Questões Militares
Comentadas para aspirante da polícia militar
Foram encontradas 622 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Sobre ela é correto afirmar, exceto:
Six things I learned from riding in a Google self-driving car
1 - Human beings are terrible drivers.
We drink. We doze. We text. In the US, 30,000 people die from automobile accidents every year. Traffic crashes are the primary cause of death worldwide for people aged 15-24, and during a crash, 40% of drivers never even hit the brakes. We’re flawed organisms, barreling around at high speeds in vessels covered in glass, metal, distraction, and death. This is one of Google’s “moonshots” – to remove human error from a job which, for the past hundred years, has been entirely human.
2 - Google self-driving cars are timid.
The car we rode in did not strike me as dangerous. It drove slowly and deliberately, and I got the impression that it’s more likely to annoy other drivers than to harm them. In the early versions they tested on closed courses, the vehicles were programmed to be highly aggressive. Apparently during these tests, which involved obstacle courses full of traffic cones and inflatable crash-test objects, there were a lot of screeching brakes, roaring engines and terrified interns.
3 - They’re cute.
Google’s new fleet was intentionally designed to look adorable. Our brains are hardwired to treat inanimate (or animate) objects with greater care, caution, and reverence when they resemble a living thing. By turning self-driving cars into an adorable Skynet Marshmallow Bumper Bots, Google hopes to spiritually disarm other drivers. I also suspect the cuteness is used to quell some of the road rage that might emerge from being stuck behind one of these things. They’re intended as moderate-distance couriers, not openroad warriors, so their max speed is 25 miles per hour.
4 - It’s not done and it’s not perfect.
Some of the scenarios autonomous vehicles have the most trouble with are the same human beings have the most trouble with, such as traversing four-way stops or handling a yellow light. The cars use a mixture of 3D laser-mapping, GPS, and radar to analyze and interpret their surroundings, and the latest versions are fully electric with a range of about 100 miles. Despite the advantages over a human being in certain scenarios, however, these cars still aren’t ready for the real world. They can’t drive in the snow or heavy rain, and there’s a variety of complex situations they do not process well, such as passing through a construction zone. Google is hoping that, eventually, the cars will be able to handle all of this as well (or better) than a human could.
5 - I want this technology to succeed, like… yesterday.
I’m biased. Earlier this year my mom had a stroke. It damaged the visual cortex of her brain, and her vision was impaired to the point that she’ll probably never drive again. This reduced her from a fully-functional, independent human being with a career and a buzzing social life into someone who is homebound, disabled, and powerless. When discussing self-driving cars, people tend to ask many superficial questions. They ignore that 45% of disabled people in the US still work. They ignore that 95% of a car’s lifetime is spent parked. They ignore how this technology could transform the lives of the elderly, or eradicate the need for parking lots or garages or gas stations. They dismiss the entire concept because they don’t think a computer could ever be as good at merging on the freeway as they are. They ignore the great, big, beautiful picture: that this technology could make our lives so much better.
6 - It wasn’t an exhilarating ride, and that’s a good thing.
Riding in a self-driving car is not the cybernetic thrill ride one might expect. The car drives like a person, and after a few minutes you forget that you’re being driven autonomously. You forget that a robot is differentiating cars from pedestrians from mopeds from raccoons. You forget that millions of photons are being fired from a laser and interpreting, processing, and reacting to the hand signals of a cyclist. You forget that instead of an organic brain, which has had millions of years to evolve the cognitive ability to fumble its way through a four-way stop, you’re being piloted by an artificial one, which was birthed in less than a decade. The unfortunate part of something this transformative is the inevitable, ardent stupidity which is going to erupt from the general public. Even if in a few years self-driving cars are proven to be ten times safer than human-operated cars, all it’s going to take is one tragic accident and the public is going to lose their minds. There will be outrage. There will be politicizing. There will be hashtags. I say look at the bigger picture. All the self-driving cars currently on the road learn from one another, and possess 40 years of driving experience. And this technology is still in its infancy.
(Adapted from:: <http://theoatmeal.com/blog/google_self_driving_car>
Six things I learned from riding in a Google self-driving car
1 - Human beings are terrible drivers.
We drink. We doze. We text. In the US, 30,000 people die from automobile accidents every year. Traffic crashes are the primary cause of death worldwide for people aged 15-24, and during a crash, 40% of drivers never even hit the brakes. We’re flawed organisms, barreling around at high speeds in vessels covered in glass, metal, distraction, and death. This is one of Google’s “moonshots” – to remove human error from a job which, for the past hundred years, has been entirely human.
2 - Google self-driving cars are timid.
The car we rode in did not strike me as dangerous. It drove slowly and deliberately, and I got the impression that it’s more likely to annoy other drivers than to harm them. In the early versions they tested on closed courses, the vehicles were programmed to be highly aggressive. Apparently during these tests, which involved obstacle courses full of traffic cones and inflatable crash-test objects, there were a lot of screeching brakes, roaring engines and terrified interns.
3 - They’re cute.
Google’s new fleet was intentionally designed to look adorable. Our brains are hardwired to treat inanimate (or animate) objects with greater care, caution, and reverence when they resemble a living thing. By turning self-driving cars into an adorable Skynet Marshmallow Bumper Bots, Google hopes to spiritually disarm other drivers. I also suspect the cuteness is used to quell some of the road rage that might emerge from being stuck behind one of these things. They’re intended as moderate-distance couriers, not openroad warriors, so their max speed is 25 miles per hour.
4 - It’s not done and it’s not perfect.
Some of the scenarios autonomous vehicles have the most trouble with are the same human beings have the most trouble with, such as traversing four-way stops or handling a yellow light. The cars use a mixture of 3D laser-mapping, GPS, and radar to analyze and interpret their surroundings, and the latest versions are fully electric with a range of about 100 miles. Despite the advantages over a human being in certain scenarios, however, these cars still aren’t ready for the real world. They can’t drive in the snow or heavy rain, and there’s a variety of complex situations they do not process well, such as passing through a construction zone. Google is hoping that, eventually, the cars will be able to handle all of this as well (or better) than a human could.
5 - I want this technology to succeed, like… yesterday.
I’m biased. Earlier this year my mom had a stroke. It damaged the visual cortex of her brain, and her vision was impaired to the point that she’ll probably never drive again. This reduced her from a fully-functional, independent human being with a career and a buzzing social life into someone who is homebound, disabled, and powerless. When discussing self-driving cars, people tend to ask many superficial questions. They ignore that 45% of disabled people in the US still work. They ignore that 95% of a car’s lifetime is spent parked. They ignore how this technology could transform the lives of the elderly, or eradicate the need for parking lots or garages or gas stations. They dismiss the entire concept because they don’t think a computer could ever be as good at merging on the freeway as they are. They ignore the great, big, beautiful picture: that this technology could make our lives so much better.
6 - It wasn’t an exhilarating ride, and that’s a good thing.
Riding in a self-driving car is not the cybernetic thrill ride one might expect. The car drives like a person, and after a few minutes you forget that you’re being driven autonomously. You forget that a robot is differentiating cars from pedestrians from mopeds from raccoons. You forget that millions of photons are being fired from a laser and interpreting, processing, and reacting to the hand signals of a cyclist. You forget that instead of an organic brain, which has had millions of years to evolve the cognitive ability to fumble its way through a four-way stop, you’re being piloted by an artificial one, which was birthed in less than a decade. The unfortunate part of something this transformative is the inevitable, ardent stupidity which is going to erupt from the general public. Even if in a few years self-driving cars are proven to be ten times safer than human-operated cars, all it’s going to take is one tragic accident and the public is going to lose their minds. There will be outrage. There will be politicizing. There will be hashtags. I say look at the bigger picture. All the self-driving cars currently on the road learn from one another, and possess 40 years of driving experience. And this technology is still in its infancy.
(Adapted from:: <http://theoatmeal.com/blog/google_self_driving_car>
Six things I learned from riding in a Google self-driving car
1 - Human beings are terrible drivers.
We drink. We doze. We text. In the US, 30,000 people die from automobile accidents every year. Traffic crashes are the primary cause of death worldwide for people aged 15-24, and during a crash, 40% of drivers never even hit the brakes. We’re flawed organisms, barreling around at high speeds in vessels covered in glass, metal, distraction, and death. This is one of Google’s “moonshots” – to remove human error from a job which, for the past hundred years, has been entirely human.
2 - Google self-driving cars are timid.
The car we rode in did not strike me as dangerous. It drove slowly and deliberately, and I got the impression that it’s more likely to annoy other drivers than to harm them. In the early versions they tested on closed courses, the vehicles were programmed to be highly aggressive. Apparently during these tests, which involved obstacle courses full of traffic cones and inflatable crash-test objects, there were a lot of screeching brakes, roaring engines and terrified interns.
3 - They’re cute.
Google’s new fleet was intentionally designed to look adorable. Our brains are hardwired to treat inanimate (or animate) objects with greater care, caution, and reverence when they resemble a living thing. By turning self-driving cars into an adorable Skynet Marshmallow Bumper Bots, Google hopes to spiritually disarm other drivers. I also suspect the cuteness is used to quell some of the road rage that might emerge from being stuck behind one of these things. They’re intended as moderate-distance couriers, not openroad warriors, so their max speed is 25 miles per hour.
4 - It’s not done and it’s not perfect.
Some of the scenarios autonomous vehicles have the most trouble with are the same human beings have the most trouble with, such as traversing four-way stops or handling a yellow light. The cars use a mixture of 3D laser-mapping, GPS, and radar to analyze and interpret their surroundings, and the latest versions are fully electric with a range of about 100 miles. Despite the advantages over a human being in certain scenarios, however, these cars still aren’t ready for the real world. They can’t drive in the snow or heavy rain, and there’s a variety of complex situations they do not process well, such as passing through a construction zone. Google is hoping that, eventually, the cars will be able to handle all of this as well (or better) than a human could.
5 - I want this technology to succeed, like… yesterday.
I’m biased. Earlier this year my mom had a stroke. It damaged the visual cortex of her brain, and her vision was impaired to the point that she’ll probably never drive again. This reduced her from a fully-functional, independent human being with a career and a buzzing social life into someone who is homebound, disabled, and powerless. When discussing self-driving cars, people tend to ask many superficial questions. They ignore that 45% of disabled people in the US still work. They ignore that 95% of a car’s lifetime is spent parked. They ignore how this technology could transform the lives of the elderly, or eradicate the need for parking lots or garages or gas stations. They dismiss the entire concept because they don’t think a computer could ever be as good at merging on the freeway as they are. They ignore the great, big, beautiful picture: that this technology could make our lives so much better.
6 - It wasn’t an exhilarating ride, and that’s a good thing.
Riding in a self-driving car is not the cybernetic thrill ride one might expect. The car drives like a person, and after a few minutes you forget that you’re being driven autonomously. You forget that a robot is differentiating cars from pedestrians from mopeds from raccoons. You forget that millions of photons are being fired from a laser and interpreting, processing, and reacting to the hand signals of a cyclist. You forget that instead of an organic brain, which has had millions of years to evolve the cognitive ability to fumble its way through a four-way stop, you’re being piloted by an artificial one, which was birthed in less than a decade. The unfortunate part of something this transformative is the inevitable, ardent stupidity which is going to erupt from the general public. Even if in a few years self-driving cars are proven to be ten times safer than human-operated cars, all it’s going to take is one tragic accident and the public is going to lose their minds. There will be outrage. There will be politicizing. There will be hashtags. I say look at the bigger picture. All the self-driving cars currently on the road learn from one another, and possess 40 years of driving experience. And this technology is still in its infancy.
(Adapted from:: <http://theoatmeal.com/blog/google_self_driving_car>
1. Drinking before driving. 2. Sending a written message while driving. 3. Sleeping for a short period of time. 4. Hitting the brakes. 5. Speeding up.
According to the text, some human mistakes that happen before or during a car accident are:
A respeito da função representada no gráfico ao lado, considere as seguintes afirmativas:
1. A função é crescente no intervalo aberto (4,6).
2. A função tem um ponto de máximo em x=1.
3. Esse gráfico representa uma função injetora.
4. Esse gráfico representa uma função polinomial de terceiro grau.
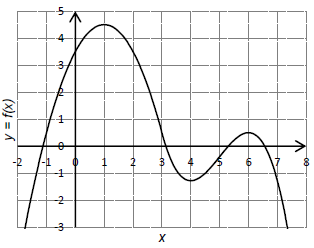
Assinale a alternativa correta.
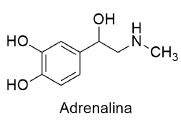
Dados – M (g mol-1 ): H = 1; C = 12; N = 14; O = 16.
Qual é o valor da massa molar (em g mol-1 ) desse composto?
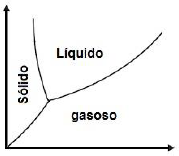
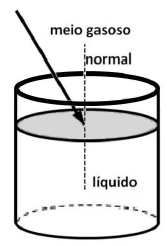
( ) Se a lente for colocada no meio gasoso, ela será denominada “convergente”.
( ) Quando a lente foi colocada no meio líquido, a sua distância focal passou a ser negativa.
( ) Em qualquer um dos meios, a distância focal da lente não se altera.
( ) O raio luminoso, ao penetrar no meio líquido, afasta-se da normal.
Assinale a alternativa que apresenta a sequência correta, de cima para baixo.
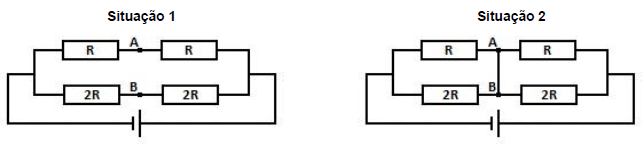
Com base nessas informações, identifique como verdadeiras (V) ou falsas (F) as seguintes afirmativas:
( ) A intensidade de corrente elétrica no gerador é a mesma para as duas situações representadas.
( ) Ao se conectar o fio condutor entre os pontos A e B, a resistência elétrica do circuito diminui.
( ) Na situação 2, a intensidade de corrente elétrica no gerador aumentará, em relação à situação 1.
( ) A diferença de potencial elétrico entre os pontos A e B, na situação 1, é maior que zero.
Assinale a alternativa que apresenta a sequência correta, de cima para baixo.
Esse tipo de interação entre formigas e plantas com nectários extraflorais pode ser categorizado como:
1. Em cnidários, tanto pólipos como medusas apresentam o mesmo sistema respiratório. 2. Larvas e adultos de equinodermos normalmente têm o mesmo tipo de simetria. 3. Girinos e sapos diferem em seus sistemas respiratórios. 4. Em algumas espécies de borboletas, imaturos podem ter uma dieta completamente diferente da dieta de adultos. 5. Larvas de crustáceos comumente mudam de um estado séssil para a vida livre durante a sua metamorfose.
Assinale a alternativa correta
(<Fonte: http://revistapesquisa.fapesp.br/2016/05/19/vacina-contra-esquistossomose>. Acessado em 08/08/2016.)
Texto 2: Pesquisadores da Universidade Estadual Paulista (UNESP) de Botucatu conseguiram autorização do Ministério da Saúde e da Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (Anvisa) para iniciar testes em humanos do soro antiapílico (antiveneno de abelhas). O soro, composto por uma imunoglobulina heteróloga, será o primeiro do mundo.
(Fonte:<http://oglobo.globo.com/sociedade/ciencia/soro-antiveneno-de-abelha-comeca-ser-testado-em-humanos-este-mes-19046264> . Acesso: 24/04/16.)
A proteína Sm14 e a imunoglobulina heteróloga atuam no organismo, respectivamente, como:
( ) Os peixes GloFish são chamados transgênicos porque possuem em seu genoma um segmento de DNA de medusa.
( ) O gene que codifica a GFP foi inserido nas células somáticas, mas não nas gaméticas dos peixes GloFish.
( ) As células fluorescentes dos GloFish produzem RNA mensageiro, que, por meio da tradução, origina a proteína GFP.
( ) Os peixes GloFish foram produzidos pela introdução de um núcleo extraído de uma célula de medusa em uma célula de peixe cujo núcleo tinha sido anteriormente removido.
Assinale a alternativa que apresenta a sequência correta, de cima para baixo.
(Disponível em:<http://noticias.uol.com.br/ultimas-noticias/agencia-brasil/2016/08/30/ibge-brasil-ja-tem-206-milhoes-de-habitantes.htm> . Acessado em 31.08.2016.)
Com base nas informações do texto e nos conhecimentos em geografia da população, assinale a alternativa correta.
Os processos industriais não imitam a natureza; a agroecologia, sim, o faz. Substitui os insumos externos, como o fertilizante, por saberes de como combinar plantas, árvores e animais, de tal forma que se reforce a produtividade da terra. […] a produtividade aumentou até 214% em 44 projetos em 20 países da África Subsaariana mediante técnicas de agroecologia em um período de 3-10 anos [...] muito mais do que qualquer cultivo geneticamente modificado alguma vez já tenha conseguido […]. Outras avaliações científicas recentes mostraram que os camponeses de 57 países que utilizam técnicas agroecológicas obtiveram aumento de até 80% na produtividade. O aumento médio dos africanos é de 116% […]. Hoje, a evidência científica demonstra que os métodos agroecológicos são muito melhores do que os fertilizantes químicos para aumentar a produção de alimentos em regiões onde vivem os famintos.
(Fontes: Stephen Leahy, Mudança climática e cultivos ecológicos, 20 dec. 2011. Disponível em<https://www.grain.org/article/entries/4439-mudanca-climatica-e-cultivos-ecologico> . Olivier de Schutter: “La agroecología y el derecho a la alimentación”, relatório apresentado no Conselho de Direitos Humanos, 8 de mar. 2011.)
Com base nas informações do texto e nos conhecimentos de geografia agrária, assinale a alternativa correta.