Questões de Vestibular CEDERJ 2017 para Vestibular - Primeiro Semestre
Foram encontradas 60 questões
Se 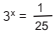 , então o valor de
, então o valor de 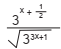 é:
é:
Cinquenta modelos de uma agência foram identificadas de acordo com a cor dos cabelos e dos olhos, conforme tabela a seguir:
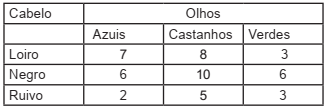
Para fazer a propaganda de certo produto, será sorteada,
ao acaso, uma das 50 modelos. A probabilidade
de a modelo sorteada ter cabelos negros ou olhos
verdes é de
Amplamente comercializado, em todo o Brasil, sobretudo por seu valor energético, o açaí contém antocianinas, substâncias responsáveis pelas colorações nos tons de azul, vermelho e arroxeado em diversos tecidos vegetais, especialmente em flores e frutos. As antocianinas mudam sua coloração conforme a acidez ou basicidade do meio em que se encontram. Isso faz com que o extrato de açaí possa atuar como um indicador ácido-base. O extrato de açaí, por exemplo, torna-se avermelhado em soluções ácidas (pH<7), esverdeado em soluções básicas (pH>7) e roxo claro em soluções neutras (pH=7).
Observando a figura abaixo, as substâncias que, em presença de extrato de açaí, apresentariam, respectivamente, colorações avermelhadas, esverdeadas e arroxeadas são:

A metilona – um derivado das anfetaminas – produz efeitos semelhantes aos do ecstasy (MDMA), sendo, portanto, um estimulante gerador de euforia e de mais energia e capaz, também, de alterar a percepção sensorial.
Observe a fórmula estrutural da metilona, apresentada a seguir.
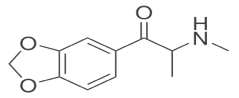
A metilona possui:
O uísque é uma bebida rigorosamente regulamentada. Possui denominações de origem e várias classes e tipos, cuja característica comum é a fermentação dos grãos e a destilação máxima de 80% de álcool para os de milho e 90% de álcool para os de outros grãos, antes da adição de água, com vistas à retenção dos sabores dos grãos usados para fazer a alcoolização.
Esse álcool é o etanol somado a pequenas quantidades de outras substâncias, dentre as quais, ácido acético e acetato de etila. Estas duas últimas substâncias teriam se formado, a partir do etanol, respectivamente, por reações de
A Astaxantina é um carotenoide que, ao contrário de outros, não se converte em Vitamina A no corpo humano, sendo um poderoso antioxidante e componente nutricional natural.
Com massa molar de aproximadamente 596 g/mol e fórmula centesimal C (80.54%), H (8.72%) e O (10.74%), esse carotenoide é representado pela fórmula molecular:
O ácido láctico é um composto orgânico de função mista que apresenta fórmula CH3 CH(OH)COOH. O organismo humano produz ácido láctico em quantidades expressivas durante a realização de exercícios físicos, sendo produzido excessivamente quando esses se intensificam. No ambiente celular, o ácido láctico transforma-se em lactato, que é a sua forma ionizada. A mistura de ácido láctico e lactato de sódio, em solução aquosa, funciona como uma solução-tampão, ou seja, como, praticamente, aquela que não muda seu pH pela adição de H+ ou OH- em pequenas quantidades.
Supondo uma solução contendo 0.15 mol/L de ácido láctico e 0.15 mol/L de lactato de sódio (Ka = 1.0 x 10-4) e negligenciando a quantidade de ácido que ioniza, o valor do pH será igual a :
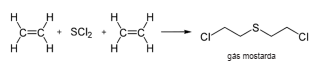
A partir da reação abaixo o volume aproximado, em metros cúbicos de etileno (d=1.18 kg/m3 ), necessário para preparar 2.0 toneladas de gás mostarda é:
Com base nas informações sobre os valores de potenciais de redução, a 25º C:
Mg+2(aq) + 2 e- ⇄ Mg (s) E° = - 2.4 V
Cu+2(aq) + 2 e- ⇄ Cu (s) E° = + 0.34 V
É correto afirmar que:
Em um acidente no laboratório, um frasco contendo 2.0 kg de NaOH foi quebrado e, para neutralizar essa soda foi proposta a reação
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l),
que liberou 660 Kcal. Se 1 cal = 4.18 J, a variação da
entalpia de neutralização, em kJ mol-1, é igual a:
Text 1
The global warming controversy
The global warming controversy is an ongoing dispute about the effects of humans on global climate and about what policies should be implemented to avoid possible undesirable effects of climate change.
The current scientific consensus on climate change is that recent warming indicates a fairly stable long-term trend, that the trend is largely human-caused, and that serious damage may result at some future date if steps are not taken to halt the trend.
Mainstream scientific organizations worldwide (Royal Society, American Geophysical Union, Joint Science Academies, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, American Meteorological Society, and American Association for the Advancement of Science) concur with the assessment that most of the observed warming over the last 50 years is likely to have been due to the human-caused increase in greenhouse gas concentrations.
However, there is also a small but vocal number of scientists in climate and climate-related fields that disagree with the consensus view.
Adapted from:< https://www.sciencedaily.com/terms/global_warming_controversy.htm.> Access 30 Sept. 2017.
Text 2
Climate change label leads to climate science acceptance
On the heels of President Donald Trump's decision to pull the United States out of the Paris climate agreement, a new Cornell University study finds that labels matter when it comes to acceptance of climate science.
The U.S. public doubts the existence of "global warming" more than it doubts "climate change".
In a nationally representative survey, 74.4 percent of respondents said they believed that climate change is really happening. But only 65.5 percent said they believed in global warming.
Nonetheless, it's important to remember that 65 percent of respondents did indicate that global warming is occurring, said co-author Peter Enns, associate professor of government. "In other words, although the term matters -- climate change versus global warming -- an overwhelming majority of people still state that global warming is happening," he said.
Adapted from:<http://mediarelations.cornell.edu/2017/06/21/climate-change-label-leads-to-climate-science-acceptance/>
Text 1
The global warming controversy
The global warming controversy is an ongoing dispute about the effects of humans on global climate and about what policies should be implemented to avoid possible undesirable effects of climate change.
The current scientific consensus on climate change is that recent warming indicates a fairly stable long-term trend, that the trend is largely human-caused, and that serious damage may result at some future date if steps are not taken to halt the trend.
Mainstream scientific organizations worldwide (Royal Society, American Geophysical Union, Joint Science Academies, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, American Meteorological Society, and American Association for the Advancement of Science) concur with the assessment that most of the observed warming over the last 50 years is likely to have been due to the human-caused increase in greenhouse gas concentrations.
However, there is also a small but vocal number of scientists in climate and climate-related fields that disagree with the consensus view.
Adapted from:< https://www.sciencedaily.com/terms/global_warming_controversy.htm.> Access 30 Sept. 2017.
Text 2
Climate change label leads to climate science acceptance
On the heels of President Donald Trump's decision to pull the United States out of the Paris climate agreement, a new Cornell University study finds that labels matter when it comes to acceptance of climate science.
The U.S. public doubts the existence of "global warming" more than it doubts "climate change".
In a nationally representative survey, 74.4 percent of respondents said they believed that climate change is really happening. But only 65.5 percent said they believed in global warming.
Nonetheless, it's important to remember that 65 percent of respondents did indicate that global warming is occurring, said co-author Peter Enns, associate professor of government. "In other words, although the term matters -- climate change versus global warming -- an overwhelming majority of people still state that global warming is happening," he said.
Adapted from:<http://mediarelations.cornell.edu/2017/06/21/climate-change-label-leads-to-climate-science-acceptance/>
Text 1
The global warming controversy
The global warming controversy is an ongoing dispute about the effects of humans on global climate and about what policies should be implemented to avoid possible undesirable effects of climate change.
The current scientific consensus on climate change is that recent warming indicates a fairly stable long-term trend, that the trend is largely human-caused, and that serious damage may result at some future date if steps are not taken to halt the trend.
Mainstream scientific organizations worldwide (Royal Society, American Geophysical Union, Joint Science Academies, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, American Meteorological Society, and American Association for the Advancement of Science) concur with the assessment that most of the observed warming over the last 50 years is likely to have been due to the human-caused increase in greenhouse gas concentrations.
However, there is also a small but vocal number of scientists in climate and climate-related fields that disagree with the consensus view.
Adapted from:< https://www.sciencedaily.com/terms/global_warming_controversy.htm.> Access 30 Sept. 2017.
Text 2
Climate change label leads to climate science acceptance
On the heels of President Donald Trump's decision to pull the United States out of the Paris climate agreement, a new Cornell University study finds that labels matter when it comes to acceptance of climate science.
The U.S. public doubts the existence of "global warming" more than it doubts "climate change".
In a nationally representative survey, 74.4 percent of respondents said they believed that climate change is really happening. But only 65.5 percent said they believed in global warming.
Nonetheless, it's important to remember that 65 percent of respondents did indicate that global warming is occurring, said co-author Peter Enns, associate professor of government. "In other words, although the term matters -- climate change versus global warming -- an overwhelming majority of people still state that global warming is happening," he said.
Adapted from:<http://mediarelations.cornell.edu/2017/06/21/climate-change-label-leads-to-climate-science-acceptance/>
Text 1
The global warming controversy
The global warming controversy is an ongoing dispute about the effects of humans on global climate and about what policies should be implemented to avoid possible undesirable effects of climate change.
The current scientific consensus on climate change is that recent warming indicates a fairly stable long-term trend, that the trend is largely human-caused, and that serious damage may result at some future date if steps are not taken to halt the trend.
Mainstream scientific organizations worldwide (Royal Society, American Geophysical Union, Joint Science Academies, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, American Meteorological Society, and American Association for the Advancement of Science) concur with the assessment that most of the observed warming over the last 50 years is likely to have been due to the human-caused increase in greenhouse gas concentrations.
However, there is also a small but vocal number of scientists in climate and climate-related fields that disagree with the consensus view.
Adapted from:< https://www.sciencedaily.com/terms/global_warming_controversy.htm.> Access 30 Sept. 2017.
Text 2
Climate change label leads to climate science acceptance
On the heels of President Donald Trump's decision to pull the United States out of the Paris climate agreement, a new Cornell University study finds that labels matter when it comes to acceptance of climate science.
The U.S. public doubts the existence of "global warming" more than it doubts "climate change".
In a nationally representative survey, 74.4 percent of respondents said they believed that climate change is really happening. But only 65.5 percent said they believed in global warming.
Nonetheless, it's important to remember that 65 percent of respondents did indicate that global warming is occurring, said co-author Peter Enns, associate professor of government. "In other words, although the term matters -- climate change versus global warming -- an overwhelming majority of people still state that global warming is happening," he said.
Adapted from:<http://mediarelations.cornell.edu/2017/06/21/climate-change-label-leads-to-climate-science-acceptance/>