Questões de Concurso
Foram encontradas 2.059 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Supondo que V e W sejam duas variáveis contínuas e mutuamente independentes, tais que P(V > 0) = 0,3 e P(W > 0) = 0,7, julgue o próximo item.
Em relação aos eventos 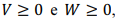 é correto afirmar
que a probabilidade condicional
é correto afirmar
que a probabilidade condicional 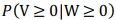 0 deve ser
superior a 0,3.
0 deve ser
superior a 0,3.
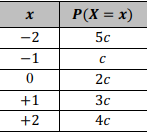
Considerando que X representa uma variável aleatória com suporte x ∈ {−2, −1, 0, +1, + 2}, cuja função de distribuição de probabilidade é dada no quadro acima, na qual c é uma constante real positiva, julgue o próximo item.
A mediana de X é igual ou superior a 1.

Considerando que X representa uma variável aleatória com suporte x ∈ {−2, −1, 0, +1, + 2}, cuja função de distribuição de probabilidade é dada no quadro acima, na qual c é uma constante real positiva, julgue o próximo item.
A média de X é igual a zero.
Essa estatística causou surpresa à instituição, que sempre acreditou que o percentual de processos de aposentadorias por invalidez indevidamente concedidas era de, aproximadamente, 10%, portanto bem abaixo dos 16% encontrados pela auditoria.
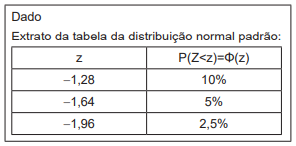
Adotando-se um nível de significância de 5%, existem motivos para se acreditar que o percentual de aposentadorias por invalidez indevidamente concedidas é maior do que 10%?
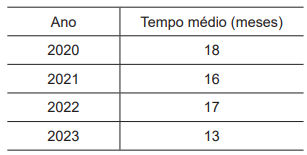
A nova gestão desse órgão mudou a dinâmica do setor, visando dar maior celeridade aos processos, e estabeleceu uma meta: reduzir o tempo médio (considerando a média dos 4 anos da Tabela) de 2 desvios padrão. Assim, o novo tempo médio de duração deverá ser o tempo médio desses 4 anos menos duas vezes o desvio padrão dos tempos médios observados nesse período.
Com isso, o valor mais próximo do tempo médio, em meses, de duração dos processos estabelecido como meta pela nova gestão é
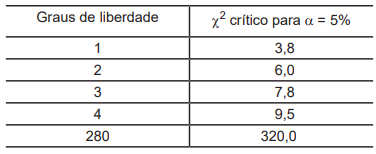
Considere a seguinte Tabela de valores críticos da estatística X2 ao nível de significância 5%:
Uma política pública visava capacitar profissionais em situação de desemprego, para facilitar-lhes a reinserção no mercado de trabalho.
Um estudo acerca da efetividade dessa política tomou uma amostra aleatória de 100 profissionais desempregados que foram capacitados no âmbito dessa política e outros 200 profissionais desempregados que, embora elegíveis para serem capacitados, não o foram.
A análise descritiva da amostra concluiu que, um ano após o término do curso, 80 profissionais dentre os 100 profissionais que foram capacitados estavam empregados e 100 profissionais dentre os 200 profissionais que não foram capacitados também estavam empregados.
Com o intuito de avaliar a efetividade dessa política pública, faz-se, dentre outras análises, um teste de independência X2 que verifica se há (ou não) relação entre ter realizado a capacitação profissional e ser reinserido no mercado de trabalho.
Ao nível de significância de 5%, conclui-se que a política pública
Tal planejamento amostral é denominado na Estatística como amostragem
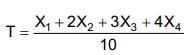
Sobre o estimador T, conclui-se que
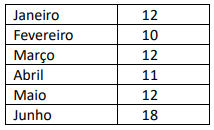
Nessa situação hipotética, a moda do conjunto de dados apresentados na tabela é igual a:
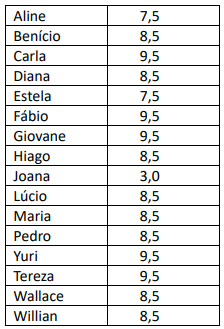
Qual a média aritmética das notas da turma, excluindo a nota de Joana que foi a pior nota?

No que se refere a mediana dos tempos dos alunos na competição universitária, assinale a alternativa correta.
Um estudo tem o objetivo de verificar se existe independência entre tipos de crimes e regiões de um país. A seguinte Tabela de Contingência mostra os números observados em uma amostra aleatória de tamanho n = 789 casos registrados nas regiões.
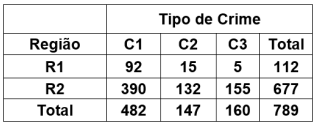
Sabe-se que 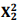 = 27,91 e P(
= 27,91 e P(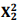 > 27,91) = 0,0000.
Então, é correto afirmar que as frequências
esperadas das células (C1, R2) e (C3, R1), o
valor-p e a decisão quanto à relação entre Tipo de
Crime e Região, do teste da hipótese de
independência entre Tipo de Crime e Região,
serão:
> 27,91) = 0,0000.
Então, é correto afirmar que as frequências
esperadas das células (C1, R2) e (C3, R1), o
valor-p e a decisão quanto à relação entre Tipo de
Crime e Região, do teste da hipótese de
independência entre Tipo de Crime e Região,
serão:
A forma geral de representar uma classe de séries temporais não estacionárias é o modelo utorregressivo integrado médias móveis de ordem (p, d, q), ou seja, ARIMA(p, d, q), em que p é o grau do polinômio aracterístico da parte autorregressiva Φ(B), q é o grau do polinômio característico da parte média móveis θ(B) e d é o grau de diferenciação ▽d, ou seja, Φ(B)▽dZt = θ(B)at em que ⊽dZt = ωt. Desse modo, tem-se Φ(B)ωt = θ(B)at que é um modelo ARMA(p, q).
A uma determinada série temporal, ajustou-se um
modelo da classe ARIMA(p, d, q), e os resultados
do ajuste estão expostos a seguir:
Modelo ARIMA ajustado à série temporal
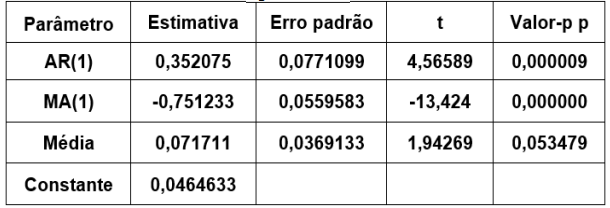
Então, é correto afirmar, com aproximação de três
(03) casas decimais, que
Considere a seguinte série temporal:
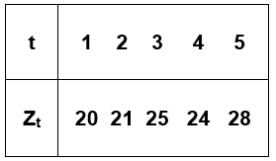
É correto afirmar que a média, a variância e a
autocorrelação de defasagem 2 dessa série
temporal, assumindo o estimador de máxima
verossimilhança para a variância, são,
respectivamente:
Se a variável aleatória X tem distribuição normal
com média μ e variância σ2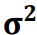
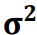 , ou seja, X ⁓ N(μ, σ2), s2 =
, ou seja, X ⁓ N(μ, σ2), s2 = 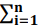 (xi–x̄)2/n–1 (variância amostral) é a estimativa
de σ2 com base em uma amostra com n
observações, [x1, x2, ... , xn]. Assim, a variável T = X – μ/s tem distribuição t de Student com n – 1
graus de liberdade, ou seja, T ~ tn-1. Nesse
caso, sabendo que P(T ≤ 2) = 0,968027 e P(T ≥ -2) = 0,031973, é correto afirmar que
(xi–x̄)2/n–1 (variância amostral) é a estimativa
de σ2 com base em uma amostra com n
observações, [x1, x2, ... , xn]. Assim, a variável T = X – μ/s tem distribuição t de Student com n – 1
graus de liberdade, ou seja, T ~ tn-1. Nesse
caso, sabendo que P(T ≤ 2) = 0,968027 e P(T ≥ -2) = 0,031973, é correto afirmar que
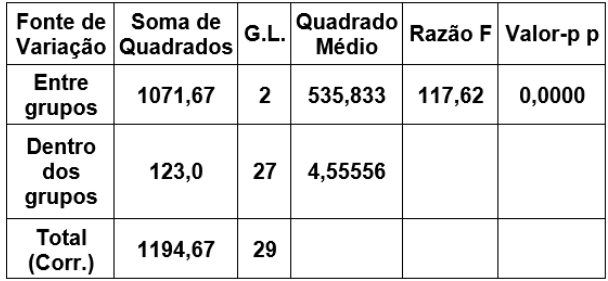
Um estatístico conduziu um experimento para verificar se existem diferenças estatisticamente significativas entre os resultados quantitativos de três procedimentos aplicados em amostras independentes. Os resultados obtidos com o experimento são:
Tabela da Análise da Variância – ANOVA
Teste de Levene para hipótese de variâncias iguais

Teste de Normalidade para os resíduos da ANOVA
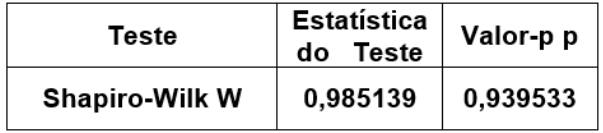
Teste de Kruskal-Wallis para hipótese de medianas iguais
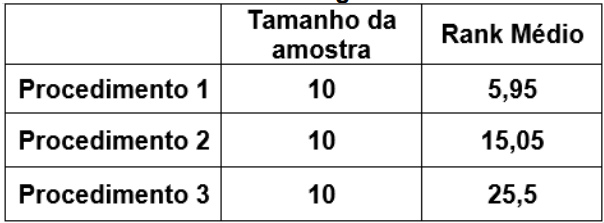
Estatística do Teste = 24,8078 Valor-p p =
0,0000041025
Então, é correto afirmar, em relação ao nível de
significância de 5%, que
O estatístico que trata da análise de dados
referentes à Justiça Federal necessita conduzir
um estudo que requer informações sobre
determinada característica quantitativa, X, dos
processados em determinada Vara Federal. Um
dos objetivos é construir um intervalo de 95% de
confiança para o valor médio da característica
quantitativa do grupo de processados, com erro
de amostragem ou precisão de 0,5 σ, meio
desvio-padrão. Ele tomou, então, uma amostra
aleatória piloto de tamanho n0 = 5 que forneceu as
seguintes estatísticas amostrais, média e
variância, para a característica: x̄0 = 127,6 e S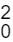 = 1290,8. A respeito das informações
anteriores, sabe-se que é possível assumir o
modelo de distribuição normal para a
característica quantitativa do grupo de
processados, que é finito com N = 2000 indivíduos
e com variância desconhecida. Assim,
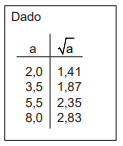
conhecendo o escore da distribuição t de t4 (0,975) = 2,78, é correto afirmar que o tamanho
definitivo da amostra n é
= 1290,8. A respeito das informações
anteriores, sabe-se que é possível assumir o
modelo de distribuição normal para a
característica quantitativa do grupo de
processados, que é finito com N = 2000 indivíduos
e com variância desconhecida. Assim,
conhecendo o escore da distribuição t de t4 (0,975) = 2,78, é correto afirmar que o tamanho
definitivo da amostra n é
Suponha as variáveis aleatórias independentes X
com distribuição Qui-quadrado com v = 5 graus
de liberdade e Y com distribuição Gama com
parâmetros α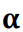
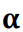
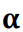 = 2 e β = 5. Então, a esperança e a
variância da variável aleatória W = X + Y são,
respectivamente,
= 2 e β = 5. Então, a esperança e a
variância da variável aleatória W = X + Y são,
respectivamente,
Considere o vetor aleatório X'= [X1 X2] cuja matriz
de covariância é Σ = 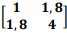 . Então, é correto
afirmar que a matriz de correlação P do vetor é
. Então, é correto
afirmar que a matriz de correlação P do vetor é
Sendo a sequência de n ensaios binomiais
independentes, tendo a mesma probabilidade 
 θ de
“sucesso” em cada ensaio, se Sn = X1 + X2 + ... +
Xn é o número de sucessos nos n primeiros
ensaios, então Sn /n
θ de
“sucesso” em cada ensaio, se Sn = X1 + X2 + ... +
Xn é o número de sucessos nos n primeiros
ensaios, então Sn /n 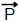 θ, ou seja, Sn /n converge em
probabilidade para
θ, ou seja, Sn /n converge em
probabilidade para 
 θ. O enunciado da Lei dos
Grandes Números a que se exprime esse
resultado é a Lei dos Grandes Números de
θ. O enunciado da Lei dos
Grandes Números a que se exprime esse
resultado é a Lei dos Grandes Números de