Questões de Concurso
Para prefeitura de montes claros - mg
Foram encontradas 1.617 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Read the following text to answer the question.
By Leo Selivan
In this article, informed by the Lexical Approach, I reflect on grammar instruction in the classroom […]. I consider the problems with ‘traditional’ grammar teaching before arguing that what we actually need is more grammar input as well as showing how lexis can provide necessary ‘crutches’ for the learner.
Lexis = vocabulary + grammar
The shift in ELT from grammar to lexis mirrors a similar change in the attitude of linguists. In the past linguists were preoccupied with the grammar of language; however the advances in corpus linguistics have pushed lexis to the forefront. The term ‘lexis’, which was traditionally used by linguists, is a common word these days and frequently used even in textbooks.
Why use a technical term borrowed from the realm of linguistics instead of the word ‘vocabulary’? Quite simply because vocabulary is typically seen as individual words (often presented in lists) whereas lexis is a somewhat wider concept and consists of collocations, chunks and formulaic expressions. It also includes certain patterns that were traditionally associated with the grammar of a language, e.g. If I were you…, I haven’t seen you for ages etc.
Recognising certain grammar structures as lexical
items means that they can be introduced much earlier,
without structural analysis or elaboration. Indeed, since the
concept of notions and functions made its way into language
teaching, particularly as Communicative Language Teaching
(CLT) gained prominence, some structures associated with
grammar started to be taught lexically (or functionally). I’d like
to is not taught as ‹the conditional› but as a chunk expressing
desire. Similarly many other ‹traditional› grammar items can
be introduced lexically relatively early on.
Less grammar or more grammar?
You are, no doubt, all familiar with students who on one hand seem to know the ‘rules’ of grammar but still fail to produce grammatically correct sentences when speaking or, on the other, sound unnatural and foreign-like even when their sentences are grammatically correct. Michael Lewis, who might be considered the founder of the Lexical Approach, once claimed that there was no direct relationship between the knowledge of grammar and speaking. In contrast, the knowledge of formulaic language has been shown by research to have a significant bearing on the natural language production.
Furthermore, certain grammar rules are practically impossible to learn. Dave Willis cites the grammar of orientation (which includes the notoriously difficult present perfect and the uses of certain modal verbs) as particularly resistant to teaching. The only way to grasp their meaning is through continuous exposure and use.
Finally, even the most authoritative English grammars never claim to provide a comprehensive description of all the grammar, hence the word ‘introduction’ often used in their titles (for instance, Huddleston & Pullum’s A Student’s Introduction to English Grammar or Halliday’s An Introduction to Functional Grammar).
If grammarians do not even attempt to address all areas of grammar, how can we, practitioners, cover all the aspects of grammar in our teaching, especially if all we seem to focus on is a limited selection of discrete items, comprised mostly of tenses and a handful of modal verbs? It would seem that we need to expose our students to a lot of naturally occurring language and frequently draw their attention to various grammar points as they arise.
For example, while teaching the expression fall asleep / be asleep you can ask your students:
• Don’t make any noise – she’s fallen asleep.
• Don’t make any noise – she’s asleep.
What does’s stand for in each of these cases (is or has)?
One of the fathers of the Communicative Language Teaching Henry Widdowson advocated using lexical items as a starting point and then ‘showing how they need to be grammatically modified to be communicatively effective’ (1990:95). For example, when exploring a text with your students, you may come across a sentence like this:
• They’ve been married for seven years.
You can ask your students: When did they get married? How should you change the sentence if the couple you are talking about is no longer married?
The above demonstrates how the teacher should be constantly on the ball and take every opportunity to draw students’ attention to grammar. Such short but frequent ‘grammar spots’ will help to slowly raise students’ awareness and build their understanding of the English grammar system.
[…]
Conclusion
So is there room for grammar instruction in the classroom? Certainly yes. But the grammar practice should always start with the exploitation of lexical items. Exposing students to a lot of natural and contextualised examples will offer a lexical way into the grammar of the language.
To sum up, grammar should play some role in language teaching but should not occupy a big part of class time. Instead grammar should be delivered in small but frequent portions. Students should be encouraged to collect a lot of examples of a particular structure before being invited to analyse it. Hence, analysis should be preceded by synthesis.
Lastly, language practitioners should bear in mind that grammar acquisition is an incremental process which requires frequent focus and refocus on the items already studied.
Available at: https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/professionaldevelopment/teachers/knowing-subject/articles/grammar-vs-lexisor-grammar-through. Accessed on: April 29, 2024.
Read the following text to answer the question.
By Leo Selivan
In this article, informed by the Lexical Approach, I reflect on grammar instruction in the classroom […]. I consider the problems with ‘traditional’ grammar teaching before arguing that what we actually need is more grammar input as well as showing how lexis can provide necessary ‘crutches’ for the learner.
Lexis = vocabulary + grammar
The shift in ELT from grammar to lexis mirrors a similar change in the attitude of linguists. In the past linguists were preoccupied with the grammar of language; however the advances in corpus linguistics have pushed lexis to the forefront. The term ‘lexis’, which was traditionally used by linguists, is a common word these days and frequently used even in textbooks.
Why use a technical term borrowed from the realm of linguistics instead of the word ‘vocabulary’? Quite simply because vocabulary is typically seen as individual words (often presented in lists) whereas lexis is a somewhat wider concept and consists of collocations, chunks and formulaic expressions. It also includes certain patterns that were traditionally associated with the grammar of a language, e.g. If I were you…, I haven’t seen you for ages etc.
Recognising certain grammar structures as lexical
items means that they can be introduced much earlier,
without structural analysis or elaboration. Indeed, since the
concept of notions and functions made its way into language
teaching, particularly as Communicative Language Teaching
(CLT) gained prominence, some structures associated with
grammar started to be taught lexically (or functionally). I’d like
to is not taught as ‹the conditional› but as a chunk expressing
desire. Similarly many other ‹traditional› grammar items can
be introduced lexically relatively early on.
Less grammar or more grammar?
You are, no doubt, all familiar with students who on one hand seem to know the ‘rules’ of grammar but still fail to produce grammatically correct sentences when speaking or, on the other, sound unnatural and foreign-like even when their sentences are grammatically correct. Michael Lewis, who might be considered the founder of the Lexical Approach, once claimed that there was no direct relationship between the knowledge of grammar and speaking. In contrast, the knowledge of formulaic language has been shown by research to have a significant bearing on the natural language production.
Furthermore, certain grammar rules are practically impossible to learn. Dave Willis cites the grammar of orientation (which includes the notoriously difficult present perfect and the uses of certain modal verbs) as particularly resistant to teaching. The only way to grasp their meaning is through continuous exposure and use.
Finally, even the most authoritative English grammars never claim to provide a comprehensive description of all the grammar, hence the word ‘introduction’ often used in their titles (for instance, Huddleston & Pullum’s A Student’s Introduction to English Grammar or Halliday’s An Introduction to Functional Grammar).
If grammarians do not even attempt to address all areas of grammar, how can we, practitioners, cover all the aspects of grammar in our teaching, especially if all we seem to focus on is a limited selection of discrete items, comprised mostly of tenses and a handful of modal verbs? It would seem that we need to expose our students to a lot of naturally occurring language and frequently draw their attention to various grammar points as they arise.
For example, while teaching the expression fall asleep / be asleep you can ask your students:
• Don’t make any noise – she’s fallen asleep.
• Don’t make any noise – she’s asleep.
What does’s stand for in each of these cases (is or has)?
One of the fathers of the Communicative Language Teaching Henry Widdowson advocated using lexical items as a starting point and then ‘showing how they need to be grammatically modified to be communicatively effective’ (1990:95). For example, when exploring a text with your students, you may come across a sentence like this:
• They’ve been married for seven years.
You can ask your students: When did they get married? How should you change the sentence if the couple you are talking about is no longer married?
The above demonstrates how the teacher should be constantly on the ball and take every opportunity to draw students’ attention to grammar. Such short but frequent ‘grammar spots’ will help to slowly raise students’ awareness and build their understanding of the English grammar system.
[…]
Conclusion
So is there room for grammar instruction in the classroom? Certainly yes. But the grammar practice should always start with the exploitation of lexical items. Exposing students to a lot of natural and contextualised examples will offer a lexical way into the grammar of the language.
To sum up, grammar should play some role in language teaching but should not occupy a big part of class time. Instead grammar should be delivered in small but frequent portions. Students should be encouraged to collect a lot of examples of a particular structure before being invited to analyse it. Hence, analysis should be preceded by synthesis.
Lastly, language practitioners should bear in mind that grammar acquisition is an incremental process which requires frequent focus and refocus on the items already studied.
Available at: https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/professionaldevelopment/teachers/knowing-subject/articles/grammar-vs-lexisor-grammar-through. Accessed on: April 29, 2024.
Read the following text to answer the question.
By Leo Selivan
In this article, informed by the Lexical Approach, I reflect on grammar instruction in the classroom […]. I consider the problems with ‘traditional’ grammar teaching before arguing that what we actually need is more grammar input as well as showing how lexis can provide necessary ‘crutches’ for the learner.
Lexis = vocabulary + grammar
The shift in ELT from grammar to lexis mirrors a similar change in the attitude of linguists. In the past linguists were preoccupied with the grammar of language; however the advances in corpus linguistics have pushed lexis to the forefront. The term ‘lexis’, which was traditionally used by linguists, is a common word these days and frequently used even in textbooks.
Why use a technical term borrowed from the realm of linguistics instead of the word ‘vocabulary’? Quite simply because vocabulary is typically seen as individual words (often presented in lists) whereas lexis is a somewhat wider concept and consists of collocations, chunks and formulaic expressions. It also includes certain patterns that were traditionally associated with the grammar of a language, e.g. If I were you…, I haven’t seen you for ages etc.
Recognising certain grammar structures as lexical
items means that they can be introduced much earlier,
without structural analysis or elaboration. Indeed, since the
concept of notions and functions made its way into language
teaching, particularly as Communicative Language Teaching
(CLT) gained prominence, some structures associated with
grammar started to be taught lexically (or functionally). I’d like
to is not taught as ‹the conditional› but as a chunk expressing
desire. Similarly many other ‹traditional› grammar items can
be introduced lexically relatively early on.
Less grammar or more grammar?
You are, no doubt, all familiar with students who on one hand seem to know the ‘rules’ of grammar but still fail to produce grammatically correct sentences when speaking or, on the other, sound unnatural and foreign-like even when their sentences are grammatically correct. Michael Lewis, who might be considered the founder of the Lexical Approach, once claimed that there was no direct relationship between the knowledge of grammar and speaking. In contrast, the knowledge of formulaic language has been shown by research to have a significant bearing on the natural language production.
Furthermore, certain grammar rules are practically impossible to learn. Dave Willis cites the grammar of orientation (which includes the notoriously difficult present perfect and the uses of certain modal verbs) as particularly resistant to teaching. The only way to grasp their meaning is through continuous exposure and use.
Finally, even the most authoritative English grammars never claim to provide a comprehensive description of all the grammar, hence the word ‘introduction’ often used in their titles (for instance, Huddleston & Pullum’s A Student’s Introduction to English Grammar or Halliday’s An Introduction to Functional Grammar).
If grammarians do not even attempt to address all areas of grammar, how can we, practitioners, cover all the aspects of grammar in our teaching, especially if all we seem to focus on is a limited selection of discrete items, comprised mostly of tenses and a handful of modal verbs? It would seem that we need to expose our students to a lot of naturally occurring language and frequently draw their attention to various grammar points as they arise.
For example, while teaching the expression fall asleep / be asleep you can ask your students:
• Don’t make any noise – she’s fallen asleep.
• Don’t make any noise – she’s asleep.
What does’s stand for in each of these cases (is or has)?
One of the fathers of the Communicative Language Teaching Henry Widdowson advocated using lexical items as a starting point and then ‘showing how they need to be grammatically modified to be communicatively effective’ (1990:95). For example, when exploring a text with your students, you may come across a sentence like this:
• They’ve been married for seven years.
You can ask your students: When did they get married? How should you change the sentence if the couple you are talking about is no longer married?
The above demonstrates how the teacher should be constantly on the ball and take every opportunity to draw students’ attention to grammar. Such short but frequent ‘grammar spots’ will help to slowly raise students’ awareness and build their understanding of the English grammar system.
[…]
Conclusion
So is there room for grammar instruction in the classroom? Certainly yes. But the grammar practice should always start with the exploitation of lexical items. Exposing students to a lot of natural and contextualised examples will offer a lexical way into the grammar of the language.
To sum up, grammar should play some role in language teaching but should not occupy a big part of class time. Instead grammar should be delivered in small but frequent portions. Students should be encouraged to collect a lot of examples of a particular structure before being invited to analyse it. Hence, analysis should be preceded by synthesis.
Lastly, language practitioners should bear in mind that grammar acquisition is an incremental process which requires frequent focus and refocus on the items already studied.
Available at: https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/professionaldevelopment/teachers/knowing-subject/articles/grammar-vs-lexisor-grammar-through. Accessed on: April 29, 2024.
Empowering language learning through assessment
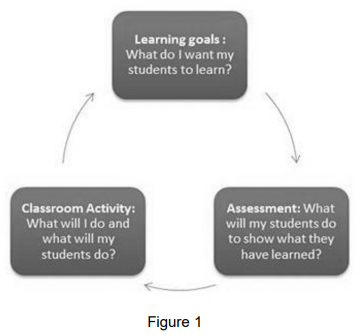
Assessment of, as, and for learning
Empowering language learning through assessment

Assessment of, as, and for learning
The word reliability is closest in meaning to
Empowering language learning through assessment

Assessment of, as, and for learning
Empowering language learning through assessment

Assessment of, as, and for learning
Empowering language learning through assessment

Assessment of, as, and for learning
I. A educação inclusiva, para sua efetivação e consolidação, deve contar com ampla participação e envolvimento da comunidade escolar e da sociedade.
II. Quando se fala de educação inclusiva, é necessário pensar na importância de substituir paradigmas normativos e prescritivos por aqueles que sejam capazes de acolher de maneira mais ampla e emancipatória a diversidade.
III. Ao considerar a deficiência intelectual como um processo unidirecional, relacionado intrinsecamente e unicamente aos aspectos do funcionamento do corpo, é possível encontrar meios de construir estratégias para promoção da educação inclusiva.
IV. Pode-se dizer que a elaboração de laudos psicológicos é prejudicial à implementação e efetivação de políticas públicas em educação inclusiva.
Estão incorretas as afirmativas
“Ela (a Política Nacional de Atenção Básica) deve ‘superar compreensões simplistas, nas quais, entre outras, há dicotomia e oposição entre a assistência e a promoção da saúde’, quando a ação, em face dos seus fenômenos, deve levar em consideração ‘múltiplos determinantes e condicionantes’” (Brasil, 2017).
CONSELHO FEDERAL DE PSICOLOGIA (CFP). Referências Técnicas para a atuação de psicólogas(os) na atenção básica a saúde. Conselho Federal de Psicologia, Conselhos Regionais de Psicologia e Centro de Referência Técnica em Psicologia e Políticas Públicas. 2. ed. Brasília: CFP, 2019.
Nesse contexto, assinale a alternativa correta.
Nesse contexto, numere a COLUNA II de acordo com a COLUNA I, relacionando o tipo de documento à sua respectiva caracterização.
COLUNA I
1. Atestado psicológico
2. Relatório psicológico
3. Laudo psicológico
4. Parecer psicológico
COLUNA II
( ) Documento que visa comunicar a atuação do profissional em diferentes processos de trabalho desenvolvidos ou em desenvolvimento, podendo gerar orientações, recomendações, encaminhamentos e intervenções pertinentes à situação em jogo. Não tem como finalidade produzir diagnóstico psicológico.
( ) É um documento que certifica, fundamentado em um diagnóstico psicológico, uma determinada situação, estado ou funcionamento psicológico. O objetivo é afirmar as condições psicológicas de quem, por requerimento, o solicita.
( ) Documento que se caracteriza por ser uma resposta a uma consulta. É um pronunciamento por escrito, que busca apresentar uma análise técnica, respondendo a uma questão-problema do campo psicológico ou a documentos psicológicos questionados.
( ) Resultado de um processo de avaliação psicológica. Objetiva subsidiar decisões relacionadas ao contexto em que surgiu a demanda. Contém informações técnicas e científicas dos fenômenos psicológicos, considerando questões históricas e sociais da pessoa, grupo ou instituição atendida.
Assinale a sequência correta.
Nesse contexto, analise as afirmativas a seguir e a relação proposta entre elas.
I. A medicalização é o que pode se produzir no momento em que se reduz as dificuldades, impasses e complexidades da vida a determinismos orgânicos.
PORQUE
II. A medicalização, como um procedimento generalizado nas escolas, pode favorecer a ocorrência de um processo de homogeneização, aplacando com isso conflitos, medos e angústias existentes no contexto escolar. Junto a isso, o potencial transformador de tais situações também perde força.
Assinale a alternativa correta.
Com relação à atuação do profissional da Psicologia, assinale a alternativa correta.
Nesse contexto, assinale a alternativa incorreta.
I. O conhecimento é uma representação do mundo externa ao observador, que tem a capacidade de apreender a partir dos processos educacionais.
II. O conhecimento tem uma função adaptativa e que deve ser viável para o mundo da experiência do sujeito cognoscente.
III. No enfoque construtivista, o ser humano, por sua estrutura ou biologia, não tem acesso objetivo à realidade, antes a constrói no convívio com os demais.
Estão corretas as afirmativas
São exemplos de transtorno de aprendizagem, exceto: