Questões de Concurso
Foram encontradas 2.072 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Text I
Brazil: Platform for growth
By Joe Leahy
On the Cidade de Angra dos Reis oil platform,
surrounded by the deep blue South Atlantic, a
Petrobras engineer turns on a tap and watches black
liquid flow into a beaker.
5____It looks and smells like ordinary crude oil.
Nevertheless, for Brazil, this represents something
much more spectacular. Pumped by the national oil
company from “pre-salt” deposits – so-called because
they lie beneath 2,000m of salt – 300km off the coast
10 of Rio de Janeiro, it is some of the first commercial
oil to flow from the country’s giant new deepwater
discoveries.
Already estimated to contain 50bn barrels, and
with much of the area still to be fully explored, the
15 fields contain the world’s largest known offshore oil
deposits. In one step, Brazil could jump up the world
rankings of national oil reserves and production, from
15th to fifth. So great are the discoveries, and the
investment required to exploit them, that they have
20 the potential to transform the country – for good or for ill.
Having seen out booms and busts before,
Brazilians are hoping that this time “the country
of the future” will at last realise its full economic
potential. The hope is that the discoveries will provide
25 a nation already rich in renewable energy with an
embarrassment of resources with which to pursue the
goal of becoming a US of the south.
The danger for Brazil, if it fails to manage this
windfall wisely, is of falling victim to “Dutch disease”.
30 The economic malaise is named after the Netherlands
in the 1970s, where the manufacturing sector withered
after its currency strengthened on the back of a large
gas field discovery combined with rising energy prices.
Even worse, Brazil could suffer a more severe
35 form of the disease, the “oil curse”, whereby nations
rich in natural resources – Nigeria and Venezuela, for
example – grow addicted to the money that flows from
them.
Petrobras chief executive says neither the
40 company nor the country’s oil industry has so far
been big enough to become a government cash cow.
But with the new discoveries, which stretch across an
800km belt off the coast of south-eastern Brazil, this is
going to change. The oil industry could grow from about
45 10 per cent of GDP to up to 25 per cent in the coming
decades, analysts say. To curb any negative effects,
Brazil is trying to support domestic manufacturing
by increasing “local content” requirements in the oil
industry.
50____Without a “firm local content policy”, says
Petrobras CEO, Dutch disease and the oil curse will
take hold. However, “if we have a firm and successful
local content policy, no – because other sectors in the
economy are going to grow as fast as Petrobras”.
55___The other long-term dividend Brazil is seeking
from the discoveries is in research and development
(R&D). Extracting oil from beneath a layer of salt at
great depth, hundreds of kilometres from the coast, is
so challenging that Brazilian engineers see it as a new
60 frontier. If they can perfect this, they can lead the way
in other markets with similar geology, such as Africa.
For its part, Petrobras is spending $800m-$900m
a year over the next five years on R&D, and has
invested $700m in the expansion of its research
65 centre.
Ultimately, Brazil’s ability to avoid Dutch disease
will depend not just on how the money from the oil
is spent. The country is the world’s second biggest
exporter of iron ore. It is the largest exporter of beef.
70 It is also the biggest producer of sugar, coffee and
orange juice, and the second-largest producer of soya
beans.
Exports of these commodities are already driving
up the exchange rate before the new oil fields have
75 fully come on stream, making it harder for Brazilian
exporters of manufactured goods. Industrial production
has faltered in recent months, with manufacturers
blaming the trend on a flood of cheap Chinese-made
imports.
80____“Brazil has everything that China doesn’t and it’s
natural that, as China continues to grow, it’s just going
to be starved for those resources,” says Harvard’s
Prof Rogoff. “At some level Brazil doesn’t just want
to be exporting natural resources – it wants a more
85 diversified economy. There are going to be some
rising tensions over that.”
Adapted from Financial Times - March 15 2011 22:54. Available in:
<http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/fa11320c-4f48-11e0-9038-00144feab49a,_i_email=y.html>
Retrieved on: June 17, 2011.
Text II
Off the Deep End in Brazil
Gerald Herbert
With crude still hemorrhaging into the Gulf of
Mexico, deep-water drilling might seem taboo just
now. In fact, extreme oil will likely be the new normal.
Despite the gulf tragedy, the quest for oil and gas in
5 the most difficult places on the planet is just getting
underway. Prospecting proceeds apace in the ultra-
deepwater reserves off the coasts of Ghana and
Nigeria, the sulfur-laden depths of the Black Sea, and
the tar sands of Venezuela’s Orinoco Basin. Brazil’s
10 Petrobras, which already controls a quarter of global
deepwater operations, is just starting to plumb its 9 to
15 billion barrels of proven reserves buried some four
miles below the Atlantic.
The reason is simple: after a century and a
15 half of breakneck oil prospecting, the easy stuff is
history. Blistering growth in emerging nations has
turned the power grid upside down. India and China
will consume 28 percent of global energy by 2030,
triple the juice they required in 1990. China is set to
20 overtake the U.S. in energy consumption by 2014.
And now that the Great Recession is easing, the
earth’s hoard of conventional oil is waning even
faster. The International Energy Agency reckons the
world will need to find 65 million additional barrels a
25 day by 2030. If the U.S. offshore-drilling moratorium
drags on, look for idled rigs heading to other shores.
Available in:
<http://www.newsweek.com/2010/06/13/off-the-deep-end-in-brazil.html>
Retrieved on: June 19, 2011.
Comparing Texts I and II,
Text I
Brazil: Platform for growth
By Joe Leahy
On the Cidade de Angra dos Reis oil platform,
surrounded by the deep blue South Atlantic, a
Petrobras engineer turns on a tap and watches black
liquid flow into a beaker.
5____It looks and smells like ordinary crude oil.
Nevertheless, for Brazil, this represents something
much more spectacular. Pumped by the national oil
company from “pre-salt” deposits – so-called because
they lie beneath 2,000m of salt – 300km off the coast
10 of Rio de Janeiro, it is some of the first commercial
oil to flow from the country’s giant new deepwater
discoveries.
Already estimated to contain 50bn barrels, and
with much of the area still to be fully explored, the
15 fields contain the world’s largest known offshore oil
deposits. In one step, Brazil could jump up the world
rankings of national oil reserves and production, from
15th to fifth. So great are the discoveries, and the
investment required to exploit them, that they have
20 the potential to transform the country – for good or for ill.
Having seen out booms and busts before,
Brazilians are hoping that this time “the country
of the future” will at last realise its full economic
potential. The hope is that the discoveries will provide
25 a nation already rich in renewable energy with an
embarrassment of resources with which to pursue the
goal of becoming a US of the south.
The danger for Brazil, if it fails to manage this
windfall wisely, is of falling victim to “Dutch disease”.
30 The economic malaise is named after the Netherlands
in the 1970s, where the manufacturing sector withered
after its currency strengthened on the back of a large
gas field discovery combined with rising energy prices.
Even worse, Brazil could suffer a more severe
35 form of the disease, the “oil curse”, whereby nations
rich in natural resources – Nigeria and Venezuela, for
example – grow addicted to the money that flows from
them.
Petrobras chief executive says neither the
40 company nor the country’s oil industry has so far
been big enough to become a government cash cow.
But with the new discoveries, which stretch across an
800km belt off the coast of south-eastern Brazil, this is
going to change. The oil industry could grow from about
45 10 per cent of GDP to up to 25 per cent in the coming
decades, analysts say. To curb any negative effects,
Brazil is trying to support domestic manufacturing
by increasing “local content” requirements in the oil
industry.
50____Without a “firm local content policy”, says
Petrobras CEO, Dutch disease and the oil curse will
take hold. However, “if we have a firm and successful
local content policy, no – because other sectors in the
economy are going to grow as fast as Petrobras”.
55___The other long-term dividend Brazil is seeking
from the discoveries is in research and development
(R&D). Extracting oil from beneath a layer of salt at
great depth, hundreds of kilometres from the coast, is
so challenging that Brazilian engineers see it as a new
60 frontier. If they can perfect this, they can lead the way
in other markets with similar geology, such as Africa.
For its part, Petrobras is spending $800m-$900m
a year over the next five years on R&D, and has
invested $700m in the expansion of its research
65 centre.
Ultimately, Brazil’s ability to avoid Dutch disease
will depend not just on how the money from the oil
is spent. The country is the world’s second biggest
exporter of iron ore. It is the largest exporter of beef.
70 It is also the biggest producer of sugar, coffee and
orange juice, and the second-largest producer of soya
beans.
Exports of these commodities are already driving
up the exchange rate before the new oil fields have
75 fully come on stream, making it harder for Brazilian
exporters of manufactured goods. Industrial production
has faltered in recent months, with manufacturers
blaming the trend on a flood of cheap Chinese-made
imports.
80____“Brazil has everything that China doesn’t and it’s
natural that, as China continues to grow, it’s just going
to be starved for those resources,” says Harvard’s
Prof Rogoff. “At some level Brazil doesn’t just want
to be exporting natural resources – it wants a more
85 diversified economy. There are going to be some
rising tensions over that.”
Adapted from Financial Times - March 15 2011 22:54. Available in:
<http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/fa11320c-4f48-11e0-9038-00144feab49a,_i_email=y.html>
Retrieved on: June 17, 2011.
The boldfaced item is synonymous with the expression in parentheses in
Text I
Brazil: Platform for growth
By Joe Leahy
On the Cidade de Angra dos Reis oil platform,
surrounded by the deep blue South Atlantic, a
Petrobras engineer turns on a tap and watches black
liquid flow into a beaker.
5____It looks and smells like ordinary crude oil.
Nevertheless, for Brazil, this represents something
much more spectacular. Pumped by the national oil
company from “pre-salt” deposits – so-called because
they lie beneath 2,000m of salt – 300km off the coast
10 of Rio de Janeiro, it is some of the first commercial
oil to flow from the country’s giant new deepwater
discoveries.
Already estimated to contain 50bn barrels, and
with much of the area still to be fully explored, the
15 fields contain the world’s largest known offshore oil
deposits. In one step, Brazil could jump up the world
rankings of national oil reserves and production, from
15th to fifth. So great are the discoveries, and the
investment required to exploit them, that they have
20 the potential to transform the country – for good or for ill.
Having seen out booms and busts before,
Brazilians are hoping that this time “the country
of the future” will at last realise its full economic
potential. The hope is that the discoveries will provide
25 a nation already rich in renewable energy with an
embarrassment of resources with which to pursue the
goal of becoming a US of the south.
The danger for Brazil, if it fails to manage this
windfall wisely, is of falling victim to “Dutch disease”.
30 The economic malaise is named after the Netherlands
in the 1970s, where the manufacturing sector withered
after its currency strengthened on the back of a large
gas field discovery combined with rising energy prices.
Even worse, Brazil could suffer a more severe
35 form of the disease, the “oil curse”, whereby nations
rich in natural resources – Nigeria and Venezuela, for
example – grow addicted to the money that flows from
them.
Petrobras chief executive says neither the
40 company nor the country’s oil industry has so far
been big enough to become a government cash cow.
But with the new discoveries, which stretch across an
800km belt off the coast of south-eastern Brazil, this is
going to change. The oil industry could grow from about
45 10 per cent of GDP to up to 25 per cent in the coming
decades, analysts say. To curb any negative effects,
Brazil is trying to support domestic manufacturing
by increasing “local content” requirements in the oil
industry.
50____Without a “firm local content policy”, says
Petrobras CEO, Dutch disease and the oil curse will
take hold. However, “if we have a firm and successful
local content policy, no – because other sectors in the
economy are going to grow as fast as Petrobras”.
55___The other long-term dividend Brazil is seeking
from the discoveries is in research and development
(R&D). Extracting oil from beneath a layer of salt at
great depth, hundreds of kilometres from the coast, is
so challenging that Brazilian engineers see it as a new
60 frontier. If they can perfect this, they can lead the way
in other markets with similar geology, such as Africa.
For its part, Petrobras is spending $800m-$900m
a year over the next five years on R&D, and has
invested $700m in the expansion of its research
65 centre.
Ultimately, Brazil’s ability to avoid Dutch disease
will depend not just on how the money from the oil
is spent. The country is the world’s second biggest
exporter of iron ore. It is the largest exporter of beef.
70 It is also the biggest producer of sugar, coffee and
orange juice, and the second-largest producer of soya
beans.
Exports of these commodities are already driving
up the exchange rate before the new oil fields have
75 fully come on stream, making it harder for Brazilian
exporters of manufactured goods. Industrial production
has faltered in recent months, with manufacturers
blaming the trend on a flood of cheap Chinese-made
imports.
80____“Brazil has everything that China doesn’t and it’s
natural that, as China continues to grow, it’s just going
to be starved for those resources,” says Harvard’s
Prof Rogoff. “At some level Brazil doesn’t just want
to be exporting natural resources – it wants a more
85 diversified economy. There are going to be some
rising tensions over that.”
Adapted from Financial Times - March 15 2011 22:54. Available in:
<http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/fa11320c-4f48-11e0-9038-00144feab49a,_i_email=y.html>
Retrieved on: June 17, 2011.
In “Without a ‘firm local content policy’, says Petrobras CEO, Dutch disease and the oil curse will take hold.” (lines 50-52), “take hold” means to
Text I
Brazil: Platform for growth
By Joe Leahy
On the Cidade de Angra dos Reis oil platform,
surrounded by the deep blue South Atlantic, a
Petrobras engineer turns on a tap and watches black
liquid flow into a beaker.
5____It looks and smells like ordinary crude oil.
Nevertheless, for Brazil, this represents something
much more spectacular. Pumped by the national oil
company from “pre-salt” deposits – so-called because
they lie beneath 2,000m of salt – 300km off the coast
10 of Rio de Janeiro, it is some of the first commercial
oil to flow from the country’s giant new deepwater
discoveries.
Already estimated to contain 50bn barrels, and
with much of the area still to be fully explored, the
15 fields contain the world’s largest known offshore oil
deposits. In one step, Brazil could jump up the world
rankings of national oil reserves and production, from
15th to fifth. So great are the discoveries, and the
investment required to exploit them, that they have
20 the potential to transform the country – for good or for ill.
Having seen out booms and busts before,
Brazilians are hoping that this time “the country
of the future” will at last realise its full economic
potential. The hope is that the discoveries will provide
25 a nation already rich in renewable energy with an
embarrassment of resources with which to pursue the
goal of becoming a US of the south.
The danger for Brazil, if it fails to manage this
windfall wisely, is of falling victim to “Dutch disease”.
30 The economic malaise is named after the Netherlands
in the 1970s, where the manufacturing sector withered
after its currency strengthened on the back of a large
gas field discovery combined with rising energy prices.
Even worse, Brazil could suffer a more severe
35 form of the disease, the “oil curse”, whereby nations
rich in natural resources – Nigeria and Venezuela, for
example – grow addicted to the money that flows from
them.
Petrobras chief executive says neither the
40 company nor the country’s oil industry has so far
been big enough to become a government cash cow.
But with the new discoveries, which stretch across an
800km belt off the coast of south-eastern Brazil, this is
going to change. The oil industry could grow from about
45 10 per cent of GDP to up to 25 per cent in the coming
decades, analysts say. To curb any negative effects,
Brazil is trying to support domestic manufacturing
by increasing “local content” requirements in the oil
industry.
50____Without a “firm local content policy”, says
Petrobras CEO, Dutch disease and the oil curse will
take hold. However, “if we have a firm and successful
local content policy, no – because other sectors in the
economy are going to grow as fast as Petrobras”.
55___The other long-term dividend Brazil is seeking
from the discoveries is in research and development
(R&D). Extracting oil from beneath a layer of salt at
great depth, hundreds of kilometres from the coast, is
so challenging that Brazilian engineers see it as a new
60 frontier. If they can perfect this, they can lead the way
in other markets with similar geology, such as Africa.
For its part, Petrobras is spending $800m-$900m
a year over the next five years on R&D, and has
invested $700m in the expansion of its research
65 centre.
Ultimately, Brazil’s ability to avoid Dutch disease
will depend not just on how the money from the oil
is spent. The country is the world’s second biggest
exporter of iron ore. It is the largest exporter of beef.
70 It is also the biggest producer of sugar, coffee and
orange juice, and the second-largest producer of soya
beans.
Exports of these commodities are already driving
up the exchange rate before the new oil fields have
75 fully come on stream, making it harder for Brazilian
exporters of manufactured goods. Industrial production
has faltered in recent months, with manufacturers
blaming the trend on a flood of cheap Chinese-made
imports.
80____“Brazil has everything that China doesn’t and it’s
natural that, as China continues to grow, it’s just going
to be starved for those resources,” says Harvard’s
Prof Rogoff. “At some level Brazil doesn’t just want
to be exporting natural resources – it wants a more
85 diversified economy. There are going to be some
rising tensions over that.”
Adapted from Financial Times - March 15 2011 22:54. Available in:
<http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/fa11320c-4f48-11e0-9038-00144feab49a,_i_email=y.html>
Retrieved on: June 17, 2011.
Concerning the referent to the pronoun it, in the fragments below,
Text I
Brazil: Platform for growth
By Joe Leahy
On the Cidade de Angra dos Reis oil platform,
surrounded by the deep blue South Atlantic, a
Petrobras engineer turns on a tap and watches black
liquid flow into a beaker.
5____It looks and smells like ordinary crude oil.
Nevertheless, for Brazil, this represents something
much more spectacular. Pumped by the national oil
company from “pre-salt” deposits – so-called because
they lie beneath 2,000m of salt – 300km off the coast
10 of Rio de Janeiro, it is some of the first commercial
oil to flow from the country’s giant new deepwater
discoveries.
Already estimated to contain 50bn barrels, and
with much of the area still to be fully explored, the
15 fields contain the world’s largest known offshore oil
deposits. In one step, Brazil could jump up the world
rankings of national oil reserves and production, from
15th to fifth. So great are the discoveries, and the
investment required to exploit them, that they have
20 the potential to transform the country – for good or for ill.
Having seen out booms and busts before,
Brazilians are hoping that this time “the country
of the future” will at last realise its full economic
potential. The hope is that the discoveries will provide
25 a nation already rich in renewable energy with an
embarrassment of resources with which to pursue the
goal of becoming a US of the south.
The danger for Brazil, if it fails to manage this
windfall wisely, is of falling victim to “Dutch disease”.
30 The economic malaise is named after the Netherlands
in the 1970s, where the manufacturing sector withered
after its currency strengthened on the back of a large
gas field discovery combined with rising energy prices.
Even worse, Brazil could suffer a more severe
35 form of the disease, the “oil curse”, whereby nations
rich in natural resources – Nigeria and Venezuela, for
example – grow addicted to the money that flows from
them.
Petrobras chief executive says neither the
40 company nor the country’s oil industry has so far
been big enough to become a government cash cow.
But with the new discoveries, which stretch across an
800km belt off the coast of south-eastern Brazil, this is
going to change. The oil industry could grow from about
45 10 per cent of GDP to up to 25 per cent in the coming
decades, analysts say. To curb any negative effects,
Brazil is trying to support domestic manufacturing
by increasing “local content” requirements in the oil
industry.
50____Without a “firm local content policy”, says
Petrobras CEO, Dutch disease and the oil curse will
take hold. However, “if we have a firm and successful
local content policy, no – because other sectors in the
economy are going to grow as fast as Petrobras”.
55___The other long-term dividend Brazil is seeking
from the discoveries is in research and development
(R&D). Extracting oil from beneath a layer of salt at
great depth, hundreds of kilometres from the coast, is
so challenging that Brazilian engineers see it as a new
60 frontier. If they can perfect this, they can lead the way
in other markets with similar geology, such as Africa.
For its part, Petrobras is spending $800m-$900m
a year over the next five years on R&D, and has
invested $700m in the expansion of its research
65 centre.
Ultimately, Brazil’s ability to avoid Dutch disease
will depend not just on how the money from the oil
is spent. The country is the world’s second biggest
exporter of iron ore. It is the largest exporter of beef.
70 It is also the biggest producer of sugar, coffee and
orange juice, and the second-largest producer of soya
beans.
Exports of these commodities are already driving
up the exchange rate before the new oil fields have
75 fully come on stream, making it harder for Brazilian
exporters of manufactured goods. Industrial production
has faltered in recent months, with manufacturers
blaming the trend on a flood of cheap Chinese-made
imports.
80____“Brazil has everything that China doesn’t and it’s
natural that, as China continues to grow, it’s just going
to be starved for those resources,” says Harvard’s
Prof Rogoff. “At some level Brazil doesn’t just want
to be exporting natural resources – it wants a more
85 diversified economy. There are going to be some
rising tensions over that.”
Adapted from Financial Times - March 15 2011 22:54. Available in:
<http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/fa11320c-4f48-11e0-9038-00144feab49a,_i_email=y.html>
Retrieved on: June 17, 2011.
Based on the meanings in Text I, the two words are antonymous in
Text I
Brazil: Platform for growth
By Joe Leahy
On the Cidade de Angra dos Reis oil platform,
surrounded by the deep blue South Atlantic, a
Petrobras engineer turns on a tap and watches black
liquid flow into a beaker.
5____It looks and smells like ordinary crude oil.
Nevertheless, for Brazil, this represents something
much more spectacular. Pumped by the national oil
company from “pre-salt” deposits – so-called because
they lie beneath 2,000m of salt – 300km off the coast
10 of Rio de Janeiro, it is some of the first commercial
oil to flow from the country’s giant new deepwater
discoveries.
Already estimated to contain 50bn barrels, and
with much of the area still to be fully explored, the
15 fields contain the world’s largest known offshore oil
deposits. In one step, Brazil could jump up the world
rankings of national oil reserves and production, from
15th to fifth. So great are the discoveries, and the
investment required to exploit them, that they have
20 the potential to transform the country – for good or for ill.
Having seen out booms and busts before,
Brazilians are hoping that this time “the country
of the future” will at last realise its full economic
potential. The hope is that the discoveries will provide
25 a nation already rich in renewable energy with an
embarrassment of resources with which to pursue the
goal of becoming a US of the south.
The danger for Brazil, if it fails to manage this
windfall wisely, is of falling victim to “Dutch disease”.
30 The economic malaise is named after the Netherlands
in the 1970s, where the manufacturing sector withered
after its currency strengthened on the back of a large
gas field discovery combined with rising energy prices.
Even worse, Brazil could suffer a more severe
35 form of the disease, the “oil curse”, whereby nations
rich in natural resources – Nigeria and Venezuela, for
example – grow addicted to the money that flows from
them.
Petrobras chief executive says neither the
40 company nor the country’s oil industry has so far
been big enough to become a government cash cow.
But with the new discoveries, which stretch across an
800km belt off the coast of south-eastern Brazil, this is
going to change. The oil industry could grow from about
45 10 per cent of GDP to up to 25 per cent in the coming
decades, analysts say. To curb any negative effects,
Brazil is trying to support domestic manufacturing
by increasing “local content” requirements in the oil
industry.
50____Without a “firm local content policy”, says
Petrobras CEO, Dutch disease and the oil curse will
take hold. However, “if we have a firm and successful
local content policy, no – because other sectors in the
economy are going to grow as fast as Petrobras”.
55___The other long-term dividend Brazil is seeking
from the discoveries is in research and development
(R&D). Extracting oil from beneath a layer of salt at
great depth, hundreds of kilometres from the coast, is
so challenging that Brazilian engineers see it as a new
60 frontier. If they can perfect this, they can lead the way
in other markets with similar geology, such as Africa.
For its part, Petrobras is spending $800m-$900m
a year over the next five years on R&D, and has
invested $700m in the expansion of its research
65 centre.
Ultimately, Brazil’s ability to avoid Dutch disease
will depend not just on how the money from the oil
is spent. The country is the world’s second biggest
exporter of iron ore. It is the largest exporter of beef.
70 It is also the biggest producer of sugar, coffee and
orange juice, and the second-largest producer of soya
beans.
Exports of these commodities are already driving
up the exchange rate before the new oil fields have
75 fully come on stream, making it harder for Brazilian
exporters of manufactured goods. Industrial production
has faltered in recent months, with manufacturers
blaming the trend on a flood of cheap Chinese-made
imports.
80____“Brazil has everything that China doesn’t and it’s
natural that, as China continues to grow, it’s just going
to be starved for those resources,” says Harvard’s
Prof Rogoff. “At some level Brazil doesn’t just want
to be exporting natural resources – it wants a more
85 diversified economy. There are going to be some
rising tensions over that.”
Adapted from Financial Times - March 15 2011 22:54. Available in:
<http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/fa11320c-4f48-11e0-9038-00144feab49a,_i_email=y.html>
Retrieved on: June 17, 2011.
According to paragraphs 9 and 10 (lines 55-65), investing in R&D
Text I
Brazil: Platform for growth
By Joe Leahy
On the Cidade de Angra dos Reis oil platform,
surrounded by the deep blue South Atlantic, a
Petrobras engineer turns on a tap and watches black
liquid flow into a beaker.
5____It looks and smells like ordinary crude oil.
Nevertheless, for Brazil, this represents something
much more spectacular. Pumped by the national oil
company from “pre-salt” deposits – so-called because
they lie beneath 2,000m of salt – 300km off the coast
10 of Rio de Janeiro, it is some of the first commercial
oil to flow from the country’s giant new deepwater
discoveries.
Already estimated to contain 50bn barrels, and
with much of the area still to be fully explored, the
15 fields contain the world’s largest known offshore oil
deposits. In one step, Brazil could jump up the world
rankings of national oil reserves and production, from
15th to fifth. So great are the discoveries, and the
investment required to exploit them, that they have
20 the potential to transform the country – for good or for ill.
Having seen out booms and busts before,
Brazilians are hoping that this time “the country
of the future” will at last realise its full economic
potential. The hope is that the discoveries will provide
25 a nation already rich in renewable energy with an
embarrassment of resources with which to pursue the
goal of becoming a US of the south.
The danger for Brazil, if it fails to manage this
windfall wisely, is of falling victim to “Dutch disease”.
30 The economic malaise is named after the Netherlands
in the 1970s, where the manufacturing sector withered
after its currency strengthened on the back of a large
gas field discovery combined with rising energy prices.
Even worse, Brazil could suffer a more severe
35 form of the disease, the “oil curse”, whereby nations
rich in natural resources – Nigeria and Venezuela, for
example – grow addicted to the money that flows from
them.
Petrobras chief executive says neither the
40 company nor the country’s oil industry has so far
been big enough to become a government cash cow.
But with the new discoveries, which stretch across an
800km belt off the coast of south-eastern Brazil, this is
going to change. The oil industry could grow from about
45 10 per cent of GDP to up to 25 per cent in the coming
decades, analysts say. To curb any negative effects,
Brazil is trying to support domestic manufacturing
by increasing “local content” requirements in the oil
industry.
50____Without a “firm local content policy”, says
Petrobras CEO, Dutch disease and the oil curse will
take hold. However, “if we have a firm and successful
local content policy, no – because other sectors in the
economy are going to grow as fast as Petrobras”.
55___The other long-term dividend Brazil is seeking
from the discoveries is in research and development
(R&D). Extracting oil from beneath a layer of salt at
great depth, hundreds of kilometres from the coast, is
so challenging that Brazilian engineers see it as a new
60 frontier. If they can perfect this, they can lead the way
in other markets with similar geology, such as Africa.
For its part, Petrobras is spending $800m-$900m
a year over the next five years on R&D, and has
invested $700m in the expansion of its research
65 centre.
Ultimately, Brazil’s ability to avoid Dutch disease
will depend not just on how the money from the oil
is spent. The country is the world’s second biggest
exporter of iron ore. It is the largest exporter of beef.
70 It is also the biggest producer of sugar, coffee and
orange juice, and the second-largest producer of soya
beans.
Exports of these commodities are already driving
up the exchange rate before the new oil fields have
75 fully come on stream, making it harder for Brazilian
exporters of manufactured goods. Industrial production
has faltered in recent months, with manufacturers
blaming the trend on a flood of cheap Chinese-made
imports.
80____“Brazil has everything that China doesn’t and it’s
natural that, as China continues to grow, it’s just going
to be starved for those resources,” says Harvard’s
Prof Rogoff. “At some level Brazil doesn’t just want
to be exporting natural resources – it wants a more
85 diversified economy. There are going to be some
rising tensions over that.”
Adapted from Financial Times - March 15 2011 22:54. Available in:
<http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/fa11320c-4f48-11e0-9038-00144feab49a,_i_email=y.html>
Retrieved on: June 17, 2011.
According to paragraphs 5 and 6 (lines 28-38), Dutch disease is a
Text I
Brazil: Platform for growth
By Joe Leahy
On the Cidade de Angra dos Reis oil platform,
surrounded by the deep blue South Atlantic, a
Petrobras engineer turns on a tap and watches black
liquid flow into a beaker.
5____It looks and smells like ordinary crude oil.
Nevertheless, for Brazil, this represents something
much more spectacular. Pumped by the national oil
company from “pre-salt” deposits – so-called because
they lie beneath 2,000m of salt – 300km off the coast
10 of Rio de Janeiro, it is some of the first commercial
oil to flow from the country’s giant new deepwater
discoveries.
Already estimated to contain 50bn barrels, and
with much of the area still to be fully explored, the
15 fields contain the world’s largest known offshore oil
deposits. In one step, Brazil could jump up the world
rankings of national oil reserves and production, from
15th to fifth. So great are the discoveries, and the
investment required to exploit them, that they have
20 the potential to transform the country – for good or for ill.
Having seen out booms and busts before,
Brazilians are hoping that this time “the country
of the future” will at last realise its full economic
potential. The hope is that the discoveries will provide
25 a nation already rich in renewable energy with an
embarrassment of resources with which to pursue the
goal of becoming a US of the south.
The danger for Brazil, if it fails to manage this
windfall wisely, is of falling victim to “Dutch disease”.
30 The economic malaise is named after the Netherlands
in the 1970s, where the manufacturing sector withered
after its currency strengthened on the back of a large
gas field discovery combined with rising energy prices.
Even worse, Brazil could suffer a more severe
35 form of the disease, the “oil curse”, whereby nations
rich in natural resources – Nigeria and Venezuela, for
example – grow addicted to the money that flows from
them.
Petrobras chief executive says neither the
40 company nor the country’s oil industry has so far
been big enough to become a government cash cow.
But with the new discoveries, which stretch across an
800km belt off the coast of south-eastern Brazil, this is
going to change. The oil industry could grow from about
45 10 per cent of GDP to up to 25 per cent in the coming
decades, analysts say. To curb any negative effects,
Brazil is trying to support domestic manufacturing
by increasing “local content” requirements in the oil
industry.
50____Without a “firm local content policy”, says
Petrobras CEO, Dutch disease and the oil curse will
take hold. However, “if we have a firm and successful
local content policy, no – because other sectors in the
economy are going to grow as fast as Petrobras”.
55___The other long-term dividend Brazil is seeking
from the discoveries is in research and development
(R&D). Extracting oil from beneath a layer of salt at
great depth, hundreds of kilometres from the coast, is
so challenging that Brazilian engineers see it as a new
60 frontier. If they can perfect this, they can lead the way
in other markets with similar geology, such as Africa.
For its part, Petrobras is spending $800m-$900m
a year over the next five years on R&D, and has
invested $700m in the expansion of its research
65 centre.
Ultimately, Brazil’s ability to avoid Dutch disease
will depend not just on how the money from the oil
is spent. The country is the world’s second biggest
exporter of iron ore. It is the largest exporter of beef.
70 It is also the biggest producer of sugar, coffee and
orange juice, and the second-largest producer of soya
beans.
Exports of these commodities are already driving
up the exchange rate before the new oil fields have
75 fully come on stream, making it harder for Brazilian
exporters of manufactured goods. Industrial production
has faltered in recent months, with manufacturers
blaming the trend on a flood of cheap Chinese-made
imports.
80____“Brazil has everything that China doesn’t and it’s
natural that, as China continues to grow, it’s just going
to be starved for those resources,” says Harvard’s
Prof Rogoff. “At some level Brazil doesn’t just want
to be exporting natural resources – it wants a more
85 diversified economy. There are going to be some
rising tensions over that.”
Adapted from Financial Times - March 15 2011 22:54. Available in:
<http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/fa11320c-4f48-11e0-9038-00144feab49a,_i_email=y.html>
Retrieved on: June 17, 2011.
The communicative intention of Text I is to
O gráfico de pontos (Dot-Plot) é uma importante ferramenta de representação gráfica para uma dada distribuição de frequência. Analise o conjunto de dados utilizado na construção do gráfico de pontos, apresentado a seguir.
Neste quadro de pontos, encontram-se as seguintes propriedades:
Texto
29 anos de democracia
_____Mais de 90 milhões de brasileiros, quase metade da população atual, não eram nascidos quando o último general-presidente, João Figueiredo, deixou o Palácio do Planalto. Outros 30 milhões ainda não eram adolescentes.
_____Maioria crescente dos brasileiros, portanto, terá nascido ou se tornado adulta na vigência do regime democrático. A Nova República já é mais longeva que todos os arranjos republicanos anteriores, à exceção do período oligárquico (1889-1930).
_____Em termos de escala, assiduidade e participação da população na escolha dos governantes, o Brasil de 1985 a 2014 parece outro país, moderno e dinâmico, no cotejo com a restrita experiência eleitoral anterior.
_____A hipótese de ruptura com o passado se fortalece quando avaliamos a extensão dos mecanismos de distribuição de oportunidades e de mitigação de desigualdades de hoje. Sozinhas, as despesas sociais no Brasil equivalem, em percentual do PIB, a quase todo o gasto público chinês.
_____A democracia brasileira contemporânea, e apenas ela na história nacional, inventou o que mais perto se pode chegar de um Estado de Bem-Estar num país de renda média. A baixa qualidade dos serviços governamentais está ligada sobretudo à limitação do PIB, e não à falta de políticas públicas social-democratas.
_____Autoritários e populistas do passado davam uma banana para o custeio –e o controle de qualidade– da educação básica. Governos democráticos a partir de 1985 fizeram disparar a despesa. Muito da redução na desigualdade de renda se deve a isso.
_____Ainda assim, a parte da esquerda viúva da ruína socialista vive a defender o “aprofundamento da democracia” e “mudanças estruturais” que nos livrem do modelo de “modernização conservadora” –seja lá o que esses termos signifiquem hoje.
_____Já ocorreu a tal “mudança estrutural”. O Brasil democrático não se parece com seu passado tristonho, embora ainda haja tanto por fazer.
(Vinicius Mota, Folha de São Paulo)
Sobre o Plano Nacional da Educação, analise as afirmativas a seguir.
I. Tem por objetivo a formação para o trabalho e o estabelecimento de limites para a aplicação de recursos públicos, não guardando relação de proporção com o produto interno bruto.
II. Tem por objetivo a melhoria da qualidade do ensino e a promoção humanística, científica e tecnológica do país.
III. Tem por objetivo a erradicação do analfabetismo e a universalização do atendimento escolar.
Assinale:
Texto
29 anos de democracia
_____Mais de 90 milhões de brasileiros, quase metade da população atual, não eram nascidos quando o último general-presidente, João Figueiredo, deixou o Palácio do Planalto. Outros 30 milhões ainda não eram adolescentes.
_____Maioria crescente dos brasileiros, portanto, terá nascido ou se tornado adulta na vigência do regime democrático. A Nova República já é mais longeva que todos os arranjos republicanos anteriores, à exceção do período oligárquico (1889-1930).
_____Em termos de escala, assiduidade e participação da população na escolha dos governantes, o Brasil de 1985 a 2014 parece outro país, moderno e dinâmico, no cotejo com a restrita experiência eleitoral anterior.
_____A hipótese de ruptura com o passado se fortalece quando avaliamos a extensão dos mecanismos de distribuição de oportunidades e de mitigação de desigualdades de hoje. Sozinhas, as despesas sociais no Brasil equivalem, em percentual do PIB, a quase todo o gasto público chinês.
_____A democracia brasileira contemporânea, e apenas ela na história nacional, inventou o que mais perto se pode chegar de um Estado de Bem-Estar num país de renda média. A baixa qualidade dos serviços governamentais está ligada sobretudo à limitação do PIB, e não à falta de políticas públicas social-democratas.
_____Autoritários e populistas do passado davam uma banana para o custeio –e o controle de qualidade– da educação básica. Governos democráticos a partir de 1985 fizeram disparar a despesa. Muito da redução na desigualdade de renda se deve a isso.
_____Ainda assim, a parte da esquerda viúva da ruína socialista vive a defender o “aprofundamento da democracia” e “mudanças estruturais” que nos livrem do modelo de “modernização conservadora” –seja lá o que esses termos signifiquem hoje.
_____Já ocorreu a tal “mudança estrutural”. O Brasil democrático não se parece com seu passado tristonho, embora ainda haja tanto por fazer.
(Vinicius Mota, Folha de São Paulo)
“Autoritários e populistas do passado davam uma banana para o custeio – e o controle de qualidade – da educação básica. Governos democráticos a partir de 1985 fizeram disparar a despesa. Muito da redução na desigualdade de renda se deve a isso.”
A palavra desse segmento que não é formada com um sufixo é
Texto
29 anos de democracia
_____Mais de 90 milhões de brasileiros, quase metade da população atual, não eram nascidos quando o último general-presidente, João Figueiredo, deixou o Palácio do Planalto. Outros 30 milhões ainda não eram adolescentes.
_____Maioria crescente dos brasileiros, portanto, terá nascido ou se tornado adulta na vigência do regime democrático. A Nova República já é mais longeva que todos os arranjos republicanos anteriores, à exceção do período oligárquico (1889-1930).
_____Em termos de escala, assiduidade e participação da população na escolha dos governantes, o Brasil de 1985 a 2014 parece outro país, moderno e dinâmico, no cotejo com a restrita experiência eleitoral anterior.
_____A hipótese de ruptura com o passado se fortalece quando avaliamos a extensão dos mecanismos de distribuição de oportunidades e de mitigação de desigualdades de hoje. Sozinhas, as despesas sociais no Brasil equivalem, em percentual do PIB, a quase todo o gasto público chinês.
_____A democracia brasileira contemporânea, e apenas ela na história nacional, inventou o que mais perto se pode chegar de um Estado de Bem-Estar num país de renda média. A baixa qualidade dos serviços governamentais está ligada sobretudo à limitação do PIB, e não à falta de políticas públicas social-democratas.
_____Autoritários e populistas do passado davam uma banana para o custeio –e o controle de qualidade– da educação básica. Governos democráticos a partir de 1985 fizeram disparar a despesa. Muito da redução na desigualdade de renda se deve a isso.
_____Ainda assim, a parte da esquerda viúva da ruína socialista vive a defender o “aprofundamento da democracia” e “mudanças estruturais” que nos livrem do modelo de “modernização conservadora” –seja lá o que esses termos signifiquem hoje.
_____Já ocorreu a tal “mudança estrutural”. O Brasil democrático não se parece com seu passado tristonho, embora ainda haja tanto por fazer.
(Vinicius Mota, Folha de São Paulo)
Assinale a opção que indica o segmento em que a conjunção e tem valor adversativo e não aditivo.
Texto
29 anos de democracia
_____Mais de 90 milhões de brasileiros, quase metade da população atual, não eram nascidos quando o último general-presidente, João Figueiredo, deixou o Palácio do Planalto. Outros 30 milhões ainda não eram adolescentes.
_____Maioria crescente dos brasileiros, portanto, terá nascido ou se tornado adulta na vigência do regime democrático. A Nova República já é mais longeva que todos os arranjos republicanos anteriores, à exceção do período oligárquico (1889-1930).
_____Em termos de escala, assiduidade e participação da população na escolha dos governantes, o Brasil de 1985 a 2014 parece outro país, moderno e dinâmico, no cotejo com a restrita experiência eleitoral anterior.
_____A hipótese de ruptura com o passado se fortalece quando avaliamos a extensão dos mecanismos de distribuição de oportunidades e de mitigação de desigualdades de hoje. Sozinhas, as despesas sociais no Brasil equivalem, em percentual do PIB, a quase todo o gasto público chinês.
_____A democracia brasileira contemporânea, e apenas ela na história nacional, inventou o que mais perto se pode chegar de um Estado de Bem-Estar num país de renda média. A baixa qualidade dos serviços governamentais está ligada sobretudo à limitação do PIB, e não à falta de políticas públicas social-democratas.
_____Autoritários e populistas do passado davam uma banana para o custeio –e o controle de qualidade– da educação básica. Governos democráticos a partir de 1985 fizeram disparar a despesa. Muito da redução na desigualdade de renda se deve a isso.
_____Ainda assim, a parte da esquerda viúva da ruína socialista vive a defender o “aprofundamento da democracia” e “mudanças estruturais” que nos livrem do modelo de “modernização conservadora” –seja lá o que esses termos signifiquem hoje.
_____Já ocorreu a tal “mudança estrutural”. O Brasil democrático não se parece com seu passado tristonho, embora ainda haja tanto por fazer.
(Vinicius Mota, Folha de São Paulo)
O texto mostra um conjunto de sinais gráficos. Assinale a opção que indica o segmento do texto em que o emprego de um desses sinais está corretamente justificado.
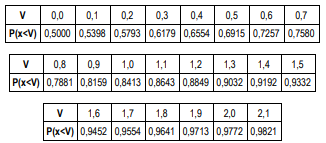
Se somarmos 9 amostras independentes da mesma variável aleatória de x, o valor mais próximo da probabilidade dessa soma ser maior que 1,8, entre as opções apresentadas a seguir, é:
Disponível em: <https://agenciagov.ebc.com.br/noticias/202311/taxa-de-desmatamento-na-amazonia-cai-22-3-em-2023-1>. Acesso em: 23 abr. 2024.
Considerando o gráfico de dupla entrada, que mostra a relação entre a área desmatada, em quilômetros quadrados, e o número de termos de autuações do Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Renováveis (Ibama), entre 2018 e 2023, assinale a alternativa correta.