Questões de Concurso
Sobre inglês
Foram encontradas 17.876 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
“Why did the student do such a mistake?”
In the Passive voice:
COMPARATIVE: better SUPERLATIVE: best ADVERB: little COMPARATIVE: _______ SUPERLATIVE: ________
“The scientist wrote down his formula.”
In the plural:
Philipp __________15 next Wednesday.
They _____________a new computer.
In 2020 people _________more hybrid cars.
Use of the Simple Future Tense
1. to talk about _______
________________________________
2. to ________/______________
Complete:
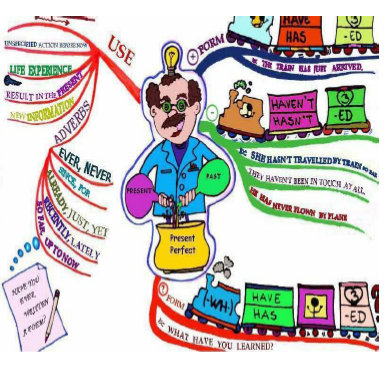
This is a mind map about: