Questões Militares
Foram encontradas 457 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
How much should your boss know about you?
By José Luis Penarredonda, 26 March 2018
We’re all being graded every day. The expensive plane tickets I bought recently have already popped up in my credit score. The fact that I've stopped jogging every morning has been noted by my fitness app - and, if it were connected with an insurance company, this change might push up my premiums. [...]. And, yes, my desirability and efficiency as a worker is also up for evaluation and can be given a number.
HR departments are crunching increasing volumes of data to measure employees in a more granular way. From software that records every keystroke, or the ‘smart’ coffee machines that will only give you a hot drink if you tap it with your work ID badge there are more opportunities than ever for bosses to measure behaviour. Some analysts think this industry could be worth more than $1 billion by 2022.
One big aim of data collection is to make “predictions about how long an'employee will stay, and it may influence hiring, firing, or retention of people" [...].
One problem with this approach is that it’s blind to some of the non-quantifiable aspects of work. Some of the subtler things I do in order to be a better writer, for instance, are not quantifiable: having a drink with someone who tells me a great story, or imagining a piece on my commute. None of these things would show up in my ‘job score'. “A lot of the qualitative aspects of work are being written out,” says Moore, “because if you can’t measure them, they don't exist”.
The dilemma of data
There are several good business reasons to collect data on employees - from doing better risk management to examining if social behaviours in the workplace can lead to gender discrimination. “Companies fundamentally don't understand how people interact and collaborate at work,” says Ben Waber, president and CEO of Humanyze, an American company which gathers and analyses data about the workplace. He says that he can show them.
Humanyze gathers data from two sources. The first is the metadata from employees’ communications: their email, phone or corporate messaging service [...]. The second area is data gathered from gadgets like Bluetooth infrared sensors which detect how many people are working in one particular part of an office and how they move around. They also use 'supercharged' ID badges that, as Waber says, are beefed up with "microphones which don't record what you say, but do voice-processing in real time.” This allows measurement of the proportion of time you speak, or how often people interrupt you.
After six weeks of research, the employer gets a 'big picture’ of the problem it wants to solve, based on the analysed data. If the aim, for instance, is to boost sales, they can analyse what their best salespeople do that others don’t.
Waber sees it as “a lens of very large work issues, like diversity, inclusion, workload assessment, workspace planning, or regulatory risk”. His business case is that these tools will help companies save millions of dollars and even years of time [...].
(Abridged from http://www.bbc.com)
Which option completes the text below correctly?
A Beijing company has unveiled spectacularly futuristic designs for a pollution-busting, elevated bus
[...] Song Youzhou, the project’s chief engineer, claimed the busses could be produced for 20% of the price of an underground train and rolled out far more quickly since the______infrastructure was relatively simple.
The project has been greeted with ______ in China, where traffic jams have grown as the country ______the United States to become the largest car market on earth in 2009.
However,______over the______ was tempered by the fact that a virtually identical contraption was unveiled at the same expo in 2010 without catching on. Its ______? A Chinese engineer by the name of Song Youzhou.
(Adapted from https://www.ltheguardian.com)
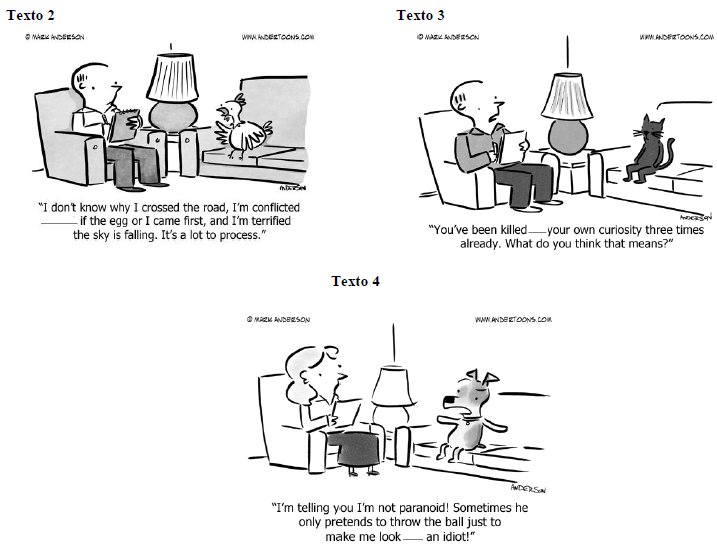
Considerando o contexto e gramática da língua inglesa, assinale a alternativa cuja palavras completam CORRETAMENTE as lacunas dos cartuns (textos 2, 3 e 4).

Mark the option that replaces the underlined words, respectively, keeping the same meaning.
“[...] many people often confuse child slavery with child labour [...]” (lines 48 and 49)
