Questões de Concurso
Comentadas para agente fiscal de tributos estaduais
Foram encontradas 87 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
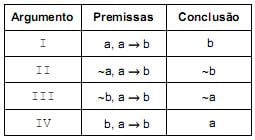
Indicando-se os argumentos legítimos por L e os ilegítimos por I, obtêm-se, na ordem dada,
 → ∼ (∼ p ∧ q ∧ r), , complete o espaço
→ ∼ (∼ p ∧ q ∧ r), , complete o espaço  com uma e uma só das sentenças simples p, q, r ou a sua negação ~ p, ~ q ou ~ r para que a sentença dada seja uma tautologia. Assinale a opção que responde a essa condição.
com uma e uma só das sentenças simples p, q, r ou a sua negação ~ p, ~ q ou ~ r para que a sentença dada seja uma tautologia. Assinale a opção que responde a essa condição.
Nos encontramos com três nativos, Sr. A, Sr. B, Sr. C, um de cada uma das raças
Observe bem o diálogo que travamos com o Sr. C
Nós: - Sr. C, o senhor é da raça zel, del ou mel?
Sr. C: - Eu sou mel. (1ª resposta)
Nós: - Sr. C, e o senhor A, de que raça é?
Sr. C: - Ele é zel. (2ª resposta)
Nós: - Mas então o Sr. B é del, não é isso, Sr. C?
Sr. C: - Claro, senhor! (3ª resposta)
Nessas condições, é verdade que os senhores A, B e C são, respectivamente,
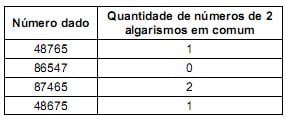
O número procurado é
Se considerarmos que p é falsa, então é verdade que
• fator RH
RH+ se tiver o antígeno RH
RH- se não tiver o antígeno RH
• Grupo sangüíneo
A se tiver o antígeno A e não tiver o B
B se tiver o antígeno B e não tiver o A
AB se tiver ambos os antígenos, A e B
O se não tiver o antígeno A nem o B
Sejam os conjuntos
H = {x | x é uma pessoa com sangue Rh+ }
A = {x | x é uma pessoa com sangue do grupo A}
B = {x | x é uma pessoa com sangue do grupo B}
M = H n (A ∆ B)
N =
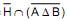
(Se X e Y são conjuntos,
 é o complementar de X e X ∆ Y é a diferença simétrica entre X e Y).
é o complementar de X e X ∆ Y é a diferença simétrica entre X e Y). Os conjuntos M e N são os conjuntos dos X tais que X é uma pessoa com sangue
I.O número de linhas de uma tabela-verdade é sempre um número par.
II. A proposição " ( 10 < √ 10 ) ↔ ( 8 - 3 = 6 )" é falsa.
III. Se p e q são proposições, então a proposição “(p → q) ∨ ( ~ q)” é uma tautologia.
É verdade o que se afirma APENAS em
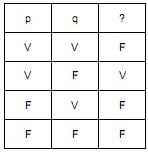
A proposição composta que substitui corretamente o ponto de interrogação é