Questões de Concurso Público UNICAMP 2019 para Bibliotecário
Foram encontradas 60 questões
Considere a planilha do MS-Excel 2010, na sua configuração padrão.

Ao pressionar CTRL+C na célula C12 e colar na célula C15 com a opção de colagem especial  , resultará no
seguinte conteúdo:
, resultará no
seguinte conteúdo:
Na figura a seguir, é mostrada uma apresentação do MS-PowerPoint 2010, em sua configuração original.
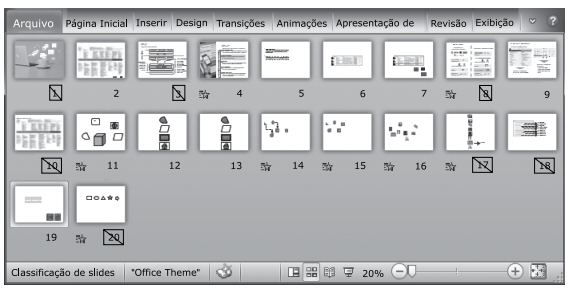
No slide 19, foi inserido o botão de ação  (configurado com hiperlink padrão) que, ao ser clicado em modo de exibição
de slides, levará a apresentação para o seguinte slide:
(configurado com hiperlink padrão) que, ao ser clicado em modo de exibição
de slides, levará a apresentação para o seguinte slide:
Considere a mensagem de correio eletrônico digitada no MS-Outlook 2010, na sua configuração padrão, pronta para ser enviada.
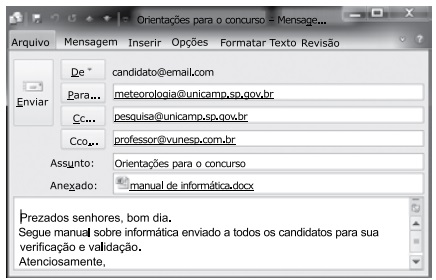
Ao receber a mensagem, [email protected]
pretende retransmiti-la apenas para a banca da Vunesp
([email protected]), mantendo o manual de
informática como anexo. Para isso, é necessário o
seguinte procedimento a partir da mensagem originalmente recebida: clicar na opção
Knowledge and the library
It was not until the development of monastic libraries in Europe around 1200 that humanity amassed in a single place what approached the collective wisdom and knowledge of the age. Libraries may be exchanges of information and market places for ideas but they are also the buildings which contain the bulk of human knowledge. Or, at least they were until the electronic digitally stored information revolution of the 1980s.
Now knowledge is virtually everywhere; it has broken free of the constraint of buildings. Today if you were today to destroy all the world’s libraries, it is unlikely that more than 20% of human knowledge would be lost. Certainly, a large amount of archival material would disappear forever, but a substantial volume of knowledge would survive. If a library is a repository of knowledge, this is now just one of its functions. The library’s prime function is now making that knowledge available and encouraging exchange and reflection upon it.
Electronic knowledge is nowadays available to everybody – in the home, workplace, airport terminal, school, and so on. The Internet has liberated the library; nevertheless, it has not removed the justification for library facilities.
(www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978185617619410017X. Adaptado)
Knowledge and the library
It was not until the development of monastic libraries in Europe around 1200 that humanity amassed in a single place what approached the collective wisdom and knowledge of the age. Libraries may be exchanges of information and market places for ideas but they are also the buildings which contain the bulk of human knowledge. Or, at least they were until the electronic digitally stored information revolution of the 1980s.
Now knowledge is virtually everywhere; it has broken free of the constraint of buildings. Today if you were today to destroy all the world’s libraries, it is unlikely that more than 20% of human knowledge would be lost. Certainly, a large amount of archival material would disappear forever, but a substantial volume of knowledge would survive. If a library is a repository of knowledge, this is now just one of its functions. The library’s prime function is now making that knowledge available and encouraging exchange and reflection upon it.
Electronic knowledge is nowadays available to everybody – in the home, workplace, airport terminal, school, and so on. The Internet has liberated the library; nevertheless, it has not removed the justification for library facilities.
(www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978185617619410017X. Adaptado)
Knowledge and the library
It was not until the development of monastic libraries in Europe around 1200 that humanity amassed in a single place what approached the collective wisdom and knowledge of the age. Libraries may be exchanges of information and market places for ideas but they are also the buildings which contain the bulk of human knowledge. Or, at least they were until the electronic digitally stored information revolution of the 1980s.
Now knowledge is virtually everywhere; it has broken free of the constraint of buildings. Today if you were today to destroy all the world’s libraries, it is unlikely that more than 20% of human knowledge would be lost. Certainly, a large amount of archival material would disappear forever, but a substantial volume of knowledge would survive. If a library is a repository of knowledge, this is now just one of its functions. The library’s prime function is now making that knowledge available and encouraging exchange and reflection upon it.
Electronic knowledge is nowadays available to everybody – in the home, workplace, airport terminal, school, and so on. The Internet has liberated the library; nevertheless, it has not removed the justification for library facilities.
(www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978185617619410017X. Adaptado)
Knowledge and the library
It was not until the development of monastic libraries in Europe around 1200 that humanity amassed in a single place what approached the collective wisdom and knowledge of the age. Libraries may be exchanges of information and market places for ideas but they are also the buildings which contain the bulk of human knowledge. Or, at least they were until the electronic digitally stored information revolution of the 1980s.
Now knowledge is virtually everywhere; it has broken free of the constraint of buildings. Today if you were today to destroy all the world’s libraries, it is unlikely that more than 20% of human knowledge would be lost. Certainly, a large amount of archival material would disappear forever, but a substantial volume of knowledge would survive. If a library is a repository of knowledge, this is now just one of its functions. The library’s prime function is now making that knowledge available and encouraging exchange and reflection upon it.
Electronic knowledge is nowadays available to everybody – in the home, workplace, airport terminal, school, and so on. The Internet has liberated the library; nevertheless, it has not removed the justification for library facilities.
(www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978185617619410017X. Adaptado)
Knowledge and the library
It was not until the development of monastic libraries in Europe around 1200 that humanity amassed in a single place what approached the collective wisdom and knowledge of the age. Libraries may be exchanges of information and market places for ideas but they are also the buildings which contain the bulk of human knowledge. Or, at least they were until the electronic digitally stored information revolution of the 1980s.
Now knowledge is virtually everywhere; it has broken free of the constraint of buildings. Today if you were today to destroy all the world’s libraries, it is unlikely that more than 20% of human knowledge would be lost. Certainly, a large amount of archival material would disappear forever, but a substantial volume of knowledge would survive. If a library is a repository of knowledge, this is now just one of its functions. The library’s prime function is now making that knowledge available and encouraging exchange and reflection upon it.
Electronic knowledge is nowadays available to everybody – in the home, workplace, airport terminal, school, and so on. The Internet has liberated the library; nevertheless, it has not removed the justification for library facilities.
(www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978185617619410017X. Adaptado)
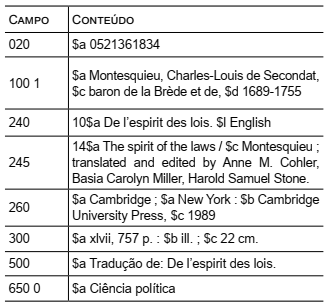
Na representação descritiva no formato MARC21, indicada no quadro a seguir, os campos que indicam exclusivamente a entidade “manifestação” do grupo 1 do FRBR são: