Questões de Concurso
Comentadas para unicamp
Foram encontradas 554 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
A utilização do filme Tempos Modernos, de Charles Chaplin, para exemplificar a forma como os trabalhadores eram vistos durante quase toda a 1a metade do século passado, o XX, tem sido recorrente para a explicação dessa visão dos trabalhadores como parte da engrenagem das máquinas, sendo “movimentados” por elas na linha de produção. As máquinas é que providenciavam o ritmo e as ações dos trabalhadores, e o grande objetivo era a manutenção e o aumento da produtividade.
Qual teoria da administração é que sustenta essa visão?
New Public Management Model
The new public management model, which emerged in the 1980s, represented an attempt to make the public sector more business-like as well as to improve the efficiency of the Government, borrowed ideas and management models from the private sector. It emphasized the centrality of citizens who were the recipient of the services or customers to the public sector.
New public management system also proposed a more decentralized control of resources. It explored other service delivery models so as to achieve better results, including a quasi-market structure where public and private service providers competed with each other in an attempt to provide better and faster services.
The Core Themes for the New Public Management were:
1. A strong focus on financial control, value for money and increasing public sector efficiency;
2. A command and control mode of functioning, identifying and setting targets and continuous monitoring of public sector performance;
3. Introducing audits and controls at professional level, using transparent means to review public worker performance, setting benchmarks, using protocols to ameliorate public sector worker professional behaviour;
4. Greater customer orientation and responsiveness and increasing the scope of roles played by non-public sector providers;
5. Deregulating the labor market, replacing collective agreements to individual rewards packages combined with short term contracts;
6. Introducing new forms of corporate governance, introducing a board model of functioning and concentrating the power to the strategic core of the organization.
(www.managementstudyguide.com/new-public-management.htm.
Adaptado.)
New Public Management Model
The new public management model, which emerged in the 1980s, represented an attempt to make the public sector more business-like as well as to improve the efficiency of the Government, borrowed ideas and management models from the private sector. It emphasized the centrality of citizens who were the recipient of the services or customers to the public sector.
New public management system also proposed a more decentralized control of resources. It explored other service delivery models so as to achieve better results, including a quasi-market structure where public and private service providers competed with each other in an attempt to provide better and faster services.
The Core Themes for the New Public Management were:
1. A strong focus on financial control, value for money and increasing public sector efficiency;
2. A command and control mode of functioning, identifying and setting targets and continuous monitoring of public sector performance;
3. Introducing audits and controls at professional level, using transparent means to review public worker performance, setting benchmarks, using protocols to ameliorate public sector worker professional behaviour;
4. Greater customer orientation and responsiveness and increasing the scope of roles played by non-public sector providers;
5. Deregulating the labor market, replacing collective agreements to individual rewards packages combined with short term contracts;
6. Introducing new forms of corporate governance, introducing a board model of functioning and concentrating the power to the strategic core of the organization.
(www.managementstudyguide.com/new-public-management.htm.
Adaptado.)
New Public Management Model
The new public management model, which emerged in the 1980s, represented an attempt to make the public sector more business-like as well as to improve the efficiency of the Government, borrowed ideas and management models from the private sector. It emphasized the centrality of citizens who were the recipient of the services or customers to the public sector.
New public management system also proposed a more decentralized control of resources. It explored other service delivery models so as to achieve better results, including a quasi-market structure where public and private service providers competed with each other in an attempt to provide better and faster services.
The Core Themes for the New Public Management were:
1. A strong focus on financial control, value for money and increasing public sector efficiency;
2. A command and control mode of functioning, identifying and setting targets and continuous monitoring of public sector performance;
3. Introducing audits and controls at professional level, using transparent means to review public worker performance, setting benchmarks, using protocols to ameliorate public sector worker professional behaviour;
4. Greater customer orientation and responsiveness and increasing the scope of roles played by non-public sector providers;
5. Deregulating the labor market, replacing collective agreements to individual rewards packages combined with short term contracts;
6. Introducing new forms of corporate governance, introducing a board model of functioning and concentrating the power to the strategic core of the organization.
(www.managementstudyguide.com/new-public-management.htm.
Adaptado.)
New Public Management Model
The new public management model, which emerged in the 1980s, represented an attempt to make the public sector more business-like as well as to improve the efficiency of the Government, borrowed ideas and management models from the private sector. It emphasized the centrality of citizens who were the recipient of the services or customers to the public sector.
New public management system also proposed a more decentralized control of resources. It explored other service delivery models so as to achieve better results, including a quasi-market structure where public and private service providers competed with each other in an attempt to provide better and faster services.
The Core Themes for the New Public Management were:
1. A strong focus on financial control, value for money and increasing public sector efficiency;
2. A command and control mode of functioning, identifying and setting targets and continuous monitoring of public sector performance;
3. Introducing audits and controls at professional level, using transparent means to review public worker performance, setting benchmarks, using protocols to ameliorate public sector worker professional behaviour;
4. Greater customer orientation and responsiveness and increasing the scope of roles played by non-public sector providers;
5. Deregulating the labor market, replacing collective agreements to individual rewards packages combined with short term contracts;
6. Introducing new forms of corporate governance, introducing a board model of functioning and concentrating the power to the strategic core of the organization.
(www.managementstudyguide.com/new-public-management.htm.
Adaptado.)
New Public Management Model
The new public management model, which emerged in the 1980s, represented an attempt to make the public sector more business-like as well as to improve the efficiency of the Government, borrowed ideas and management models from the private sector. It emphasized the centrality of citizens who were the recipient of the services or customers to the public sector.
New public management system also proposed a more decentralized control of resources. It explored other service delivery models so as to achieve better results, including a quasi-market structure where public and private service providers competed with each other in an attempt to provide better and faster services.
The Core Themes for the New Public Management were:
1. A strong focus on financial control, value for money and increasing public sector efficiency;
2. A command and control mode of functioning, identifying and setting targets and continuous monitoring of public sector performance;
3. Introducing audits and controls at professional level, using transparent means to review public worker performance, setting benchmarks, using protocols to ameliorate public sector worker professional behaviour;
4. Greater customer orientation and responsiveness and increasing the scope of roles played by non-public sector providers;
5. Deregulating the labor market, replacing collective agreements to individual rewards packages combined with short term contracts;
6. Introducing new forms of corporate governance, introducing a board model of functioning and concentrating the power to the strategic core of the organization.
(www.managementstudyguide.com/new-public-management.htm.
Adaptado.)
Tem-se a seguinte planilha, criada no Microsoft Excel 2010, em sua configuração padrão. Considere que apenas as células A1 e A6 estão selecionadas. A seleção foi feita com o usuário tendo clicado com o botão principal do mouse primeiro sobre a célula A1, e depois pressionado a tecla CTRL e, com a tecla mantida pressionada, o usuário clicando com o botão principal do mouse sobre a célula A6
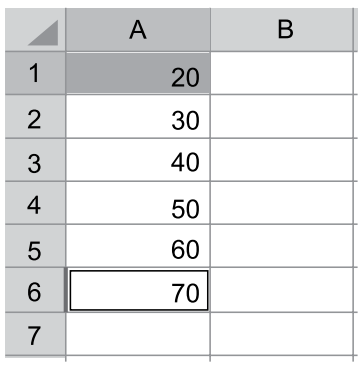
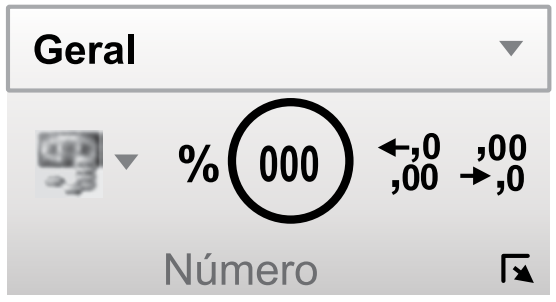
Assinale a alternativa que indica o resultado correto, quando o usuário clica sobre o ícone destacado, do grupo Número, da Guia Página Inicial.
Tem-se o seguinte conteúdo editado no Bloco de Notas do Microsoft Windows 7, em sua configuração original.
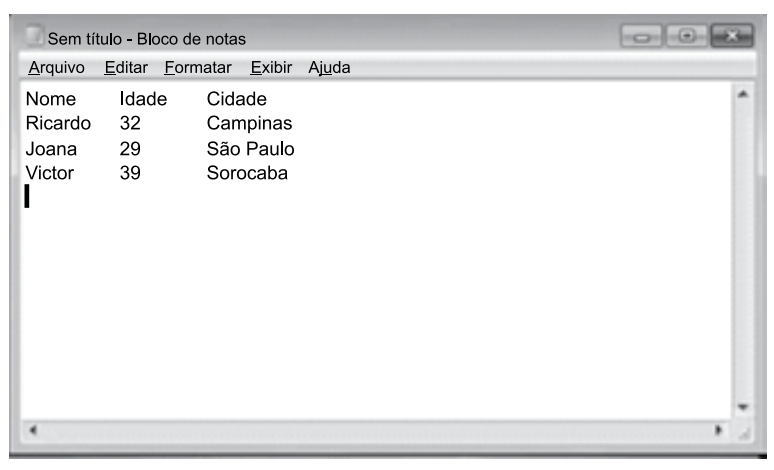
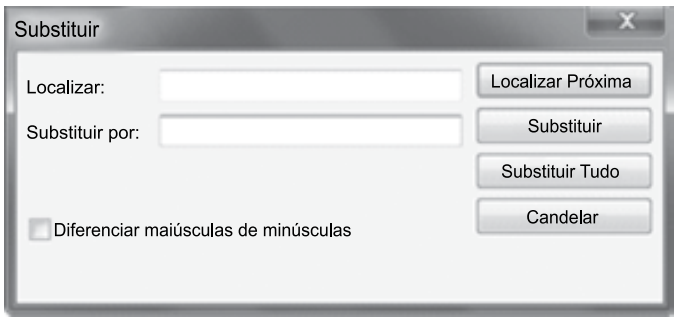
As informações de nome, idade e cidade são separadas por um TAB. Assinale a alternativa com o procedimento correto para substituir todas essas separações por um ponto-e-vírgula, considerando o preenchimento do campo Localizar na janela Substituir, acessada através do atalho CTRL+H, apresentada a seguir, e que o campo Substituir por terá o ponto-e-vírgula e será clicado no botão Substituir Tudo.
Os pontos N e O pertencem aos lados de um quadrado JKLM, determinando o paralelogramo KNMO cuja área é igual a 1/3 da área do quadrado, conforme a figura.
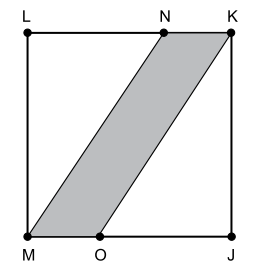
Se a medida do lado do quadrado é 6 cm, o perímetro do
paralelogramo, em cm, é igual a