Questões de Concurso
Comentadas para uega
Foram encontradas 10 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
There are lots of things you can do to save energy at home, from simple things like washing at 30 °C, saving water and recycling, to insulating your loft and cavity walls. By saving energy you’ll be reducing your home’s carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions and helping to fight climate change.
Why should you save energy? Over 40 per cent of the UK’s man-made CO₂ emissions actually come from energy we use every day – at home and when we travel. To generate that energy, we burn fossil fuels (coal, oil and gas) that produce ‘greenhouse’ gases – in particular CO₂ – which are changing our climate and damaging the environment.
The greenhouse effect CO₂ and various other gases wrap the Earth in an invisible ‘blanket’, helping to prevent heat from escaping. Without this greenhouse effect, the average temperature on Earth would be around -18 ºC, compared with the current average of around +15 ºC. This blanket of gases has remained at a constant concentration for many thousands of years. Since the Industrial Revolution began around 200 years ago, people have been burning more fossil fuels. This has increased the heating effect of the ‘blanket’, trapping more of the sun’s energy inside our atmosphere. In turn the Earth’s temperature has increased more rapidly in a shorter period of time than it has for thousands of years.
The impact of climate change People sometimes think that climate change will be a positive thing for the UK, giving us warmer summers and fewer cold winters. But hotter summers and less rain in the south and east will mean water shortages, forest fires and damage to crops and wildlife. In the north and west there could be much heavier rain and more flooding. As the polar ice caps continue to melt, rising sea levels will threaten many coastal communities. Overall, the cost to society, the environment, our health and the economy is likely to far outweigh any benefits.
Make a difference The average UK household creates around six tonnes of CO₂ every year – that’s 6,000 kg – to heat and power their home. Making your home more energy efficient could save you up to £340 a year and reduce your home’s CO₂ emissions by up to 1,500–2,000 kg. You could save even more by switching to renewable energy sources, by walking, cycling or using public transport whenever possible, and by driving more efficiently.
(Texto introdutório ao manual “A guide to energy saving in the home”, disponível em: http://www.energysavingtrust.org.uk/Resources/Publications.)
Among some actions to save energy at home, in the text we find:
1. A estrutura deve ser matricial e com holdings relacionadas, sem estruturas híbridas.
2. O ambiente deve estar aberto a novos mercados e considerar a concorrência global, a desregulamentação e a informação/tecnologia.
3. A estrutura de informação e o processo decisório apresentam um uso distribuído de tecnologia, capacidade online e facilidade de operacionalização.
4. As tarefas devem estar focadas na melhoria física da organização.
A nova lógica das organizações pressupõe:
There are lots of things you can do to save energy at home, from simple things like washing at 30 °C, saving water and
recycling, to insulating your loft and cavity walls. By saving energy you’ll be reducing your home’s carbon dioxide (
 ) emissions
) emissions and helping to fight climate change.
Why should you save energy?
Over 40 per cent of the UK’s man-made
 emissions actually come from energy we use every day – at home and when
emissions actually come from energy we use every day – at home and when we travel. To generate that energy, we burn fossil fuels (coal, oil and gas) that produce ‘greenhouse’ gases – in particular
 –
– which are changing our climate and damaging the environment.
The greenhouse effect
 and various other gases wrap the Earth in an invisible ‘blanket’, helping to prevent heat from escaping. Without this
and various other gases wrap the Earth in an invisible ‘blanket’, helping to prevent heat from escaping. Without this greenhouse effect, the average temperature on Earth would be around -18 ºC, compared with the current average of around +15
ºC. This blanket of gases has remained at a constant concentration for many thousands of years. Since the Industrial Revolution
began around 200 years ago, people have been burning more fossil fuels. This has increased the heating effect of the ‘blanket’,
trapping more of the sun’s energy inside our atmosphere. In turn the Earth’s temperature has increased more rapidly in a shorter
period of time than it has for thousands of years.
The impact of climate change
People sometimes think that climate change will be a positive thing for the UK, giving us warmer summers and fewer cold
winters. But hotter summers and less rain in the south and east will mean water shortages, forest fires and damage to crops and
wildlife. In the north and west there could be much heavier rain and more flooding. As the polar ice caps continue to melt, rising sea
levels will threaten many coastal communities. Overall, the cost to society, the environment, our health and the economy is likely to
far outweigh any benefits.
Make a difference
The average UK household creates around six tonnes of
 every year – that’s 6,000 kg – to heat and power their home.
every year – that’s 6,000 kg – to heat and power their home. Making your home more energy efficient could save you up to £340 a year and reduce your home’s
 emissions by up to 1,500–
emissions by up to 1,500–2,000 kg. You could save even more by switching to renewable energy sources, by walking, cycling or using public transport
whenever possible, and by driving more efficiently.
(Texto introdutório ao manual “A guide to energy saving in the home”, disponível em: http://www.energysavingtrust.org.uk/Resources/Publications.)
1. because we spend less money.
2. because a great part of the
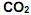 produced by humans is a result of energy used at home and when travelling.
produced by humans is a result of energy used at home and when travelling. 3. because the world does not have enough fossil fuels.
4. because fossil fuels are too expensive.
5. to fight climate change.
Based on the statements above, choose ONE alternative:
1. Se o prejuízo do credor exceder o limite dos juros moratórios previstos contratualmente, ele não poderá pretender indenização suplementar aos juros cumulada com a cobrança de cláusula penal.
2. O pagamento do valor previsto na cláusula penal compensatória sempre pode ser exigido pelo credor cumulativamente com o cumprimento, ainda que intempestivo, da prestação devida.
3. As arras confirmatórias são aquelas que indicam a conclusão do contrato e o pagamento do chamado “sinal” de negócio. Têm dupla função, vez que, ao lado da natureza confirmatória, atribuem ao contratante o direito de arrependimento, motivo pelo qual são perdidas por aquele que desiste do negócio.
4. Silente o contrato de mútuo sobre a remuneração do mutuante, presume-se que seja gratuito.
5. Salvo convenção em contrário, responde o vendedor pelos riscos inerentes à coisa até o momento em que executa sua prestação, entregando-a ao comprador ou a quem o represente.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
1. Para os fins legais, é considerada sociedade estrangeira aquela em que o sócio majoritário possua sede ou domicílio em país diverso do Brasil.
2. No regime de direito internacional privado brasileiro, a sanção da fraude à lei é a invalidade do negócio jurídico, vez que não pode surtir efeitos em território nacional.
3. De acordo com o atual regime do processo civil brasileiro, admite-se que, havendo procedimento judicial em trâmite no Brasil, desde que já efetuada a citação, é possível obstar a homologação de sentença estrangeira alegando-se litispendência.
4. No que concerne aos contratos internacionais, pode-se afirmar que é dispensável o registro e consularização de contratos celebrados em países estrangeiros para que produzam efeito, no Brasil, entre as partes.
5. O principal objeto do direito internacional privado é a uniformização legislativa entre os diferentes países, indispensável em tempos de globalização econômica.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
1. Por se tratar, a evicção, de garantia legal instituída em favor de contratante que se depara com direito de terceiro e, em razão disso, perde, total ou parcialmente, o bem objeto de contrato oneroso, não se pode admitir sua renúncia.
2. Entre os princípios fundamentais do direito contratual, encontra-se o princípio da boa-fé objetiva. Embora ele não esteja positivado, é tratado como cláusula geral pela legislação civil brasileira e deve ser respeitado pelos contratantes na formação, na execução e na conclusão do contrato.
3. Em caso de urgência e de recusa ou mora do devedor, o credor pode, independentemente de autorização judicial, mandar executar, por terceiro, o fato que constitui o objeto da prestação de obrigação de fazer, transformando-a em obrigação pecuniária.
4. Segundo o atual tratamento dispensado pela legislação civil aos vícios redibitórios, pode-se afirmar que, se o vício redibitório for oculto, a fluência do prazo decadencial para que o adquirente enjeite a coisa ou exija abatimento do preço se inicia com a ciência do vício; já se for o caso de vício redibitório aparente, o prazo se inicia a partir da data em que aconteceu a tradição da coisa a ser enjeitada.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
1. As empresas públicas são entidades que compõem a Administração Pública Indireta e se apresentam como pessoas jurídicas de direito privado, constituídas sob quaisquer das formas admitidas no direito comercial e com capital formado exclusivamente por recursos provenientes das pessoas jurídicas de direito público.
2. As sociedades de economia mista são pessoas jurídicas de direito privado, autorizadas por lei, constituídas sob a forma de sociedade anônima, cujo capital votante deve ser majoritariamente público, tendo suas atividades regidas pelo regime jurídico preponderantemente privado.
3. As autarquias são pessoas jurídicas de direito privado, criadas por lei, com autonomia administrativa para o exercício de determinadas atividades típicas do Estado, submetidas ao regime jurídico de direito público.
4. As empresas estatais, não obstante a sua personalidade jurídica de direito privado e sua sujeição ao regime jurídico de direito privado, têm sua contratação de pessoal subordinada à realização de concurso público.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
A respeito do assunto tratado no trecho acima, assinale a alternativa INCORRETA.
A respeito do assunto tratado no trecho acima, assinale a alternativa correta.