Questões de Vestibular
Comentadas sobre interpretação de texto | reading comprehension em inglês
Foram encontradas 680 questões
TEXT 1
Houston’s Poor Neighborhoods Could Be Prime Zika Real Estate
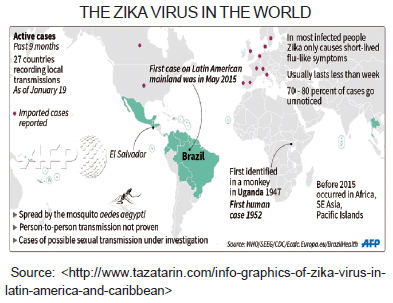
The World Health Organization (WHO) has warned of the potential for the explosive spread of the Zika virus through the Americas. Margaret Chan, the director of the WHO, advised that the Americas could be hit by 4 million cases of Zika this year. The outbreak of Zika virus now centered in Brazil has been linked to a sudden increase in severe birth defects including microcephaly, babies born with smaller heads and brains. The National Public Radio – USA (NPR) recently reported that other neurological problems, such as babies born blind, may also be linked to Zika. Researchers do not fully understand Zika or have not yet proven causality, but the circumstantial evidence connecting the Zika outbreak to the sudden, large increase in birth defects is very strong.
Reports quoted experts who said that Zika was a low risk to the United States because the U.S. doesn’t have the poverty and high population densities that have caused the explosive spread of Zika in Brazil. However, Dr. Peter Hotez, a tropical disease researcher who lives in Texas, has warned that poverty and high population density makes Houston highly vulnerable to a Zika outbreak. He warned that the whole Mexican Gulf coast is already sufferingfrom increasing levels of tropical diseases spread by mosquitoes, in particular dengue fever. Because Zika virus is related to dengue fever and has the same mosquito vector, the expansion of dengue in the Gulf coast region is a good indicator of the potential spread of Zika virus
Adapted from: <http://www.democraticunderground.com/
112796307>
TEXT 1
Houston’s Poor Neighborhoods Could Be Prime Zika Real Estate
The World Health Organization (WHO) has warned of the potential for the explosive spread of the Zika virus through the Americas. Margaret Chan, the director of the WHO, advised that the Americas could be hit by 4 million cases of Zika this year. The outbreak of Zika virus now centered in Brazil has been linked to a sudden increase in severe birth defects including microcephaly, babies born with smaller heads and brains. The National Public Radio – USA (NPR) recently reported that other neurological problems, such as babies born blind, may also be linked to Zika. Researchers do not fully understand Zika or have not yet proven causality, but the circumstantial evidence connecting the Zika outbreak to the sudden, large increase in birth defects is very strong.
Reports quoted experts who said that Zika was a low risk to the United States because the U.S. doesn’t have the poverty and high population densities that have caused the explosive spread of Zika in Brazil. However, Dr. Peter Hotez, a tropical disease researcher who lives in Texas, has warned that poverty and high population density makes Houston highly vulnerable to a Zika outbreak. He warned that the whole Mexican Gulf coast is already suffering from increasing levels of tropical diseases spread by mosquitoes, in particular dengue fever. Because Zika virus is related to dengue fever and has the same mosquito vector, the expansion of dengue in the Gulf coast region is a good indicator of the potential spread of Zika virus.
Adapted from: <http://www.democraticunderground.com/
112796307>
TEXT 1
Houston’s Poor Neighborhoods Could Be Prime Zika Real Estate
The World Health Organization (WHO) has warned of the potential for the explosive spread of the Zika virus through the Americas. Margaret Chan, the director of the WHO, advised that the Americas could be hit by 4 million cases of Zika this year. The outbreak of Zika virus now centered in Brazil has been linked to a sudden increase in severe birth defects including microcephaly, babies born with smaller heads and brains. The National Public Radio – USA (NPR) recently reported that other neurological problems, such as babies born blind, may also be linked to Zika. Researchers do not fully understand Zika or have not yet proven causality, but the circumstantial evidence connecting the Zika outbreak to the sudden, large increase in birth defects is very strong.
Reports quoted experts who said that Zika was a low risk to the United States because the U.S. doesn’t have the poverty and high population densities that have caused the explosive spread of Zika in Brazil. However, Dr. Peter Hotez, a tropical disease researcher who lives in Texas, has warned that poverty and high population density makes Houston highly vulnerable to a Zika outbreak. He warned that the whole Mexican Gulf coast is already suffering from increasing levels of tropical diseases spread by mosquitoes, in particular dengue fever. Because Zika virus is related to dengue fever and has the same mosquito vector, the expansion of dengue in the Gulf coast region is a good indicator of the potential spread of Zika virus.
Adapted from: <http://www.democraticunderground.com/
112796307>
The classic fairy tale finishes by the woodchopper killing another character. However, this does not happen in this modern version.
In the end of this version, the woodchopper carries out the act of:
This form includes a permission to perform the following action:
This modern version of the fairy tale Little Red Riding Hood addresses different social issues.
One of these issues is:
Leia o texto para responder à questão.
Disparity in life spans of the rich and the poor is growing
Sabrina Tavernise
February 12, 2016

Experts have long known that rich people generally live longer than poor people. But a growing body of data shows a more disturbing pattern: Despite big advances in medicine, technology and education, the longevity gap between high-income and low-income Americans has been widening sharply.
The poor are losing ground not only in income, but also in years of life, the most basic measure of well-being. In the early 1970s, a 60-year-old man in the top half of the earnings ladder could expect to live 1.2 years longer than a man of the same age in the bottom half, according to an analysis by the Social Security Administration. Fast-forward to 2001, and he could expect to live 5.8 years longer than his poorer counterpart.
New research released this month contains even more jarring numbers. Looking at the extreme ends of the income spectrum, economists at the Brookings Institution found that for men born in 1920, there was a six-year difference in life expectancy between the top 10 percent of earners and the bottom 10 percent. For men born in 1950, that difference had more than doubled, to 14 years. For women, the gap grew to 13 years, from 4.7 years. “There has been this huge spreading out,” said Gary Burtless, one of the authors of the study.
The growing chasm is alarming policy makers, and has surfaced in the presidential campaign. During a Democratic debate, Senator Bernie Sanders and Hillary Clinton expressed concern over shortening life spans for some Americans. “This may be the next frontier of the inequality discussion,” said Peter Orszag, a former Obama administration official now at Citigroup, who was among the first to highlight the pattern. The causes are still being investigated, but public health researchers say that deep declines in smoking among the affluent and educated may partly explain the difference.
Overall, according to the Brookings study, life expectancy for the bottom 10 percent of wage earners improved by just 3 percent for men born in 1950 compared with those born in 1920. For the top 10 percent, though, it jumped by about 28 percent. (The researchers used a common measure – life expectancy at age 50 – and included data from 1984 to 2012.)
(www.nytimes.com. Adaptado.)
Leia o texto para responder à questão.
Disparity in life spans of the rich and the poor is growing
Sabrina Tavernise
February 12, 2016

Experts have long known that rich people generally live longer than poor people. But a growing body of data shows a more disturbing pattern: Despite big advances in medicine, technology and education, the longevity gap between high-income and low-income Americans has been widening sharply.
The poor are losing ground not only in income, but also in years of life, the most basic measure of well-being. In the early 1970s, a 60-year-old man in the top half of the earnings ladder could expect to live 1.2 years longer than a man of the same age in the bottom half, according to an analysis by the Social Security Administration. Fast-forward to 2001, and he could expect to live 5.8 years longer than his poorer counterpart.
New research released this month contains even more jarring numbers. Looking at the extreme ends of the income spectrum, economists at the Brookings Institution found that for men born in 1920, there was a six-year difference in life expectancy between the top 10 percent of earners and the bottom 10 percent. For men born in 1950, that difference had more than doubled, to 14 years. For women, the gap grew to 13 years, from 4.7 years. “There has been this huge spreading out,” said Gary Burtless, one of the authors of the study.
The growing chasm is alarming policy makers, and has surfaced in the presidential campaign. During a Democratic debate, Senator Bernie Sanders and Hillary Clinton expressed concern over shortening life spans for some Americans. “This may be the next frontier of the inequality discussion,” said Peter Orszag, a former Obama administration official now at Citigroup, who was among the first to highlight the pattern. The causes are still being investigated, but public health researchers say that deep declines in smoking among the affluent and educated may partly explain the difference.
Overall, according to the Brookings study, life expectancy for the bottom 10 percent of wage earners improved by just 3 percent for men born in 1950 compared with those born in 1920. For the top 10 percent, though, it jumped by about 28 percent. (The researchers used a common measure – life expectancy at age 50 – and included data from 1984 to 2012.)
(www.nytimes.com. Adaptado.)
Leia o texto para responder à questão.
Disparity in life spans of the rich and the poor is growing
Sabrina Tavernise
February 12, 2016

Experts have long known that rich people generally live longer than poor people. But a growing body of data shows a more disturbing pattern: Despite big advances in medicine, technology and education, the longevity gap between high-income and low-income Americans has been widening sharply.
The poor are losing ground not only in income, but also in years of life, the most basic measure of well-being. In the early 1970s, a 60-year-old man in the top half of the earnings ladder could expect to live 1.2 years longer than a man of the same age in the bottom half, according to an analysis by the Social Security Administration. Fast-forward to 2001, and he could expect to live 5.8 years longer than his poorer counterpart.
New research released this month contains even more jarring numbers. Looking at the extreme ends of the income spectrum, economists at the Brookings Institution found that for men born in 1920, there was a six-year difference in life expectancy between the top 10 percent of earners and the bottom 10 percent. For men born in 1950, that difference had more than doubled, to 14 years. For women, the gap grew to 13 years, from 4.7 years. “There has been this huge spreading out,” said Gary Burtless, one of the authors of the study.
The growing chasm is alarming policy makers, and has surfaced in the presidential campaign. During a Democratic debate, Senator Bernie Sanders and Hillary Clinton expressed concern over shortening life spans for some Americans. “This may be the next frontier of the inequality discussion,” said Peter Orszag, a former Obama administration official now at Citigroup, who was among the first to highlight the pattern. The causes are still being investigated, but public health researchers say that deep declines in smoking among the affluent and educated may partly explain the difference.
Overall, according to the Brookings study, life expectancy for the bottom 10 percent of wage earners improved by just 3 percent for men born in 1950 compared with those born in 1920. For the top 10 percent, though, it jumped by about 28 percent. (The researchers used a common measure – life expectancy at age 50 – and included data from 1984 to 2012.)
(www.nytimes.com. Adaptado.)
Leia o texto para responder à questão.
Disparity in life spans of the rich and the poor is growing
Sabrina Tavernise
February 12, 2016

Experts have long known that rich people generally live longer than poor people. But a growing body of data shows a more disturbing pattern: Despite big advances in medicine, technology and education, the longevity gap between high-income and low-income Americans has been widening sharply.
The poor are losing ground not only in income, but also in years of life, the most basic measure of well-being. In the early 1970s, a 60-year-old man in the top half of the earnings ladder could expect to live 1.2 years longer than a man of the same age in the bottom half, according to an analysis by the Social Security Administration. Fast-forward to 2001, and he could expect to live 5.8 years longer than his poorer counterpart.
New research released this month contains even more jarring numbers. Looking at the extreme ends of the income spectrum, economists at the Brookings Institution found that for men born in 1920, there was a six-year difference in life expectancy between the top 10 percent of earners and the bottom 10 percent. For men born in 1950, that difference had more than doubled, to 14 years. For women, the gap grew to 13 years, from 4.7 years. “There has been this huge spreading out,” said Gary Burtless, one of the authors of the study.
The growing chasm is alarming policy makers, and has surfaced in the presidential campaign. During a Democratic debate, Senator Bernie Sanders and Hillary Clinton expressed concern over shortening life spans for some Americans. “This may be the next frontier of the inequality discussion,” said Peter Orszag, a former Obama administration official now at Citigroup, who was among the first to highlight the pattern. The causes are still being investigated, but public health researchers say that deep declines in smoking among the affluent and educated may partly explain the difference.
Overall, according to the Brookings study, life expectancy for the bottom 10 percent of wage earners improved by just 3 percent for men born in 1950 compared with those born in 1920. For the top 10 percent, though, it jumped by about 28 percent. (The researchers used a common measure – life expectancy at age 50 – and included data from 1984 to 2012.)
(www.nytimes.com. Adaptado.)
Leia o texto para responder à questão.
Disparity in life spans of the rich and the poor is growing
Sabrina Tavernise
February 12, 2016

Experts have long known that rich people generally live longer than poor people. But a growing body of data shows a more disturbing pattern: Despite big advances in medicine, technology and education, the longevity gap between high-income and low-income Americans has been widening sharply.
The poor are losing ground not only in income, but also in years of life, the most basic measure of well-being. In the early 1970s, a 60-year-old man in the top half of the earnings ladder could expect to live 1.2 years longer than a man of the same age in the bottom half, according to an analysis by the Social Security Administration. Fast-forward to 2001, and he could expect to live 5.8 years longer than his poorer counterpart.
New research released this month contains even more jarring numbers. Looking at the extreme ends of the income spectrum, economists at the Brookings Institution found that for men born in 1920, there was a six-year difference in life expectancy between the top 10 percent of earners and the bottom 10 percent. For men born in 1950, that difference had more than doubled, to 14 years. For women, the gap grew to 13 years, from 4.7 years. “There has been this huge spreading out,” said Gary Burtless, one of the authors of the study.
The growing chasm is alarming policy makers, and has surfaced in the presidential campaign. During a Democratic debate, Senator Bernie Sanders and Hillary Clinton expressed concern over shortening life spans for some Americans. “This may be the next frontier of the inequality discussion,” said Peter Orszag, a former Obama administration official now at Citigroup, who was among the first to highlight the pattern. The causes are still being investigated, but public health researchers say that deep declines in smoking among the affluent and educated may partly explain the difference.
Overall, according to the Brookings study, life expectancy for the bottom 10 percent of wage earners improved by just 3 percent for men born in 1950 compared with those born in 1920. For the top 10 percent, though, it jumped by about 28 percent. (The researchers used a common measure – life expectancy at age 50 – and included data from 1984 to 2012.)
(www.nytimes.com. Adaptado.)
Leia a charge para responder à questão.

Leia a charge para responder à questão.

Some Animals Can Suffer From Mental Illness, Too
Disponível em: http://nymag.com/scienceofus/ 2015/09/some-animals-can-suffer-from-mental-illness-too.html. Acessado em 16/10/2015.
Adaptado para fins educacionais.
By Melissa Dahl Follow @melissadahl

Maybe you've had or heard about a pet cat on Prozac, or a dog that doesn't quite seem like itself in the weeks following the death of another animal in the home. On the one hand, it's hard not to question whether there is some owner-projection or anthropomorphism happening here. But on the other, some scientists are starting to seriously investigate the inner lives of animals, including potential signs of mental illness.
De acordo com o texto,
We’ve modified our behavior so we can text and walk
Texting – or checking social media or reading/responding to mail or reading the news or checking the weather or watching a video – while walking is a pretty common phenomenon. It’s so common that most people who own a mobile device have become texting walkers.
Research suggests that these texters adopt protective measures to minimize the risk of accidents when walking. They’re less likely to trip because they shorten their step length, reduce step frequency, lengthen the time during which both feet are in contact with the ground, and increase obstacle clearance height. Taken together this creates an exaggerated image of walking, but it apparently slows the walker enough so that he registers some of what is happening around him and can compensate for it.
(Adaptado de http://blogs.scientificamerican.com/anthropology-in-practice/we-ve-modified-our-behavior-so-we-can-text-and-walk/.)
We’ve modified our behavior so we can text and walk
Texting – or checking social media or reading/responding to mail or reading the news or checking the weather or watching a video – while walking is a pretty common phenomenon. It’s so common that most people who own a mobile device have become texting walkers.
Research suggests that these texters adopt protective measures to minimize the risk of accidents when walking. They’re less likely to trip because they shorten their step length, reduce step frequency, lengthen the time during which both feet are in contact with the ground, and increase obstacle clearance height. Taken together this creates an exaggerated image of walking, but it apparently slows the walker enough so that he registers some of what is happening around him and can compensate for it.
(Adaptado de http://blogs.scientificamerican.com/anthropology-in-practice/we-ve-modified-our-behavior-so-we-can-text-and-walk/.)
If apes go extinct, so could entire forests
Bonobos eat a lot of fruit, and fruit contains seeds. Those seeds travel through a bonobo’s digestive system while bonobo itself travels around the forest. A few hours later, the seeds end up being deposited far from where the fruits were plucked. And that is where the new trees come from.
According to a paper recently published, if the bonobos disappeared, the plants would also likely go extinct, for many trees and plants species in Congo rely almost exclusively on bonobos for seed dispersal.
The bonobo has two major functions here. First of all, many seeds will not germinate well unless they have been “handled” by another species. Stomach acids and intestinal processes make the seed more able to absorb water and later sprout.
Secondly, many seeds will not succeed if they remain too close to their parental trees. The seeds that fell to the ground near their parents did not survive because they were choked off by the nearby plants. The bonobos eat about 3,5 hours every day and travel a mean of 1.2 kilometers from meal sites before defecating.
(Adaptado de http://blogs.scientificamerican.com/extinction-countdown /if-apes-go-extinct-so-could-entire-forests/.)
Qual é a explicação para o título?
Advice for new students from those who know (old students)
The first day of college I was a ball of nerves. I remember walking into my first class and running to the first seat I found, thinking everyone would be staring at me. But nobody seemed to notice and then it hit me: The fact that nobody knew me meant nobody would judge, which, upon reflection, was what I was scared of the most. I told myself to let go. All along the year, I forced myself into situations that were uncomfortable for me – for example, auditioning for a dance piece. Believe it or not, that performance was a highlight of my freshman year. My advice: challenge yourself to try something new, something you couldn’t have done in high school. – Ria Jagasia, Vanderbilt University, ’18.
(Adaptado de http://www.nytimes.com/2015/08/02/ education/edlife/ advice-for-new-students-from-those-who-know-old-students.html?ref= edlife.)
Advice for new students from those who know (old students)
The first day of college I was a ball of nerves. I remember walking into my first class and running to the first seat I found, thinking everyone would be staring at me. But nobody seemed to notice and then it hit me: The fact that nobody knew me meant nobody would judge, which, upon reflection, was what I was scared of the most. I told myself to let go. All along the year, I forced myself into situations that were uncomfortable for me – for example, auditioning for a dance piece. Believe it or not, that performance was a highlight of my freshman year. My advice: challenge yourself to try something new, something you couldn’t have done in high school. – Ria Jagasia, Vanderbilt University, ’18.
(Adaptado de http://www.nytimes.com/2015/08/02/ education/edlife/ advice-for-new-students-from-those-who-know-old-students.html?ref= edlife.)