Questões de Concurso
Comentadas para vestibular
Foram encontradas 622 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Está(ão) correta(s):
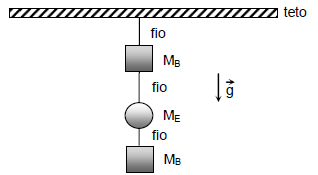
1) O processo de dispersão industrial no Brasil começa no final da década de 1980, tanto no território nacional, como na região Sudeste. 2) A chamada “guerra fiscal” foi um fator decisivo para o processo de descentralização industrial no Brasil. 3) O Espírito Santo, em 2003, obteve o mais alto índice de crescimento da região; mesmo assim, é o Estado menos industrializado do Sudeste. 4) A região Sul é a segunda região brasileira mais industrializada, tendo como característica a aglutinação de suas indústrias em polos industriais. 5) A Região Nordeste ocupa, atualmente, a terceira posição, em relação ao total do desempenho industrialnacional.
Estão corretas apenas:
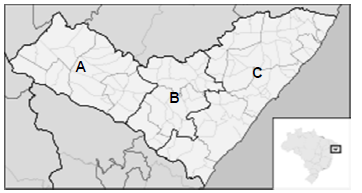
Este mapa está representando as :
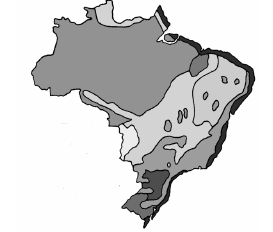
Leia, com atenção, o texto a seguir.
“Ocorre, naturalmente, na estratosfera, onde, aproximadamente entre 15 e 40km, num trecho possui concentrações elevadas. Absorve grande parte da energia ultravioleta oriunda do Sol, gerando o aumento das temperaturas, com a altitude, que se dá a partir dessa camada. Também atua na retenção da energia infravermelha oriunda do espaço ou emitida pela superfície."
(TAVARES, A.C. Reflexões sobre a Geografia Física no Brasil. Rio de Janeiro: Bertrand Brasil, 2004)
O texto, especificamente, está se referindo ao:
Read the text below and answer the following question based on it.
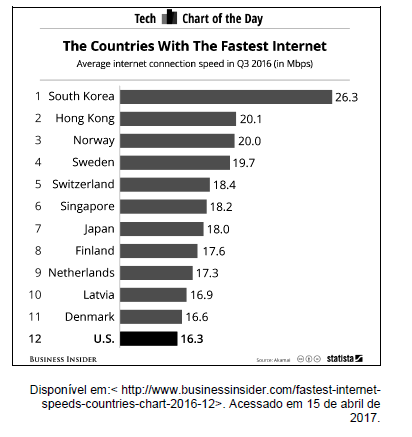
According to the graphic, it is true to assert that
The findings suggest that students’ well-being also
depend on their teachers’
Read the text below and answer the following question based on it.
Natural tooth repair method, using Alzheimer's drug, could revolutionise dental treatments
A new method of stimulating the renewal of living stem cells in tooth pulp using an Alzheimer’s drug has been discovered by a team of researchers at King’s College London.
Following trauma or an infection, the inner, soft pulp of a tooth can become exposed and infected. In order to protect the tooth from infection, a thin band of dentine is naturally produced and this seals the tooth pulp, but it is insufficient to effectively repair large cavities. Currently dentists use manmade cements or fillings, such as calcium and silicon-based products, to treat these larger cavities and fill holes in teeth. This cement remains in the tooth and fails to disintegrate, meaning that the normal mineral level of the tooth is never completely restored.
However, in a paper published today in Scientific Reports, scientists from the Dental Institute at King’s College London have proven a way to stimulate the stem cells contained in the pulp of the tooth and generate new dentine in large cavities, potentially reducing the need for fillings or cements.
The novel biological approach could see teeth use their natural ability to repair large cavities rather than using cements or fillings.
Significantly, one of the small molecules used by the team to stimulate the renewal of the stem cells included Tideglusib, which has previously been used in clinical trials to treat neurological disorders including Alzheimer’s disease.
Using biodegradable collagen sponges to deliver the treatment, the team applied low doses of small molecule glycogen synthase kinase (GSK-3) inhibitors to the tooth. They found that the sponge degraded over time and that new dentine replaced it, leading to complete, natural repair. Collagen sponges are commercially-available and clinicallyapproved, again adding to the potential of the treatment’s swift pick-up and use in dental clinics.
Disponível em:
Read the text below and answer the following question based on it.
Natural tooth repair method, using Alzheimer's drug, could revolutionise dental treatments
A new method of stimulating the renewal of living stem cells in tooth pulp using an Alzheimer’s drug has been discovered by a team of researchers at King’s College London.
Following trauma or an infection, the inner, soft pulp of a tooth can become exposed and infected. In order to protect the tooth from infection, a thin band of dentine is naturally produced and this seals the tooth pulp, but it is insufficient to effectively repair large cavities. Currently dentists use manmade cements or fillings, such as calcium and silicon-based products, to treat these larger cavities and fill holes in teeth. This cement remains in the tooth and fails to disintegrate, meaning that the normal mineral level of the tooth is never completely restored.
However, in a paper published today in Scientific Reports, scientists from the Dental Institute at King’s College London have proven a way to stimulate the stem cells contained in the pulp of the tooth and generate new dentine in large cavities, potentially reducing the need for fillings or cements.
The novel biological approach could see teeth use their natural ability to repair large cavities rather than using cements or fillings.
Significantly, one of the small molecules used by the team to stimulate the renewal of the stem cells included Tideglusib, which has previously been used in clinical trials to treat neurological disorders including Alzheimer’s disease.
Using biodegradable collagen sponges to deliver the treatment, the team applied low doses of small molecule glycogen synthase kinase (GSK-3) inhibitors to the tooth. They found that the sponge degraded over time and that new dentine replaced it, leading to complete, natural repair. Collagen sponges are commercially-available and clinicallyapproved, again adding to the potential of the treatment’s swift pick-up and use in dental clinics.
Disponível em:
Read the text below and answer the following question based on it.
Natural tooth repair method, using Alzheimer's drug, could revolutionise dental treatments
A new method of stimulating the renewal of living stem cells in tooth pulp using an Alzheimer’s drug has been discovered by a team of researchers at King’s College London.
Following trauma or an infection, the inner, soft pulp of a tooth can become exposed and infected. In order to protect the tooth from infection, a thin band of dentine is naturally produced and this seals the tooth pulp, but it is insufficient to effectively repair large cavities. Currently dentists use manmade cements or fillings, such as calcium and silicon-based products, to treat these larger cavities and fill holes in teeth. This cement remains in the tooth and fails to disintegrate, meaning that the normal mineral level of the tooth is never completely restored.
However, in a paper published today in Scientific Reports, scientists from the Dental Institute at King’s College London have proven a way to stimulate the stem cells contained in the pulp of the tooth and generate new dentine in large cavities, potentially reducing the need for fillings or cements.
The novel biological approach could see teeth use their natural ability to repair large cavities rather than using cements or fillings.
Significantly, one of the small molecules used by the team to stimulate the renewal of the stem cells included Tideglusib, which has previously been used in clinical trials to treat neurological disorders including Alzheimer’s disease.
Using biodegradable collagen sponges to deliver the treatment, the team applied low doses of small molecule glycogen synthase kinase (GSK-3) inhibitors to the tooth. They found that the sponge degraded over time and that new dentine replaced it, leading to complete, natural repair. Collagen sponges are commercially-available and clinicallyapproved, again adding to the potential of the treatment’s swift pick-up and use in dental clinics.
Disponível em:
The correct alternatives are:
Ora, se deu que chegou
(isso já faz muito tempo)
no banguê dum meu avô
uma negra bonitinha,
chamada negra Fulô.
Essa negra Fulô!
Essa negra Fulô!
Ó Fulô! Ó Fulô!
(Era a fala da Sinhá)
- Vai forrar a minha cama
pentear os meus cabelos,
vem ajudar a tirar
a minha roupa, Fulô!
(...)
Essa negrinha Fulô
ficou logo pra mucama
pra vigiar a Sinhá,
pra engomar pro Sinhô!
O poema acima é de autoria de Jorge de Lima, poeta alagoano e um dos principais representantes da segunda geração da poesia modernista. No poema, podemos destacar características dessa geração de poetas, como:
1) a opção por uma linguagem despretensiosa, bem próxima dos padrões coloquiais.
2) uma interlocução dialógica, mesmo que não esteja evidente a participação do interlocutor.
3) ainda que o cenário sugira uma situação de desigualdade social, pode-se ver no uso dos diminutivos uma atitude de carinho.
4) fidelidade à sintaxe lusitana, reforçando os ideais da primeira geração dos poetas modernistas.
Estão corretas: