Questões de Concurso
Comentadas para cespe / cebraspe
Foram encontradas 42.750 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
I Em sistemas de avaliações contínuas, há aplicativos que verificam todas as contas a pagar e identificam aquelas que estão fora do padrão, de modo que, quando são detectadas anormalidades, estas são encaminhadas para a verificação de possíveis irregularidades ou pendências. II Para garantir o sigilo e a segurança da informação, as informações relevantes para fins de controle devem ser capturadas e reportadas apenas à área responsável pelo sistema de controles internos. III A fixação de limites máximos de exposição a riscos assumidos por um operador de mercado para cada horizonte de investimento é exemplo de uma atividade de prevenção, enquanto que a confrontação da mesma informação com dados vindos de bases diferentes, adotando as ações corretivas, quando necessário, constitui um tipo de atividade de detecção.
Assinale a opção correta.
Três diferentes metodologias de trabalho – M1, M2 e M3 – propiciam diferentes probabilidades de sucesso na execução de uma tarefa e, do ponto de vista probabilístico, essas probabilidades são P(S|M1) = 0,9, P(S|M2) = 8 e P(S|M3) = 0,7, em que S é o evento que indica sucesso na execução da tarefa. Os eventos M1, M2 e M3 formam uma partição do espaço amostral e P(M1) = 0,2 e P(M2) = 0,3.
De acordo com essas informações, caso uma tarefa tenha
sucesso, a probabilidade de que ela tenha sido executada pela
metodologia M1 será igual a
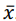 , mediana amostral Md e
moda amostral Mo.
, mediana amostral Md e
moda amostral Mo. Nessa situação hipotética, a razão
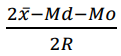 será igual a
será igual a 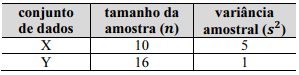
Nessa situação hipotética, se os dois conjuntos de dados forem reunidos, formando um único conjunto de dados com 26 observações, a variância amostral desse novo conjunto será igual a
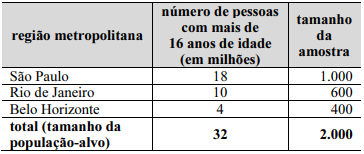
Conforme a descrição precedente, o levantamento estatístico em apreço remete a uma amostragem
Text CB1A2-II

Jorge Cham. Piled higher and deeper. Internet: <www.phdcomics.com>.
Text CB1A2-II

Jorge Cham. Piled higher and deeper. Internet: <www.phdcomics.com>.
Text CB1A2-II

Jorge Cham. Piled higher and deeper. Internet: <www.phdcomics.com>.
Text CB1A2-I
Although an oft-cited poll showed that 85% of Americans approve of organ donation, less than half had made a decision about donating, and fewer still (28%) had granted permission by signing a donor card, a pattern also observed in Germany, Spain, and Sweden. Given the shortage of donors, the gap between approval and action is a matter of life and death.
What drives the decision to become a potential donor? Within the European Union, donation rates vary by nearly an order of magnitude across countries and these differences are stable from year to year. Even when controlling for variables such as transplant infrastructure, economic and educational status, and religion, large differences in donation rates persist. Why?
Most public policy choices have a no-action default, that is, a condition is imposed when an individual fails to make a decision. In the case of organ donation, European countries have one of two default policies. In presumed-consent states, people are organ donors unless they register not to be, and in explicitconsent countries, nobody is an organ donor without registering to be one.
We examined the rate of agreement to become a donor across European countries with explicit and presumed consent laws. If preferences concerning organ donation are strong, we would expect defaults to have little or no effect. However, defaults appear to make a large difference: the four opt-in countries (Denmark, Netherlands, United Kingdom, Germany) had lower rates than the six opt-out countries (Austria, Belgium, France, Hungary, Poland, Portugal, Sweden). The two distributions have no overlap, and nearly 60 percentage points separate the two groups
Our data suggest changes in defaults could increase donations in the United States of additional thousands of donors a year. Because each donor can donate for about three transplants, the consequences are substantial in lives saved. Our results stand in contrast with the suggestion that defaults do not matter. Policy-makers performing analysis in this and other domains should consider that defaults make a difference.
Eric J. Johnson; Daniel Goldstein. Do Defaults Save Lives?
Internet: <www.dangoldstein.com> (adapted).
Text CB1A2-I
Although an oft-cited poll showed that 85% of Americans approve of organ donation, less than half had made a decision about donating, and fewer still (28%) had granted permission by signing a donor card, a pattern also observed in Germany, Spain, and Sweden. Given the shortage of donors, the gap between approval and action is a matter of life and death.
What drives the decision to become a potential donor? Within the European Union, donation rates vary by nearly an order of magnitude across countries and these differences are stable from year to year. Even when controlling for variables such as transplant infrastructure, economic and educational status, and religion, large differences in donation rates persist. Why?
Most public policy choices have a no-action default, that is, a condition is imposed when an individual fails to make a decision. In the case of organ donation, European countries have one of two default policies. In presumed-consent states, people are organ donors unless they register not to be, and in explicitconsent countries, nobody is an organ donor without registering to be one.
We examined the rate of agreement to become a donor across European countries with explicit and presumed consent laws. If preferences concerning organ donation are strong, we would expect defaults to have little or no effect. However, defaults appear to make a large difference: the four opt-in countries (Denmark, Netherlands, United Kingdom, Germany) had lower rates than the six opt-out countries (Austria, Belgium, France, Hungary, Poland, Portugal, Sweden). The two distributions have no overlap, and nearly 60 percentage points separate the two groups
Our data suggest changes in defaults could increase donations in the United States of additional thousands of donors a year. Because each donor can donate for about three transplants, the consequences are substantial in lives saved. Our results stand in contrast with the suggestion that defaults do not matter. Policy-makers performing analysis in this and other domains should consider that defaults make a difference.
Eric J. Johnson; Daniel Goldstein. Do Defaults Save Lives?
Internet: <www.dangoldstein.com> (adapted).