Questões Militares
Para nc-ufpr
Foram encontradas 431 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
A figura abaixo ilustra um corrimão instalado numa rampa de acesso.
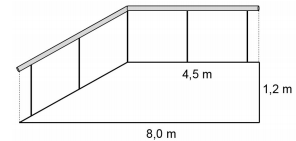
Com base nessa figura, o comprimento do corrimão é
de:
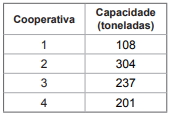
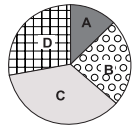
De acordo com o gráfico de setores, à direita da tabela, as regiões A, B, C e D correspondem respectivamente às seguintes cooperativas:
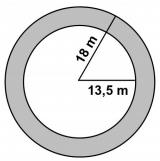
Use π = 22/7.
Comprimento (cm) 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9
Quantidade 1 3 4 4 3 4 n 1
Sabendo que a média de comprimento dos insetos do grupo foi de 0,6 cm, qual é a quantidade de formigas cujo comprimento é de 0,8 cm?
Considere o seguinte trecho:
Vivos ou mortos, ____________, pois, ser estímulo para os sonhos alheios, sem que ____________ responsáveis pelo que então ____________, ____________ ou ____________. Não somos responsáveis por nossas imagens, mesmo porque não somos idênticos a elas.
(COSTA LIMA, Luiz. O controle do imaginário. Rio de Janeiro: Forense Universitária, 1989. p. 61.)
Assinale a alternativa que preenche corretamente as
lacunas acima, na ordem em que aparecem no texto.
O texto a seguir é referência para a questão.
‘Speed watching’: o que você perde quando acelera a velocidade do filme?
Com a pandemia de coronavírus, uma legião de confinados passou a sentir o tempo de forma diferente. Um exemplo disso é o crescente hábito de consumir produções audiovisuais em velocidade acelerada. Cada vez mais plataformas de streaming têm oferecido ferramentas de speed watching, que permitem alterar o ritmo do que se assiste ou se escuta. Na Netflix, é possível ver um filme ou série com até o dobro da velocidade original. As possibilidades são as mesmas no Youtube e no Spotify. Isso estende a funcionalidade para podcasts, palestras e até aulas online.
Especialistas entendem que essa tendência é uma resposta ao atual momento: mais do que nunca, a tecnologia é a principal interface das pessoas com o mundo ao redor. Isso interfere no ritmo com o qual se vive e se consomem conteúdos. O psiquiatra Adriano Aguiar lembra que, durante muito tempo, a rotina das pessoas era ditada pela natureza. Depois, com a chegada da televisão, os programas passaram a interferir no dia a dia das famílias. “Algumas iam dormir só depois da novela ou do programa do Jô Soares”, exemplifica o médico. Hoje, em meio à explosão do mercado de streaming, que dá a possibilidade de se assistir ao que se quer e quando se quer, esses limites se dissolveram. “Estamos jogados no ilimitado da informação e submetidos ao funcionamento de algoritmos que deliberadamente trabalham para gerar uma adição”, defende Aguiar.
É diante desse fluxo frenético que as pessoas se veem impelidas a consumir em pouco tempo a maior quantidade de conteúdo possível. Isso pode levar à chamada síndrome de FOMO, sigla do inglês “fear of missing out”: aquele medo desesperado de perder alguma coisa frente a uma avalanche de dados. O “speed watching” se insere nesse contexto.
Assistir a um filme em velocidade acelerada ajuda a ganhar tempo. Por outro lado, um hábito que serviria para descansar a mente acaba alimentando a ansiedade, conforme explica a psiquiatra e professora da Universidade Positivo, Raquel Heep. O cérebro do ansioso pode operar em um sistema de recompensa: consumindo mais em menos tempo e sentindo os ganhos disso, terá dificuldade em desfrutar de uma obra no ritmo original. Para Heep, há uma confusão entre absorver fatos e ter um momento de contemplação. O cineasta Alexandre Rafael Garcia concorda. Ele argumenta que receber informações é diferente de assimilá-las mediante a reflexão que um filme ou série promovem sob um ritmo determinado. “Eu sei que o homem de ferro morre, mas ver o homem de ferro morrendo é outra coisa. E a nossa sociedade está muito centrada no volume do que se consegue absorver”, diz Garcia, que é também professor de cinema da Universidade Estadual do Paraná (Unespar).
Embora acelerar um filme atrapalhe a experiência de assistir a um grande clássico, cineastas e neurocientistas concordam que o cérebro humano pode estar ficando mais rápido e, com isso, os filmes também. O premiado diretor de cinema Fernando Meirelles está entre os que enxergam esse movimento. Para ele, o fato de nossa cabeça estar ficando mais veloz impacta a recepção das produções cinematográficas agora. “A quantidade do que processamos hoje é muitas vezes maior do que o que recebíamos há 40 anos”, diz.
O neurocientista Marcelo de Meira Santos Lima, da Universidade Federal do Paraná, explica que, embora não haja estudos comprovando a influência do “speed watching” no cérebro, esse órgão pode, sim, sofrer impactos de longo prazo, a começar pelas sinapses. Coletivamente, a formação de novas redes neurais poderia originar cérebros mais eficientes e rápidos, embora com uma demanda de energia atípica e capaz de impulsionar quadros de ansiedade, insônia, distúrbios de atenção e depressão.
Enquanto a ciência não decifra esse mistério, muitos seguirão acelerando conteúdos. Ao menos de vez em quando, como faz o próprio Fernando Meirelles. Ele confessa que em alguns casos, quando um filme lhe parece previsível ou desinteressante, opta por escaneá-lo, na expectativa de que alguma cena para frente o prenda. “Acelerar para mim é o estágio que vem antes de abandonar”.
(Lívia Inácio, 14/03/2021. Disponível em: https://www.bbc.com/portuguese/geral-56368238.)
Com relação à estrutura textual, considere as seguintes afirmativas:
1. A autora opta pela problematização do tema já no primeiro parágrafo.
2. A pergunta que faz parte do título é respondida ao longo do texto.
3. Meirelles é a favor da aceleração dos filmes clássicos para que eles possam ser absorvidos pelo cérebro humano.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
O texto a seguir é referência para a questão.
‘Speed watching’: o que você perde quando acelera a velocidade do filme?
Com a pandemia de coronavírus, uma legião de confinados passou a sentir o tempo de forma diferente. Um exemplo disso é o crescente hábito de consumir produções audiovisuais em velocidade acelerada. Cada vez mais plataformas de streaming têm oferecido ferramentas de speed watching, que permitem alterar o ritmo do que se assiste ou se escuta. Na Netflix, é possível ver um filme ou série com até o dobro da velocidade original. As possibilidades são as mesmas no Youtube e no Spotify. Isso estende a funcionalidade para podcasts, palestras e até aulas online.
Especialistas entendem que essa tendência é uma resposta ao atual momento: mais do que nunca, a tecnologia é a principal interface das pessoas com o mundo ao redor. Isso interfere no ritmo com o qual se vive e se consomem conteúdos. O psiquiatra Adriano Aguiar lembra que, durante muito tempo, a rotina das pessoas era ditada pela natureza. Depois, com a chegada da televisão, os programas passaram a interferir no dia a dia das famílias. “Algumas iam dormir só depois da novela ou do programa do Jô Soares”, exemplifica o médico. Hoje, em meio à explosão do mercado de streaming, que dá a possibilidade de se assistir ao que se quer e quando se quer, esses limites se dissolveram. “Estamos jogados no ilimitado da informação e submetidos ao funcionamento de algoritmos que deliberadamente trabalham para gerar uma adição”, defende Aguiar.
É diante desse fluxo frenético que as pessoas se veem impelidas a consumir em pouco tempo a maior quantidade de conteúdo possível. Isso pode levar à chamada síndrome de FOMO, sigla do inglês “fear of missing out”: aquele medo desesperado de perder alguma coisa frente a uma avalanche de dados. O “speed watching” se insere nesse contexto.
Assistir a um filme em velocidade acelerada ajuda a ganhar tempo. Por outro lado, um hábito que serviria para descansar a mente acaba alimentando a ansiedade, conforme explica a psiquiatra e professora da Universidade Positivo, Raquel Heep. O cérebro do ansioso pode operar em um sistema de recompensa: consumindo mais em menos tempo e sentindo os ganhos disso, terá dificuldade em desfrutar de uma obra no ritmo original. Para Heep, há uma confusão entre absorver fatos e ter um momento de contemplação. O cineasta Alexandre Rafael Garcia concorda. Ele argumenta que receber informações é diferente de assimilá-las mediante a reflexão que um filme ou série promovem sob um ritmo determinado. “Eu sei que o homem de ferro morre, mas ver o homem de ferro morrendo é outra coisa. E a nossa sociedade está muito centrada no volume do que se consegue absorver”, diz Garcia, que é também professor de cinema da Universidade Estadual do Paraná (Unespar).
Embora acelerar um filme atrapalhe a experiência de assistir a um grande clássico, cineastas e neurocientistas concordam que o cérebro humano pode estar ficando mais rápido e, com isso, os filmes também. O premiado diretor de cinema Fernando Meirelles está entre os que enxergam esse movimento. Para ele, o fato de nossa cabeça estar ficando mais veloz impacta a recepção das produções cinematográficas agora. “A quantidade do que processamos hoje é muitas vezes maior do que o que recebíamos há 40 anos”, diz.
O neurocientista Marcelo de Meira Santos Lima, da Universidade Federal do Paraná, explica que, embora não haja estudos comprovando a influência do “speed watching” no cérebro, esse órgão pode, sim, sofrer impactos de longo prazo, a começar pelas sinapses. Coletivamente, a formação de novas redes neurais poderia originar cérebros mais eficientes e rápidos, embora com uma demanda de energia atípica e capaz de impulsionar quadros de ansiedade, insônia, distúrbios de atenção e depressão.
Enquanto a ciência não decifra esse mistério, muitos seguirão acelerando conteúdos. Ao menos de vez em quando, como faz o próprio Fernando Meirelles. Ele confessa que em alguns casos, quando um filme lhe parece previsível ou desinteressante, opta por escaneá-lo, na expectativa de que alguma cena para frente o prenda. “Acelerar para mim é o estágio que vem antes de abandonar”.
(Lívia Inácio, 14/03/2021. Disponível em: https://www.bbc.com/portuguese/geral-56368238.)
Com base no texto, considere as seguintes inferências:
1. O cineasta Fernando Meireles é uma das pessoas que se rendeu ao speed watching.
2. A chegada da televisão alterou a rotina das pessoas, mas ainda assim manteve uma certa disciplina no ritmo de vida das famílias.
3. O speed watching passou de opção a regra, perdendo sua função prática.
É(São) inferência(s) que pode(m) ser feita(s) a partir da
leitura do texto:
O texto a seguir é referência para a questão.
‘Speed watching’: o que você perde quando acelera a velocidade do filme?
Com a pandemia de coronavírus, uma legião de confinados passou a sentir o tempo de forma diferente. Um exemplo disso é o crescente hábito de consumir produções audiovisuais em velocidade acelerada. Cada vez mais plataformas de streaming têm oferecido ferramentas de speed watching, que permitem alterar o ritmo do que se assiste ou se escuta. Na Netflix, é possível ver um filme ou série com até o dobro da velocidade original. As possibilidades são as mesmas no Youtube e no Spotify. Isso estende a funcionalidade para podcasts, palestras e até aulas online.
Especialistas entendem que essa tendência é uma resposta ao atual momento: mais do que nunca, a tecnologia é a principal interface das pessoas com o mundo ao redor. Isso interfere no ritmo com o qual se vive e se consomem conteúdos. O psiquiatra Adriano Aguiar lembra que, durante muito tempo, a rotina das pessoas era ditada pela natureza. Depois, com a chegada da televisão, os programas passaram a interferir no dia a dia das famílias. “Algumas iam dormir só depois da novela ou do programa do Jô Soares”, exemplifica o médico. Hoje, em meio à explosão do mercado de streaming, que dá a possibilidade de se assistir ao que se quer e quando se quer, esses limites se dissolveram. “Estamos jogados no ilimitado da informação e submetidos ao funcionamento de algoritmos que deliberadamente trabalham para gerar uma adição”, defende Aguiar.
É diante desse fluxo frenético que as pessoas se veem impelidas a consumir em pouco tempo a maior quantidade de conteúdo possível. Isso pode levar à chamada síndrome de FOMO, sigla do inglês “fear of missing out”: aquele medo desesperado de perder alguma coisa frente a uma avalanche de dados. O “speed watching” se insere nesse contexto.
Assistir a um filme em velocidade acelerada ajuda a ganhar tempo. Por outro lado, um hábito que serviria para descansar a mente acaba alimentando a ansiedade, conforme explica a psiquiatra e professora da Universidade Positivo, Raquel Heep. O cérebro do ansioso pode operar em um sistema de recompensa: consumindo mais em menos tempo e sentindo os ganhos disso, terá dificuldade em desfrutar de uma obra no ritmo original. Para Heep, há uma confusão entre absorver fatos e ter um momento de contemplação. O cineasta Alexandre Rafael Garcia concorda. Ele argumenta que receber informações é diferente de assimilá-las mediante a reflexão que um filme ou série promovem sob um ritmo determinado. “Eu sei que o homem de ferro morre, mas ver o homem de ferro morrendo é outra coisa. E a nossa sociedade está muito centrada no volume do que se consegue absorver”, diz Garcia, que é também professor de cinema da Universidade Estadual do Paraná (Unespar).
Embora acelerar um filme atrapalhe a experiência de assistir a um grande clássico, cineastas e neurocientistas concordam que o cérebro humano pode estar ficando mais rápido e, com isso, os filmes também. O premiado diretor de cinema Fernando Meirelles está entre os que enxergam esse movimento. Para ele, o fato de nossa cabeça estar ficando mais veloz impacta a recepção das produções cinematográficas agora. “A quantidade do que processamos hoje é muitas vezes maior do que o que recebíamos há 40 anos”, diz.
O neurocientista Marcelo de Meira Santos Lima, da Universidade Federal do Paraná, explica que, embora não haja estudos comprovando a influência do “speed watching” no cérebro, esse órgão pode, sim, sofrer impactos de longo prazo, a começar pelas sinapses. Coletivamente, a formação de novas redes neurais poderia originar cérebros mais eficientes e rápidos, embora com uma demanda de energia atípica e capaz de impulsionar quadros de ansiedade, insônia, distúrbios de atenção e depressão.
Enquanto a ciência não decifra esse mistério, muitos seguirão acelerando conteúdos. Ao menos de vez em quando, como faz o próprio Fernando Meirelles. Ele confessa que em alguns casos, quando um filme lhe parece previsível ou desinteressante, opta por escaneá-lo, na expectativa de que alguma cena para frente o prenda. “Acelerar para mim é o estágio que vem antes de abandonar”.
(Lívia Inácio, 14/03/2021. Disponível em: https://www.bbc.com/portuguese/geral-56368238.)
De acordo com o texto, considere as seguintes afirmativas:
1. A possibilidade de se alterar a velocidade com que se assiste a vídeos e áudios surgiu com a disponibilização de acesso à informação decorrente da pandemia.
2. O crescimento na tendência de consumir produtos audiovisuais foi ocasionado pela redução nas interações físicas, que levou as pessoas a se ajustarem ao ritmo da internet.
3. A ferramenta speed watching tem criado um descompasso entre a velocidade com que recebemos informações e nossa capacidade de processá-las.
4. A síndrome de FOMO é causada pelos algoritmos da internet que atuam sobre o comportamento dos usuários.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
Leia a seguinte tirinha do menino Calvin e seu tigre Haroldo:

(WATTERSON, Bill. Calvin e Haroldo: E foi assim que tudo começou. São Paulo: Conrad, 2007. p. 95.)
Com base na tira, considere as seguintes afirmativas:
1. As ações descritas pelo menino fazem parte de seu plano com relação à possível vinda de um irmão ou irmã.
2. A resposta de Calvin à pergunta de Haroldo indica que ele já pode abandonar o plano que vinha executando.
3. O menino adora sábados por se tratar de dia estratégico para dar mais visibilidade aos seus esforços.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
Considere o seguinte excerto:
_____ narrativa da testemunha, no entanto, pareceu-nos faltar _____ observação de que _____ ela não cabia julgar os fatos, mas deles dar conhecimento tais quais aconteceram, cabendo _____ Comissão incumbida de interpretá-los – e _____ mais ninguém – deles fazer juízo.
Assinale a alternativa que preenche corretamente as
lacunas acima, na ordem em que aparecem no texto.
Como a depressão chegou ao posto de diagnóstico mais frequente para se descrever as formas de sofrimento mental em nossa época?
Assinale a alternativa que apresenta a resposta correta a essa pergunta.
O texto a seguir é referência para a questão.

(FISCHER, Ernst. A necessidade da arte. 8. ed. Rio de Janeiro: Zahar, 1981.
p. 51-2.)
O texto a seguir é referência para a questão.

(FISCHER, Ernst. A necessidade da arte. 8. ed. Rio de Janeiro: Zahar, 1981.
p. 51-2.)
O texto a seguir é referência para a questão.

(FISCHER, Ernst. A necessidade da arte. 8. ed. Rio de Janeiro: Zahar, 1981.
p. 51-2.)
Com relação ao emprego de pronomes, considere as seguintes afirmativas:
1. Em “risco de levá-lo” (linha 3), “lo” refere-se a “coletivo”.
2. Em “fazendo-o” (linha 18), “o” refere-se a “artista”.
3. Em “desvendando-lhe” (linha 21), “lhe” refere-se a “público”.
4. Em “cabia-lhe” (linha 22), “lhe” refere-se a “homem”.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
Há 12 mil anos, abóboras eram refeições exclusivas de grandes mamíferos, como os mamutes, mastodontes e preguiças gigantes – a megafauna do Paleolítico.
Numere os parênteses abaixo, identificando a ordem das ideias que vêm na sequência, para que o conjunto apresente lógica textual.
( ) Quando eles foram extintos, as plantas ficaram “órfãs”, sem ter ninguém para distribuir suas sementes, o que os grandes mamíferos faziam pelas fezes. ( ) Após a extinção da megafauna americana, várias espécies de cucurbitáceas – a família da abóbora – acabaram extintas por falta de disseminação. ( ) Eram plantas amargas demais para o ser humano, mas esses bichos não tinham dificuldade em tolerá-las, pela forma diferente como percebiam os sabores. ( ) Essa é a conclusão de um estudo da University Park, dos Estados Unidos, que testou plantas modernas versus suas ancestrais e versões selvagens atuais. ( ) As adotadas por humanos prosperaram. ( ) Os humanos então adotaram as plantas, provavelmente como cabeças e boias para redes de pesca, antes de elas desenvolverem o atual sabor aceitável, por seleção artificial.
Assinale a alternativa que apresenta a numeração correta dos parênteses, de cima para baixo.