Questões de Concurso
Para prefeitura de niterói - rj
Foram encontradas 1.858 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!

(Source: http://www.information-age.com/approach-cloud-computingcyber-security-2017-123466624/ Retrieved on January 26th, 2018)
How to approach cloud computing and cyber security in 2017
The adoption of cloud computing has been on the up since as far back as 2008, when a survey conducted by the Pew Research Institute found that cloud services were used by nearly 69% of Americans. Since then, the industry has experienced hypergrowth and exceeded the already vast predictions of how big it would become.
IDC predicts that the cloud computing market in 2017 will be worth $107 billion and, according to Gartner, by 2020 a corporate ‘no-cloud’ policy will be as unusual as a ‘no-internet’ policy would be today. Indeed, it would be difficult to imagine an organisation in 2017 that did not use webmail, file sharing and storage, and data backup.
As the use of cloud computing spreads so does awareness of the associated risks. At the time of writing, there have been 456 data breaches worldwide this year according to the Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC). The ITRC also noted a 40% increase in data breaches in 2016 compared to the previous year. Yet, despite the well-documented cases of data breaches, organisations continue to invest in and adopt cloud computing services because the benefits usually outweigh the risks.
To understand why the growth of cloud computing has continued in the face of high-profile data breaches, look first to what it can offer an organisation.
Cheaper, bigger, better
Cloud computing is a virtual environment that can adapt to meet user needs. It is not constrained by physical limits, and is easily scalable – making it an obvious choice for start-ups. Cloud computing makes state-of-the-art capability available to anyone with an internet connection and a browser, reducing hardware and IT personnel costs.
Cloud services and software applications are managed and upgraded off-site by the provider, meaning organisations can access technology they would not have been able to afford to install and manage on their own. The popularity of the cloud essentially comes down to its provision of advanced, nextgeneration IT resources in an environment that is cheaper and more scalable than local networks.
The risks involved with cloud computing are mostly securitybased. Clouds are often made up of multiple entities, which means that no configuration can be more secure than its weakest link. The link between separate entities means that attacks to multiple sites can occur simultaneously. When cloud providers do not employ adequate cyber security measures, those clouds become a target for cybercriminals.
Yet, it’s not all bad news. A user survey conducted by one cloud service provider found that concerns about security fell to 25% compared to 29% last year. And as more becomes known about security risks so too does our knowledge around what organisations can do to protect themselves.
(Source: http://www.information-age.com/approach-cloud-computingcyber-security-2017-123466624/. Retrieved on January 25th, 2018)

(Source: http://www.information-age.com/approach-cloud-computingcyber-security-2017-123466624/ Retrieved on January 26th, 2018)
How to approach cloud computing and cyber security in 2017
The adoption of cloud computing has been on the up since as far back as 2008, when a survey conducted by the Pew Research Institute found that cloud services were used by nearly 69% of Americans. Since then, the industry has experienced hypergrowth and exceeded the already vast predictions of how big it would become.
IDC predicts that the cloud computing market in 2017 will be worth $107 billion and, according to Gartner, by 2020 a corporate ‘no-cloud’ policy will be as unusual as a ‘no-internet’ policy would be today. Indeed, it would be difficult to imagine an organisation in 2017 that did not use webmail, file sharing and storage, and data backup.
As the use of cloud computing spreads so does awareness of the associated risks. At the time of writing, there have been 456 data breaches worldwide this year according to the Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC). The ITRC also noted a 40% increase in data breaches in 2016 compared to the previous year. Yet, despite the well-documented cases of data breaches, organisations continue to invest in and adopt cloud computing services because the benefits usually outweigh the risks.
To understand why the growth of cloud computing has continued in the face of high-profile data breaches, look first to what it can offer an organisation.
Cheaper, bigger, better
Cloud computing is a virtual environment that can adapt to meet user needs. It is not constrained by physical limits, and is easily scalable – making it an obvious choice for start-ups. Cloud computing makes state-of-the-art capability available to anyone with an internet connection and a browser, reducing hardware and IT personnel costs.
Cloud services and software applications are managed and upgraded off-site by the provider, meaning organisations can access technology they would not have been able to afford to install and manage on their own. The popularity of the cloud essentially comes down to its provision of advanced, nextgeneration IT resources in an environment that is cheaper and more scalable than local networks.
The risks involved with cloud computing are mostly securitybased. Clouds are often made up of multiple entities, which means that no configuration can be more secure than its weakest link. The link between separate entities means that attacks to multiple sites can occur simultaneously. When cloud providers do not employ adequate cyber security measures, those clouds become a target for cybercriminals.
Yet, it’s not all bad news. A user survey conducted by one cloud service provider found that concerns about security fell to 25% compared to 29% last year. And as more becomes known about security risks so too does our knowledge around what organisations can do to protect themselves.
(Source: http://www.information-age.com/approach-cloud-computingcyber-security-2017-123466624/. Retrieved on January 25th, 2018)

(Source: http://www.information-age.com/approach-cloud-computingcyber-security-2017-123466624/ Retrieved on January 26th, 2018)
How to approach cloud computing and cyber security in 2017
The adoption of cloud computing has been on the up since as far back as 2008, when a survey conducted by the Pew Research Institute found that cloud services were used by nearly 69% of Americans. Since then, the industry has experienced hypergrowth and exceeded the already vast predictions of how big it would become.
IDC predicts that the cloud computing market in 2017 will be worth $107 billion and, according to Gartner, by 2020 a corporate ‘no-cloud’ policy will be as unusual as a ‘no-internet’ policy would be today. Indeed, it would be difficult to imagine an organisation in 2017 that did not use webmail, file sharing and storage, and data backup.
As the use of cloud computing spreads so does awareness of the associated risks. At the time of writing, there have been 456 data breaches worldwide this year according to the Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC). The ITRC also noted a 40% increase in data breaches in 2016 compared to the previous year. Yet, despite the well-documented cases of data breaches, organisations continue to invest in and adopt cloud computing services because the benefits usually outweigh the risks.
To understand why the growth of cloud computing has continued in the face of high-profile data breaches, look first to what it can offer an organisation.
Cheaper, bigger, better
Cloud computing is a virtual environment that can adapt to meet user needs. It is not constrained by physical limits, and is easily scalable – making it an obvious choice for start-ups. Cloud computing makes state-of-the-art capability available to anyone with an internet connection and a browser, reducing hardware and IT personnel costs.
Cloud services and software applications are managed and upgraded off-site by the provider, meaning organisations can access technology they would not have been able to afford to install and manage on their own. The popularity of the cloud essentially comes down to its provision of advanced, nextgeneration IT resources in an environment that is cheaper and more scalable than local networks.
The risks involved with cloud computing are mostly securitybased. Clouds are often made up of multiple entities, which means that no configuration can be more secure than its weakest link. The link between separate entities means that attacks to multiple sites can occur simultaneously. When cloud providers do not employ adequate cyber security measures, those clouds become a target for cybercriminals.
Yet, it’s not all bad news. A user survey conducted by one cloud service provider found that concerns about security fell to 25% compared to 29% last year. And as more becomes known about security risks so too does our knowledge around what organisations can do to protect themselves.
(Source: http://www.information-age.com/approach-cloud-computingcyber-security-2017-123466624/. Retrieved on January 25th, 2018)

(Source: http://www.information-age.com/approach-cloud-computingcyber-security-2017-123466624/ Retrieved on January 26th, 2018)
How to approach cloud computing and cyber security in 2017
The adoption of cloud computing has been on the up since as far back as 2008, when a survey conducted by the Pew Research Institute found that cloud services were used by nearly 69% of Americans. Since then, the industry has experienced hypergrowth and exceeded the already vast predictions of how big it would become.
IDC predicts that the cloud computing market in 2017 will be worth $107 billion and, according to Gartner, by 2020 a corporate ‘no-cloud’ policy will be as unusual as a ‘no-internet’ policy would be today. Indeed, it would be difficult to imagine an organisation in 2017 that did not use webmail, file sharing and storage, and data backup.
As the use of cloud computing spreads so does awareness of the associated risks. At the time of writing, there have been 456 data breaches worldwide this year according to the Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC). The ITRC also noted a 40% increase in data breaches in 2016 compared to the previous year. Yet, despite the well-documented cases of data breaches, organisations continue to invest in and adopt cloud computing services because the benefits usually outweigh the risks.
To understand why the growth of cloud computing has continued in the face of high-profile data breaches, look first to what it can offer an organisation.
Cheaper, bigger, better
Cloud computing is a virtual environment that can adapt to meet user needs. It is not constrained by physical limits, and is easily scalable – making it an obvious choice for start-ups. Cloud computing makes state-of-the-art capability available to anyone with an internet connection and a browser, reducing hardware and IT personnel costs.
Cloud services and software applications are managed and upgraded off-site by the provider, meaning organisations can access technology they would not have been able to afford to install and manage on their own. The popularity of the cloud essentially comes down to its provision of advanced, nextgeneration IT resources in an environment that is cheaper and more scalable than local networks.
The risks involved with cloud computing are mostly securitybased. Clouds are often made up of multiple entities, which means that no configuration can be more secure than its weakest link. The link between separate entities means that attacks to multiple sites can occur simultaneously. When cloud providers do not employ adequate cyber security measures, those clouds become a target for cybercriminals.
Yet, it’s not all bad news. A user survey conducted by one cloud service provider found that concerns about security fell to 25% compared to 29% last year. And as more becomes known about security risks so too does our knowledge around what organisations can do to protect themselves.
(Source: http://www.information-age.com/approach-cloud-computingcyber-security-2017-123466624/. Retrieved on January 25th, 2018)
Text I deals with cloud computing and cyber security. In this respect, analyse the following statements:
I. The risks of breaches in cloud computing are minimal.
II. Cloud computing has developed beyond projections.
III. Results of a survey indicate users are becoming more confident about security.
Choose the correct answer:
A Matriz BCG foi utilizada por uma empresa do ramo de alimentos e bebidas para análise de seu portfólio de produtos. Sobre as análises permitidas pela BCG, analise as afirmativas a seguir.
I. Uma marca de biscoito já consolidada no mercado, que gera uma alta receita sem necessidade de alto investimento em marketing, é um exemplo de vaca leiteira.II. Um refrigerante com baixo desempenho em um mercado em declínio é um exemplo de ponto de interrogação.
III. Um doce alocado no grupo das estrelas gera pouco custo para a manutenção da sua fatia de mercado.
Assinale a opção que indica as afirmativas corretas.
No edital de concurso de uma sociedade de economia mista existe a exigência de que o candidato possua 6 meses de experiência mínima na área do cargo especificado.
Conforme a perspectiva da gestão por competências, essa exigência está relacionada à competência
Após obter com especialistas as estimativas temporais “otimista”, “pessimista” e “mais provável” para um projeto, o gerente de projetos, baseado nas interfaces e interações das várias etapas, chega ao valor ponderado.
Assinale a opção que indica a ferramenta por ele utilizada.
O Prefeito, entusiasmado com a criação de uma Controladoria Geral do Município durante sua gestão, decide fazer a divulgação da novidade por meio de outdoors espalhados pelo centro da cidade.
Em relação à conduta do Prefeito, considerando a perspectiva dos elementos da comunicação, assinale a afirmativa correta.
Uma nova lei é editada prevendo que todos os novos taxistas, a partir da edição da lei, deverão ter curso superior.
Conforme a concepção do modelo das 5 forças proposto por Michael Porter, essa medida pode ser entendida como
Analise o gráfico do ciclo de vida de um projeto, proposto pelo guia PMBOK, a seguir.
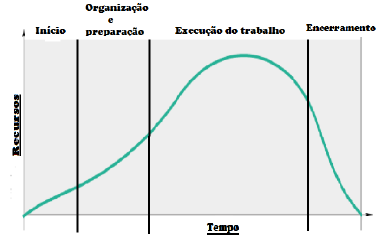
Sobre as fases do ciclo de vida de um projeto, assinale a afirmativa correta.
Ao analisar os indicadores estratégicos de sua companhia, João Pedro verificou que as faltas dos funcionários eram um problema recorrente.
Em relação ao mapa estratégico, a companhia possui uma situação adversa sob a perspectiva
Leia a frase a seguir.
“As Lojas Piririco têm o prazer de anunciar o apoio ao projeto social ´música para todos´ na comunidade Vila Carente”.
A frase pode ser considerada um exemplo de comunicação
Um empresário do setor de commodities, após participar de um workshop sobre gestão, decide aplicar uma política salarial em sua empresa pela qual todos receberiam um salário base mais uma comissão em função da produtividade, pautando-se na ideia de que os esforços são exclusivamente relacionados aos incentivos financeiros.
Esse entendimento do empresário tem influência da
Eugênia, para adotar um estilo de liderança mais adequado em uma organização não governamental (ONG) de proteção dos direitos humanos, decidiu fazer uma pesquisa sobre o assunto na Biblioteca Municipal.
Após alguns dias, Eugênia se depara com o modelo denominado continuum de liderança e verifica que precisa analisar três conjuntos de forças para encontrar o estilo de liderança mais adequado para seu contexto.
Assinale a opção que os indica.
Visando reduzir o número de assaltos na cidade, a Prefeitura lança um aplicativo para celular que conta com a colaboração da população para notificar onde ocorreram assaltos, criando assim um mapa regional do crime.
Decorrido 1 ano do lançamento do aplicativo, a Prefeitura elabora um diagrama de dispersão para avaliar a utilidade do aplicativo.
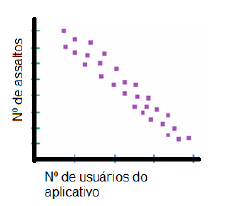
De acordo com o diagrama apresentado, assinale a afirmativa correta.
Para que o gerenciamento por diretrizes funcione adequadamente, é imprescindível que se consiga alinhar a estratégia da empresa com cada um dos níveis organizacionais, utilizando-se para isso dois sistemas de gerenciamento, o interfuncional e o funcional.
Com base nesses sistemas, relacione as características a seguir assinalando (I) para interfuncional e (F) para funcional.
( ) Desdobramento das Diretrizes
( ) Manutenção de Padrões
( ) Solução de problemas prioritários da alta administração
( ) Gerenciamento da rotina
Assinale a opção que relaciona corretamente as características.
Analise as afirmativas a seguir e assinale (V) para a verdadeira e (F) para a falsa.
( ) A implementação do Plano Real se baseou em três fases: (i) ajuste fiscal; (ii) indexação da economia, utilizando a URV; (iii) conversão da URV na nova moeda (real).
( ) A terceira fase do Plano Real adotou o lastreamento da oferta monetária doméstica, a fixação de limites máximos para o estoque de base monetária e instituiu mudanças no funcionamento do Conselho Monetário Nacional.
( ) Uma das consequências imediatas do Plano Real foi a de que a atividade econômica gerou uma queda do desemprego em 1995.
As afirmativas, na ordem apresentada, são, respectivamente,