Questões de Concurso
Para marinha
Foram encontradas 1.398 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Para entender e controlar sistemas complexos, deve-se obter modelos matemáticos quantitativos desses sistemas. Sobre a modelagem de sistemas físicos, marque V para verdadeiro ou F para falso e, em seguida, assinale a alternativa que apresenta a sequência correta.
( ) As variáveis generalizadas de um dado sistema são aquelas cujo produto é igual à potência entrando ou saindo do sistema.
( ) Sob o enfoque energético, pode-se classificar os elementos de sistemas físicos em três tipos: fonte de energia, armazenadores de energia e dissipadores de energia.
( ) No par de variáveis generalizadas, identificam-se dois tipos de variáveis, que dependem da forma com que elas agem nos elementos dos sistemas. Assim, têm-se variáveis ENTRE (corrente, força) e variáveis ATRAVÉS (tensão, velocidade).
Supondo que ocorra uma transformação radioativa natural
em dois estágios de um nuclídeo pai 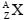 para um
nuclídeo filho
para um
nuclídeo filho 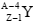 , assinale a alternativa que apresenta
os decaimentos que possivelmente ocorreram nos dois
estágios para essa transformação.
, assinale a alternativa que apresenta
os decaimentos que possivelmente ocorreram nos dois
estágios para essa transformação.
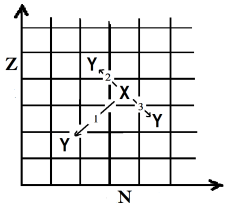
A história da física nuclear teve início com a descoberta da radioatividade. A radioatividade envolve processos de desintegração espontânea de núcleos atômicos instáveis, sendo que cada tipo de emissão está associado a determinado tipo de estabilidade nuclear. No gráfico abaixo, que representa uma carta de nuclídeos, vê-se a representação de três transições nucleares (X → Y), em que as transformações nucleares convertem um núcleo pai X em um núcleo filho Y . Sobre as transições 1, 2 e 3, indicadas no gráfico Z( × )N , é correto afirmar que elas representam, respectivamente, os seguintes decaimentos:
NASA’s Nuclear Frontier: The Plum Brook Reactor Facility
There are three main types of nuclear reactors: power, research, and test. Research and test reactors as scientific tools are more common than most people realize. While power reactors frequently appear in newspaper headlines and are conspicuous because of their size and power, research reactors can be quietly tucked away, even in the midst of a college campus. Power reactors generate heat, which can easily be converted to other useable forms of energy, such as electricity. Research reactors operate at very low thermal power levels – so low, in fact, that they do not even require any type of forced cooling. They are used to measure nuclear parameters and other characteristics, which can then be used to build other reactors or to design experiments for test reactors. Test reactors are more powerful than research reactors and are able to produce much more intense radiation fields. Though they are still much less powerful than the power reactors, they generate enough heat to require a closed-loop forced-circulation coolant system. This system will remove the heat from the reactor by transferring it to a secondary cooling system, which releases it into the atmosphere through cooling towers.
NASA’s Nuclear Frontier: The Plum Brook Reactor Facility. Pages 36 to 40.
Read the sentence below taken from the text.
“Though they are still much less powerful than the power reactors, they generate enough heat to require a closed-loop forced-circulation coolant system.”
Choose the alternative that presents a word or expression that can susbtitute the bold and underlined one above, considering the context and without changing meaning.
NASA’s Nuclear Frontier: The Plum Brook Reactor Facility
There are three main types of nuclear reactors: power, research, and test. Research and test reactors as scientific tools are more common than most people realize. While power reactors frequently appear in newspaper headlines and are conspicuous because of their size and power, research reactors can be quietly tucked away, even in the midst of a college campus. Power reactors generate heat, which can easily be converted to other useable forms of energy, such as electricity. Research reactors operate at very low thermal power levels – so low, in fact, that they do not even require any type of forced cooling. They are used to measure nuclear parameters and other characteristics, which can then be used to build other reactors or to design experiments for test reactors. Test reactors are more powerful than research reactors and are able to produce much more intense radiation fields. Though they are still much less powerful than the power reactors, they generate enough heat to require a closed-loop forced-circulation coolant system. This system will remove the heat from the reactor by transferring it to a secondary cooling system, which releases it into the atmosphere through cooling towers.
NASA’s Nuclear Frontier: The Plum Brook Reactor Facility. Pages 36 to 40.
Consider the words in bold and underlined in the following excerpts taken from the text.
I. “[...] power reactors frequently appear in newspaper headlines [...]”
II. “[...] research reactors can be quietly tucked away [...]”
III. “[...] which can easily be converted to other useable forms of energy [...]”
Choose the alternative in which the words in bold and underlined have the same grammar classification as the ones above.
NASA’s Nuclear Frontier: The Plum Brook Reactor Facility
There are three main types of nuclear reactors: power, research, and test. Research and test reactors as scientific tools are more common than most people realize. While power reactors frequently appear in newspaper headlines and are conspicuous because of their size and power, research reactors can be quietly tucked away, even in the midst of a college campus. Power reactors generate heat, which can easily be converted to other useable forms of energy, such as electricity. Research reactors operate at very low thermal power levels – so low, in fact, that they do not even require any type of forced cooling. They are used to measure nuclear parameters and other characteristics, which can then be used to build other reactors or to design experiments for test reactors. Test reactors are more powerful than research reactors and are able to produce much more intense radiation fields. Though they are still much less powerful than the power reactors, they generate enough heat to require a closed-loop forced-circulation coolant system. This system will remove the heat from the reactor by transferring it to a secondary cooling system, which releases it into the atmosphere through cooling towers.
NASA’s Nuclear Frontier: The Plum Brook Reactor Facility. Pages 36 to 40.
NASA’s Nuclear Frontier: The Plum Brook Reactor Facility
There are three main types of nuclear reactors: power, research, and test. Research and test reactors as scientific tools are more common than most people realize. While power reactors frequently appear in newspaper headlines and are conspicuous because of their size and power, research reactors can be quietly tucked away, even in the midst of a college campus. Power reactors generate heat, which can easily be converted to other useable forms of energy, such as electricity. Research reactors operate at very low thermal power levels – so low, in fact, that they do not even require any type of forced cooling. They are used to measure nuclear parameters and other characteristics, which can then be used to build other reactors or to design experiments for test reactors. Test reactors are more powerful than research reactors and are able to produce much more intense radiation fields. Though they are still much less powerful than the power reactors, they generate enough heat to require a closed-loop forced-circulation coolant system. This system will remove the heat from the reactor by transferring it to a secondary cooling system, which releases it into the atmosphere through cooling towers.
NASA’s Nuclear Frontier: The Plum Brook Reactor Facility. Pages 36 to 40.
According to the text, analyse the assertions below.
I. Power reactors are bigger than research reactors.
II. Research reactors generate more heat than power reactors.
III. Power reactors are more powerful than test or research reactors.
The correct assertion(s) is(are)
NASA’s Nuclear Frontier: The Plum Brook Reactor Facility
There are three main types of nuclear reactors: power, research, and test. Research and test reactors as scientific tools are more common than most people realize. While power reactors frequently appear in newspaper headlines and are conspicuous because of their size and power, research reactors can be quietly tucked away, even in the midst of a college campus. Power reactors generate heat, which can easily be converted to other useable forms of energy, such as electricity. Research reactors operate at very low thermal power levels – so low, in fact, that they do not even require any type of forced cooling. They are used to measure nuclear parameters and other characteristics, which can then be used to build other reactors or to design experiments for test reactors. Test reactors are more powerful than research reactors and are able to produce much more intense radiation fields. Though they are still much less powerful than the power reactors, they generate enough heat to require a closed-loop forced-circulation coolant system. This system will remove the heat from the reactor by transferring it to a secondary cooling system, which releases it into the atmosphere through cooling towers.
NASA’s Nuclear Frontier: The Plum Brook Reactor Facility. Pages 36 to 40.
Consider the sentence below taken from the text.
“Power reactors generate heat, which can easily be converted to other useable forms of energy, such as electricity.”
It is correct to affirm that the word in bold and underlined above refers to