Questões Militares
Para pm-sp
Foram encontradas 5.471 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
 R, dadaporf(x) = ax2 – 16x + c, tem um valor máximo e admite duas raízes reais e iguais. Nessas condições, e sabendo-se que c = a, é correto afirmar que o par ordenado que representa o vértice dessa parábola é
R, dadaporf(x) = ax2 – 16x + c, tem um valor máximo e admite duas raízes reais e iguais. Nessas condições, e sabendo-se que c = a, é correto afirmar que o par ordenado que representa o vértice dessa parábola é 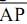 .
.
O perímetro da sub-região determinada pelo triângulo ABP é igual, em quilômetros, a
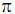 m2.
m2.
A área do canteiro de formato circular é igual, em metros quadrados, a
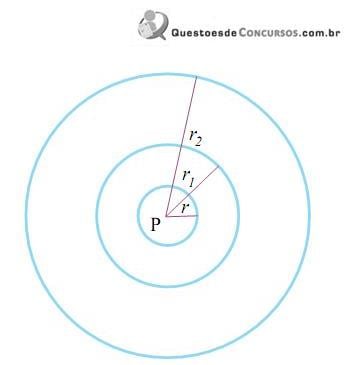
Sabe-se que as medidas dos raios r, r 1 e r 2 estão, nessa ordem, em progressão geométrica. Se r + r 1 + r 2 = 52 cm, e r . r 2 = 144 cm, então r + r 2 é igual, em centímetros, a
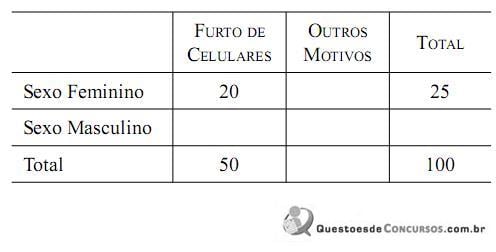
Tomando-se ao acaso uma das pessoas detidas por outros motivos, a probabilidade de que ela seja do sexo masculino é de
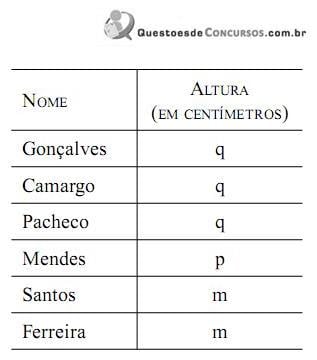
Sabendo-se que a moda, a mediana e a média aritmética das alturas desses alunos são, respectivamente, 173 cm, 174,5 cm e 175,5 cm, pode-se concluir que a altura do aluno Ferreira é igual, em centímetros, a
(O Estado de S. Paulo, 12.04.2014. Adaptado)
Considere os ônibus A e B, com tanques de combustíveis de capacidades iguais e inicialmente vazios, e admita que:
• No tanque do ônibus A sejam colocados 250 litros de diesel comum, e em seguida seja adicionada certa quantidade de biodiesel, na proporção indicada na notícia, enchendo-o completamente.
•O tanque do ônibus B seja totalmente preenchido somente com diesel comum.
Nessas condições, é correto afirmar que o custo do abastecimento do ônibus A terá, em relação ao do ônibus B, um acréscimo de
The Right to a “Custody Hearing” under International Law
by Maria Laura Canineu
February 3, 2014
A person who is arrested has a right to be brought promptly before a judge. This is a longstanding and fundamental principle of international law, crucial for ensuring that the person’s arrest, treatment, and any ongoing detention are lawful.
Yet, until now, Brazil has not respected this right. Detainees often go months before seeing a judge. For instance, in São Paulo state, which houses 37 percent of Brazil’s total prison population, most detainees are not brought before a judge for at least three months. The risk of ill-treatment is often highest during the initial stages of detention, when police are questioning a suspect. The delay makes detainees more vulnerable to torture and other serious forms of mistreatment by abusive police officers.
In 2012, the UN Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment reported that it had received “repeated and consistent accounts of torture and ill-treatment” in São Paulo and other Brazilian states, “committed by, in particular, the military and civil police.” The torture had allegedly occurred in police custody or at the moment of arrest, on the street, inside private homes, or in hidden outdoor areas, and was described as “gratuitous violence, as a form of punishment, to extract confessions, and as a means of extortion.”
In addition to violating the rights of detainees, these abusive practices make it more difficult for the police to establish the kind of public trust that is often crucial for effective crime control. These practices undermine legitimate efforts to promote public security and curb violent crime, and thus have a negative impact on Brazilian society as a whole.
The right to be brought before a judge without unnecessary delay is enshrined in treaties long ago ratified by Brazil, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the American Convention on Human Rights. The United Nations Human Rights Committee, which is responsible for interpreting the ICCPR, has determined that the delay between the arrest of an accused and the time before he is brought before a judicial authority “should not exceed a few days,” even during states of emergency.
Other countries in Latin America have incorporated this right into their domestic law. For instance, in Argentina, the federal Criminal Procedure Code requires that in cases of arrest without a judicial order, the detainee must be brought to a competent judicial authority within six hours.
In contrast, Brazil’s criminal procedure code requires that when an adult is arrested in flagrante and held in police custody, only the police files of the case need to be presented to the judge within 24 hours, not the actual detainee. Judges evaluate the legality of the arrest and make the decision about whether to order continued detention or other precautionary measures based solely on the written documents provided by the police.
The code establishes a maximum of 60 days for the first judicial hearing with the detainee, but does not explicitly say when this period begins. In practice, this often means that police in Brazil can keep people detained, with formal judicial authorization, for several months, without giving the detainee a chance to actually see a judge.
According to the code, the only circumstance in which police need to bring a person before the judge immediately applies to cases of crimes not subject to bail in which arresting officer was not able to exhibit the arrest order to the person arrested at the time of arrest. Otherwise, the detainee may also not see a judge for several months.
(www.hrw.org. Editado e adaptado)
The Right to a “Custody Hearing” under International Law
by Maria Laura Canineu
February 3, 2014
A person who is arrested has a right to be brought promptly before a judge. This is a longstanding and fundamental principle of international law, crucial for ensuring that the person’s arrest, treatment, and any ongoing detention are lawful.
Yet, until now, Brazil has not respected this right. Detainees often go months before seeing a judge. For instance, in São Paulo state, which houses 37 percent of Brazil’s total prison population, most detainees are not brought before a judge for at least three months. The risk of ill-treatment is often highest during the initial stages of detention, when police are questioning a suspect. The delay makes detainees more vulnerable to torture and other serious forms of mistreatment by abusive police officers.
In 2012, the UN Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment reported that it had received “repeated and consistent accounts of torture and ill-treatment” in São Paulo and other Brazilian states, “committed by, in particular, the military and civil police.” The torture had allegedly occurred in police custody or at the moment of arrest, on the street, inside private homes, or in hidden outdoor areas, and was described as “gratuitous violence, as a form of punishment, to extract confessions, and as a means of extortion.”
In addition to violating the rights of detainees, these abusive practices make it more difficult for the police to establish the kind of public trust that is often crucial for effective crime control. These practices undermine legitimate efforts to promote public security and curb violent crime, and thus have a negative impact on Brazilian society as a whole.
The right to be brought before a judge without unnecessary delay is enshrined in treaties long ago ratified by Brazil, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the American Convention on Human Rights. The United Nations Human Rights Committee, which is responsible for interpreting the ICCPR, has determined that the delay between the arrest of an accused and the time before he is brought before a judicial authority “should not exceed a few days,” even during states of emergency.
Other countries in Latin America have incorporated this right into their domestic law. For instance, in Argentina, the federal Criminal Procedure Code requires that in cases of arrest without a judicial order, the detainee must be brought to a competent judicial authority within six hours.
In contrast, Brazil’s criminal procedure code requires that when an adult is arrested in flagrante and held in police custody, only the police files of the case need to be presented to the judge within 24 hours, not the actual detainee. Judges evaluate the legality of the arrest and make the decision about whether to order continued detention or other precautionary measures based solely on the written documents provided by the police.
The code establishes a maximum of 60 days for the first judicial hearing with the detainee, but does not explicitly say when this period begins. In practice, this often means that police in Brazil can keep people detained, with formal judicial authorization, for several months, without giving the detainee a chance to actually see a judge.
According to the code, the only circumstance in which police need to bring a person before the judge immediately applies to cases of crimes not subject to bail in which arresting officer was not able to exhibit the arrest order to the person arrested at the time of arrest. Otherwise, the detainee may also not see a judge for several months.
(www.hrw.org. Editado e adaptado)
The Right to a “Custody Hearing” under International Law
by Maria Laura Canineu
February 3, 2014
A person who is arrested has a right to be brought promptly before a judge. This is a longstanding and fundamental principle of international law, crucial for ensuring that the person’s arrest, treatment, and any ongoing detention are lawful.
Yet, until now, Brazil has not respected this right. Detainees often go months before seeing a judge. For instance, in São Paulo state, which houses 37 percent of Brazil’s total prison population, most detainees are not brought before a judge for at least three months. The risk of ill-treatment is often highest during the initial stages of detention, when police are questioning a suspect. The delay makes detainees more vulnerable to torture and other serious forms of mistreatment by abusive police officers.
In 2012, the UN Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment reported that it had received “repeated and consistent accounts of torture and ill-treatment” in São Paulo and other Brazilian states, “committed by, in particular, the military and civil police.” The torture had allegedly occurred in police custody or at the moment of arrest, on the street, inside private homes, or in hidden outdoor areas, and was described as “gratuitous violence, as a form of punishment, to extract confessions, and as a means of extortion.”
In addition to violating the rights of detainees, these abusive practices make it more difficult for the police to establish the kind of public trust that is often crucial for effective crime control. These practices undermine legitimate efforts to promote public security and curb violent crime, and thus have a negative impact on Brazilian society as a whole.
The right to be brought before a judge without unnecessary delay is enshrined in treaties long ago ratified by Brazil, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the American Convention on Human Rights. The United Nations Human Rights Committee, which is responsible for interpreting the ICCPR, has determined that the delay between the arrest of an accused and the time before he is brought before a judicial authority “should not exceed a few days,” even during states of emergency.
Other countries in Latin America have incorporated this right into their domestic law. For instance, in Argentina, the federal Criminal Procedure Code requires that in cases of arrest without a judicial order, the detainee must be brought to a competent judicial authority within six hours.
In contrast, Brazil’s criminal procedure code requires that when an adult is arrested in flagrante and held in police custody, only the police files of the case need to be presented to the judge within 24 hours, not the actual detainee. Judges evaluate the legality of the arrest and make the decision about whether to order continued detention or other precautionary measures based solely on the written documents provided by the police.
The code establishes a maximum of 60 days for the first judicial hearing with the detainee, but does not explicitly say when this period begins. In practice, this often means that police in Brazil can keep people detained, with formal judicial authorization, for several months, without giving the detainee a chance to actually see a judge.
According to the code, the only circumstance in which police need to bring a person before the judge immediately applies to cases of crimes not subject to bail in which arresting officer was not able to exhibit the arrest order to the person arrested at the time of arrest. Otherwise, the detainee may also not see a judge for several months.
(www.hrw.org. Editado e adaptado)
The Right to a “Custody Hearing” under International Law
by Maria Laura Canineu
February 3, 2014
A person who is arrested has a right to be brought promptly before a judge. This is a longstanding and fundamental principle of international law, crucial for ensuring that the person’s arrest, treatment, and any ongoing detention are lawful.
Yet, until now, Brazil has not respected this right. Detainees often go months before seeing a judge. For instance, in São Paulo state, which houses 37 percent of Brazil’s total prison population, most detainees are not brought before a judge for at least three months. The risk of ill-treatment is often highest during the initial stages of detention, when police are questioning a suspect. The delay makes detainees more vulnerable to torture and other serious forms of mistreatment by abusive police officers.
In 2012, the UN Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment reported that it had received “repeated and consistent accounts of torture and ill-treatment” in São Paulo and other Brazilian states, “committed by, in particular, the military and civil police.” The torture had allegedly occurred in police custody or at the moment of arrest, on the street, inside private homes, or in hidden outdoor areas, and was described as “gratuitous violence, as a form of punishment, to extract confessions, and as a means of extortion.”
In addition to violating the rights of detainees, these abusive practices make it more difficult for the police to establish the kind of public trust that is often crucial for effective crime control. These practices undermine legitimate efforts to promote public security and curb violent crime, and thus have a negative impact on Brazilian society as a whole.
The right to be brought before a judge without unnecessary delay is enshrined in treaties long ago ratified by Brazil, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the American Convention on Human Rights. The United Nations Human Rights Committee, which is responsible for interpreting the ICCPR, has determined that the delay between the arrest of an accused and the time before he is brought before a judicial authority “should not exceed a few days,” even during states of emergency.
Other countries in Latin America have incorporated this right into their domestic law. For instance, in Argentina, the federal Criminal Procedure Code requires that in cases of arrest without a judicial order, the detainee must be brought to a competent judicial authority within six hours.
In contrast, Brazil’s criminal procedure code requires that when an adult is arrested in flagrante and held in police custody, only the police files of the case need to be presented to the judge within 24 hours, not the actual detainee. Judges evaluate the legality of the arrest and make the decision about whether to order continued detention or other precautionary measures based solely on the written documents provided by the police.
The code establishes a maximum of 60 days for the first judicial hearing with the detainee, but does not explicitly say when this period begins. In practice, this often means that police in Brazil can keep people detained, with formal judicial authorization, for several months, without giving the detainee a chance to actually see a judge.
According to the code, the only circumstance in which police need to bring a person before the judge immediately applies to cases of crimes not subject to bail in which arresting officer was not able to exhibit the arrest order to the person arrested at the time of arrest. Otherwise, the detainee may also not see a judge for several months.
(www.hrw.org. Editado e adaptado)
The Right to a “Custody Hearing” under International Law
by Maria Laura Canineu
February 3, 2014
A person who is arrested has a right to be brought promptly before a judge. This is a longstanding and fundamental principle of international law, crucial for ensuring that the person’s arrest, treatment, and any ongoing detention are lawful.
Yet, until now, Brazil has not respected this right. Detainees often go months before seeing a judge. For instance, in São Paulo state, which houses 37 percent of Brazil’s total prison population, most detainees are not brought before a judge for at least three months. The risk of ill-treatment is often highest during the initial stages of detention, when police are questioning a suspect. The delay makes detainees more vulnerable to torture and other serious forms of mistreatment by abusive police officers.
In 2012, the UN Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment reported that it had received “repeated and consistent accounts of torture and ill-treatment” in São Paulo and other Brazilian states, “committed by, in particular, the military and civil police.” The torture had allegedly occurred in police custody or at the moment of arrest, on the street, inside private homes, or in hidden outdoor areas, and was described as “gratuitous violence, as a form of punishment, to extract confessions, and as a means of extortion.”
In addition to violating the rights of detainees, these abusive practices make it more difficult for the police to establish the kind of public trust that is often crucial for effective crime control. These practices undermine legitimate efforts to promote public security and curb violent crime, and thus have a negative impact on Brazilian society as a whole.
The right to be brought before a judge without unnecessary delay is enshrined in treaties long ago ratified by Brazil, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the American Convention on Human Rights. The United Nations Human Rights Committee, which is responsible for interpreting the ICCPR, has determined that the delay between the arrest of an accused and the time before he is brought before a judicial authority “should not exceed a few days,” even during states of emergency.
Other countries in Latin America have incorporated this right into their domestic law. For instance, in Argentina, the federal Criminal Procedure Code requires that in cases of arrest without a judicial order, the detainee must be brought to a competent judicial authority within six hours.
In contrast, Brazil’s criminal procedure code requires that when an adult is arrested in flagrante and held in police custody, only the police files of the case need to be presented to the judge within 24 hours, not the actual detainee. Judges evaluate the legality of the arrest and make the decision about whether to order continued detention or other precautionary measures based solely on the written documents provided by the police.
The code establishes a maximum of 60 days for the first judicial hearing with the detainee, but does not explicitly say when this period begins. In practice, this often means that police in Brazil can keep people detained, with formal judicial authorization, for several months, without giving the detainee a chance to actually see a judge.
According to the code, the only circumstance in which police need to bring a person before the judge immediately applies to cases of crimes not subject to bail in which arresting officer was not able to exhibit the arrest order to the person arrested at the time of arrest. Otherwise, the detainee may also not see a judge for several months.
(www.hrw.org. Editado e adaptado)
The Right to a “Custody Hearing” under International Law
by Maria Laura Canineu
February 3, 2014
A person who is arrested has a right to be brought promptly before a judge. This is a longstanding and fundamental principle of international law, crucial for ensuring that the person’s arrest, treatment, and any ongoing detention are lawful.
Yet, until now, Brazil has not respected this right. Detainees often go months before seeing a judge. For instance, in São Paulo state, which houses 37 percent of Brazil’s total prison population, most detainees are not brought before a judge for at least three months. The risk of ill-treatment is often highest during the initial stages of detention, when police are questioning a suspect. The delay makes detainees more vulnerable to torture and other serious forms of mistreatment by abusive police officers.
In 2012, the UN Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment reported that it had received “repeated and consistent accounts of torture and ill-treatment” in São Paulo and other Brazilian states, “committed by, in particular, the military and civil police.” The torture had allegedly occurred in police custody or at the moment of arrest, on the street, inside private homes, or in hidden outdoor areas, and was described as “gratuitous violence, as a form of punishment, to extract confessions, and as a means of extortion.”
In addition to violating the rights of detainees, these abusive practices make it more difficult for the police to establish the kind of public trust that is often crucial for effective crime control. These practices undermine legitimate efforts to promote public security and curb violent crime, and thus have a negative impact on Brazilian society as a whole.
The right to be brought before a judge without unnecessary delay is enshrined in treaties long ago ratified by Brazil, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the American Convention on Human Rights. The United Nations Human Rights Committee, which is responsible for interpreting the ICCPR, has determined that the delay between the arrest of an accused and the time before he is brought before a judicial authority “should not exceed a few days,” even during states of emergency.
Other countries in Latin America have incorporated this right into their domestic law. For instance, in Argentina, the federal Criminal Procedure Code requires that in cases of arrest without a judicial order, the detainee must be brought to a competent judicial authority within six hours.
In contrast, Brazil’s criminal procedure code requires that when an adult is arrested in flagrante and held in police custody, only the police files of the case need to be presented to the judge within 24 hours, not the actual detainee. Judges evaluate the legality of the arrest and make the decision about whether to order continued detention or other precautionary measures based solely on the written documents provided by the police.
The code establishes a maximum of 60 days for the first judicial hearing with the detainee, but does not explicitly say when this period begins. In practice, this often means that police in Brazil can keep people detained, with formal judicial authorization, for several months, without giving the detainee a chance to actually see a judge.
According to the code, the only circumstance in which police need to bring a person before the judge immediately applies to cases of crimes not subject to bail in which arresting officer was not able to exhibit the arrest order to the person arrested at the time of arrest. Otherwise, the detainee may also not see a judge for several months.
(www.hrw.org. Editado e adaptado)
The Right to a “Custody Hearing” under International Law
by Maria Laura Canineu
February 3, 2014
A person who is arrested has a right to be brought promptly before a judge. This is a longstanding and fundamental principle of international law, crucial for ensuring that the person’s arrest, treatment, and any ongoing detention are lawful.
Yet, until now, Brazil has not respected this right. Detainees often go months before seeing a judge. For instance, in São Paulo state, which houses 37 percent of Brazil’s total prison population, most detainees are not brought before a judge for at least three months. The risk of ill-treatment is often highest during the initial stages of detention, when police are questioning a suspect. The delay makes detainees more vulnerable to torture and other serious forms of mistreatment by abusive police officers.
In 2012, the UN Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment reported that it had received “repeated and consistent accounts of torture and ill-treatment” in São Paulo and other Brazilian states, “committed by, in particular, the military and civil police.” The torture had allegedly occurred in police custody or at the moment of arrest, on the street, inside private homes, or in hidden outdoor areas, and was described as “gratuitous violence, as a form of punishment, to extract confessions, and as a means of extortion.”
In addition to violating the rights of detainees, these abusive practices make it more difficult for the police to establish the kind of public trust that is often crucial for effective crime control. These practices undermine legitimate efforts to promote public security and curb violent crime, and thus have a negative impact on Brazilian society as a whole.
The right to be brought before a judge without unnecessary delay is enshrined in treaties long ago ratified by Brazil, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the American Convention on Human Rights. The United Nations Human Rights Committee, which is responsible for interpreting the ICCPR, has determined that the delay between the arrest of an accused and the time before he is brought before a judicial authority “should not exceed a few days,” even during states of emergency.
Other countries in Latin America have incorporated this right into their domestic law. For instance, in Argentina, the federal Criminal Procedure Code requires that in cases of arrest without a judicial order, the detainee must be brought to a competent judicial authority within six hours.
In contrast, Brazil’s criminal procedure code requires that when an adult is arrested in flagrante and held in police custody, only the police files of the case need to be presented to the judge within 24 hours, not the actual detainee. Judges evaluate the legality of the arrest and make the decision about whether to order continued detention or other precautionary measures based solely on the written documents provided by the police.
The code establishes a maximum of 60 days for the first judicial hearing with the detainee, but does not explicitly say when this period begins. In practice, this often means that police in Brazil can keep people detained, with formal judicial authorization, for several months, without giving the detainee a chance to actually see a judge.
According to the code, the only circumstance in which police need to bring a person before the judge immediately applies to cases of crimes not subject to bail in which arresting officer was not able to exhibit the arrest order to the person arrested at the time of arrest. Otherwise, the detainee may also not see a judge for several months.
(www.hrw.org. Editado e adaptado)
The Right to a “Custody Hearing” under International Law
by Maria Laura Canineu
February 3, 2014
A person who is arrested has a right to be brought promptly before a judge. This is a longstanding and fundamental principle of international law, crucial for ensuring that the person’s arrest, treatment, and any ongoing detention are lawful.
Yet, until now, Brazil has not respected this right. Detainees often go months before seeing a judge. For instance, in São Paulo state, which houses 37 percent of Brazil’s total prison population, most detainees are not brought before a judge for at least three months. The risk of ill-treatment is often highest during the initial stages of detention, when police are questioning a suspect. The delay makes detainees more vulnerable to torture and other serious forms of mistreatment by abusive police officers.
In 2012, the UN Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment reported that it had received “repeated and consistent accounts of torture and ill-treatment” in São Paulo and other Brazilian states, “committed by, in particular, the military and civil police.” The torture had allegedly occurred in police custody or at the moment of arrest, on the street, inside private homes, or in hidden outdoor areas, and was described as “gratuitous violence, as a form of punishment, to extract confessions, and as a means of extortion.”
In addition to violating the rights of detainees, these abusive practices make it more difficult for the police to establish the kind of public trust that is often crucial for effective crime control. These practices undermine legitimate efforts to promote public security and curb violent crime, and thus have a negative impact on Brazilian society as a whole.
The right to be brought before a judge without unnecessary delay is enshrined in treaties long ago ratified by Brazil, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the American Convention on Human Rights. The United Nations Human Rights Committee, which is responsible for interpreting the ICCPR, has determined that the delay between the arrest of an accused and the time before he is brought before a judicial authority “should not exceed a few days,” even during states of emergency.
Other countries in Latin America have incorporated this right into their domestic law. For instance, in Argentina, the federal Criminal Procedure Code requires that in cases of arrest without a judicial order, the detainee must be brought to a competent judicial authority within six hours.
In contrast, Brazil’s criminal procedure code requires that when an adult is arrested in flagrante and held in police custody, only the police files of the case need to be presented to the judge within 24 hours, not the actual detainee. Judges evaluate the legality of the arrest and make the decision about whether to order continued detention or other precautionary measures based solely on the written documents provided by the police.
The code establishes a maximum of 60 days for the first judicial hearing with the detainee, but does not explicitly say when this period begins. In practice, this often means that police in Brazil can keep people detained, with formal judicial authorization, for several months, without giving the detainee a chance to actually see a judge.
According to the code, the only circumstance in which police need to bring a person before the judge immediately applies to cases of crimes not subject to bail in which arresting officer was not able to exhibit the arrest order to the person arrested at the time of arrest. Otherwise, the detainee may also not see a judge for several months.
(www.hrw.org. Editado e adaptado)
The Right to a “Custody Hearing” under International Law
by Maria Laura Canineu
February 3, 2014
A person who is arrested has a right to be brought promptly before a judge. This is a longstanding and fundamental principle of international law, crucial for ensuring that the person’s arrest, treatment, and any ongoing detention are lawful.
Yet, until now, Brazil has not respected this right. Detainees often go months before seeing a judge. For instance, in São Paulo state, which houses 37 percent of Brazil’s total prison population, most detainees are not brought before a judge for at least three months. The risk of ill-treatment is often highest during the initial stages of detention, when police are questioning a suspect. The delay makes detainees more vulnerable to torture and other serious forms of mistreatment by abusive police officers.
In 2012, the UN Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment reported that it had received “repeated and consistent accounts of torture and ill-treatment” in São Paulo and other Brazilian states, “committed by, in particular, the military and civil police.” The torture had allegedly occurred in police custody or at the moment of arrest, on the street, inside private homes, or in hidden outdoor areas, and was described as “gratuitous violence, as a form of punishment, to extract confessions, and as a means of extortion.”
In addition to violating the rights of detainees, these abusive practices make it more difficult for the police to establish the kind of public trust that is often crucial for effective crime control. These practices undermine legitimate efforts to promote public security and curb violent crime, and thus have a negative impact on Brazilian society as a whole.
The right to be brought before a judge without unnecessary delay is enshrined in treaties long ago ratified by Brazil, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the American Convention on Human Rights. The United Nations Human Rights Committee, which is responsible for interpreting the ICCPR, has determined that the delay between the arrest of an accused and the time before he is brought before a judicial authority “should not exceed a few days,” even during states of emergency.
Other countries in Latin America have incorporated this right into their domestic law. For instance, in Argentina, the federal Criminal Procedure Code requires that in cases of arrest without a judicial order, the detainee must be brought to a competent judicial authority within six hours.
In contrast, Brazil’s criminal procedure code requires that when an adult is arrested in flagrante and held in police custody, only the police files of the case need to be presented to the judge within 24 hours, not the actual detainee. Judges evaluate the legality of the arrest and make the decision about whether to order continued detention or other precautionary measures based solely on the written documents provided by the police.
The code establishes a maximum of 60 days for the first judicial hearing with the detainee, but does not explicitly say when this period begins. In practice, this often means that police in Brazil can keep people detained, with formal judicial authorization, for several months, without giving the detainee a chance to actually see a judge.
According to the code, the only circumstance in which police need to bring a person before the judge immediately applies to cases of crimes not subject to bail in which arresting officer was not able to exhibit the arrest order to the person arrested at the time of arrest. Otherwise, the detainee may also not see a judge for several months.
(www.hrw.org. Editado e adaptado)
The Right to a “Custody Hearing” under International Law
by Maria Laura Canineu
February 3, 2014
A person who is arrested has a right to be brought promptly before a judge. This is a longstanding and fundamental principle of international law, crucial for ensuring that the person’s arrest, treatment, and any ongoing detention are lawful.
Yet, until now, Brazil has not respected this right. Detainees often go months before seeing a judge. For instance, in São Paulo state, which houses 37 percent of Brazil’s total prison population, most detainees are not brought before a judge for at least three months. The risk of ill-treatment is often highest during the initial stages of detention, when police are questioning a suspect. The delay makes detainees more vulnerable to torture and other serious forms of mistreatment by abusive police officers.
In 2012, the UN Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment reported that it had received “repeated and consistent accounts of torture and ill-treatment” in São Paulo and other Brazilian states, “committed by, in particular, the military and civil police.” The torture had allegedly occurred in police custody or at the moment of arrest, on the street, inside private homes, or in hidden outdoor areas, and was described as “gratuitous violence, as a form of punishment, to extract confessions, and as a means of extortion.”
In addition to violating the rights of detainees, these abusive practices make it more difficult for the police to establish the kind of public trust that is often crucial for effective crime control. These practices undermine legitimate efforts to promote public security and curb violent crime, and thus have a negative impact on Brazilian society as a whole.
The right to be brought before a judge without unnecessary delay is enshrined in treaties long ago ratified by Brazil, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the American Convention on Human Rights. The United Nations Human Rights Committee, which is responsible for interpreting the ICCPR, has determined that the delay between the arrest of an accused and the time before he is brought before a judicial authority “should not exceed a few days,” even during states of emergency.
Other countries in Latin America have incorporated this right into their domestic law. For instance, in Argentina, the federal Criminal Procedure Code requires that in cases of arrest without a judicial order, the detainee must be brought to a competent judicial authority within six hours.
In contrast, Brazil’s criminal procedure code requires that when an adult is arrested in flagrante and held in police custody, only the police files of the case need to be presented to the judge within 24 hours, not the actual detainee. Judges evaluate the legality of the arrest and make the decision about whether to order continued detention or other precautionary measures based solely on the written documents provided by the police.
The code establishes a maximum of 60 days for the first judicial hearing with the detainee, but does not explicitly say when this period begins. In practice, this often means that police in Brazil can keep people detained, with formal judicial authorization, for several months, without giving the detainee a chance to actually see a judge.
According to the code, the only circumstance in which police need to bring a person before the judge immediately applies to cases of crimes not subject to bail in which arresting officer was not able to exhibit the arrest order to the person arrested at the time of arrest. Otherwise, the detainee may also not see a judge for several months.
(www.hrw.org. Editado e adaptado)
O tio Sabino, paramentado de rico, fez ainda sair da maleta de couro uma espécie de saco de lona com fechos de correias. Debaixo da cama, por esquecimento, tinham ficado as alpargatas do Carvalhosa. O tio Sabino calçou-as, as suas narinas palpitavam. Correu o fecho da porta cautelosamente, foi até ao escritório do Carvalhosa e sacou da gaveta do contador uns rolinhos de libras; de passagem pelo toilette arrecadou o cofre de joias, os anéis e a caixa de pó de arroz; de cima da banquinha de noite desapareceu a palmatória de prata dourada e tudo foi arrecadado no saco.
Fechou destramente o saco, tendo-lhe metido primeiro a camisa de chita que despira, a fim de não tinirem dentro os metais. E de chapéu à banda e cachimbo na boca saiu, o saco pendente, fechando a porta e tirando-lhe a chave. Ninguém estava no corredor; Maria do Resgate engomava na saleta; as crianças na cozinha cortavam papagaios, chilreando.
- Até logo, minha sobrinha, até logo.
Ela veio correndo, com o seu riso afetuoso.
- O jantar é às cinco, sim? Mas, querendo, dá-se ordem para mais tarde.
- Qual! Não temos precisão de incômodos. Às quatro e meia estou.
E com a mala pendente, o lenço escarlate fora do bolso do fraque e bengala debaixo do braço, desceu a escada cantarolando.
Eram seis horas da tarde e nada do tio Sabino.
Sete horas, e Maria do Resgate acaba de notar a porta da alcova fechada. Diabo...
No dia seguinte a polícia andava em campo para descobrir o larápio, que com tamanha pilhéria roubara a família Carvalhosa.
(Fialho de Oliveira, O Tio da América. Em: Contos. Adaptado)
O tio Sabino, paramentado de rico, fez ainda sair da maleta de couro uma espécie de saco de lona com fechos de correias. Debaixo da cama, por esquecimento, tinham ficado as alpargatas do Carvalhosa. O tio Sabino calçou-as, as suas narinas palpitavam. Correu o fecho da porta cautelosamente, foi até ao escritório do Carvalhosa e sacou da gaveta do contador uns rolinhos de libras; de passagem pelo toilette arrecadou o cofre de joias, os anéis e a caixa de pó de arroz; de cima da banquinha de noite desapareceu a palmatória de prata dourada e tudo foi arrecadado no saco.
Fechou destramente o saco, tendo-lhe metido primeiro a camisa de chita que despira, a fim de não tinirem dentro os metais. E de chapéu à banda e cachimbo na boca saiu, o saco pendente, fechando a porta e tirando-lhe a chave. Ninguém estava no corredor; Maria do Resgate engomava na saleta; as crianças na cozinha cortavam papagaios, chilreando.
- Até logo, minha sobrinha, até logo.
Ela veio correndo, com o seu riso afetuoso.
- O jantar é às cinco, sim? Mas, querendo, dá-se ordem para mais tarde.
- Qual! Não temos precisão de incômodos. Às quatro e meia estou.
E com a mala pendente, o lenço escarlate fora do bolso do fraque e bengala debaixo do braço, desceu a escada cantarolando.
Eram seis horas da tarde e nada do tio Sabino.
Sete horas, e Maria do Resgate acaba de notar a porta da alcova fechada. Diabo...
No dia seguinte a polícia andava em campo para descobrir o larápio, que com tamanha pilhéria roubara a família Carvalhosa.
(Fialho de Oliveira, O Tio da América. Em: Contos. Adaptado)
O tio Sabino, paramentado de rico, fez ainda sair da maleta de couro uma espécie de saco de lona com fechos de correias. Debaixo da cama, por esquecimento, tinham ficado as alpargatas do Carvalhosa. O tio Sabino calçou-as, as suas narinas palpitavam. Correu o fecho da porta cautelosamente, foi até ao escritório do Carvalhosa e sacou da gaveta do contador uns rolinhos de libras; de passagem pelo toilette arrecadou o cofre de joias, os anéis e a caixa de pó de arroz; de cima da banquinha de noite desapareceu a palmatória de prata dourada e tudo foi arrecadado no saco.
Fechou destramente o saco, tendo-lhe metido primeiro a camisa de chita que despira, a fim de não tinirem dentro os metais. E de chapéu à banda e cachimbo na boca saiu, o saco pendente, fechando a porta e tirando-lhe a chave. Ninguém estava no corredor; Maria do Resgate engomava na saleta; as crianças na cozinha cortavam papagaios, chilreando.
- Até logo, minha sobrinha, até logo.
Ela veio correndo, com o seu riso afetuoso.
- O jantar é às cinco, sim? Mas, querendo, dá-se ordem para mais tarde.
- Qual! Não temos precisão de incômodos. Às quatro e meia estou.
E com a mala pendente, o lenço escarlate fora do bolso do fraque e bengala debaixo do braço, desceu a escada cantarolando.
Eram seis horas da tarde e nada do tio Sabino.
Sete horas, e Maria do Resgate acaba de notar a porta da alcova fechada. Diabo...
No dia seguinte a polícia andava em campo para descobrir o larápio, que com tamanha pilhéria roubara a família Carvalhosa.
(Fialho de Oliveira, O Tio da América. Em: Contos. Adaptado)