Questões Militares
Foram encontradas 7.428 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Nossa relação com os animais repete, de maneira invertida, os cuidados que recebemos na primeira infância. Nós também fomos, no início, dependentes, desamparados e estávamos nas mãos de uma figura prestativa e generosa, mas que tinha todo poder sobre nós. Nossa capacidade de sentir piedade vem daí. A irresistível combinação de piedade, simpatia e acolhimento que a imagem de um animal fofinho desperta em nós, também. Contudo, esse é um amor de baixa qualidade e de grande aptidão à dispersão quando falamos em um projeto de longo prazo. Animais de estimação são como filhos. Mas filhos que não crescem, não resistem para ir à escola, não reclamam por autonomias adolescentes nem vão embora para a faculdade e se casam, deixando-nos para trás.
Com os animais de estimação cada um revive a forma de amar e ser amado que Freud descreveu como narcisismo. Nele, confunde-se o amar o outro e o amar-se a si mesmo através do outro. E muitas vezes essa confusão se infiltra e atrapalha decisivamente a vida dos casais. Quando alguém declara que ama os cães a ponto de ter dois ou sete deles em casa, isso não representa nenhuma contradição com o ato de maltratá-los. Tudo depende da qualidade do laço que se estabelece nesse amor.
Quando amamos nossos cães, nossos filhos ou nossas mulheres como a nós mesmos, podemos chegar a maltratá-los da pior maneira. Daí a importância de amar o outro conferindo algum espaço para o fato de que ele é um estranho, alguém diferente de mim. O amor não é garantia nem de si mesmo nem do desejo que ele deve habilitar. Isso vai aparecer na relação com os animais, como uma espécie de raio x das nossas formas de amar. Quem trata seus animais como uma parte de si mesmo, humanizando-os realmente como filhos, chamando-os de nenês, por exemplo, pode estar indicando uma forma mais simples e narcísica de amar.
(Christian Dunker, Reinvenção da intimidade – políticas do sofrimento cotidiano. Adaptado)
A figura mostra um prisma ABCDEFGH. Sabe-se que A(0, 0, 0), B(2, 0, 0), C(2, 1, 0), D(0, 1, 0), e que π é o plano de equação x + y + z = 6 que contém a face EFGH do prisma.
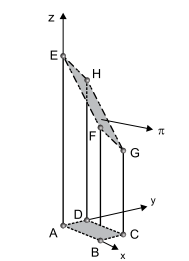
O volume do prisma ABCDEFGH, em unidades de
volume consistente com a unidade de comprimento usada nos eixos x, y e z, é igual a
A figura mostra um prisma ABCDEFGH. Sabe-se que A(0, 0, 0), B(2, 0, 0), C(2, 1, 0), D(0, 1, 0), e que π é o plano de equação x + y + z = 6 que contém a face EFGH do prisma.

Na situação descrita, o volume do prisma, em unidades
de volume consistente com a unidade de comprimento
usada nos eixos x, y e z, pode ser calculado por meio de
A figura indica o gráfico da função f: ℝ - {5/2} → ℝ, definida por , e o segmento de reta PQ, que intersecta o gráfico de f(x) em P(3, yP) e Q(5, yQ).
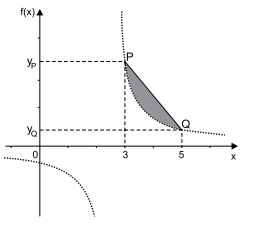
Nas condições dadas, a área da região marcada em
cinza na figura, em unidades de área do plano cartesiano
de eixos ortogonais, é igual a
Quanto às distinções entre tipos de texto e gêneros de texto/discurso, a mais famosa a esse respeito é a de Marcuschi (2002), que os define como
I. Usamos a expressão tipo textual para designar uma espécie de construção teórica definida pela natureza linguística de sua composição {aspectos lexicais, sintáticos, tempos verbais, relações lógicas}. Em geral, os tipos textuais abrangem cerca de meia dúzia de categorias conhecidas: descrição, narração, dissertação/ argumentação, exposição e injunção.
II. Usamos a expressão gênero textual como uma noção propositalmente vaga para referir os textos materializados que encontramos em nossa vida diária e que apresentam características sócio-comunicativas definidas por conteúdos, propriedades funcionais, estilo e composição característica. Se os tipos textuais são apenas meia dúzia, os gêneros são inúmeros.
Tipos de textos vem sendo ensinados na escola há pelo menos uma centena de anos, o que faz deles gêneros escolares. Na escola, escrevemos narrações, na vida, lemos notícias, relatamos nossa vida, recontamos um filme. Na escola, redigimos “uma composição à vista de gravura” (descrição) fora dela, contamos como decoramos nosso apartamento, instruímos uma pessoa como chegar a um lugar desconhecido. Os gêneros de texto, ao contrário, não são classes gramaticais para classificar textos: são entidades da vida.
(ROJO, R. H. R.; BARBOSA, J. P. Hipermodernidade,
multiletramentos e gêneros discursivos.
São Paulo: Parábola Editorial, 2015. Adaptado)
Quanto às distinções entre tipos de texto e gêneros de texto/discurso, a mais famosa a esse respeito é a de Marcuschi (2002), que os define como
I. Usamos a expressão tipo textual para designar uma espécie de construção teórica definida pela natureza linguística de sua composição {aspectos lexicais, sintáticos, tempos verbais, relações lógicas}. Em geral, os tipos textuais abrangem cerca de meia dúzia de categorias conhecidas: descrição, narração, dissertação/ argumentação, exposição e injunção.
II. Usamos a expressão gênero textual como uma noção propositalmente vaga para referir os textos materializados que encontramos em nossa vida diária e que apresentam características sócio-comunicativas definidas por conteúdos, propriedades funcionais, estilo e composição característica. Se os tipos textuais são apenas meia dúzia, os gêneros são inúmeros.
Tipos de textos vem sendo ensinados na escola há pelo menos uma centena de anos, o que faz deles gêneros escolares. Na escola, escrevemos narrações, na vida, lemos notícias, relatamos nossa vida, recontamos um filme. Na escola, redigimos “uma composição à vista de gravura” (descrição) fora dela, contamos como decoramos nosso apartamento, instruímos uma pessoa como chegar a um lugar desconhecido. Os gêneros de texto, ao contrário, não são classes gramaticais para classificar textos: são entidades da vida.
(ROJO, R. H. R.; BARBOSA, J. P. Hipermodernidade,
multiletramentos e gêneros discursivos.
São Paulo: Parábola Editorial, 2015. Adaptado)
Quanto às distinções entre tipos de texto e gêneros de texto/discurso, a mais famosa a esse respeito é a de Marcuschi (2002), que os define como
I. Usamos a expressão tipo textual para designar uma espécie de construção teórica definida pela natureza linguística de sua composição {aspectos lexicais, sintáticos, tempos verbais, relações lógicas}. Em geral, os tipos textuais abrangem cerca de meia dúzia de categorias conhecidas: descrição, narração, dissertação/ argumentação, exposição e injunção.
II. Usamos a expressão gênero textual como uma noção propositalmente vaga para referir os textos materializados que encontramos em nossa vida diária e que apresentam características sócio-comunicativas definidas por conteúdos, propriedades funcionais, estilo e composição característica. Se os tipos textuais são apenas meia dúzia, os gêneros são inúmeros.
Tipos de textos vem sendo ensinados na escola há pelo menos uma centena de anos, o que faz deles gêneros escolares. Na escola, escrevemos narrações, na vida, lemos notícias, relatamos nossa vida, recontamos um filme. Na escola, redigimos “uma composição à vista de gravura” (descrição) fora dela, contamos como decoramos nosso apartamento, instruímos uma pessoa como chegar a um lugar desconhecido. Os gêneros de texto, ao contrário, não são classes gramaticais para classificar textos: são entidades da vida.
(ROJO, R. H. R.; BARBOSA, J. P. Hipermodernidade,
multiletramentos e gêneros discursivos.
São Paulo: Parábola Editorial, 2015. Adaptado)
Language-centered methods are those that seek to provide opportunities for learners to practice preselected linguistic structures through form-focused exercises in class. The assumption is that language practice will ultimately lead to a mastery of the target language and that learners can draw from this formal repertoire whenever they wish to communicate in the target language outside the class. According to this belief, language development is largely intentional rather than incidental; and language learning seen as a linear, additive process.
Learner-centered methods are those that are principally concerned with language use and learner needs. These methods seek to provide opportunities for learners to practice preselected, presequenced grammatical structures as well as communicative functions (i.e., speech acts such as apologizing, requesting, etc.) through meaning-focused activities. Proponents of learner-centered methods believe in accumulated entities, represented by structures plus notions and functions.
Learning-centered methods are those that are principally concerned with learning processes. These methods seek to provide opportunities for learners to participate in open-ended meaningful interaction through communicative activities or problem-solving tasks in class. The assumption is that a preoccupation with meaning-making will most likely lead to grammatical as well as communicative mastery of the language and that learners can learn through the process of communication. In this approach, unlike the other two, language development is a nonlinear process and considered more incidental than intentional. Proponents of learningcentered methods believe that language is best learned when the learner’s attention is focused on understanding, saying and doing something with language, and not when their attention is focused explicitly on linguistic features.
(Kumaravadivelu, B. Beyond Methods: Macrostrategies for language learning. Haven and London: Yale University Press. 2003. Adaptado)
Language-centered methods are those that seek to provide opportunities for learners to practice preselected linguistic structures through form-focused exercises in class. The assumption is that language practice will ultimately lead to a mastery of the target language and that learners can draw from this formal repertoire whenever they wish to communicate in the target language outside the class. According to this belief, language development is largely intentional rather than incidental; and language learning seen as a linear, additive process.
Learner-centered methods are those that are principally concerned with language use and learner needs. These methods seek to provide opportunities for learners to practice preselected, presequenced grammatical structures as well as communicative functions (i.e., speech acts such as apologizing, requesting, etc.) through meaning-focused activities. Proponents of learner-centered methods believe in accumulated entities, represented by structures plus notions and functions.
Learning-centered methods are those that are principally concerned with learning processes. These methods seek to provide opportunities for learners to participate in open-ended meaningful interaction through communicative activities or problem-solving tasks in class. The assumption is that a preoccupation with meaning-making will most likely lead to grammatical as well as communicative mastery of the language and that learners can learn through the process of communication. In this approach, unlike the other two, language development is a nonlinear process and considered more incidental than intentional. Proponents of learningcentered methods believe that language is best learned when the learner’s attention is focused on understanding, saying and doing something with language, and not when their attention is focused explicitly on linguistic features.
(Kumaravadivelu, B. Beyond Methods: Macrostrategies for language learning. Haven and London: Yale University Press. 2003. Adaptado)
Language-centered methods are those that seek to provide opportunities for learners to practice preselected linguistic structures through form-focused exercises in class. The assumption is that language practice will ultimately lead to a mastery of the target language and that learners can draw from this formal repertoire whenever they wish to communicate in the target language outside the class. According to this belief, language development is largely intentional rather than incidental; and language learning seen as a linear, additive process.
Learner-centered methods are those that are principally concerned with language use and learner needs. These methods seek to provide opportunities for learners to practice preselected, presequenced grammatical structures as well as communicative functions (i.e., speech acts such as apologizing, requesting, etc.) through meaning-focused activities. Proponents of learner-centered methods believe in accumulated entities, represented by structures plus notions and functions.
Learning-centered methods are those that are principally concerned with learning processes. These methods seek to provide opportunities for learners to participate in open-ended meaningful interaction through communicative activities or problem-solving tasks in class. The assumption is that a preoccupation with meaning-making will most likely lead to grammatical as well as communicative mastery of the language and that learners can learn through the process of communication. In this approach, unlike the other two, language development is a nonlinear process and considered more incidental than intentional. Proponents of learningcentered methods believe that language is best learned when the learner’s attention is focused on understanding, saying and doing something with language, and not when their attention is focused explicitly on linguistic features.
(Kumaravadivelu, B. Beyond Methods: Macrostrategies for language learning. Haven and London: Yale University Press. 2003. Adaptado)
Language-centered methods are those that seek to provide opportunities for learners to practice preselected linguistic structures through form-focused exercises in class. The assumption is that language practice will ultimately lead to a mastery of the target language and that learners can draw from this formal repertoire whenever they wish to communicate in the target language outside the class. According to this belief, language development is largely intentional rather than incidental; and language learning seen as a linear, additive process.
Learner-centered methods are those that are principally concerned with language use and learner needs. These methods seek to provide opportunities for learners to practice preselected, presequenced grammatical structures as well as communicative functions (i.e., speech acts such as apologizing, requesting, etc.) through meaning-focused activities. Proponents of learner-centered methods believe in accumulated entities, represented by structures plus notions and functions.
Learning-centered methods are those that are principally concerned with learning processes. These methods seek to provide opportunities for learners to participate in open-ended meaningful interaction through communicative activities or problem-solving tasks in class. The assumption is that a preoccupation with meaning-making will most likely lead to grammatical as well as communicative mastery of the language and that learners can learn through the process of communication. In this approach, unlike the other two, language development is a nonlinear process and considered more incidental than intentional. Proponents of learningcentered methods believe that language is best learned when the learner’s attention is focused on understanding, saying and doing something with language, and not when their attention is focused explicitly on linguistic features.
(Kumaravadivelu, B. Beyond Methods: Macrostrategies for language learning. Haven and London: Yale University Press. 2003. Adaptado)
Implications of the humanistic approach
Hamachek (1977) provides some useful examples of the kind of educational implications that follow from taking a humanistic approach. First, every learning experience should be seen within the context of helping learners to develop a sense of personal identity. This is in keeping with the view that one important task for the teacher is differentiation, i.e. identifying and seeking to meet the individual learner’s needs within the context of the classroom group. Second, learners should be encouraged to make choices for themselves in what and how they learn. This again is in sharp contrast to the view that the curriculum content for every learner of a similar age should be set in ‘tablets of stone’. Third, it is important for teachers to empathise with their learners by seeking to understand the ways in which they make sense of the world, rather than always seeking to impose their own viewpoints. Fourth, it is important to provide optimum conditions for individualised and group learning of an authentic nature to take place.Thus, from a humanistic perspective, a learning experience of personal consequence occurs when the learner assumes the responsibility of evaluating the degree to which he or she is personally moving toward knowledge rather than looking to an external source for such evaluation.
(Williams, M.; Burden, R.L. Psychology for Language Teachers: A Social Constructivist Approach. Cambridge:CUP, 1999. Adaptado)
The expression ‘rather than’, in the concluding sentence of the text, means
Implications of the humanistic approach
Hamachek (1977) provides some useful examples of the kind of educational implications that follow from taking a humanistic approach. First, every learning experience should be seen within the context of helping learners to develop a sense of personal identity. This is in keeping with the view that one important task for the teacher is differentiation, i.e. identifying and seeking to meet the individual learner’s needs within the context of the classroom group. Second, learners should be encouraged to make choices for themselves in what and how they learn. This again is in sharp contrast to the view that the curriculum content for every learner of a similar age should be set in ‘tablets of stone’. Third, it is important for teachers to empathise with their learners by seeking to understand the ways in which they make sense of the world, rather than always seeking to impose their own viewpoints. Fourth, it is important to provide optimum conditions for individualised and group learning of an authentic nature to take place.Thus, from a humanistic perspective, a learning experience of personal consequence occurs when the learner assumes the responsibility of evaluating the degree to which he or she is personally moving toward knowledge rather than looking to an external source for such evaluation.
(Williams, M.; Burden, R.L. Psychology for Language Teachers: A Social Constructivist Approach. Cambridge:CUP, 1999. Adaptado)
Implications of the humanistic approach
Hamachek (1977) provides some useful examples of the kind of educational implications that follow from taking a humanistic approach. First, every learning experience should be seen within the context of helping learners to develop a sense of personal identity. This is in keeping with the view that one important task for the teacher is differentiation, i.e. identifying and seeking to meet the individual learner’s needs within the context of the classroom group. Second, learners should be encouraged to make choices for themselves in what and how they learn. This again is in sharp contrast to the view that the curriculum content for every learner of a similar age should be set in ‘tablets of stone’. Third, it is important for teachers to empathise with their learners by seeking to understand the ways in which they make sense of the world, rather than always seeking to impose their own viewpoints. Fourth, it is important to provide optimum conditions for individualised and group learning of an authentic nature to take place.Thus, from a humanistic perspective, a learning experience of personal consequence occurs when the learner assumes the responsibility of evaluating the degree to which he or she is personally moving toward knowledge rather than looking to an external source for such evaluation.
(Williams, M.; Burden, R.L. Psychology for Language Teachers: A Social Constructivist Approach. Cambridge:CUP, 1999. Adaptado)
Implications of the humanistic approach
Hamachek (1977) provides some useful examples of the kind of educational implications that follow from taking a humanistic approach. First, every learning experience should be seen within the context of helping learners to develop a sense of personal identity. This is in keeping with the view that one important task for the teacher is differentiation, i.e. identifying and seeking to meet the individual learner’s needs within the context of the classroom group. Second, learners should be encouraged to make choices for themselves in what and how they learn. This again is in sharp contrast to the view that the curriculum content for every learner of a similar age should be set in ‘tablets of stone’. Third, it is important for teachers to empathise with their learners by seeking to understand the ways in which they make sense of the world, rather than always seeking to impose their own viewpoints. Fourth, it is important to provide optimum conditions for individualised and group learning of an authentic nature to take place.Thus, from a humanistic perspective, a learning experience of personal consequence occurs when the learner assumes the responsibility of evaluating the degree to which he or she is personally moving toward knowledge rather than looking to an external source for such evaluation.
(Williams, M.; Burden, R.L. Psychology for Language Teachers: A Social Constructivist Approach. Cambridge:CUP, 1999. Adaptado)
Implications of the humanistic approach
Hamachek (1977) provides some useful examples of the kind of educational implications that follow from taking a humanistic approach. First, every learning experience should be seen within the context of helping learners to develop a sense of personal identity. This is in keeping with the view that one important task for the teacher is differentiation, i.e. identifying and seeking to meet the individual learner’s needs within the context of the classroom group. Second, learners should be encouraged to make choices for themselves in what and how they learn. This again is in sharp contrast to the view that the curriculum content for every learner of a similar age should be set in ‘tablets of stone’. Third, it is important for teachers to empathise with their learners by seeking to understand the ways in which they make sense of the world, rather than always seeking to impose their own viewpoints. Fourth, it is important to provide optimum conditions for individualised and group learning of an authentic nature to take place.Thus, from a humanistic perspective, a learning experience of personal consequence occurs when the learner assumes the responsibility of evaluating the degree to which he or she is personally moving toward knowledge rather than looking to an external source for such evaluation.
(Williams, M.; Burden, R.L. Psychology for Language Teachers: A Social Constructivist Approach. Cambridge:CUP, 1999. Adaptado)
If styles are general characteristics that differentiate one individual from another, then strategies are those specific “attacks” that we make on a given problem, and that vary considerably within each individual. They are the momentby-moment techniques that we employ to solve “problems” posed by second language input and output. Chamot (2005, p. 112) defines strategies quite broadly as “procedures that facilitate a learning task.”
Second language acquisition has distinguished between two types of strategy: learning strategies and communication strategies. The former relate to input — to processing, storage, and retrieval, that is, to taking in messages from others. The latter pertain to output, how we productively express meaning, how we deliver messages to others.
(Brown, H.D. Principles of Language Learning and Teaching. 5th ed. White Plains, NY: Addison Wesley Longman, 2006. Adaptado)
If styles are general characteristics that differentiate one individual from another, then strategies are those specific “attacks” that we make on a given problem, and that vary considerably within each individual. They are the momentby-moment techniques that we employ to solve “problems” posed by second language input and output. Chamot (2005, p. 112) defines strategies quite broadly as “procedures that facilitate a learning task.”
Second language acquisition has distinguished between two types of strategy: learning strategies and communication strategies. The former relate to input — to processing, storage, and retrieval, that is, to taking in messages from others. The latter pertain to output, how we productively express meaning, how we deliver messages to others.
(Brown, H.D. Principles of Language Learning and Teaching. 5th ed. White Plains, NY: Addison Wesley Longman, 2006. Adaptado)
O termo validade, para referir-se à avaliação de aprendizagem, pode ser definido como o grau pelo qual as notas de um teste nos permitem tirar conclusões em relação ao objetivo do mesmo. Há diversos tipos de validade, dentro os quais destacamos:
validade de construto – é uma espécie de validade conceitual. Uma avaliação tem validade de construto se pudermos demonstrar que ela mede, exatamente, o construto que deve medir (Hughes, 1989:26). No caso de inglês, poderíamos pensar em habilidades, por exemplo. Dessa forma, uma prova teria validade de construto se medisse a habilidade que deseja medir.
validade de conteúdo – têm as provas cujo conteúdo
apresenta uma quantidade representativa daquilo que tenha
sido estudado anteriormente.
FIDALGO, S.S. Livros Didáticos e Avaliação de Aprendizagem: Uma Revisão teórico-Prática. IN: Maria Cristina Damianovic (org). Material Didático: Elaboração e Avaliação. Taubaté: Cabral -Editora e Livraria Universitária. 2007. p. 287-318. Adaptado)