Questões de Concurso
Comentadas para prefeitura de jaboatão dos guararapes - pe
Foram encontradas 257 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
( ) English as a Lingua Franca (ELF) and as a Foreign Language (EFL) present different perspectives. ( ) In an ELF context, learners look up to native language speakers as models. ( ) Research in the area of ELF has involved areas other than pedagogical settings.
The statements are, respectively:
Assinale a afirmativa que identifica corretamente um dos impactos do processo de globalização no campo cultural.
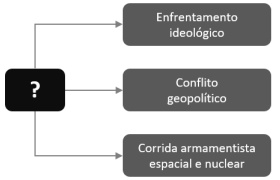
Assinale a afirmativa que completa corretamente o diagrama, identificando o processo histórico relacionado à confluência dos três aspectos assinalados.

Capa da revista ilustrada em quadrinhos “Aliança Para o Progresso: Plano de 10 pontos do Presidente Kennedy para a Família de Nações Americanas”. Rio de Janeiro: Bloch, sem data.
Aliança para o Progresso foi um programa de assistência ao desenvolvimento socioeconômico da América Latina formalizado pelos Estados Unidos e 22 outras nações do hemisfério, entre elas o Brasil, mediante a assinatura da Carta de Punta del Este, em 1961.
Considerando o contexto histórico em que esse programa foi implementado, assinale a afirmativa que descreve corretamente um de seus objetivos.

Cena de Triunfo da Vontade. Riefenstahl, L. (1935).
Uma característica dos sistemas totalitários que é bem representada na imagem é
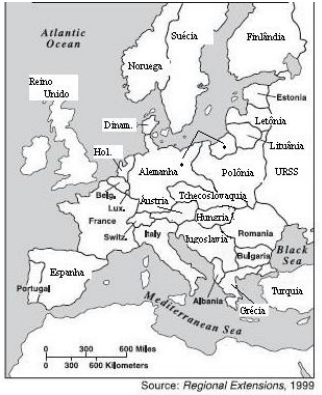
O mapa representa a divisão política da Europa no contexto
A respeito de suas causas, relacione as principais correntes listadas a seguir às respectivas interpretações.
1. Keynesianos 2. Monetaristas
( ) A Grande Depressão foi provocada por uma atuação equivocada do Banco Central norte-americano (FED) que, para combater a especulação na bolsa de Nova York, adotou uma política restritiva que diminuiu a liquidez e transformou uma recessão em uma depressão econômica.
( ) A recessão se transformou em uma depressão porque a ela se associaram eventos que provocaram escassez de demanda, como as mudanças tecnológicas que reduziram a massa salarial que poderia sustentar o consumo, por isso os governos deveriam ter intervindo e injetado recursos.
( ) A redução da taxa de crescimento da população contribuiu para uma redução da demanda no setor de construção civil habitacional e na indústria automobilística, o que agravou o quadro recessivo.
( ) As falências bancárias, somadas à omissão de socorro por parte do FED, reduziram o estoque de moeda da economia, o que provocou deflação e o aumento do valor nominal das dívidas.
Assinale a opção que indica a relação correta, na ordem apresentada.
Um de seus objetivos é aprofundar a integração entre as economias dos seus países membros e definir ações conjuntas para o estabelecimento de relações mais diretas com áreas estratégicas do comércio internacional, principalmente com a Ásia, por sua importância no cenário econômico atual e para os países integrantes do bloco.
Assinale a opção que identifica corretamente a iniciativa de integração descrita acima.
Adaptado de BITTENCOURT, Circe. “Procedimentos Metodológicos no Ensino de História”. In: Ensino de História: fundamentos e métodos. São Paulo: Cortez, 2011, pp. 58 e 59.
No trecho, a autora refere-se ao procedimento metodológico de
Assinale a opção que apresenta atribuições conferidas ao monarca pelo poder moderador.