The Internet at Risk
Some 12,000 people convened last week in Tunisia for
a United Nations conference about the Internet. Many delegates
want an end to the U.S. Commerce Department's control over
the assignment of Web site addresses (for example,
http://www.washington-%20post.com/ ) and e-mail accounts (for
example, [email protected]). The delegates' argument is that
unilateral U.S. control over these domain names reflects no
more than the historical accident of the Internet's origins. Why
should the United States continue to control the registration of
French and Chinese Internet addresses? It doesn't control the
registration of French and Chinese cars, whatever Henry Ford's
historic role in democratizing travel was.
The reformers' argument is attractive in theory and
dangerous in practice. In an ideal world, unilateralism should be
avoided. But in an imperfect world, unilateral solutions that run
efficiently can be better than multilateral ones that ....51....
The job of assigning domain names offers huge
opportunities for abuse. ....52.... controls this function can decide to
keep certain types of individuals or organizations offline
(dissidents or opposition political groups, for example). Or it can
allow them on in exchange for large fees. The striking feature of
U.S. oversight of the Internet is that such abuses have not
occurred.
It's possible that a multilateral overseer of the Internet
might be just as efficient. But the ponderous International
Telecommunication Union, the U.N. body that would be a
leading candidate to take over the domain registry, has a record
of resisting innovation - including the advent of the Internet.
Moreover, a multilateral domain-registering body would
be caught between the different visions of its members: on the
one side, autocratic regimes such as Saudi Arabia and China
that want to restrict access to the Internet; on the other side,
open societies that want low barriers to entry. These clashes of
vision would probably make multilateral regulation inefficiently
political.
You may say that this is a fair price to pay to uphold the
principle of sovereignty. If a country wants to keep certain users
from registering domain names (Nazi groups, child
pornographers, criminals), then perhaps it has a right to do so.
But the clinching argument is that countries can exercise that
sovereignty to a reasonable degree without controlling domain
names. They can order Internet users in their territory to take
offensive material down. They can order their banks or credit
card companies to refuse to process payments to unsavory Web sites based abroad. Indeed, governments' ample ability to
regulate the Internet has already been demonstrated by some of
the countries pushing for reform, such as authoritarian China.
The sovereign nations of the world have no need to wrest
control of the Internet from the United States, because they
already have it.
(Adapted from Washington Post, November 21, 2005; A14)
 . O número de resultados possíveis para expressar, em
. O número de resultados possíveis para expressar, em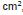 , a medida da área do quadrado original é exatamente igual a
, a medida da área do quadrado original é exatamente igual a 
