Questões de Concurso
Comentadas para analista de sistemas júnior
Foram encontradas 239 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Suponha que uma aplicação WEB, escrita em PHP, receba dados livres do usuário em um campo de formulário. Os dados recebidos são armazenados em uma variável "entrada", que é inserida diretamente, sem filtros, na consulta abaixo.
$consulta = "SELECT * FROM localidades WHERE nome='$entrada'";
Em seguida, a aplicação executa essa consulta no banco de dados. Desconsiderando mecanismos de defesa no banco de dados ou configurações especiais no servidor PHP, essa aplicação é vulnerável a ataques do tipo:
Utilizando a análise por pontos de função em uma determinada porção de um software, foram obtidos os seguintes valores:
Nível de influência geral = 38
Pontos de função não ajustados = 3100
Qual a quantidade de pontos de função ajustados?
Sejam:
H1 o algoritmo SHA-256
H2 o algoritmo MD5
E1 a String "Prova"
E2 a String "Cesgranrio"
S1 a saída de H1 com entrada E1
S2 a saída de H1 com entrada E2
M1 a saída de H2 com entrada E1
M2 a saída de H2 com entrada E2
Observe as seguintes afirmativas:
I - S2 possui 5 bytes a mais do que S1;
II - H1 com entrada S1 gera E1;
III - M1 e M2 têm o mesmo tamanho.
Está(ão) correta(s) a(s) afirmativa(s):
Abaixo é dado um algoritmo. Para que o algoritmo tenha início, escolhe-se um número natural e, a seguir, executa-se sucessivamente cada um dos passos descritos. Durante a execução do algoritmo, é necessário o uso de uma variável que chamaremos de N.
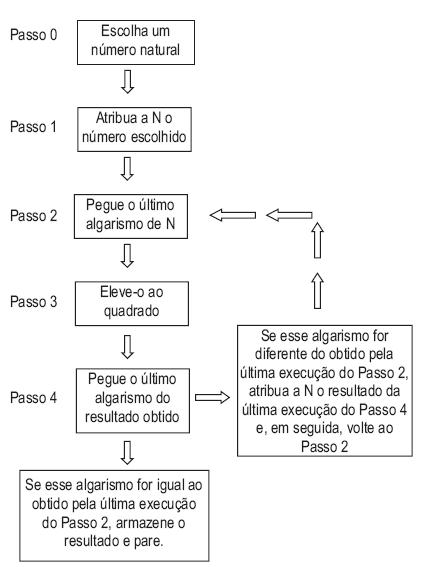
De acordo com o algoritmo proposto, se o número inicialmente escolhido for:
Biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel can
significantly reduce global dependence on oil, according
to a new report by the Worldwatch Institute.
Last year, world biofuel production surpassed 670,000
barrels per day, the equivalent of about 1 percent of the
global transport fuel market. Although oil still accounts for
more than 96 percent of transport fuel use, biofuel
production has doubled since 2001 and is poised for even
stronger growth as the industry responds to higher fuel
prices and supportive government policies. "Coordinated
action to expand biofuel markets and advance new
technologies could relieve pressure on oil prices while
strengthening agricultural economies and reducing climatealtering
emissions," says Worldwatch Institute President
Christopher Flavin.
Brazil is the world's biofuel leader, with half of its
sugar cane crop providing more than 40 percent of its nondiesel
transport fuel. In the United States, where 15 percent
of the corn crop provides about 2 percent of the non-diesel
transport fuel, ethanol production is growing even more
rapidly. This surging growth may allow the U.S. to overtake
Brazil as the world's biofuel leader this year. Both countries
are now estimated to be producing ethanol at less than
the current cost of gasoline.
Figures cited in the report reveal that biofuels could
provide 37 percent of U.S. transport fuel within the next 25
years, and up to 75 percent if automobile fuel economy
doubles. Biofuels could replace 20-30 percent of the oil
used in European Union countries during the same time
frame.
As the first-ever global assessment of the potential
social and environmental impacts of biofuels, Biofuels for
Transportation warns that the large-scale use of biofuels
carries significant agricultural and ecological risks. "It is
essential that government incentives be used to minimize
competition between food and fuel crops and to discourage
expansion onto ecologically valuable lands," says
Worldwatch Biofuels Project Manager Suzanne Hunt.
However, the report also finds that biofuels have the potential
to increase energy security, create new economic
opportunities in rural areas, and reduce local pollution and
emissions of greenhouse gases.
The long-term potential of biofuels is in the use of
non-food feedstock that include agricultural, municipal, and
forestry wastes as well as fast-growing, cellulose-rich
energy crops such as switchgrass. It is expected that the
combination of cellulosic biomass resources and "nextgeneration"
biofuel conversion technologies will compete
with conventional gasoline and diesel fuel without subsidies
in the medium term.
The report recommends policies to accelerate the
development of biofuels, while maximizing the benefits and
minimizing the risks. Recommendations include:
strengthening the market (i.e. focusing on market
development, infrastructure development, and the building
of transportation fleets that are able to use the new fuels),
speeding the transition to next-generation
technologies allowing for dramatically increased
production at lower cost, and facilitating sustainable
international biofuel trade, developing a true
international market unimpeded by the trade restrictions
in place today.
Adapted from: http://www.worldwatch.org/node/4079
Biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel can
significantly reduce global dependence on oil, according
to a new report by the Worldwatch Institute.
Last year, world biofuel production surpassed 670,000
barrels per day, the equivalent of about 1 percent of the
global transport fuel market. Although oil still accounts for
more than 96 percent of transport fuel use, biofuel
production has doubled since 2001 and is poised for even
stronger growth as the industry responds to higher fuel
prices and supportive government policies. "Coordinated
action to expand biofuel markets and advance new
technologies could relieve pressure on oil prices while
strengthening agricultural economies and reducing climatealtering
emissions," says Worldwatch Institute President
Christopher Flavin.
Brazil is the world's biofuel leader, with half of its
sugar cane crop providing more than 40 percent of its nondiesel
transport fuel. In the United States, where 15 percent
of the corn crop provides about 2 percent of the non-diesel
transport fuel, ethanol production is growing even more
rapidly. This surging growth may allow the U.S. to overtake
Brazil as the world's biofuel leader this year. Both countries
are now estimated to be producing ethanol at less than
the current cost of gasoline.
Figures cited in the report reveal that biofuels could
provide 37 percent of U.S. transport fuel within the next 25
years, and up to 75 percent if automobile fuel economy
doubles. Biofuels could replace 20-30 percent of the oil
used in European Union countries during the same time
frame.
As the first-ever global assessment of the potential
social and environmental impacts of biofuels, Biofuels for
Transportation warns that the large-scale use of biofuels
carries significant agricultural and ecological risks. "It is
essential that government incentives be used to minimize
competition between food and fuel crops and to discourage
expansion onto ecologically valuable lands," says
Worldwatch Biofuels Project Manager Suzanne Hunt.
However, the report also finds that biofuels have the potential
to increase energy security, create new economic
opportunities in rural areas, and reduce local pollution and
emissions of greenhouse gases.
The long-term potential of biofuels is in the use of
non-food feedstock that include agricultural, municipal, and
forestry wastes as well as fast-growing, cellulose-rich
energy crops such as switchgrass. It is expected that the
combination of cellulosic biomass resources and "nextgeneration"
biofuel conversion technologies will compete
with conventional gasoline and diesel fuel without subsidies
in the medium term.
The report recommends policies to accelerate the
development of biofuels, while maximizing the benefits and
minimizing the risks. Recommendations include:
strengthening the market (i.e. focusing on market
development, infrastructure development, and the building
of transportation fleets that are able to use the new fuels),
speeding the transition to next-generation
technologies allowing for dramatically increased
production at lower cost, and facilitating sustainable
international biofuel trade, developing a true
international market unimpeded by the trade restrictions
in place today.
Adapted from: http://www.worldwatch.org/node/4079
Biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel can
significantly reduce global dependence on oil, according
to a new report by the Worldwatch Institute.
Last year, world biofuel production surpassed 670,000
barrels per day, the equivalent of about 1 percent of the
global transport fuel market. Although oil still accounts for
more than 96 percent of transport fuel use, biofuel
production has doubled since 2001 and is poised for even
stronger growth as the industry responds to higher fuel
prices and supportive government policies. "Coordinated
action to expand biofuel markets and advance new
technologies could relieve pressure on oil prices while
strengthening agricultural economies and reducing climatealtering
emissions," says Worldwatch Institute President
Christopher Flavin.
Brazil is the world's biofuel leader, with half of its
sugar cane crop providing more than 40 percent of its nondiesel
transport fuel. In the United States, where 15 percent
of the corn crop provides about 2 percent of the non-diesel
transport fuel, ethanol production is growing even more
rapidly. This surging growth may allow the U.S. to overtake
Brazil as the world's biofuel leader this year. Both countries
are now estimated to be producing ethanol at less than
the current cost of gasoline.
Figures cited in the report reveal that biofuels could
provide 37 percent of U.S. transport fuel within the next 25
years, and up to 75 percent if automobile fuel economy
doubles. Biofuels could replace 20-30 percent of the oil
used in European Union countries during the same time
frame.
As the first-ever global assessment of the potential
social and environmental impacts of biofuels, Biofuels for
Transportation warns that the large-scale use of biofuels
carries significant agricultural and ecological risks. "It is
essential that government incentives be used to minimize
competition between food and fuel crops and to discourage
expansion onto ecologically valuable lands," says
Worldwatch Biofuels Project Manager Suzanne Hunt.
However, the report also finds that biofuels have the potential
to increase energy security, create new economic
opportunities in rural areas, and reduce local pollution and
emissions of greenhouse gases.
The long-term potential of biofuels is in the use of
non-food feedstock that include agricultural, municipal, and
forestry wastes as well as fast-growing, cellulose-rich
energy crops such as switchgrass. It is expected that the
combination of cellulosic biomass resources and "nextgeneration"
biofuel conversion technologies will compete
with conventional gasoline and diesel fuel without subsidies
in the medium term.
The report recommends policies to accelerate the
development of biofuels, while maximizing the benefits and
minimizing the risks. Recommendations include:
strengthening the market (i.e. focusing on market
development, infrastructure development, and the building
of transportation fleets that are able to use the new fuels),
speeding the transition to next-generation
technologies allowing for dramatically increased
production at lower cost, and facilitating sustainable
international biofuel trade, developing a true
international market unimpeded by the trade restrictions
in place today.
Adapted from: http://www.worldwatch.org/node/4079
Biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel can
significantly reduce global dependence on oil, according
to a new report by the Worldwatch Institute.
Last year, world biofuel production surpassed 670,000
barrels per day, the equivalent of about 1 percent of the
global transport fuel market. Although oil still accounts for
more than 96 percent of transport fuel use, biofuel
production has doubled since 2001 and is poised for even
stronger growth as the industry responds to higher fuel
prices and supportive government policies. "Coordinated
action to expand biofuel markets and advance new
technologies could relieve pressure on oil prices while
strengthening agricultural economies and reducing climatealtering
emissions," says Worldwatch Institute President
Christopher Flavin.
Brazil is the world's biofuel leader, with half of its
sugar cane crop providing more than 40 percent of its nondiesel
transport fuel. In the United States, where 15 percent
of the corn crop provides about 2 percent of the non-diesel
transport fuel, ethanol production is growing even more
rapidly. This surging growth may allow the U.S. to overtake
Brazil as the world's biofuel leader this year. Both countries
are now estimated to be producing ethanol at less than
the current cost of gasoline.
Figures cited in the report reveal that biofuels could
provide 37 percent of U.S. transport fuel within the next 25
years, and up to 75 percent if automobile fuel economy
doubles. Biofuels could replace 20-30 percent of the oil
used in European Union countries during the same time
frame.
As the first-ever global assessment of the potential
social and environmental impacts of biofuels, Biofuels for
Transportation warns that the large-scale use of biofuels
carries significant agricultural and ecological risks. "It is
essential that government incentives be used to minimize
competition between food and fuel crops and to discourage
expansion onto ecologically valuable lands," says
Worldwatch Biofuels Project Manager Suzanne Hunt.
However, the report also finds that biofuels have the potential
to increase energy security, create new economic
opportunities in rural areas, and reduce local pollution and
emissions of greenhouse gases.
The long-term potential of biofuels is in the use of
non-food feedstock that include agricultural, municipal, and
forestry wastes as well as fast-growing, cellulose-rich
energy crops such as switchgrass. It is expected that the
combination of cellulosic biomass resources and "nextgeneration"
biofuel conversion technologies will compete
with conventional gasoline and diesel fuel without subsidies
in the medium term.
The report recommends policies to accelerate the
development of biofuels, while maximizing the benefits and
minimizing the risks. Recommendations include:
strengthening the market (i.e. focusing on market
development, infrastructure development, and the building
of transportation fleets that are able to use the new fuels),
speeding the transition to next-generation
technologies allowing for dramatically increased
production at lower cost, and facilitating sustainable
international biofuel trade, developing a true
international market unimpeded by the trade restrictions
in place today.
Adapted from: http://www.worldwatch.org/node/4079
Biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel can
significantly reduce global dependence on oil, according
to a new report by the Worldwatch Institute.
Last year, world biofuel production surpassed 670,000
barrels per day, the equivalent of about 1 percent of the
global transport fuel market. Although oil still accounts for
more than 96 percent of transport fuel use, biofuel
production has doubled since 2001 and is poised for even
stronger growth as the industry responds to higher fuel
prices and supportive government policies. "Coordinated
action to expand biofuel markets and advance new
technologies could relieve pressure on oil prices while
strengthening agricultural economies and reducing climatealtering
emissions," says Worldwatch Institute President
Christopher Flavin.
Brazil is the world's biofuel leader, with half of its
sugar cane crop providing more than 40 percent of its nondiesel
transport fuel. In the United States, where 15 percent
of the corn crop provides about 2 percent of the non-diesel
transport fuel, ethanol production is growing even more
rapidly. This surging growth may allow the U.S. to overtake
Brazil as the world's biofuel leader this year. Both countries
are now estimated to be producing ethanol at less than
the current cost of gasoline.
Figures cited in the report reveal that biofuels could
provide 37 percent of U.S. transport fuel within the next 25
years, and up to 75 percent if automobile fuel economy
doubles. Biofuels could replace 20-30 percent of the oil
used in European Union countries during the same time
frame.
As the first-ever global assessment of the potential
social and environmental impacts of biofuels, Biofuels for
Transportation warns that the large-scale use of biofuels
carries significant agricultural and ecological risks. "It is
essential that government incentives be used to minimize
competition between food and fuel crops and to discourage
expansion onto ecologically valuable lands," says
Worldwatch Biofuels Project Manager Suzanne Hunt.
However, the report also finds that biofuels have the potential
to increase energy security, create new economic
opportunities in rural areas, and reduce local pollution and
emissions of greenhouse gases.
The long-term potential of biofuels is in the use of
non-food feedstock that include agricultural, municipal, and
forestry wastes as well as fast-growing, cellulose-rich
energy crops such as switchgrass. It is expected that the
combination of cellulosic biomass resources and "nextgeneration"
biofuel conversion technologies will compete
with conventional gasoline and diesel fuel without subsidies
in the medium term.
The report recommends policies to accelerate the
development of biofuels, while maximizing the benefits and
minimizing the risks. Recommendations include:
strengthening the market (i.e. focusing on market
development, infrastructure development, and the building
of transportation fleets that are able to use the new fuels),
speeding the transition to next-generation
technologies allowing for dramatically increased
production at lower cost, and facilitating sustainable
international biofuel trade, developing a true
international market unimpeded by the trade restrictions
in place today.
Adapted from: http://www.worldwatch.org/node/4079
Biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel can
significantly reduce global dependence on oil, according
to a new report by the Worldwatch Institute.
Last year, world biofuel production surpassed 670,000
barrels per day, the equivalent of about 1 percent of the
global transport fuel market. Although oil still accounts for
more than 96 percent of transport fuel use, biofuel
production has doubled since 2001 and is poised for even
stronger growth as the industry responds to higher fuel
prices and supportive government policies. "Coordinated
action to expand biofuel markets and advance new
technologies could relieve pressure on oil prices while
strengthening agricultural economies and reducing climatealtering
emissions," says Worldwatch Institute President
Christopher Flavin.
Brazil is the world's biofuel leader, with half of its
sugar cane crop providing more than 40 percent of its nondiesel
transport fuel. In the United States, where 15 percent
of the corn crop provides about 2 percent of the non-diesel
transport fuel, ethanol production is growing even more
rapidly. This surging growth may allow the U.S. to overtake
Brazil as the world's biofuel leader this year. Both countries
are now estimated to be producing ethanol at less than
the current cost of gasoline.
Figures cited in the report reveal that biofuels could
provide 37 percent of U.S. transport fuel within the next 25
years, and up to 75 percent if automobile fuel economy
doubles. Biofuels could replace 20-30 percent of the oil
used in European Union countries during the same time
frame.
As the first-ever global assessment of the potential
social and environmental impacts of biofuels, Biofuels for
Transportation warns that the large-scale use of biofuels
carries significant agricultural and ecological risks. "It is
essential that government incentives be used to minimize
competition between food and fuel crops and to discourage
expansion onto ecologically valuable lands," says
Worldwatch Biofuels Project Manager Suzanne Hunt.
However, the report also finds that biofuels have the potential
to increase energy security, create new economic
opportunities in rural areas, and reduce local pollution and
emissions of greenhouse gases.
The long-term potential of biofuels is in the use of
non-food feedstock that include agricultural, municipal, and
forestry wastes as well as fast-growing, cellulose-rich
energy crops such as switchgrass. It is expected that the
combination of cellulosic biomass resources and "nextgeneration"
biofuel conversion technologies will compete
with conventional gasoline and diesel fuel without subsidies
in the medium term.
The report recommends policies to accelerate the
development of biofuels, while maximizing the benefits and
minimizing the risks. Recommendations include:
strengthening the market (i.e. focusing on market
development, infrastructure development, and the building
of transportation fleets that are able to use the new fuels),
speeding the transition to next-generation
technologies allowing for dramatically increased
production at lower cost, and facilitating sustainable
international biofuel trade, developing a true
international market unimpeded by the trade restrictions
in place today.
Adapted from: http://www.worldwatch.org/node/4079
Biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel can
significantly reduce global dependence on oil, according
to a new report by the Worldwatch Institute.
Last year, world biofuel production surpassed 670,000
barrels per day, the equivalent of about 1 percent of the
global transport fuel market. Although oil still accounts for
more than 96 percent of transport fuel use, biofuel
production has doubled since 2001 and is poised for even
stronger growth as the industry responds to higher fuel
prices and supportive government policies. "Coordinated
action to expand biofuel markets and advance new
technologies could relieve pressure on oil prices while
strengthening agricultural economies and reducing climatealtering
emissions," says Worldwatch Institute President
Christopher Flavin.
Brazil is the world's biofuel leader, with half of its
sugar cane crop providing more than 40 percent of its nondiesel
transport fuel. In the United States, where 15 percent
of the corn crop provides about 2 percent of the non-diesel
transport fuel, ethanol production is growing even more
rapidly. This surging growth may allow the U.S. to overtake
Brazil as the world's biofuel leader this year. Both countries
are now estimated to be producing ethanol at less than
the current cost of gasoline.
Figures cited in the report reveal that biofuels could
provide 37 percent of U.S. transport fuel within the next 25
years, and up to 75 percent if automobile fuel economy
doubles. Biofuels could replace 20-30 percent of the oil
used in European Union countries during the same time
frame.
As the first-ever global assessment of the potential
social and environmental impacts of biofuels, Biofuels for
Transportation warns that the large-scale use of biofuels
carries significant agricultural and ecological risks. "It is
essential that government incentives be used to minimize
competition between food and fuel crops and to discourage
expansion onto ecologically valuable lands," says
Worldwatch Biofuels Project Manager Suzanne Hunt.
However, the report also finds that biofuels have the potential
to increase energy security, create new economic
opportunities in rural areas, and reduce local pollution and
emissions of greenhouse gases.
The long-term potential of biofuels is in the use of
non-food feedstock that include agricultural, municipal, and
forestry wastes as well as fast-growing, cellulose-rich
energy crops such as switchgrass. It is expected that the
combination of cellulosic biomass resources and "nextgeneration"
biofuel conversion technologies will compete
with conventional gasoline and diesel fuel without subsidies
in the medium term.
The report recommends policies to accelerate the
development of biofuels, while maximizing the benefits and
minimizing the risks. Recommendations include:
strengthening the market (i.e. focusing on market
development, infrastructure development, and the building
of transportation fleets that are able to use the new fuels),
speeding the transition to next-generation
technologies allowing for dramatically increased
production at lower cost, and facilitating sustainable
international biofuel trade, developing a true
international market unimpeded by the trade restrictions
in place today.
Adapted from: http://www.worldwatch.org/node/4079