Questões de Concurso
Para agência reguladora
Foram encontradas 21.523 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Leia a notícia publicada pela IDG Now:
A empresa Intel opera num ciclo bienal conhecido como “tic-toc”. Num “tic” a empresa introduz um novo processo de fabricação de seus componentes. Em 2010 a família de processadores “Clarkdale”, para desktops, reduziu a microarquitetura Nehalem a 32 nanômetros, resultando em melhor desempenho e economia de energia. Num “toc” a Intel introduz uma nova microarquitetura, e em 2011 tivemos os processadores Sandy Bridge, com desempenho superior à família Clarkdale, menor consumo de energia e um sistema gráfico integrado aprimorado.
O próximo “tic” acontece em 2012, quando a Intel irá começar a produzir processadores baseados numa revisão da arquitetura Sandy Bridge em um processo de 22 nanômetros. Os novos chips, de codinome Ivy Bridge, novamente prometem ainda melhor desempenho e menor consumo de energia, assim como fizeram as duas gerações anteriores.
(http://idgnow.uol.com.br/mercado/2012/01/03/o-que-esperar-dos-processadores-em-2012/#&panel2-1)
Em relação aos processadores e considerando as informações da notícia, é correto afirmar que
Considere o algoritmo em pseudocódigo:

Os valores de R1, R2 e R3, após a execução do algoritmo são:
Considere o número em base 2 (binário):
1111101
Este número, convertido para a base 10, representa o valor decimal 125.
Já o número binário 1111101.110, convertido para a base 10, representa o valor
Sistema Operacional (SO) é uma camada de software colocada sobre o hardware para gerenciar todos os componentes do sistema, apresentando-o ao usuário como uma interface simples de entender e de programar. Considere as afirmativas a seguir sobre Sistemas Operacionais.
I. Os programas de aplicação solicitam serviços ao SO através da execução de chamadas de sistema. Os SOs oferecem Application Program Interfaces (APIs) para que os programadores usem funções para interagir com suas rotinas.
II. O Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) é um dispositivo de hardware que assegura que todos os recursos funcionem em conjunto num computador.
III. Firmware são programas ou instruções gravados no hardware da máquina que permitem a comunicação com outros dispositivos eletrônicos.
IV. A interface entre o SO e os programas de aplicação é definida pelo conjunto de instruções estendidas fornecidas pelo SO. Estas instruções são conhecidas como Dynamic Link Library (DLL).
Está correto o que se afirma em
O gráfico abaixo mostra a relação de dominação assintótica entre funções de complexidade de algoritmos. Os valores de tempo e tamanho do problema são apenas referenciais. Considere apenas os seus valores crescentes.
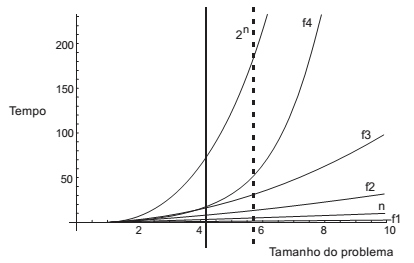
Com base no gráfico, é correto afirmar que
Para responder a questão, considere o texto a seguir:
Environmental law in Brazil
BRAZIL’S gridlocked Congress often ends up passing contentious laws only after the combatants collapse in exhaustion. So it is with the revision of the Forest Code, a set of rules that, ...A... the name, apply to all privately owned rural land, not just plots in wooded areas. The code, originally approved in 1965, requires owners to keep native vegetation on parts of their land − 80% in the Amazon, less elsewhere − and in erosion-prone and biodiverse areas such as riverbanks and mangrove swamps. But it was long ignored.
Since harsher penalties and enforcement were introduced in the late 1990s the ruralistas, as Brazil’s powerful farming lobby is known, have been trying to revise the code. On April 25th, after 13 years of arguments, rewrites and stalling, the final text landed on the desk of the president, Dilma Rousseff. It was far from the version she wanted. Two government defeats in the ruralista-packed lower house meant it contained few of her own previous revisions or those of the more green-friendly Senate.
The president faced a difficult choice: to scrap the text and start again − which would probably be taken as a declaration of war by the ruralistas − or to make the best of a bad job. She chose the latter. On May 25th ministers went to Congress to say that the president would veto 12 of the new code’s 84 articles and make 32 smaller cuts. The resulting holes would be backfilled in a separate executive decree. Only on May 28th were the details published.
Under Ms Rousseff’s veto, the amnesty sought by ruralistas will apply only to smallholders, who will still have to replant 20% of their plots. Everyone else will have five years to right past wrongs and add their properties to a new Rural Environmental Register. Holdouts will be denied bank loans and face prosecution.
Rubens Ricupero, one of ten former environment ministers consulted by the president before the veto, praises her attempt to strike a balance. Treating small landowners more leniently was both practical, he thinks − they account for 90% of rural properties by number but just 24% by area − and socially just: few could afford much replanting.
(Adapted from http://www.economist.com/node/21556245?zid=305&ah=417bd5664dc76da5d98af4f7a640fd8a)
Para responder a questão, considere o texto a seguir:
Environmental law in Brazil
BRAZIL’S gridlocked Congress often ends up passing contentious laws only after the combatants collapse in exhaustion. So it is with the revision of the Forest Code, a set of rules that, ...A... the name, apply to all privately owned rural land, not just plots in wooded areas. The code, originally approved in 1965, requires owners to keep native vegetation on parts of their land − 80% in the Amazon, less elsewhere − and in erosion-prone and biodiverse areas such as riverbanks and mangrove swamps. But it was long ignored.
Since harsher penalties and enforcement were introduced in the late 1990s the ruralistas, as Brazil’s powerful farming lobby is known, have been trying to revise the code. On April 25th, after 13 years of arguments, rewrites and stalling, the final text landed on the desk of the president, Dilma Rousseff. It was far from the version she wanted. Two government defeats in the ruralista-packed lower house meant it contained few of her own previous revisions or those of the more green-friendly Senate.
The president faced a difficult choice: to scrap the text and start again − which would probably be taken as a declaration of war by the ruralistas − or to make the best of a bad job. She chose the latter. On May 25th ministers went to Congress to say that the president would veto 12 of the new code’s 84 articles and make 32 smaller cuts. The resulting holes would be backfilled in a separate executive decree. Only on May 28th were the details published.
Under Ms Rousseff’s veto, the amnesty sought by ruralistas will apply only to smallholders, who will still have to replant 20% of their plots. Everyone else will have five years to right past wrongs and add their properties to a new Rural Environmental Register. Holdouts will be denied bank loans and face prosecution.
Rubens Ricupero, one of ten former environment ministers consulted by the president before the veto, praises her attempt to strike a balance. Treating small landowners more leniently was both practical, he thinks − they account for 90% of rural properties by number but just 24% by area − and socially just: few could afford much replanting.
(Adapted from http://www.economist.com/node/21556245?zid=305&ah=417bd5664dc76da5d98af4f7a640fd8a)
Para responder a questão, considere o texto a seguir:
Environmental law in Brazil
BRAZIL’S gridlocked Congress often ends up passing contentious laws only after the combatants collapse in exhaustion. So it is with the revision of the Forest Code, a set of rules that, ...A... the name, apply to all privately owned rural land, not just plots in wooded areas. The code, originally approved in 1965, requires owners to keep native vegetation on parts of their land − 80% in the Amazon, less elsewhere − and in erosion-prone and biodiverse areas such as riverbanks and mangrove swamps. But it was long ignored.
Since harsher penalties and enforcement were introduced in the late 1990s the ruralistas, as Brazil’s powerful farming lobby is known, have been trying to revise the code. On April 25th, after 13 years of arguments, rewrites and stalling, the final text landed on the desk of the president, Dilma Rousseff. It was far from the version she wanted. Two government defeats in the ruralista-packed lower house meant it contained few of her own previous revisions or those of the more green-friendly Senate.
The president faced a difficult choice: to scrap the text and start again − which would probably be taken as a declaration of war by the ruralistas − or to make the best of a bad job. She chose the latter. On May 25th ministers went to Congress to say that the president would veto 12 of the new code’s 84 articles and make 32 smaller cuts. The resulting holes would be backfilled in a separate executive decree. Only on May 28th were the details published.
Under Ms Rousseff’s veto, the amnesty sought by ruralistas will apply only to smallholders, who will still have to replant 20% of their plots. Everyone else will have five years to right past wrongs and add their properties to a new Rural Environmental Register. Holdouts will be denied bank loans and face prosecution.
Rubens Ricupero, one of ten former environment ministers consulted by the president before the veto, praises her attempt to strike a balance. Treating small landowners more leniently was both practical, he thinks − they account for 90% of rural properties by number but just 24% by area − and socially just: few could afford much replanting.
(Adapted from http://www.economist.com/node/21556245?zid=305&ah=417bd5664dc76da5d98af4f7a640fd8a)
Para responder a questão, considere o texto a seguir:
Environmental law in Brazil
BRAZIL’S gridlocked Congress often ends up passing contentious laws only after the combatants collapse in exhaustion. So it is with the revision of the Forest Code, a set of rules that, ...A... the name, apply to all privately owned rural land, not just plots in wooded areas. The code, originally approved in 1965, requires owners to keep native vegetation on parts of their land − 80% in the Amazon, less elsewhere − and in erosion-prone and biodiverse areas such as riverbanks and mangrove swamps. But it was long ignored.
Since harsher penalties and enforcement were introduced in the late 1990s the ruralistas, as Brazil’s powerful farming lobby is known, have been trying to revise the code. On April 25th, after 13 years of arguments, rewrites and stalling, the final text landed on the desk of the president, Dilma Rousseff. It was far from the version she wanted. Two government defeats in the ruralista-packed lower house meant it contained few of her own previous revisions or those of the more green-friendly Senate.
The president faced a difficult choice: to scrap the text and start again − which would probably be taken as a declaration of war by the ruralistas − or to make the best of a bad job. She chose the latter. On May 25th ministers went to Congress to say that the president would veto 12 of the new code’s 84 articles and make 32 smaller cuts. The resulting holes would be backfilled in a separate executive decree. Only on May 28th were the details published.
Under Ms Rousseff’s veto, the amnesty sought by ruralistas will apply only to smallholders, who will still have to replant 20% of their plots. Everyone else will have five years to right past wrongs and add their properties to a new Rural Environmental Register. Holdouts will be denied bank loans and face prosecution.
Rubens Ricupero, one of ten former environment ministers consulted by the president before the veto, praises her attempt to strike a balance. Treating small landowners more leniently was both practical, he thinks − they account for 90% of rural properties by number but just 24% by area − and socially just: few could afford much replanting.
(Adapted from http://www.economist.com/node/21556245?zid=305&ah=417bd5664dc76da5d98af4f7a640fd8a)
Para responder a questão, considere o texto a seguir:
Environmental law in Brazil
BRAZIL’S gridlocked Congress often ends up passing contentious laws only after the combatants collapse in exhaustion. So it is with the revision of the Forest Code, a set of rules that, ...A... the name, apply to all privately owned rural land, not just plots in wooded areas. The code, originally approved in 1965, requires owners to keep native vegetation on parts of their land − 80% in the Amazon, less elsewhere − and in erosion-prone and biodiverse areas such as riverbanks and mangrove swamps. But it was long ignored.
Since harsher penalties and enforcement were introduced in the late 1990s the ruralistas, as Brazil’s powerful farming lobby is known, have been trying to revise the code. On April 25th, after 13 years of arguments, rewrites and stalling, the final text landed on the desk of the president, Dilma Rousseff. It was far from the version she wanted. Two government defeats in the ruralista-packed lower house meant it contained few of her own previous revisions or those of the more green-friendly Senate.
The president faced a difficult choice: to scrap the text and start again − which would probably be taken as a declaration of war by the ruralistas − or to make the best of a bad job. She chose the latter. On May 25th ministers went to Congress to say that the president would veto 12 of the new code’s 84 articles and make 32 smaller cuts. The resulting holes would be backfilled in a separate executive decree. Only on May 28th were the details published.
Under Ms Rousseff’s veto, the amnesty sought by ruralistas will apply only to smallholders, who will still have to replant 20% of their plots. Everyone else will have five years to right past wrongs and add their properties to a new Rural Environmental Register. Holdouts will be denied bank loans and face prosecution.
Rubens Ricupero, one of ten former environment ministers consulted by the president before the veto, praises her attempt to strike a balance. Treating small landowners more leniently was both practical, he thinks − they account for 90% of rural properties by number but just 24% by area − and socially just: few could afford much replanting.
(Adapted from http://www.economist.com/node/21556245?zid=305&ah=417bd5664dc76da5d98af4f7a640fd8a)
Para responder a questão, considere o texto a seguir:
Environmental law in Brazil
BRAZIL’S gridlocked Congress often ends up passing contentious laws only after the combatants collapse in exhaustion. So it is with the revision of the Forest Code, a set of rules that, ...A... the name, apply to all privately owned rural land, not just plots in wooded areas. The code, originally approved in 1965, requires owners to keep native vegetation on parts of their land − 80% in the Amazon, less elsewhere − and in erosion-prone and biodiverse areas such as riverbanks and mangrove swamps. But it was long ignored.
Since harsher penalties and enforcement were introduced in the late 1990s the ruralistas, as Brazil’s powerful farming lobby is known, have been trying to revise the code. On April 25th, after 13 years of arguments, rewrites and stalling, the final text landed on the desk of the president, Dilma Rousseff. It was far from the version she wanted. Two government defeats in the ruralista-packed lower house meant it contained few of her own previous revisions or those of the more green-friendly Senate.
The president faced a difficult choice: to scrap the text and start again − which would probably be taken as a declaration of war by the ruralistas − or to make the best of a bad job. She chose the latter. On May 25th ministers went to Congress to say that the president would veto 12 of the new code’s 84 articles and make 32 smaller cuts. The resulting holes would be backfilled in a separate executive decree. Only on May 28th were the details published.
Under Ms Rousseff’s veto, the amnesty sought by ruralistas will apply only to smallholders, who will still have to replant 20% of their plots. Everyone else will have five years to right past wrongs and add their properties to a new Rural Environmental Register. Holdouts will be denied bank loans and face prosecution.
Rubens Ricupero, one of ten former environment ministers consulted by the president before the veto, praises her attempt to strike a balance. Treating small landowners more leniently was both practical, he thinks − they account for 90% of rural properties by number but just 24% by area − and socially just: few could afford much replanting.
(Adapted from http://www.economist.com/node/21556245?zid=305&ah=417bd5664dc76da5d98af4f7a640fd8a)
Para responder a questão, considere o texto a seguir:
Historically, cachaça is directly linked to the introduction of sugarcane and the production of sugar in Brazil during the mid- 1500s. The slaves who were working at the sugar mills discovered that the garapa, the cooked sugarcane juice that was left standing, would ferment, turning into an alcoholic beverage. Apparently in the beginning, the beverage was given only to slaves at the end of their workday, but soon it became a popular drink consumed by all types of people. With the increase of demand, cachaça distilleries proliferated, and cachaça turned into the favorite alcoholic drink of the whole colony, becoming a threat to bagaceira, a Portuguese brandy made with grapes. As a consequence, during the gold rush, the consumption of cachaça was such that a royal court order of 1743 prohibited the distilleries in all Minas Gerais, probably starting cachaça’s first steps on its long social underground history. (Only in the 1990s did cachaça exit this social stigma to gain status and national and then international recognition.)
With the excuse of producing sugar, people continued to secretly produce cachaça, which prompted the court to attach high taxation on the Brazilian beverage.
Later, during the first movements for independence, cachaça was converted to a political statement when Brazilians served it instead of Porto wine during important receptions.
(Roberts, Yara Castro & Richard Roberts. 2009. The Brazilian Table. Salt Lake City: Gibbs Smith., p. 29)
Para responder a questão, considere o texto a seguir:
Historically, cachaça is directly linked to the introduction of sugarcane and the production of sugar in Brazil during the mid- 1500s. The slaves who were working at the sugar mills discovered that the garapa, the cooked sugarcane juice that was left standing, would ferment, turning into an alcoholic beverage. Apparently in the beginning, the beverage was given only to slaves at the end of their workday, but soon it became a popular drink consumed by all types of people. With the increase of demand, cachaça distilleries proliferated, and cachaça turned into the favorite alcoholic drink of the whole colony, becoming a threat to bagaceira, a Portuguese brandy made with grapes. As a consequence, during the gold rush, the consumption of cachaça was such that a royal court order of 1743 prohibited the distilleries in all Minas Gerais, probably starting cachaça’s first steps on its long social underground history. (Only in the 1990s did cachaça exit this social stigma to gain status and national and then international recognition.)
With the excuse of producing sugar, people continued to secretly produce cachaça, which prompted the court to attach high taxation on the Brazilian beverage.
Later, during the first movements for independence, cachaça was converted to a political statement when Brazilians served it instead of Porto wine during important receptions.
(Roberts, Yara Castro & Richard Roberts. 2009. The Brazilian Table. Salt Lake City: Gibbs Smith., p. 29)
Considere as seguintes assertivas concernentes aos contratos de parcerias público-privadas:
I. O prazo de vigência do contrato não será inferior a 5 anos, nem superior a 35 anos, incluindo eventual prorrogação.
II. É cláusula contratual obrigatória a realização de vistoria dos bens reversíveis, não podendo o parceiro público reter pagamentos ao parceiro privado, ainda que detectadas eventuais irregularidades.
III. O contrato não poderá prever o pagamento ao parceiro privado de remuneração variável vinculada ao seu desempenho.
IV. Constitui cláusula contratual obrigatória o compartilhamento com a Administração Pública de ganhos econômicos efetivos do parceiro privado decorrentes da redução do risco de crédito dos financiamentos utilizados pelo parceiro privado.
Nos termos da Lei Estadual n° 14.391/2009, está correto o que consta APENAS em