. A estaca pré-moldada caracteriza-se por ser cravada no terreno por percussão, prensagem ou vibração, fazendo parte do grupo denominado estaca de deslocamento.
III. A estaca tipo Franki é de concreto armado moldada no solo, usa um tubo de revestimento cravado dinamicamente com ponta fechada por meio de bucha e recuperado ao ser concretada a estaca.
Com relação à execução de alvenaria sem função estrutural, analise as afirmativas a seguir:
( ) Para se evitar que uma viga com grande carga concentrada no apoio incida diretamente sobre uma parede de alvenaria, deve-se usar um coxim de concreto para que haja distribuição de carga.
( ) Sobre o vão de portas e janelas devem ser moldadas ou colocadas contra-vergas. Sob o vão da janela ou caixilhos diversos devem ser moldadas ou colocadas vergas.
( ) Deve-se utilizar um escantilhão como guia das juntas horizontais na execução de paredes de alvenaria.
Sendo V para a(s) verdadeira(s) e F para a(s) falsa(s), a sequência correta é:
Considere as seguintes informações sobre critérios gerais para cálculo de esforços atuantes em estados limites últimos acerca de tipos de furos em peças de estrutura de madeira, X e Y:
X: o furo pode ser ignorado apenas quando preenchido por pregos;
Y: o furo pode ser ignorado, desde que a redução da área resistente não supere 10% da área da zona da peça íntegra. Analisando as informações de cada uma, é correto concluir que:
Relacione o tipo de impermeabilização com seu respectivo material constituinte principal da camada impermeável.
1. Cimentício
2. Asfáltico
3. Polimérico
( ) membrana de emulsão asfáltica
( ) argamassa com aditivo impermeabilizante
( ) manta de policloreto de vinila
( ) argamassa polimérica
A relação correta, de cima para baixo, é:
Com relação à execução de estacas de fundação na construção, analise as afirmativas a seguir.
I. A janela de correr é formada por uma ou várias folhas que podem ser movimentadas por deslizamento horizontal, no plano da janela.
II. A janela projetante-deslizante é formada por uma ou mais folhas que podem ser movimentadas por deslizamento vertical, no plano da janela.
III. A janela guilhotina é formada por uma ou mais folhas que podem ser movimentadas em torno de um eixo horizontal, com translação simultânea desse eixo.
Está correto o que se afirma em: