Questões de Vestibular UDESC 2011 para Vestibular, Prova 1
Foram encontradas 60 questões
Recycle – Reduce – Reuse
Easier – Recycle means to process old, used items in order that the material can be used to make new products. Examples of things that are often recycled are glass, plastic, newspapers, aluminum cans, used motor oil, and batteries. Here, reduce refers to lessening the amount of items or resources that are consumed, using only the amount that is needed, and looking for alternatives that will lessen our use. And reuse means extending the 'life' or repurposing an item rather than discarding or throwing it away. Harder – Recycling is the processes of collecting, processing, remanufacturing, and reusing materials instead of discarding them. This helps conserve raw materials and energy that manufacturers would otherwise use in producing new products. Recycling also reduces the amount of material going into landfills. Recycling helps lessen the pollution that may result from waste disposal. Reducing our consumption of materials and reducing the waste of materials also adds to the conservation of our resources. Disponível em: Acesso em: abr. 2011.
Recycle – Reduce – Reuse
Easier – Recycle means to process old, used items in order that the material can be used to make new products. Examples of things that are often recycled are glass, plastic, newspapers, aluminum cans, used motor oil, and batteries. Here, reduce refers to lessening the amount of items or resources that are consumed, using only the amount that is needed, and looking for alternatives that will lessen our use. And reuse means extending the 'life' or repurposing an item rather than discarding or throwing it away. Harder – Recycling is the processes of collecting, processing, remanufacturing, and reusing materials instead of discarding them. This helps conserve raw materials and energy that manufacturers would otherwise use in producing new products. Recycling also reduces the amount of material going into landfills. Recycling helps lessen the pollution that may result from waste disposal. Reducing our consumption of materials and reducing the waste of materials also adds to the conservation of our resources. Disponível em: Acesso em: abr. 2011.
Recycle – Reduce – Reuse
Easier – Recycle means to process old, used items in order that the material can be used to make new products. Examples of things that are often recycled are glass, plastic, newspapers, aluminum cans, used motor oil, and batteries. Here, reduce refers to lessening the amount of items or resources that are consumed, using only the amount that is needed, and looking for alternatives that will lessen our use. And reuse means extending the 'life' or repurposing an item rather than discarding or throwing it away. Harder – Recycling is the processes of collecting, processing, remanufacturing, and reusing materials instead of discarding them. This helps conserve raw materials and energy that manufacturers would otherwise use in producing new products. Recycling also reduces the amount of material going into landfills. Recycling helps lessen the pollution that may result from waste disposal. Reducing our consumption of materials and reducing the waste of materials also adds to the conservation of our resources. Disponível em: Acesso em: abr. 2011.
Recycle – Reduce – Reuse
Easier – Recycle means to process old, used items in order that the material can be used to make new products. Examples of things that are often recycled are glass, plastic, newspapers, aluminum cans, used motor oil, and batteries. Here, reduce refers to lessening the amount of items or resources that are consumed, using only the amount that is needed, and looking for alternatives that will lessen our use. And reuse means extending the 'life' or repurposing an item rather than discarding or throwing it away. Harder – Recycling is the processes of collecting, processing, remanufacturing, and reusing materials instead of discarding them. This helps conserve raw materials and energy that manufacturers would otherwise use in producing new products. Recycling also reduces the amount of material going into landfills. Recycling helps lessen the pollution that may result from waste disposal. Reducing our consumption of materials and reducing the waste of materials also adds to the conservation of our resources. Disponível em: Acesso em: abr. 2011.
Recycle – Reduce – Reuse
Easier – Recycle means to process old, used items in order that the material can be used to make new products. Examples of things that are often recycled are glass, plastic, newspapers, aluminum cans, used motor oil, and batteries. Here, reduce refers to lessening the amount of items or resources that are consumed, using only the amount that is needed, and looking for alternatives that will lessen our use. And reuse means extending the 'life' or repurposing an item rather than discarding or throwing it away. Harder – Recycling is the processes of collecting, processing, remanufacturing, and reusing materials instead of discarding them. This helps conserve raw materials and energy that manufacturers would otherwise use in producing new products. Recycling also reduces the amount of material going into landfills. Recycling helps lessen the pollution that may result from waste disposal. Reducing our consumption of materials and reducing the waste of materials also adds to the conservation of our resources. Disponível em: Acesso em: abr. 2011.
TEXT 2
Pros and Cons of Nuclear Power
Sergei Supinsky: This storage facility near the site of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant currently houses nuclear waste. What's nuclear power's biggest advantage? It doesn't depend on fossil fuels and isn't affected by fluctuating oil and gas prices. Coal and natural gas power plants emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which contributes to climate change. With nuclear power plants, CO2 emissions are minimal. According to the Nuclear Energy Institute, the power produced by the world's nuclear plants would normally produce 2 billion metric tons of CO2 per year if they depended on fossil fuels. In fact, a properly functioning nuclear power plant actually releases less radioactivity into the atmosphere than a coal-fired power plant. Plus, all this comes with a far lighter fuel requirement. Nuclear fission produces roughly a million times more energy per unit weight than fossil fuel alternatives. And then there are the negatives. Historically, mining and purifying uranium hasn't been a very clean process. Even transporting nuclear fuel to and from plants poses a contamination risk. And once the fuel is spent, you can't just throw it in the city dump. It's still radioactive and potentially deadly. On average, a nuclear power plant annually generates 20 metric tons of used nuclear fuel, classified as high-level radioactive waste. When you take into account every nuclear plant on Earth, the combined total climbs to roughly 2,000 metric tons a year. All of this waste emits radiation and heat, meaning that it will eventually corrode any container that holds it. It can also prove lethal to nearby life forms. As if this weren't bad enough, nuclear power plants produce a great deal of low-level radioactive waste in the form of radiated parts and equipment. Over time, spent nuclear fuel decays to safe radioactive levels, but this process takes tens of thousands of years. Even low-level radioactive waste requires centuries to reach acceptable levels. Currently, the nuclear industry lets waste cool for years before mixing it with glass and storing it in massive cooled, concrete structures. This waste has to be maintained, monitored and guarded to prevent the materials from falling into the wrong hands. All of these services and added materials cost money -- on top of the high costs required to build a plant. Disponível em: Acesso em: abr. 2011.
TEXT 2
Pros and Cons of Nuclear Power
Sergei Supinsky: This storage facility near the site of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant currently houses nuclear waste. What's nuclear power's biggest advantage? It doesn't depend on fossil fuels and isn't affected by fluctuating oil and gas prices. Coal and natural gas power plants emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which contributes to climate change. With nuclear power plants, CO2 emissions are minimal. According to the Nuclear Energy Institute, the power produced by the world's nuclear plants would normally produce 2 billion metric tons of CO2 per year if they depended on fossil fuels. In fact, a properly functioning nuclear power plant actually releases less radioactivity into the atmosphere than a coal-fired power plant. Plus, all this comes with a far lighter fuel requirement. Nuclear fission produces roughly a million times more energy per unit weight than fossil fuel alternatives. And then there are the negatives. Historically, mining and purifying uranium hasn't been a very clean process. Even transporting nuclear fuel to and from plants poses a contamination risk. And once the fuel is spent, you can't just throw it in the city dump. It's still radioactive and potentially deadly. On average, a nuclear power plant annually generates 20 metric tons of used nuclear fuel, classified as high-level radioactive waste. When you take into account every nuclear plant on Earth, the combined total climbs to roughly 2,000 metric tons a year. All of this waste emits radiation and heat, meaning that it will eventually corrode any container that holds it. It can also prove lethal to nearby life forms. As if this weren't bad enough, nuclear power plants produce a great deal of low-level radioactive waste in the form of radiated parts and equipment. Over time, spent nuclear fuel decays to safe radioactive levels, but this process takes tens of thousands of years. Even low-level radioactive waste requires centuries to reach acceptable levels. Currently, the nuclear industry lets waste cool for years before mixing it with glass and storing it in massive cooled, concrete structures. This waste has to be maintained, monitored and guarded to prevent the materials from falling into the wrong hands. All of these services and added materials cost money -- on top of the high costs required to build a plant. Disponível em: Acesso em: abr. 2011.
TEXT 2
Pros and Cons of Nuclear Power
Sergei Supinsky: This storage facility near the site of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant currently houses nuclear waste. What's nuclear power's biggest advantage? It doesn't depend on fossil fuels and isn't affected by fluctuating oil and gas prices. Coal and natural gas power plants emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which contributes to climate change. With nuclear power plants, CO2 emissions are minimal. According to the Nuclear Energy Institute, the power produced by the world's nuclear plants would normally produce 2 billion metric tons of CO2 per year if they depended on fossil fuels. In fact, a properly functioning nuclear power plant actually releases less radioactivity into the atmosphere than a coal-fired power plant. Plus, all this comes with a far lighter fuel requirement. Nuclear fission produces roughly a million times more energy per unit weight than fossil fuel alternatives. And then there are the negatives. Historically, mining and purifying uranium hasn't been a very clean process. Even transporting nuclear fuel to and from plants poses a contamination risk. And once the fuel is spent, you can't just throw it in the city dump. It's still radioactive and potentially deadly. On average, a nuclear power plant annually generates 20 metric tons of used nuclear fuel, classified as high-level radioactive waste. When you take into account every nuclear plant on Earth, the combined total climbs to roughly 2,000 metric tons a year. All of this waste emits radiation and heat, meaning that it will eventually corrode any container that holds it. It can also prove lethal to nearby life forms. As if this weren't bad enough, nuclear power plants produce a great deal of low-level radioactive waste in the form of radiated parts and equipment. Over time, spent nuclear fuel decays to safe radioactive levels, but this process takes tens of thousands of years. Even low-level radioactive waste requires centuries to reach acceptable levels. Currently, the nuclear industry lets waste cool for years before mixing it with glass and storing it in massive cooled, concrete structures. This waste has to be maintained, monitored and guarded to prevent the materials from falling into the wrong hands. All of these services and added materials cost money -- on top of the high costs required to build a plant. Disponível em: Acesso em: abr. 2011.
TEXT 2
Pros and Cons of Nuclear Power
Sergei Supinsky: This storage facility near the site of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant currently houses nuclear waste. What's nuclear power's biggest advantage? It doesn't depend on fossil fuels and isn't affected by fluctuating oil and gas prices. Coal and natural gas power plants emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which contributes to climate change. With nuclear power plants, CO2 emissions are minimal. According to the Nuclear Energy Institute, the power produced by the world's nuclear plants would normally produce 2 billion metric tons of CO2 per year if they depended on fossil fuels. In fact, a properly functioning nuclear power plant actually releases less radioactivity into the atmosphere than a coal-fired power plant. Plus, all this comes with a far lighter fuel requirement. Nuclear fission produces roughly a million times more energy per unit weight than fossil fuel alternatives. And then there are the negatives. Historically, mining and purifying uranium hasn't been a very clean process. Even transporting nuclear fuel to and from plants poses a contamination risk. And once the fuel is spent, you can't just throw it in the city dump. It's still radioactive and potentially deadly. On average, a nuclear power plant annually generates 20 metric tons of used nuclear fuel, classified as high-level radioactive waste. When you take into account every nuclear plant on Earth, the combined total climbs to roughly 2,000 metric tons a year. All of this waste emits radiation and heat, meaning that it will eventually corrode any container that holds it. It can also prove lethal to nearby life forms. As if this weren't bad enough, nuclear power plants produce a great deal of low-level radioactive waste in the form of radiated parts and equipment. Over time, spent nuclear fuel decays to safe radioactive levels, but this process takes tens of thousands of years. Even low-level radioactive waste requires centuries to reach acceptable levels. Currently, the nuclear industry lets waste cool for years before mixing it with glass and storing it in massive cooled, concrete structures. This waste has to be maintained, monitored and guarded to prevent the materials from falling into the wrong hands. All of these services and added materials cost money -- on top of the high costs required to build a plant. Disponível em: Acesso em: abr. 2011.
( ) Nuclear power seldom produces toxic waste.
( ) Fossil fuels are far better than nuclear power concerning to prices.
( ) Nuclear power has little emission of CO 2 into the atmosphere.
( ) Nuclear waste is mixed with glass before storing.
( ) A coal fired power plant produces less pollution than nuclear power.
The correct sequence fromtop to bottom is:
TEXT 2
Pros and Cons of Nuclear Power
Sergei Supinsky: This storage facility near the site of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant currently houses nuclear waste. What's nuclear power's biggest advantage? It doesn't depend on fossil fuels and isn't affected by fluctuating oil and gas prices. Coal and natural gas power plants emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which contributes to climate change. With nuclear power plants, CO2 emissions are minimal. According to the Nuclear Energy Institute, the power produced by the world's nuclear plants would normally produce 2 billion metric tons of CO2 per year if they depended on fossil fuels. In fact, a properly functioning nuclear power plant actually releases less radioactivity into the atmosphere than a coal-fired power plant. Plus, all this comes with a far lighter fuel requirement. Nuclear fission produces roughly a million times more energy per unit weight than fossil fuel alternatives. And then there are the negatives. Historically, mining and purifying uranium hasn't been a very clean process. Even transporting nuclear fuel to and from plants poses a contamination risk. And once the fuel is spent, you can't just throw it in the city dump. It's still radioactive and potentially deadly. On average, a nuclear power plant annually generates 20 metric tons of used nuclear fuel, classified as high-level radioactive waste. When you take into account every nuclear plant on Earth, the combined total climbs to roughly 2,000 metric tons a year. All of this waste emits radiation and heat, meaning that it will eventually corrode any container that holds it. It can also prove lethal to nearby life forms. As if this weren't bad enough, nuclear power plants produce a great deal of low-level radioactive waste in the form of radiated parts and equipment. Over time, spent nuclear fuel decays to safe radioactive levels, but this process takes tens of thousands of years. Even low-level radioactive waste requires centuries to reach acceptable levels. Currently, the nuclear industry lets waste cool for years before mixing it with glass and storing it in massive cooled, concrete structures. This waste has to be maintained, monitored and guarded to prevent the materials from falling into the wrong hands. All of these services and added materials cost money -- on top of the high costs required to build a plant. Disponível em: Acesso em: abr. 2011.
“Os Kaigáng do Chapecó fazem parte de uma tradição ancestral que vem transformando-se com contato de outros povos, outras culturas. Essa dinâmica cultural devido ao contato estabelecido, inicialmente com os pampeanos, sambaqueiros, guarani e por fim, o colonizador, o não índio, tem gerado transformações nos costumes tradicionais, onde observamos hábitos da sociedade nacional incorporados e reelaborados pela sociedade kaingáng, tanto na religião, estrutura social, como na forma de habitação e artesanato."
NÖTZOLD, Ana Lucia. Nosso vizinho Kaigáng. Florianópolis: Imprensa Universitária da UFSC, 2003. p. 94-95.
Considerando o exposto acima e a situação atual em SC, analise as proposições abaixo.
I. O texto faz referência a uma determinada população indígena, radicada em Santa Catarina, e às suas condições de vida, deixando claro que é uma situação restrita à realidade local, pois nas demais regiões do Estado, a situação dos índios é muito mais adequada.
II. Não existe reserva indígena em Santa Catarina, e o texto indica que, se houvesse, esta seria uma solução para os inúmeros problemas sociais enfrentados pelos índios no Estado.
III. A região citada no excerto se localiza no Sul do Estado, onde a população indígena foi integrada desde cedo à comunidade nacional por meio do trabalho nas minas de carvão em Criciúma.
IV. O excerto enfatiza as condições de vida e a realidade social das populações indígenas no Estado.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
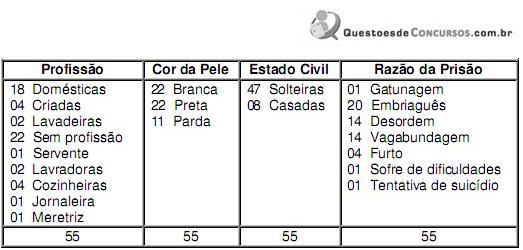
Fonte: Relatórios de Polícia 1910-1911 – Arquivo Público do Estado de Santa Catarina.
Apud: PEDRO, Joana Maria. Mulheres honestas e mulheres faladas: uma questão de classe.
Florianópolis: Ed. UFSC, 1994, p. 157.
A partir dos dados informados no quadro e da história de Santa Catarina, especialmente a da capital do Estado no início do século XX, analise as proposições abaixo.
I. O quadro sobre a prisão de mulheres sugere questões sobre as relações de gênero, entrecruzadas às de classe e etnia. Embora a maioria da população de Florianópolis fosse branca à época, o número de mulheres presas declaradas pretas e pardas, nos relatórios da polícia, é superior ao de mulheres brancas.
II. O número de mulheres solteiras presas – muito superior ao de casadas – evidencia o quanto o casamento traz benefícios para uma mulher, capaz de torná-la honesta. Mulher solteira ou sem um homem de pulso que lhe dê razão está mais sujeita a confusões que podem levá-la à prisão.
III. A quantidade de mulheres identificadas como “sem profissão" e “doméstica" não significa propriamente que estas mulheres não exercessem outras atividades para sobreviver, afinal o quadro sugere que essas mulheres presas eram pobres.
IV. O quadro evidencia que o número de prisão por embriaguês entre as mulheres no período foi muito superior ao número de prisão por furto e gatunagem juntos. Esse e outros dados, observados no quadro, sugerem que nem todas as mulheres do período, sobretudo as mais pobres, puderam seguir as regras de comportamento e distinção social esperadas para elas, que incluíam: casamento, maternidade, domesticidade, delicadeza, retidão de caráter, etc.
V. As profissões indicadas no quadro evidenciam que as mulheres catarinenses já estavam inseridas no mercado de trabalho. Esse é o maior indício de que havia igualdade entre homens e mulheres, em Florianópolis, mesmo no início do século XX.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
“O Estado comporta[va] uma multiplicidade de culturas étnicas. Apesar do esforço para amalgamar a diversidade cultural numa única – luso-brasileira –, os outros povos, bem ou mal, não abandonaram completamente suas tradições. No momento em que a proibição das suas manifestações culturais deixou de atuar, elas [as tradições] voltaram, embora não possamos afirmar que tenham retornado da mesma forma. Trazem suas modificações para servirem às novas experiências dos novos tempos."
FLORES, Maria Bernardete Ramos. Povoadores da Fronteira:
os casais açorianos rumo ao Sul do Brasil. Florianópolis: UFSC, 2000, p. 77.
Considerando o que é posto, e a realidade de SC, analise as proposições.
I. O texto sugere que em determinado momento houve esforços para mostrar a cultura catarinense como única e relacionada à cultura luso-brasileira.
II. Em Santa Catarina houve proibição de algumas práticas culturais, uma delas certamente a farra do boi, que segue sendo praticada mesmo nos dias atuais.
III. Não foram somente os farristas do boi que tiveram suas práticas vigiadas e proibidas. No passado, entre a população de germanodescendentes houve inclusive a proibição do uso da língua alemã e, entre os afrodescendentes, a proibição da entrada em bailes e em outros eventos festivos feitos apenas “para brancos".
IV. É possível afirmar que, apesar das proibições ocorridas no passado, muitas manifestações culturais ainda permanecem, mesmo que adaptadas aos novos tempos.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
I. Concentração fundiária, devido à concentração de capital.
II. Falta de terras produtivas.
III. Herança da terra que parcela as propriedades de tal forma que ficam insuficientes para o sustento de uma família.
IV. Ocupação desordenada de terra.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
Analise as proposições sobre esta diversidade da colonização catarinense.
I. As primeiras povoações no litoral catarinense foram erguidas pelos missionários espanhóis (franciscanos) e missionários portugueses, que reuniram os indígenas. Só mais tarde, no século XVIII, foram fundadas povoações por vicentistas (pessoas oriundas da Capitania de São Vicente).
II. Na segunda metade do século XVIII, chegaram a Santa Catarina mais de seis mil açorianos e mais de meia centena de madeirenses, que se fixaram em São Francisco do Sul, até além de Laguna.
III. Enquanto no litoral se fixavam os casais vindos de Açores e Madeira, no planalto, em função do comércio de gado do sul para a região de mineração, iniciava-se a ocupação das pastagens, que pouco a pouco deram lugar aos pousos para as tropas. Os condutores das tropas eram os tropeiros, daí a atividade se chamar tropeirismo.
IV. A colonização alemã se deu no século XIX, seguida da italiana.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
Assinale a alternativa que complementa a informação acima.