Questões de Concurso Público ITAIPU BINACIONAL 2017 para Profissional de Nível Superior Jr - Informática ou Computação – Geoprocessamento
Foram encontradas 60 questões
Computer that reads body language
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University’s Robotics Institute have enabled a computer to understand body poses and movements of multiple people from video in real time – including, for the first time, the pose of each individual’s hands and fingers.
Carnegie Mellon University researchers have developed methods to detect the body pose, including facial expressions and hand positions, of multiple individuals. This enables computers to not only identify parts of the body, but to understand how they are moving and positioned.
This new method was developed with the help of the Panoptic Studio, a two-story dome embedded with 500 video cameras. The insights gained from experiments in that facility now make it possible to detect the pose of a group of people using a single camera and a laptop computer.
Yaser Sheikh, associate professor of robotics, said these methods for tracking 2-D human form and motion open up new ways for people and machines to interact with each other, and for people to use machines to better understand the world around them. The ability to recognize hand poses, for instance, will make it possible for people to interact with computers in new and more natural ways, such as communicating with computers simply by pointing at things.
Detecting the nuances of nonverbal communication between individuals will allow robots to serve in social spaces, allowing robots to perceive what people around them are doing, what moods they are in and whether they can be interrupted. A self-driving car could get an early warning that a pedestrian is about to step into the street by monitoring body language. In sports analytics, real-time pose detection will make it possible for computers not only to track the position of each player on the field of play, as is now the case, but to also know what players are doing with their arms, legs and heads at each point in time. The methods can be used for live events or applied to existing videos.
“The Panoptic Studio supercharges our research”, Sheikh said. It now is being used to improve body, face and hand detectors by jointly training them. Also, as work progresses to move from the 2-D models of humans to 3-D models, the facility’s ability to automatically generate annotated images will be crucial.
When the Panoptic Studio was built a decade ago with support from the National Science Foundation, it was not clear what impact it would have, Sheikh said.
“Now, we’re able to break through a number of technical barriers primarily as a result of a grant 10 years ago”, he added. “We’re sharing the code, but we’re also sharing all the data captured in the Panoptic Studio”.
(Disponível: <https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/07/170706143158.htm>
Com base no texto, considere as seguintes informações:
1. O nome da instituição que desenvolveu a pesquisa.
2. O local onde está situado o estúdio Panoptic.
3. O número de pessoas que serviram como cobaias no experimento.
4. A época em que o estúdio foi construído.
5. A dificuldade de serem encontrados modelos humanos para interagir com computadores.
O texto apresenta as informações contidas nos itens:
Computer that reads body language
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University’s Robotics Institute have enabled a computer to understand body poses and movements of multiple people from video in real time – including, for the first time, the pose of each individual’s hands and fingers.
Carnegie Mellon University researchers have developed methods to detect the body pose, including facial expressions and hand positions, of multiple individuals. This enables computers to not only identify parts of the body, but to understand how they are moving and positioned.
This new method was developed with the help of the Panoptic Studio, a two-story dome embedded with 500 video cameras. The insights gained from experiments in that facility now make it possible to detect the pose of a group of people using a single camera and a laptop computer.
Yaser Sheikh, associate professor of robotics, said these methods for tracking 2-D human form and motion open up new ways for people and machines to interact with each other, and for people to use machines to better understand the world around them. The ability to recognize hand poses, for instance, will make it possible for people to interact with computers in new and more natural ways, such as communicating with computers simply by pointing at things.
Detecting the nuances of nonverbal communication between individuals will allow robots to serve in social spaces, allowing robots to perceive what people around them are doing, what moods they are in and whether they can be interrupted. A self-driving car could get an early warning that a pedestrian is about to step into the street by monitoring body language. In sports analytics, real-time pose detection will make it possible for computers not only to track the position of each player on the field of play, as is now the case, but to also know what players are doing with their arms, legs and heads at each point in time. The methods can be used for live events or applied to existing videos.
“The Panoptic Studio supercharges our research”, Sheikh said. It now is being used to improve body, face and hand detectors by jointly training them. Also, as work progresses to move from the 2-D models of humans to 3-D models, the facility’s ability to automatically generate annotated images will be crucial.
When the Panoptic Studio was built a decade ago with support from the National Science Foundation, it was not clear what impact it would have, Sheikh said.
“Now, we’re able to break through a number of technical barriers primarily as a result of a grant 10 years ago”, he added. “We’re sharing the code, but we’re also sharing all the data captured in the Panoptic Studio”.
(Disponível: <https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/07/170706143158.htm>
Computer that reads body language
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University’s Robotics Institute have enabled a computer to understand body poses and movements of multiple people from video in real time – including, for the first time, the pose of each individual’s hands and fingers.
Carnegie Mellon University researchers have developed methods to detect the body pose, including facial expressions and hand positions, of multiple individuals. This enables computers to not only identify parts of the body, but to understand how they are moving and positioned.
This new method was developed with the help of the Panoptic Studio, a two-story dome embedded with 500 video cameras. The insights gained from experiments in that facility now make it possible to detect the pose of a group of people using a single camera and a laptop computer.
Yaser Sheikh, associate professor of robotics, said these methods for tracking 2-D human form and motion open up new ways for people and machines to interact with each other, and for people to use machines to better understand the world around them. The ability to recognize hand poses, for instance, will make it possible for people to interact with computers in new and more natural ways, such as communicating with computers simply by pointing at things.
Detecting the nuances of nonverbal communication between individuals will allow robots to serve in social spaces, allowing robots to perceive what people around them are doing, what moods they are in and whether they can be interrupted. A self-driving car could get an early warning that a pedestrian is about to step into the street by monitoring body language. In sports analytics, real-time pose detection will make it possible for computers not only to track the position of each player on the field of play, as is now the case, but to also know what players are doing with their arms, legs and heads at each point in time. The methods can be used for live events or applied to existing videos.
“The Panoptic Studio supercharges our research”, Sheikh said. It now is being used to improve body, face and hand detectors by jointly training them. Also, as work progresses to move from the 2-D models of humans to 3-D models, the facility’s ability to automatically generate annotated images will be crucial.
When the Panoptic Studio was built a decade ago with support from the National Science Foundation, it was not clear what impact it would have, Sheikh said.
“Now, we’re able to break through a number of technical barriers primarily as a result of a grant 10 years ago”, he added. “We’re sharing the code, but we’re also sharing all the data captured in the Panoptic Studio”.
(Disponível: <https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/07/170706143158.htm>
Com relação aos anagramas da palavra ITAIPU, identifique como verdadeiras (V) ou falsas (F) as seguintes afirmativas:
( ) Há 360 anagramas distintos.
( ) Há 30 anagramas distintos em que as duas consoantes estão juntas.
( ) Há 24 anagramas que começam e terminam com a letra I.
( ) Há 200 anagramas em que as letras I estão separadas.
Assinale a alternativa que apresenta a sequência correta, de cima para baixo.
Seja T = R2 → R2 uma transformação linear cuja matriz, em relação às bases canônicas, é
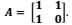
Considere as seguintes afirmativas:
1. O núcleo N(T) = {v ∈ R2; Tv = 0 } contém apenas o vetor nulo.
2. A transformação T é sobrejetiva.
3. A transformação T possui dois autovalores distintos.
4. A transformação T é diagonalizável.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
Computer that reads body language
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University’s Robotics Institute have enabled a computer to understand body poses and movements of multiple people from video in real time – including, for the first time, the pose of each individual’s hands and fingers.
Carnegie Mellon University researchers have developed methods to detect the body pose, including facial expressions and hand positions, of multiple individuals.
This enables computers to not only identify parts of the body, but to understand how they are moving and positioned. This new method was developed with the help of the Panoptic Studio, a two-story dome embedded with 500 video cameras. The insights gained from experiments in that facility now make it possible to detect the pose of a group of people using a single camera and a laptop computer.
Yaser Sheikh, associate professor of robotics, said these methods for tracking 2-D human form and motion open up new ways for people and machines to interact with each other, and for people to use machines to better understand the world around them. The ability to recognize hand poses, for instance, will make it possible for people to interact with computers in new and more natural ways, such as communicating with computers simply by pointing at things.
Detecting the nuances of nonverbal communication between individuals will allow robots to serve in social spaces, allowing robots to perceive what people around them are doing, what moods they are in and whether they can be interrupted. A self-driving car could get an early warning that a pedestrian is about to step into the street by monitoring body language. In sports analytics, real-time pose detection will make it possible for computers not only to track the position of each player on the field of play, as is now the case, but to also know what players are doing with their arms, legs and heads at each point in time. The methods can be used for live events or applied to existing videos.
“The Panoptic Studio supercharges our research”, Sheikh said. It now is being used to improve body, face and hand detectors by jointly training them. Also, as work progresses to move from the 2-D models of humans to 3-D models, the facility’s ability to automatically generate annotated images will be crucial.
When the Panoptic Studio was built a decade ago with support from the National Science Foundation, it was not clear what impact it would have, Sheikh said.
“Now, we’re able to break through a number of technical barriers primarily as a result of a grant 10 years ago”, he added. “We’re sharing the code, but we’re also sharing all the data captured in the Panoptic Studio”.
(Disponível:<https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/07/170706143158.htm>
A respeito do Panoptic Studio, local que serviu de apoio para o projeto, considere as seguintes afirmativas:
1. Recebeu uma doação para esse projeto há dez anos.
2. Tem dois andares.
3. Apresenta arquitetura com uma superfície arredondada.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
Computer that reads body language
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University’s Robotics Institute have enabled a computer to understand body poses and movements of multiple people from video in real time – including, for the first time, the pose of each individual’s hands and fingers.
Carnegie Mellon University researchers have developed methods to detect the body pose, including facial expressions and hand positions, of multiple individuals.
This enables computers to not only identify parts of the body, but to understand how they are moving and positioned. This new method was developed with the help of the Panoptic Studio, a two-story dome embedded with 500 video cameras. The insights gained from experiments in that facility now make it possible to detect the pose of a group of people using a single camera and a laptop computer.
Yaser Sheikh, associate professor of robotics, said these methods for tracking 2-D human form and motion open up new ways for people and machines to interact with each other, and for people to use machines to better understand the world around them. The ability to recognize hand poses, for instance, will make it possible for people to interact with computers in new and more natural ways, such as communicating with computers simply by pointing at things.
Detecting the nuances of nonverbal communication between individuals will allow robots to serve in social spaces, allowing robots to perceive what people around them are doing, what moods they are in and whether they can be interrupted. A self-driving car could get an early warning that a pedestrian is about to step into the street by monitoring body language. In sports analytics, real-time pose detection will make it possible for computers not only to track the position of each player on the field of play, as is now the case, but to also know what players are doing with their arms, legs and heads at each point in time. The methods can be used for live events or applied to existing videos.
“The Panoptic Studio supercharges our research”, Sheikh said. It now is being used to improve body, face and hand detectors by jointly training them. Also, as work progresses to move from the 2-D models of humans to 3-D models, the facility’s ability to automatically generate annotated images will be crucial.
When the Panoptic Studio was built a decade ago with support from the National Science Foundation, it was not clear what impact it would have, Sheikh said.
“Now, we’re able to break through a number of technical barriers primarily as a result of a grant 10 years ago”, he added. “We’re sharing the code, but we’re also sharing all the data captured in the Panoptic Studio”.
(Disponível:<https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/07/170706143158.htm>
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham suggest that brainwave-sensing headsets, also known as EEG or electroencephalograph headsets, need better security after a study reveals hackers could guess a user’s passwords by monitoring their brainwaves.
(Disponível: <https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/07/170701081756.htm>
De acordo com o texto, é correto afirmar que pesquisadores da Universidade do Alabama:
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham suggest that brainwave-sensing headsets, also known as EEG or electroencephalograph headsets, need better security after a study reveals hackers could guess a user’s passwords by monitoring their brainwaves.
(Disponível: <https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/07/170701081756.htm>
Sobre a sigla EEG, considere as seguintes expressões:
1. Brainwave-sensing headsets.
2. Electroencephalograph headsets.
3. User’s passwords.
É/São expressão(ões) que substitui(em) a sigla EEG:
Asem Hasna lost his leg in Syria – now he’s 3D-printing a second chance for fellow amputees
The story of Refugee Open Ware, and one wounded refugee’s efforts to help his countrymen back on their feet.
For most people, the first time they use a 3D printer is to create a simple object – a fridge magnet or a bookmark. Asem Hasna, then a 20-year-old Syrian refugee in Jordan, began with a prosthetic hand for a woman who lost hers in Syria’s civil war.
Hasna had met the woman in 2014 in Zaatari, the refugee camp 65 kilometers north-east of Amman, the capital of Jordan. The young woman, who has requested anonymity, lost her right hand during an attack and was struggling to care for her two daughters. Hasna, now 23, had just joined Refugee Open Ware (ROW), an Amman-based organisation that taught refugees how to 3D-print affordable artificial limbs for amputees.
(http://www.wired.co.uk/article/asem-hasna-prosthetics-syria)
A respeito do texto acima, considere as seguintes afirmativas:
1. Asem Hasna teve sua perna amputada antes de completar 23 anos.
2. Hasna, refugiado sírio, tem ajudado seus compatriotas feridos em conflitos confeccionando próteses em 3D.
3. Os primeiros objetos em 3D confeccionados por Hasna foram um marcador de livros e um ímã de geladeira.
4. A mulher que perdeu sua mão direita na guerra da Síria ajuda seu compatriota Hasna, confeccionando membros em 3D.
5. A organização – ROW –, situada em Amman, ensina refugiados a confeccionar membros em 3D a um preço acessível.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
Para avaliar o nível de satisfação dos empregados em relação ao seu trabalho e ao salário, o departamento de recursos humanos de uma empresa dividiu a análise dos dados segundo as seguintes faixas salariais:
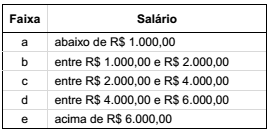
Após entrevistar todos os empregados, foram obtidos os seguintes conjuntos fuzzy:
• S = {(a; 0,5), (b; 0,4), (c; 0,7), (d; 0,5), (e; 0,25)} (percepção quanto à satisfação com o salário) e
• T = {(a; 0,7), (b; 0,6), (c; 0,8), (d; 0,7), (e; 0,5)} (percepção quanto à satisfação com o trabalho que executa)
Denote por μS (x) e μT (x) os graus de pertinência do elemento x aos conjuntos S e T, respectivamente – por exemplo, μS (b) = 0,4 e μT (c) = 0,8.
Considere as seguintes afirmativas:
1. S ⊂ T .
2. μS∪T(a) = max { μS(a), μT(a)} = 0,7.
3. μS∩T (e) = min { μS (e), μT(e)} = 0,25.
4. μT c(d) = 1 − μT (d) =0,3.
Assinale a alternativa correta.