Questões de Concurso
Para analista treinee - matemática
Foram encontradas 51 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Y1 = 1/3 X1 + 1/3 X2 + 1/3 X3
Y2 = 1/4 X1 + 1/3 X2 + 5/12 X3
Y3 = 1/8 X1 + 1/4 X2 + 5/8 X3
De acordo com a teoria da estimação,
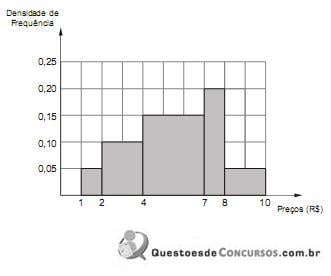
Analisando a distribuição dos preços unitários desta peça, tem-se que
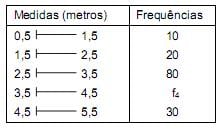
A respectiva mediana destas medidas, obtida pelo método da interpolação linear, apresenta o valor de
Posted on Friday March 27th, 2009 by Jebediah Reed
To give some sense of the pace of public works construction in China, the city of Guangzhou is planning to open 83 miles of new subway lines by the end of next year. Meanwhile, New York - a city of about the same size - has been playing around with the 1.7-mile Second Avenue line for
decades now. China also builds subways rather cheaply - $100 million per mile versus $ 2.4 billion per mile in the Big Apple.
Not surprisingly, projects there are more aggressive in all respects: there are 60 tunnel boring machines operating in Guangzhou, while only one is slated for the Second Avenue project;workers put in five 12-hour shifts a week (and if they don’t like it, they can go pound glacial till); and seizing property is a breeze.
An article in the Business section of today’s NY Times (Clash of Subways and Car Culture in Chinese Cities by Keith Bradsher) [VERB] a smart look at the forces at play as China goes on a transit infrastructure spending spree while it simultaneously becomes evermore sprawling and car-centric.
Here’s one interesting passage, [CONJUNCTION] the story is worth reading in its entirety:
Western mass transit experts applaud China for investing billions in systems that will put less stress on the environment and on cities. But they warn that other Chinese policies, like allowing real estate developers to build sprawling new suburbs, undermine the benefits of the mass transit boom.
Mr. Chan Shao Zhang , a 67-year-old engineer in charge of the works in Guangzhou, defended Guangzhou’s combination of cars and subways, saying that the city built a subway line to a new Toyota assembly plant to help employees and suppliers reach it.
Subways have been most competitive in cities like New York that have high prices for parking, and tolls for bridges and tunnels, discouraging car use. Few Chinese cities have been willing to follow suit, other than Shanghai, which charges a fee of several thousand dollars for each license plate.
The cost and physical limitations of subways have discouraged most cities from building new ones. For instance, only Tokyo has a subway system that carries more people than its buses. The buses are cheaper and able to serve far more streets but move more slowly, pollute more and contribute to traffic congestion.
China has reason to worry. It surpassed the United States in total vehicle sales for the first time in January, although the United States remained slightly ahead in car sales. But in February, China overtook the United States in both, in part because the global downturn has hurt auto sales much more in the United States than in China.
There are many countervaling forces
 . China has passed its own stimulus package and the government is eager to put people to work, create economic activity, and build modern infrastructure. The Guangzhou project is part of major national transit buildout. But the nation’s cities are also sprawling beasts, and in that sense, more suited to cars than trains. Not shockingly, many Chinese prefer the former.
. China has passed its own stimulus package and the government is eager to put people to work, create economic activity, and build modern infrastructure. The Guangzhou project is part of major national transit buildout. But the nation’s cities are also sprawling beasts, and in that sense, more suited to cars than trains. Not shockingly, many Chinese prefer the former. (Adapted from http://www.infrastructurist.com/2009/03/27/-building-a-subway-is-96-percent-cheaper-in-china/)
 at the end of the text is
at the end of the text is Posted on Friday March 27th, 2009 by Jebediah Reed
To give some sense of the pace of public works
construction in China, the city of Guangzhou is planning to open
83 miles of new subway lines by the end of next year.
Meanwhile, New York ? a city of about the same size ? has
been playing around with the 1.7-mile Second Avenue line for
decades now. China also builds subways rather cheaply ? $100
million per mile versus $ 2.4 billion per mile in the Big Apple.
Not surprisingly, projects there are more aggressive in all
respects: there are 60 tunnel boring machines operating in
Guangzhou, while only one is slated for the Second Avenue
project; workers put in five 12-hour shifts a week (and if they
don't like it, they can go pound glacial till); and seizing property
is a breeze.
An article in the Business section of today's NY Times
(Clash of Subways and Car Culture in Chinese Cities by Keith
Bradsher) [VERB] a smart look at the forces at play as China
goes on a transit infrastructure spending spree while it
simultaneously becomes evermore sprawling and car-centric.
Here's one interesting passage, [CONJUNCTION] the
story is worth reading in its entirety:
Western mass transit experts applaud China for investing
billions in systems that will put less stress on the environment
and on cities. But they warn that other Chinese policies, like
allowing real estate developers to build sprawling new suburbs,
undermine the benefits of the mass transit boom.
Mr. Chan Shao Zhang , a 67-year-old engineer in charge
of the works in Guangzhou, defended Guangzhou's combination
of cars and subways, saying that the city built a subway line to a new Toyota assembly plant to help employees and suppliers
reach it.
Subways have been most competitive in cities like New
York that have high prices for parking, and tolls for bridges and
tunnels, discouraging car use. Few Chinese cities have been
willing to follow suit, other than Shanghai, which charges a fee of
several thousand dollars for each license plate.
The cost and physical limitations of subways have
discouraged most cities from building new ones. For instance,
only Tokyo has a subway system that carries more people than
its buses. The buses are cheaper and able to serve far more
streets but move more slowly, pollute more and contribute to
traffic congestion.
China has reason to worry. It surpassed the United
States in total vehicle sales for the first time in January, although
the United States remained slightly ahead in car sales. But in
February, China overtook the United States in both, in part
because the global downturn has hurt auto sales much more in
the United States than in China.
There are many countervaling forces ..X.. China has
passed its own stimulus package and the government is eager
to put people to work, create economic activity, and build
modern infrastructure. The Guangzhou project is part of major
national transit buildout. But the nation's cities are also sprawling
beasts, and in that sense, more suited to cars than trains. Not
shockingly, many Chinese prefer the former.
(Adapted from http://www.infrastructurist.com/2009/03/27/-
building-a-subway-is-96-percent-cheaper-in-china/)
Posted on Friday March 27th, 2009 by Jebediah Reed
To give some sense of the pace of public works
construction in China, the city of Guangzhou is planning to open
83 miles of new subway lines by the end of next year.
Meanwhile, New York ? a city of about the same size ? has
been playing around with the 1.7-mile Second Avenue line for
decades now. China also builds subways rather cheaply ? $100
million per mile versus $ 2.4 billion per mile in the Big Apple.
Not surprisingly, projects there are more aggressive in all
respects: there are 60 tunnel boring machines operating in
Guangzhou, while only one is slated for the Second Avenue
project; workers put in five 12-hour shifts a week (and if they
don't like it, they can go pound glacial till); and seizing property
is a breeze.
An article in the Business section of today's NY Times
(Clash of Subways and Car Culture in Chinese Cities by Keith
Bradsher) [VERB] a smart look at the forces at play as China
goes on a transit infrastructure spending spree while it
simultaneously becomes evermore sprawling and car-centric.
Here's one interesting passage, [CONJUNCTION] the
story is worth reading in its entirety:
Western mass transit experts applaud China for investing
billions in systems that will put less stress on the environment
and on cities. But they warn that other Chinese policies, like
allowing real estate developers to build sprawling new suburbs,
undermine the benefits of the mass transit boom.
Mr. Chan Shao Zhang , a 67-year-old engineer in charge
of the works in Guangzhou, defended Guangzhou's combination
of cars and subways, saying that the city built a subway line to a new Toyota assembly plant to help employees and suppliers
reach it.
Subways have been most competitive in cities like New
York that have high prices for parking, and tolls for bridges and
tunnels, discouraging car use. Few Chinese cities have been
willing to follow suit, other than Shanghai, which charges a fee of
several thousand dollars for each license plate.
The cost and physical limitations of subways have
discouraged most cities from building new ones. For instance,
only Tokyo has a subway system that carries more people than
its buses. The buses are cheaper and able to serve far more
streets but move more slowly, pollute more and contribute to
traffic congestion.
China has reason to worry. It surpassed the United
States in total vehicle sales for the first time in January, although
the United States remained slightly ahead in car sales. But in
February, China overtook the United States in both, in part
because the global downturn has hurt auto sales much more in
the United States than in China.
There are many countervaling forces ..X.. China has
passed its own stimulus package and the government is eager
to put people to work, create economic activity, and build
modern infrastructure. The Guangzhou project is part of major
national transit buildout. But the nation's cities are also sprawling
beasts, and in that sense, more suited to cars than trains. Not
shockingly, many Chinese prefer the former.
(Adapted from http://www.infrastructurist.com/2009/03/27/-
building-a-subway-is-96-percent-cheaper-in-china/)
Posted on Friday March 27th, 2009 by Jebediah Reed
To give some sense of the pace of public works
construction in China, the city of Guangzhou is planning to open
83 miles of new subway lines by the end of next year.
Meanwhile, New York ? a city of about the same size ? has
been playing around with the 1.7-mile Second Avenue line for
decades now. China also builds subways rather cheaply ? $100
million per mile versus $ 2.4 billion per mile in the Big Apple.
Not surprisingly, projects there are more aggressive in all
respects: there are 60 tunnel boring machines operating in
Guangzhou, while only one is slated for the Second Avenue
project; workers put in five 12-hour shifts a week (and if they
don't like it, they can go pound glacial till); and seizing property
is a breeze.
An article in the Business section of today's NY Times
(Clash of Subways and Car Culture in Chinese Cities by Keith
Bradsher) [VERB] a smart look at the forces at play as China
goes on a transit infrastructure spending spree while it
simultaneously becomes evermore sprawling and car-centric.
Here's one interesting passage, [CONJUNCTION] the
story is worth reading in its entirety:
Western mass transit experts applaud China for investing
billions in systems that will put less stress on the environment
and on cities. But they warn that other Chinese policies, like
allowing real estate developers to build sprawling new suburbs,
undermine the benefits of the mass transit boom.
Mr. Chan Shao Zhang , a 67-year-old engineer in charge
of the works in Guangzhou, defended Guangzhou's combination
of cars and subways, saying that the city built a subway line to a new Toyota assembly plant to help employees and suppliers
reach it.
Subways have been most competitive in cities like New
York that have high prices for parking, and tolls for bridges and
tunnels, discouraging car use. Few Chinese cities have been
willing to follow suit, other than Shanghai, which charges a fee of
several thousand dollars for each license plate.
The cost and physical limitations of subways have
discouraged most cities from building new ones. For instance,
only Tokyo has a subway system that carries more people than
its buses. The buses are cheaper and able to serve far more
streets but move more slowly, pollute more and contribute to
traffic congestion.
China has reason to worry. It surpassed the United
States in total vehicle sales for the first time in January, although
the United States remained slightly ahead in car sales. But in
February, China overtook the United States in both, in part
because the global downturn has hurt auto sales much more in
the United States than in China.
There are many countervaling forces ..X.. China has
passed its own stimulus package and the government is eager
to put people to work, create economic activity, and build
modern infrastructure. The Guangzhou project is part of major
national transit buildout. But the nation's cities are also sprawling
beasts, and in that sense, more suited to cars than trains. Not
shockingly, many Chinese prefer the former.
(Adapted from http://www.infrastructurist.com/2009/03/27/-
building-a-subway-is-96-percent-cheaper-in-china/)
Posted on Friday March 27th, 2009 by Jebediah Reed
To give some sense of the pace of public works
construction in China, the city of Guangzhou is planning to open
83 miles of new subway lines by the end of next year.
Meanwhile, New York ? a city of about the same size ? has
been playing around with the 1.7-mile Second Avenue line for
decades now. China also builds subways rather cheaply ? $100
million per mile versus $ 2.4 billion per mile in the Big Apple.
Not surprisingly, projects there are more aggressive in all
respects: there are 60 tunnel boring machines operating in
Guangzhou, while only one is slated for the Second Avenue
project; workers put in five 12-hour shifts a week (and if they
don't like it, they can go pound glacial till); and seizing property
is a breeze.
An article in the Business section of today's NY Times
(Clash of Subways and Car Culture in Chinese Cities by Keith
Bradsher) [VERB] a smart look at the forces at play as China
goes on a transit infrastructure spending spree while it
simultaneously becomes evermore sprawling and car-centric.
Here's one interesting passage, [CONJUNCTION] the
story is worth reading in its entirety:
Western mass transit experts applaud China for investing
billions in systems that will put less stress on the environment
and on cities. But they warn that other Chinese policies, like
allowing real estate developers to build sprawling new suburbs,
undermine the benefits of the mass transit boom.
Mr. Chan Shao Zhang , a 67-year-old engineer in charge
of the works in Guangzhou, defended Guangzhou's combination
of cars and subways, saying that the city built a subway line to a new Toyota assembly plant to help employees and suppliers
reach it.
Subways have been most competitive in cities like New
York that have high prices for parking, and tolls for bridges and
tunnels, discouraging car use. Few Chinese cities have been
willing to follow suit, other than Shanghai, which charges a fee of
several thousand dollars for each license plate.
The cost and physical limitations of subways have
discouraged most cities from building new ones. For instance,
only Tokyo has a subway system that carries more people than
its buses. The buses are cheaper and able to serve far more
streets but move more slowly, pollute more and contribute to
traffic congestion.
China has reason to worry. It surpassed the United
States in total vehicle sales for the first time in January, although
the United States remained slightly ahead in car sales. But in
February, China overtook the United States in both, in part
because the global downturn has hurt auto sales much more in
the United States than in China.
There are many countervaling forces ..X.. China has
passed its own stimulus package and the government is eager
to put people to work, create economic activity, and build
modern infrastructure. The Guangzhou project is part of major
national transit buildout. But the nation's cities are also sprawling
beasts, and in that sense, more suited to cars than trains. Not
shockingly, many Chinese prefer the former.
(Adapted from http://www.infrastructurist.com/2009/03/27/-
building-a-subway-is-96-percent-cheaper-in-china/)
O BNDES tem um programa de apoio a projetos de
transportes públicos, abrangendo todos os investimentos necessários
à qualificação do espaço urbano no entorno do empreendimento.
O apoio pode se dar visando a forma de operação
específica, sempre com a preocupação de mirar os seguintes
objetivos: a) racionalização econômica, com redução
dos custos totais do sistema; b) privilégio do transporte coletivo
sobre o individual; c) integração tarifária e física, com redução
do ônus e do tempo de deslocamento do usuário; d) acessibilidade
universal, inclusive para os usuários com necessidades
especiais; e) aprimoramento da gestão e da fiscalização do sistema;
f) redução dos níveis de poluição sonora e do ar, do consumo
energético e dos congestionamentos; g) revalorização urbana
do entorno dos projetos.
O BNDES admite um nível de participação em até
100%, no caso de municípios de baixa renda ou de média renda
inferior localizados nas regiões Norte e Nordeste.
(Baseado em informações do site oficial do BNDES)
O BNDES tem um programa de apoio a projetos de
transportes públicos, abrangendo todos os investimentos necessários
à qualificação do espaço urbano no entorno do empreendimento.
O apoio pode se dar visando a forma de operação
específica, sempre com a preocupação de mirar os seguintes
objetivos: a) racionalização econômica, com redução
dos custos totais do sistema; b) privilégio do transporte coletivo
sobre o individual; c) integração tarifária e física, com redução
do ônus e do tempo de deslocamento do usuário; d) acessibilidade
universal, inclusive para os usuários com necessidades
especiais; e) aprimoramento da gestão e da fiscalização do sistema;
f) redução dos níveis de poluição sonora e do ar, do consumo
energético e dos congestionamentos; g) revalorização urbana
do entorno dos projetos.
O BNDES admite um nível de participação em até
100%, no caso de municípios de baixa renda ou de média renda
inferior localizados nas regiões Norte e Nordeste.
(Baseado em informações do site oficial do BNDES)
No caso de municípios de baixa renda ou de renda média inferior localizados nas regiões Norte e Nordeste,
O BNDES tem um programa de apoio a projetos de
transportes públicos, abrangendo todos os investimentos necessários
à qualificação do espaço urbano no entorno do empreendimento.
O apoio pode se dar visando a forma de operação
específica, sempre com a preocupação de mirar os seguintes
objetivos: a) racionalização econômica, com redução
dos custos totais do sistema; b) privilégio do transporte coletivo
sobre o individual; c) integração tarifária e física, com redução
do ônus e do tempo de deslocamento do usuário; d) acessibilidade
universal, inclusive para os usuários com necessidades
especiais; e) aprimoramento da gestão e da fiscalização do sistema;
f) redução dos níveis de poluição sonora e do ar, do consumo
energético e dos congestionamentos; g) revalorização urbana
do entorno dos projetos.
O BNDES admite um nível de participação em até
100%, no caso de municípios de baixa renda ou de média renda
inferior localizados nas regiões Norte e Nordeste.
(Baseado em informações do site oficial do BNDES)
O BNDES tem um programa de apoio a projetos de
transportes públicos, abrangendo todos os investimentos necessários
à qualificação do espaço urbano no entorno do empreendimento.
O apoio pode se dar visando a forma de operação
específica, sempre com a preocupação de mirar os seguintes
objetivos: a) racionalização econômica, com redução
dos custos totais do sistema; b) privilégio do transporte coletivo
sobre o individual; c) integração tarifária e física, com redução
do ônus e do tempo de deslocamento do usuário; d) acessibilidade
universal, inclusive para os usuários com necessidades
especiais; e) aprimoramento da gestão e da fiscalização do sistema;
f) redução dos níveis de poluição sonora e do ar, do consumo
energético e dos congestionamentos; g) revalorização urbana
do entorno dos projetos.
O BNDES admite um nível de participação em até
100%, no caso de municípios de baixa renda ou de média renda
inferior localizados nas regiões Norte e Nordeste.
(Baseado em informações do site oficial do BNDES)
considera, antes de mais nada, a
Não fique com medo de embarcar caso chegue à plataforma
de uma das estações do Metrô em São Paulo e veja um
trem sem condutor. Os novos vagões da linha amarela dispensam
o profissional a bordo. Esse é apenas um detalhe de
uma lista de recursos tecnológicos que estão sendo implementados
para transportar os paulistas com mais eficiência. Escadas
rolantes com sensores de presença, câmeras de vídeo que
enviam imagens para a central por Wi-Fi, comunicação com os
passageiros por VoIP e freios inteligentes são outras novidades.
O Metrô está passando por uma modernização que
não é só cosmética. Com ar condicionado, os novos trens não
precisam de muitas frestas para entrada de ar. Não é só uma
questão de conforto térmico, mas acústico. Nas novas escadas
rolantes, sensores infravermelho detectam a presença de pessoas;
não havendo ninguém, a rolagem é mais lenta, e economiza-
se energia elétrica.
(Adaptado de Kátia Arima, da INFO. http://info.abril.com.br/noticias)