Questões de Concurso
Comentadas para prefeitura de cerquilho - sp
Foram encontradas 1.040 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
A tabela apresenta informações sobre o número de funcionários em um escritório e os salários que são pagos a eles. Utilize as informações para responder à questão seguinte.

A tabela apresenta informações sobre o número de funcionários em um escritório e os salários que são pagos a eles. Utilize as informações para responder à questão seguinte.

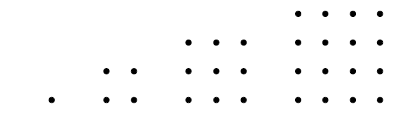 As diferenças entre o segundo e o primeiro números
quadrangulares, entre o terceiro e o segundo números
quadrangulares, entre o quarto e o terceiro números
quadrangulares, e assim sucessivamente, formam uma
sequência numérica S. O sexagésimo terceiro termo da
sequência S é
As diferenças entre o segundo e o primeiro números
quadrangulares, entre o terceiro e o segundo números
quadrangulares, entre o quarto e o terceiro números
quadrangulares, e assim sucessivamente, formam uma
sequência numérica S. O sexagésimo terceiro termo da
sequência S éSabendo-se que, obedecidas as condições de existência, 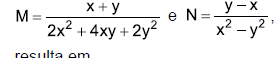 a operação M ÷ N
resulta em
a operação M ÷ N
resulta em
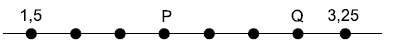 Dividindo-se P por Q, tem-se como quociente o número
Dividindo-se P por Q, tem-se como quociente o número Considere o conjunto 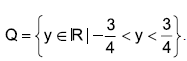 Se t corresponde ao produto de dois elementos quaisquer desse
conjunto, então
Se t corresponde ao produto de dois elementos quaisquer desse
conjunto, então
1. Considere o conjunto 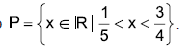 Se z corresponde à soma de dois elementos quaisquer desse
conjunto, então
Se z corresponde à soma de dois elementos quaisquer desse
conjunto, então
I have suggested that many, if not most teachers, could usefully adjust the values they emphasise. Here, three of them:
1. From Short-Term to Long-Term Aims
Learning a foreign language can be a valuable, long-term personal asset for the student. lt can be inhibited by over-emphasising short-term objectives — tests, pressure to speak before you are ready etc.
2. From Knowledge to Skill
Knowledge involves answers and explanations and is necessary, but not sufficient. What matters is not what you know, but what you can do. ‘Knowing’ a foreign language may be interesting; the ability to use it is life-enhancing.
3. From Accuracy to Communication
Successful communication always involves at least limited accuracy. Accuracy need not involve communication at all. Communication is a wider, more useful concept; successful language is more valuable than language which is only accurate.
(Michael Lewis. The lexical approach. 2002. Adaptado)
I have suggested that many, if not most teachers, could usefully adjust the values they emphasise. Here, three of them:
1. From Short-Term to Long-Term Aims
Learning a foreign language can be a valuable, long-term personal asset for the student. lt can be inhibited by over-emphasising short-term objectives — tests, pressure to speak before you are ready etc.
2. From Knowledge to Skill
Knowledge involves answers and explanations and is necessary, but not sufficient. What matters is not what you know, but what you can do. ‘Knowing’ a foreign language may be interesting; the ability to use it is life-enhancing.
3. From Accuracy to Communication
Successful communication always involves at least limited accuracy. Accuracy need not involve communication at all. Communication is a wider, more useful concept; successful language is more valuable than language which is only accurate.
(Michael Lewis. The lexical approach. 2002. Adaptado)
I have suggested that many, if not most teachers, could usefully adjust the values they emphasise. Here, three of them:
1. From Short-Term to Long-Term Aims
Learning a foreign language can be a valuable, long-term personal asset for the student. lt can be inhibited by over-emphasising short-term objectives — tests, pressure to speak before you are ready etc.
2. From Knowledge to Skill
Knowledge involves answers and explanations and is necessary, but not sufficient. What matters is not what you know, but what you can do. ‘Knowing’ a foreign language may be interesting; the ability to use it is life-enhancing.
3. From Accuracy to Communication
Successful communication always involves at least limited accuracy. Accuracy need not involve communication at all. Communication is a wider, more useful concept; successful language is more valuable than language which is only accurate.
(Michael Lewis. The lexical approach. 2002. Adaptado)
Characteristics of a good test
In order to judge the effectiveness of any test, it is sensible to lay down criteria against which the test can be measured, as follows:
Validity: a test is valid if it tests what it is supposed to test. Thus it is not valid, for example, to test writing ability with an essay question that demands specialist knowledge of history or biology — unless it is known that all students share this knowledge before they do the test.
A particular kind of ‘validity’ that concerns most test designers is face validity. This means that the test should look, on the ‘face’ of it, as if it is valid. A test which consisted of only three multiple choice items would not convince students of its face validity however reliable or practical teachers thought it to be.
Reliability: a good test should give consistent results. For example, if the same group of students took the same test twice within two days — without reflecting on the first test before they sat it again — they should get the same results on each occasion. If two groups who were demonstrably alike took the test, the marking range would be the same.
In practice, ‘reliability’ is enhanced by making the test instructions absolutely clear, restricting the scope for variety in the answers. Reliability also depends on the people who mark the tests. Clearly a test is unreliable if the result depends to any large extent on who is marking it. Much thought has gone into making the scoring of tests as reliable as possible.
(Jeremy Harmer. The practice of English language teaching. 2007. Adaptado)
Characteristics of a good test
In order to judge the effectiveness of any test, it is sensible to lay down criteria against which the test can be measured, as follows:
Validity: a test is valid if it tests what it is supposed to test. Thus it is not valid, for example, to test writing ability with an essay question that demands specialist knowledge of history or biology — unless it is known that all students share this knowledge before they do the test.
A particular kind of ‘validity’ that concerns most test designers is face validity. This means that the test should look, on the ‘face’ of it, as if it is valid. A test which consisted of only three multiple choice items would not convince students of its face validity however reliable or practical teachers thought it to be.
Reliability: a good test should give consistent results. For example, if the same group of students took the same test twice within two days — without reflecting on the first test before they sat it again — they should get the same results on each occasion. If two groups who were demonstrably alike took the test, the marking range would be the same.
In practice, ‘reliability’ is enhanced by making the test instructions absolutely clear, restricting the scope for variety in the answers. Reliability also depends on the people who mark the tests. Clearly a test is unreliable if the result depends to any large extent on who is marking it. Much thought has gone into making the scoring of tests as reliable as possible.
(Jeremy Harmer. The practice of English language teaching. 2007. Adaptado)
Characteristics of a good test
In order to judge the effectiveness of any test, it is sensible to lay down criteria against which the test can be measured, as follows:
Validity: a test is valid if it tests what it is supposed to test. Thus it is not valid, for example, to test writing ability with an essay question that demands specialist knowledge of history or biology — unless it is known that all students share this knowledge before they do the test.
A particular kind of ‘validity’ that concerns most test designers is face validity. This means that the test should look, on the ‘face’ of it, as if it is valid. A test which consisted of only three multiple choice items would not convince students of its face validity however reliable or practical teachers thought it to be.
Reliability: a good test should give consistent results. For example, if the same group of students took the same test twice within two days — without reflecting on the first test before they sat it again — they should get the same results on each occasion. If two groups who were demonstrably alike took the test, the marking range would be the same.
In practice, ‘reliability’ is enhanced by making the test instructions absolutely clear, restricting the scope for variety in the answers. Reliability also depends on the people who mark the tests. Clearly a test is unreliable if the result depends to any large extent on who is marking it. Much thought has gone into making the scoring of tests as reliable as possible.
(Jeremy Harmer. The practice of English language teaching. 2007. Adaptado)
Characteristics of a good test
In order to judge the effectiveness of any test, it is sensible to lay down criteria against which the test can be measured, as follows:
Validity: a test is valid if it tests what it is supposed to test. Thus it is not valid, for example, to test writing ability with an essay question that demands specialist knowledge of history or biology — unless it is known that all students share this knowledge before they do the test.
A particular kind of ‘validity’ that concerns most test designers is face validity. This means that the test should look, on the ‘face’ of it, as if it is valid. A test which consisted of only three multiple choice items would not convince students of its face validity however reliable or practical teachers thought it to be.
Reliability: a good test should give consistent results. For example, if the same group of students took the same test twice within two days — without reflecting on the first test before they sat it again — they should get the same results on each occasion. If two groups who were demonstrably alike took the test, the marking range would be the same.
In practice, ‘reliability’ is enhanced by making the test instructions absolutely clear, restricting the scope for variety in the answers. Reliability also depends on the people who mark the tests. Clearly a test is unreliable if the result depends to any large extent on who is marking it. Much thought has gone into making the scoring of tests as reliable as possible.
(Jeremy Harmer. The practice of English language teaching. 2007. Adaptado)
Leia a charge.

This cartoon can be used as a resource to teach or review
the use of prefixes in the English language. You may offer
your students the following words and ask them to choose
the alternative in which the prefix has the same meaning
as “un”. Your students should mark alternative