Questões de Concurso
Comentadas para banco do brasil
Foram encontradas 1.463 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
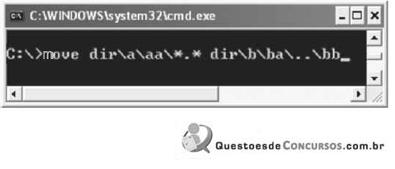
informática utilizados em ambiente de escritório.
informática utilizados em ambiente de escritório.
informática utilizados em ambiente de escritório.

A figura acima apresenta a configuração de um sistema
computacional em determinado instante de tempo.


Considerando a figura acima, que apresenta a janela da Central de
Segurança sendo executada em um computador com o sistema
operacional Windows XP, julgue os itens seguintes, a respeito de
conceitos de proteção e segurança.

Tendo como referência a figura acima, que mostra os valores das
taxas de juros anuais, em dois anos consecutivos, denominados
anterior e atual, em 10 países, julgue os itens seguintes.

Tendo como referência a figura acima, que mostra os valores das
taxas de juros anuais, em dois anos consecutivos, denominados
anterior e atual, em 10 países, julgue os itens seguintes.
em dezembro de 2008 pelos ministros da Defesa, Nelson Jobim, e
da Secretaria de Assuntos Estratégicos, Roberto Mangabeira
Unger. A END, documento de alto nível estabelecido como política
de Estado, afasta a possibilidade de transformação das Forças
Armadas em milícias de segurança interna. Estabelece o vínculo
entre o conceito e a política de independência nacional, de um
lado, e as Forças Armadas como seu elemento de resguardo,
de outro.
A estratégia nacional de defesa. In: Revista Tecnologia
e Defesa. São Paulo, ano 25, n.º 116, 2008-9, p. 13 (com adaptações).
Tendo o texto acima como referência inicial, julgue os itens que se
seguem.
que o Reino Unido apoia a candidatura brasileira a uma vaga
permanente no Conselho de Segurança da Organização das
Nações Unidas (ONU). "O Brasil tem o respaldo total do
governo britânico para ser membro permanente do Conselho de
Segurança da ONU", disse Brown, durante um seminário sobre
a próxima cúpula do G-20.
Brown ressaltou que, além da vaga no conselho, o
Brasil também deve participar mais da agenda global, sendo
mais efetivo na administração do Fundo Monetário
Internacional (FMI) e do Banco Mundial. Segundo ele, o Brasil
terá um papel importante na solução dos quatro grandes
desafios que o mundo tem para enfrentar: a estabilidade
financeira, as mudanças climáticas, o extremismo social e
religioso e o crescimento da pobreza.
Inglaterra quer Brasil na ONU. In: Diário do
Nordeste. Fortaleza, 27/3/2009 (com adaptações).
Tendo o texto acima como referência inicial, julgue os itens
subsequentes.
que o Reino Unido apoia a candidatura brasileira a uma vaga
permanente no Conselho de Segurança da Organização das
Nações Unidas (ONU). "O Brasil tem o respaldo total do
governo britânico para ser membro permanente do Conselho de
Segurança da ONU", disse Brown, durante um seminário sobre
a próxima cúpula do G-20.
Brown ressaltou que, além da vaga no conselho, o
Brasil também deve participar mais da agenda global, sendo
mais efetivo na administração do Fundo Monetário
Internacional (FMI) e do Banco Mundial. Segundo ele, o Brasil
terá um papel importante na solução dos quatro grandes
desafios que o mundo tem para enfrentar: a estabilidade
financeira, as mudanças climáticas, o extremismo social e
religioso e o crescimento da pobreza.
Inglaterra quer Brasil na ONU. In: Diário do
Nordeste. Fortaleza, 27/3/2009 (com adaptações).
Tendo o texto acima como referência inicial, julgue os itens
subsequentes.
próximos itens.

World Bank Brazil – country brief
1 With an estimated 167 million inhabitants, Brazil has the
largest population in Latin America and ranks sixth in the world. The
majority live in the south-central area, which includes industrial cities
4 such as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and Belo Horizonte. 80% of the
population now lives in urban areas. Rapid growth in the urban
population has aided economic development but also created serious
7 problems for major cities.
Brazil’s “miracle years” were in the late 1960s and early 1970s
when double digit-annual growth rates were recorded and the structure
10 of the economy underwent rapid change.
In the 1980s, however, Brazil’s economic performance was
poor in comparison with its potential. Annual Gross Domestic Product
13 (GDP) growth only averaged 1.5 percent over the period from 1980
to 1993. This reflected the economy’s inability to respond to
international events in the late 1970s and the 1980s: the second oil
16 shock; increase in international real interest rates; the Latin American
external debt crisis and the ensuing cutoff of foreign credit and foreign
direct investment. This lack of responsiveness reflected the largely
19 inward-looking policy orientation that had been in place since the
1960s.
Economic flexibility was further impaired by provisions of the
22 1988 Constitution, which introduced significant rigidities in budgeting
and public expenditure. An outcome of these pressures was a steady
rise in the rate of inflation, which reached monthly rates of 50% by the
25 middle of 1994.
Internet: <http://lnweb18.worldbank.org/Exter…/
abe36259ca656c4985256914005207e3?OpenDocumen> (with adaptations).
The sentence "Rapid growth in the urban population has aided economic development but also created serious problems for major cities" (R.5-7) means the same as
World Bank Brazil – country brief
1 With an estimated 167 million inhabitants, Brazil has the
largest population in Latin America and ranks sixth in the world. The
majority live in the south-central area, which includes industrial cities
4 such as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and Belo Horizonte. 80% of the
population now lives in urban areas. Rapid growth in the urban
population has aided economic development but also created serious
7 problems for major cities.
Brazil’s “miracle years” were in the late 1960s and early 1970s
when double digit-annual growth rates were recorded and the structure
10 of the economy underwent rapid change.
In the 1980s, however, Brazil’s economic performance was
poor in comparison with its potential. Annual Gross Domestic Product
13 (GDP) growth only averaged 1.5 percent over the period from 1980
to 1993. This reflected the economy’s inability to respond to
international events in the late 1970s and the 1980s: the second oil
16 shock; increase in international real interest rates; the Latin American
external debt crisis and the ensuing cutoff of foreign credit and foreign
direct investment. This lack of responsiveness reflected the largely
19 inward-looking policy orientation that had been in place since the
1960s.
Economic flexibility was further impaired by provisions of the
22 1988 Constitution, which introduced significant rigidities in budgeting
and public expenditure. An outcome of these pressures was a steady
rise in the rate of inflation, which reached monthly rates of 50% by the
25 middle of 1994.
Internet: <http://lnweb18.worldbank.org/Exter…/
abe36259ca656c4985256914005207e3?OpenDocumen> (with adaptations).
The sentence "Rapid growth in the urban population has aided economic development but also created serious problems for major cities" (R.5-7) means the same as
World Bank Brazil – country brief
1 With an estimated 167 million inhabitants, Brazil has the
largest population in Latin America and ranks sixth in the world. The
majority live in the south-central area, which includes industrial cities
4 such as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and Belo Horizonte. 80% of the
population now lives in urban areas. Rapid growth in the urban
population has aided economic development but also created serious
7 problems for major cities.
Brazil’s “miracle years” were in the late 1960s and early 1970s
when double digit-annual growth rates were recorded and the structure
10 of the economy underwent rapid change.
In the 1980s, however, Brazil’s economic performance was
poor in comparison with its potential. Annual Gross Domestic Product
13 (GDP) growth only averaged 1.5 percent over the period from 1980
to 1993. This reflected the economy’s inability to respond to
international events in the late 1970s and the 1980s: the second oil
16 shock; increase in international real interest rates; the Latin American
external debt crisis and the ensuing cutoff of foreign credit and foreign
direct investment. This lack of responsiveness reflected the largely
19 inward-looking policy orientation that had been in place since the
1960s.
Economic flexibility was further impaired by provisions of the
22 1988 Constitution, which introduced significant rigidities in budgeting
and public expenditure. An outcome of these pressures was a steady
rise in the rate of inflation, which reached monthly rates of 50% by the
25 middle of 1994.
Internet: <http://lnweb18.worldbank.org/Exter…/
abe36259ca656c4985256914005207e3?OpenDocumen> (with adaptations).
The sentence "Rapid growth in the urban population has aided economic development but also created serious problems for major cities" (R.5-7) means the same as
World Bank Brazil – country brief
1 With an estimated 167 million inhabitants, Brazil has the
largest population in Latin America and ranks sixth in the world. The
majority live in the south-central area, which includes industrial cities
4 such as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and Belo Horizonte. 80% of the
population now lives in urban areas. Rapid growth in the urban
population has aided economic development but also created serious
7 problems for major cities.
Brazil’s “miracle years” were in the late 1960s and early 1970s
when double digit-annual growth rates were recorded and the structure
10 of the economy underwent rapid change.
In the 1980s, however, Brazil’s economic performance was
poor in comparison with its potential. Annual Gross Domestic Product
13 (GDP) growth only averaged 1.5 percent over the period from 1980
to 1993. This reflected the economy’s inability to respond to
international events in the late 1970s and the 1980s: the second oil
16 shock; increase in international real interest rates; the Latin American
external debt crisis and the ensuing cutoff of foreign credit and foreign
direct investment. This lack of responsiveness reflected the largely
19 inward-looking policy orientation that had been in place since the
1960s.
Economic flexibility was further impaired by provisions of the
22 1988 Constitution, which introduced significant rigidities in budgeting
and public expenditure. An outcome of these pressures was a steady
rise in the rate of inflation, which reached monthly rates of 50% by the
25 middle of 1994.
Internet: <http://lnweb18.worldbank.org/Exter…/
abe36259ca656c4985256914005207e3?OpenDocumen> (with adaptations).
The sentence "Rapid growth in the urban population has aided economic development but also created serious problems for major cities" (R.5-7) means the same as
World Bank Brazil – country brief
1 With an estimated 167 million inhabitants, Brazil has the
largest population in Latin America and ranks sixth in the world. The
majority live in the south-central area, which includes industrial cities
4 such as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and Belo Horizonte. 80% of the
population now lives in urban areas. Rapid growth in the urban
population has aided economic development but also created serious
7 problems for major cities.
Brazil’s “miracle years” were in the late 1960s and early 1970s
when double digit-annual growth rates were recorded and the structure
10 of the economy underwent rapid change.
In the 1980s, however, Brazil’s economic performance was
poor in comparison with its potential. Annual Gross Domestic Product
13 (GDP) growth only averaged 1.5 percent over the period from 1980
to 1993. This reflected the economy’s inability to respond to
international events in the late 1970s and the 1980s: the second oil
16 shock; increase in international real interest rates; the Latin American
external debt crisis and the ensuing cutoff of foreign credit and foreign
direct investment. This lack of responsiveness reflected the largely
19 inward-looking policy orientation that had been in place since the
1960s.
Economic flexibility was further impaired by provisions of the
22 1988 Constitution, which introduced significant rigidities in budgeting
and public expenditure. An outcome of these pressures was a steady
rise in the rate of inflation, which reached monthly rates of 50% by the
25 middle of 1994.
Internet: <http://lnweb18.worldbank.org/Exter…/
abe36259ca656c4985256914005207e3?OpenDocumen> (with adaptations).
The sentence "Rapid growth in the urban population has aided economic development but also created serious problems for major cities" (R.5-7) means the same as
World Bank Brazil – country brief
1 With an estimated 167 million inhabitants, Brazil has the
largest population in Latin America and ranks sixth in the world. The
majority live in the south-central area, which includes industrial cities
4 such as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and Belo Horizonte. 80% of the
population now lives in urban areas. Rapid growth in the urban
population has aided economic development but also created serious
7 problems for major cities.
Brazil’s “miracle years” were in the late 1960s and early 1970s
when double digit-annual growth rates were recorded and the structure
10 of the economy underwent rapid change.
In the 1980s, however, Brazil’s economic performance was
poor in comparison with its potential. Annual Gross Domestic Product
13 (GDP) growth only averaged 1.5 percent over the period from 1980
to 1993. This reflected the economy’s inability to respond to
international events in the late 1970s and the 1980s: the second oil
16 shock; increase in international real interest rates; the Latin American
external debt crisis and the ensuing cutoff of foreign credit and foreign
direct investment. This lack of responsiveness reflected the largely
19 inward-looking policy orientation that had been in place since the
1960s.
Economic flexibility was further impaired by provisions of the
22 1988 Constitution, which introduced significant rigidities in budgeting
and public expenditure. An outcome of these pressures was a steady
rise in the rate of inflation, which reached monthly rates of 50% by the
25 middle of 1994.
Internet: <http://lnweb18.worldbank.org/Exter…/
abe36259ca656c4985256914005207e3?OpenDocumen> (with adaptations).
With the help of text VII, judge the following items.
World Bank Brazil – country brief
1 With an estimated 167 million inhabitants, Brazil has the
largest population in Latin America and ranks sixth in the world. The
majority live in the south-central area, which includes industrial cities
4 such as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and Belo Horizonte. 80% of the
population now lives in urban areas. Rapid growth in the urban
population has aided economic development but also created serious
7 problems for major cities.
Brazil’s “miracle years” were in the late 1960s and early 1970s
when double digit-annual growth rates were recorded and the structure
10 of the economy underwent rapid change.
In the 1980s, however, Brazil’s economic performance was
poor in comparison with its potential. Annual Gross Domestic Product
13 (GDP) growth only averaged 1.5 percent over the period from 1980
to 1993. This reflected the economy’s inability to respond to
international events in the late 1970s and the 1980s: the second oil
16 shock; increase in international real interest rates; the Latin American
external debt crisis and the ensuing cutoff of foreign credit and foreign
direct investment. This lack of responsiveness reflected the largely
19 inward-looking policy orientation that had been in place since the
1960s.
Economic flexibility was further impaired by provisions of the
22 1988 Constitution, which introduced significant rigidities in budgeting
and public expenditure. An outcome of these pressures was a steady
rise in the rate of inflation, which reached monthly rates of 50% by the
25 middle of 1994.
Internet: <http://lnweb18.worldbank.org/Exter…/
abe36259ca656c4985256914005207e3?OpenDocumen> (with adaptations).
With the help of text VII, judge the following items.
World Bank Brazil – country brief
1 With an estimated 167 million inhabitants, Brazil has the
largest population in Latin America and ranks sixth in the world. The
majority live in the south-central area, which includes industrial cities
4 such as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and Belo Horizonte. 80% of the
population now lives in urban areas. Rapid growth in the urban
population has aided economic development but also created serious
7 problems for major cities.
Brazil’s “miracle years” were in the late 1960s and early 1970s
when double digit-annual growth rates were recorded and the structure
10 of the economy underwent rapid change.
In the 1980s, however, Brazil’s economic performance was
poor in comparison with its potential. Annual Gross Domestic Product
13 (GDP) growth only averaged 1.5 percent over the period from 1980
to 1993. This reflected the economy’s inability to respond to
international events in the late 1970s and the 1980s: the second oil
16 shock; increase in international real interest rates; the Latin American
external debt crisis and the ensuing cutoff of foreign credit and foreign
direct investment. This lack of responsiveness reflected the largely
19 inward-looking policy orientation that had been in place since the
1960s.
Economic flexibility was further impaired by provisions of the
22 1988 Constitution, which introduced significant rigidities in budgeting
and public expenditure. An outcome of these pressures was a steady
rise in the rate of inflation, which reached monthly rates of 50% by the
25 middle of 1994.
Internet: <http://lnweb18.worldbank.org/Exter…/
abe36259ca656c4985256914005207e3?OpenDocumen> (with adaptations).
With the help of text VII, judge the following items.
World Bank Brazil – country brief
1 With an estimated 167 million inhabitants, Brazil has the
largest population in Latin America and ranks sixth in the world. The
majority live in the south-central area, which includes industrial cities
4 such as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and Belo Horizonte. 80% of the
population now lives in urban areas. Rapid growth in the urban
population has aided economic development but also created serious
7 problems for major cities.
Brazil’s “miracle years” were in the late 1960s and early 1970s
when double digit-annual growth rates were recorded and the structure
10 of the economy underwent rapid change.
In the 1980s, however, Brazil’s economic performance was
poor in comparison with its potential. Annual Gross Domestic Product
13 (GDP) growth only averaged 1.5 percent over the period from 1980
to 1993. This reflected the economy’s inability to respond to
international events in the late 1970s and the 1980s: the second oil
16 shock; increase in international real interest rates; the Latin American
external debt crisis and the ensuing cutoff of foreign credit and foreign
direct investment. This lack of responsiveness reflected the largely
19 inward-looking policy orientation that had been in place since the
1960s.
Economic flexibility was further impaired by provisions of the
22 1988 Constitution, which introduced significant rigidities in budgeting
and public expenditure. An outcome of these pressures was a steady
rise in the rate of inflation, which reached monthly rates of 50% by the
25 middle of 1994.
Internet: <http://lnweb18.worldbank.org/Exter…/
abe36259ca656c4985256914005207e3?OpenDocumen> (with adaptations).
With the help of text VII, judge the following items.