Questões de Concurso
Comentadas para prefeitura de serrana - sp
Foram encontradas 904 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
A partir do Microsoft Word 2010, em sua configuração original, um usuário está editando o seguinte documento e clicou uma vez com o botão principal do mouse sobre o número 1 da lista numerada, deixando esse marcador selecionado e os demais destacados, conforme a imagem a seguir.
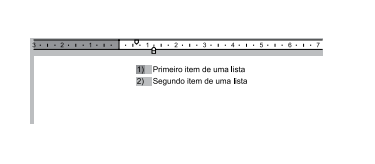
Assinale a alternativa que apresenta o resultado correto quando o usuário pressiona a tecla DEL.
A partir do Microsoft Word 2010, em sua configuração original, um usuário está editando o seguinte documento e clicou uma vez com o botão principal do mouse sobre o número 1 da lista numerada, deixando esse marcador selecionado e os demais destacados, conforme a imagem a seguir.

Assinale a alternativa que apresenta o resultado correto quando o usuário pressiona a tecla DEL.