Questões de Vestibular
Comentadas sobre interpretação de texto | reading comprehension em inglês
Foram encontradas 680 questões
Exam ine the follow ing cartoon to answ er question.

Sobre o cartoon, qual das afirmações a seguir é FALSA?

Na tirinha ao lado:


Fonte: http://constitutionus.com/ Acesso em: 10 de novembro de 2017.
Nesse sentido, a mensagem verbo-visual dos referidos cartazes busca:
Leia o texto publicitário abaixo e responda:
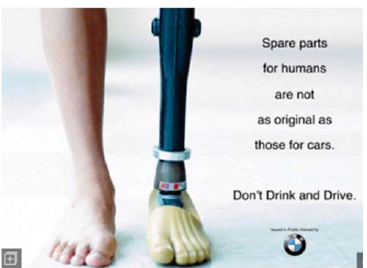
Esta campanha publicitária busca conscientizar as
pessoas acerca do perigo da associação entre bebida
alcoólica e condução de veículos automotores. Que
mensagem a campanha constrói para convencer as
pessoas em relação ao perigo dessa associação?
A partir da leitura da tirinha abaixo, pode-se inferir que:

Considere o cartoon a seguir para responder à questão:

(https://latuffcartoons.wordpress.com/page/2/ acesso em 19/03/2015)
Segundo o contexto da charge, o presidente estadunidense, representado pelo personagem de terno,
 Na fala da espiga de milho à direita “I spent too much time in
there, instead!”, o termo em destaque se refere
Na fala da espiga de milho à direita “I spent too much time in
there, instead!”, o termo em destaque se refere Na fala da espiga de milho à esquerda “I couldn’t reach the
fridge...”, o termo em destaque pode ser substituído, sem
alteração de sentido, por
Na fala da espiga de milho à esquerda “I couldn’t reach the
fridge...”, o termo em destaque pode ser substituído, sem
alteração de sentido, por 
In developing countries there are high levels of what is known as “food loss”, which is unintentional wastage, often due to poor equipment, transportation and infrastructure. In wealthy countries, there are low levels of unintentional losses but high levels of “food waste”, which involves food being thrown away by consumers because they have purchased too much, or by retailers who reject food because of exacting aesthetic standards.
(www.theguardian.com)
 The corncob on the left
The corncob on the left
A friend is someone who brings out the best in you;
Good friends are always happy to help when you run into a
problem;
A friend is someone who cheers you up when you’re feeling
bad;
True friends don’t drift apart even after many years of
separation;
A real friend will always stand up for you when others
are putting you down;
Never be afraid to open up and ask a friend for advice. A true
friend will never turn you down;
Make new friends but hang on to the old ones;
Good friends are hard to come by, harder to leave, and
impossible to do without.
file:///j:/top%2010%20reasons%20why%20learning%20english
É extremamente comum em inglês combinações de verbos
com partículas adverbiais ou preposicionais. Essas
combinações são geralmente chamadas de verbos frasais
(phrasal verbs), preposicionados ou de duas palavras. No
texto, encontram-se vários exemplos de verbos frasais
negritados. A correlação correta entre o verbo e seu sentido
está contemplada em

About one hundred years ago many educated people learned and spoke French when they met people from other countries. Today most people speak English when they meet foreigners. It has become the new international language. There are more people who speak English as a second language than people who speak English as a first language. Why is this? There are many reasons why English has become so popular. One of them is that English has become the language of business. Another important reason is that popular American culture (like movies, music, and McDonald's) has quickly spread throughout the world. It has brought its language with it.
file:///J:/English%20as%20an%20International%20Language%20- %20Level%20A %20-%20Teacher%20Len.html
According to the text, it is correct to say that

Muitos verbos em inglês consistem em duas partes: um verbo
“base” (tais como bring, take, go, come) acompanhados de uma
preposição ou de uma partícula adverbial (tais como up, down,
out, in, off). No segundo quadro da tirinha, foi retirada a palavra
que acompanha o verbo GO. A preposição que completa o
sentido do verbo na fala do personagem é
Drinking coffee could help you live longer Coffee not only helps you feel full of beans, it might add years to your life as well, two major studies have shown. Scientists in Europe and the US have uncovered the clearest evidence yet that drinking coffee reduces the risk of death.
One study of more than half a million people from 10 European countries found that men who downed at least three cups of coffee a day were 18% less likely to die from any cause than non-coffee drinkers. Women drinking the same amount benefited less, but still experienced an 8% reduction in mortality over the period measured.
Similar results were reported by American scientists who conducted a separate investigation, recruiting 185855 participants from different ethnic backgrounds. Irrespective of ethnicity, people who drank two to three cups of coffee daily had an 18% reduced risk of death.
Each of the studies, both published in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine, showed no advantage from drinking either caffeinated or decaffeinated coffee. Experts believe the antioxidant plant compounds in coffee rather than caffeine are responsible for the life-extending effect. Previous research has suggested that drinking coffee can reduce the risk of heart disease, diabetes, liver disease, and some cancers.
Dr Marc Gunter, from the International Agency for Research on Cancer, who led the European study with colleagues from Imperial College London, said: “We found that higher coffee consumption was associated with a lower risk of death from any cause and specifically for circulatory diseases and digestive diseases. Importantly, these results were similar across all of the 10 European countries, with variable coffee drinking habits and customs. Our study also offers important insights into the possible mechanisms for the beneficial health effects of coffee.”
(www.huffingtonpost.co.uk, 11.07.2017. Adaptado.)
Drinking coffee could help you live longer Coffee not only helps you feel full of beans, it might add years to your life as well, two major studies have shown. Scientists in Europe and the US have uncovered the clearest evidence yet that drinking coffee reduces the risk of death.
One study of more than half a million people from 10 European countries found that men who downed at least three cups of coffee a day were 18% less likely to die from any cause than non-coffee drinkers. Women drinking the same amount benefited less, but still experienced an 8% reduction in mortality over the period measured.
Similar results were reported by American scientists who conducted a separate investigation, recruiting 185855 participants from different ethnic backgrounds. Irrespective of ethnicity, people who drank two to three cups of coffee daily had an 18% reduced risk of death.
Each of the studies, both published in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine, showed no advantage from drinking either caffeinated or decaffeinated coffee. Experts believe the antioxidant plant compounds in coffee rather than caffeine are responsible for the life-extending effect. Previous research has suggested that drinking coffee can reduce the risk of heart disease, diabetes, liver disease, and some cancers.
Dr Marc Gunter, from the International Agency for Research on Cancer, who led the European study with colleagues from Imperial College London, said: “We found that higher coffee consumption was associated with a lower risk of death from any cause and specifically for circulatory diseases and digestive diseases. Importantly, these results were similar across all of the 10 European countries, with variable coffee drinking habits and customs. Our study also offers important insights into the possible mechanisms for the beneficial health effects of coffee.”
(www.huffingtonpost.co.uk, 11.07.2017. Adaptado.)
Drinking coffee could help you live longer Coffee not only helps you feel full of beans, it might add years to your life as well, two major studies have shown. Scientists in Europe and the US have uncovered the clearest evidence yet that drinking coffee reduces the risk of death.
One study of more than half a million people from 10 European countries found that men who downed at least three cups of coffee a day were 18% less likely to die from any cause than non-coffee drinkers. Women drinking the same amount benefited less, but still experienced an 8% reduction in mortality over the period measured.
Similar results were reported by American scientists who conducted a separate investigation, recruiting 185855 participants from different ethnic backgrounds. Irrespective of ethnicity, people who drank two to three cups of coffee daily had an 18% reduced risk of death.
Each of the studies, both published in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine, showed no advantage from drinking either caffeinated or decaffeinated coffee. Experts believe the antioxidant plant compounds in coffee rather than caffeine are responsible for the life-extending effect. Previous research has suggested that drinking coffee can reduce the risk of heart disease, diabetes, liver disease, and some cancers.
Dr Marc Gunter, from the International Agency for Research on Cancer, who led the European study with colleagues from Imperial College London, said: “We found that higher coffee consumption was associated with a lower risk of death from any cause and specifically for circulatory diseases and digestive diseases. Importantly, these results were similar across all of the 10 European countries, with variable coffee drinking habits and customs. Our study also offers important insights into the possible mechanisms for the beneficial health effects of coffee.”
(www.huffingtonpost.co.uk, 11.07.2017. Adaptado.)
At Hwaban, Mihyun Han with her husband, Key Kim, will present their take on Korean fare, traditional and personalized with modern touches. The serene, neutral-toned dining room with pale brick walls, accented by dark furniture, is the setting for their varied menu. Some of the small plates to start are shrimp or scallop, an organic egg with king crab in a pine nut sauce, and pan-seared zucchini with shrimp in a soy sauce. More substantial dishes include poached lemon sole with vegetables, chicken with root vegetables, and grilled New York strip steak with Korean mountain greens and mustard dressing. Classics like bibimbap, kimchi stew with pork belly, and galbi (short ribs) are also served, and there is a set array of dishes called Hwaban Table. The name of the restaurant means “as beautiful as a flower,” and there are floral elements in the dining room and on some plates.
(Florence Fabricant. www.nytimes.com, 14.08.2018. Adaptado.)
At Hwaban, Mihyun Han with her husband, Key Kim, will present their take on Korean fare, traditional and personalized with modern touches. The serene, neutral-toned dining room with pale brick walls, accented by dark furniture, is the setting for their varied menu. Some of the small plates to start are shrimp or scallop, an organic egg with king crab in a pine nut sauce, and pan-seared zucchini with shrimp in a soy sauce. More substantial dishes include poached lemon sole with vegetables, chicken with root vegetables, and grilled New York strip steak with Korean mountain greens and mustard dressing. Classics like bibimbap, kimchi stew with pork belly, and galbi (short ribs) are also served, and there is a set array of dishes called Hwaban Table. The name of the restaurant means “as beautiful as a flower,” and there are floral elements in the dining room and on some plates.
(Florence Fabricant. www.nytimes.com, 14.08.2018. Adaptado.)
Fake news can distort people’s beliefs even after being debunked. A study recently published in the journal Intelligence suggests that some people may have an especially difficult time rejecting misinformation. Asked to rate a fictitious person on a range of character traits, people who scored low on a test of cognitive ability continued to be influenced by damaging information about the person even after they were explicitly told the information was false. The study is significant because it identifies what may be a major risk factor for vulnerability to fake news.
One possible explanation for this finding is based on the theory that a person’s cognitive ability reflects how well they can regulate the contents of working memory – their “mental workspace” for processing information. First proposed by the cognitive psychologists Lynn Hasher and Rose Zacks, this theory holds that some people are more prone to “mental clutter” than other people. In other words, some people are less able to discard (or “inhibit”) information from their working memory that is no longer relevant to the task at hand, or information that has been discredited. Research on cognitive aging indicates that, in adulthood, this ability declines considerably with advancing age, suggesting that older adults may also be especially vulnerable to fake news. Another reason why cognitive ability may predict vulnerability to fake news is that it correlates highly with education. Through education, people may develop meta-cognitive skills – strategies for monitoring and regulating one’s own thinking – that can be used to combat the effects of misinformation.
(www.scientificamerican.com, 06.02.2018. Adaptado.)

A partir da associação entre o texto e o cartum, depreende-
-se que a expressão “mental clutter”, empregada no segundo
parágrafo do texto, significa
Fake news can distort people’s beliefs even after being debunked. A study recently published in the journal Intelligence suggests that some people may have an especially difficult time rejecting misinformation. Asked to rate a fictitious person on a range of character traits, people who scored low on a test of cognitive ability continued to be influenced by damaging information about the person even after they were explicitly told the information was false. The study is significant because it identifies what may be a major risk factor for vulnerability to fake news.
One possible explanation for this finding is based on the theory that a person’s cognitive ability reflects how well they can regulate the contents of working memory – their “mental workspace” for processing information. First proposed by the cognitive psychologists Lynn Hasher and Rose Zacks, this theory holds that some people are more prone to “mental clutter” than other people. In other words, some people are less able to discard (or “inhibit”) information from their working memory that is no longer relevant to the task at hand, or information that has been discredited. Research on cognitive aging indicates that, in adulthood, this ability declines considerably with advancing age, suggesting that older adults may also be especially vulnerable to fake news. Another reason why cognitive ability may predict vulnerability to fake news is that it correlates highly with education. Through education, people may develop meta-cognitive skills – strategies for monitoring and regulating one’s own thinking – that can be used to combat the effects of misinformation.
(www.scientificamerican.com, 06.02.2018. Adaptado.)
Fake news can distort people’s beliefs even after being debunked. A study recently published in the journal Intelligence suggests that some people may have an especially difficult time rejecting misinformation. Asked to rate a fictitious person on a range of character traits, people who scored low on a test of cognitive ability continued to be influenced by damaging information about the person even after they were explicitly told the information was false. The study is significant because it identifies what may be a major risk factor for vulnerability to fake news.
One possible explanation for this finding is based on the theory that a person’s cognitive ability reflects how well they can regulate the contents of working memory – their “mental workspace” for processing information. First proposed by the cognitive psychologists Lynn Hasher and Rose Zacks, this theory holds that some people are more prone to “mental clutter” than other people. In other words, some people are less able to discard (or “inhibit”) information from their working memory that is no longer relevant to the task at hand, or information that has been discredited. Research on cognitive aging indicates that, in adulthood, this ability declines considerably with advancing age, suggesting that older adults may also be especially vulnerable to fake news. Another reason why cognitive ability may predict vulnerability to fake news is that it correlates highly with education. Through education, people may develop meta-cognitive skills – strategies for monitoring and regulating one’s own thinking – that can be used to combat the effects of misinformation.
(www.scientificamerican.com, 06.02.2018. Adaptado.)