Questões de Concurso
Para sefaz-sp
Foram encontradas 1.479 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
By Michelle Singletary, Published: January 15, 2013
It’s not nice to tell people “I told you so.” But if anybody has the right to say that, it’s Nina E. Olson, the national taxpayer advocate.
Olson recently submitted her annual report to Congress and top on her list of things that need to be fixed is the complexity of the tax
code, which she called the most serious problem facing taxpayers.
Let’s just look at the most recent evidence of complexity run amok. The Internal Revenue Service had to delay the tax-filing season so it
could update forms and its programming to accommodate recent changes made under the American Taxpayer Relief Act. The IRS won’t start
processing individual income tax returns until Jan. 30. Yet one thing remains unchanged − the April 15 tax deadline.
Because of the new tax laws, the IRS also had to release updated income-tax withholding tables for 2013. These replace the tables
issued Dec. 31. Yes, let’s just keep making more work for the agency that is already overburdened. Not to mention the extra work for
employers, who have to use the revised information to correct the amount of Social Security tax withheld in 2013. And they have to make that
correction in order to withhold a larger Social Security tax of 6.2 percent on wages, following the expiration of the payroll tax cut in effect for
2011 and 2012.
Oh, and there was the near miss with the alternative minimum tax that could have delayed the tax filing season to late March. The AMT
was created to target high-income taxpayers who were claiming so many deductions that they owed little or no income tax. Olson and many
others have complained for years that the AMT wasn’t indexed for inflation.
“Many middle- and upper-middle-class taxpayers pay the AMT, while most wealthy taxpayers do not, and thousands of millionaires pay
..A.. income tax at all,” Olson said.
As part of the recent “fiscal cliff” deal, the AMT is now fixed, a move that the IRS was anticipating. It had already decided to program its
systems on the assumption that an AMT patch would be passed, Olson said. Had the agency not taken the risk, the time it would have taken to
update the systems “would have brought about the most chaotic filing season in memory,” she said in her report.
The tax code contains almost 4 million words. Since 2001, there have been about 4,680 changes, or an average of more than one
change a day. What else troubles Olson? Here’s what:
− Nearly 60 percent of taxpayers hire paid preparers, and another 30 percent rely on commercial software to prepare their returns.
− Many taxpayers don’t really know how their taxes are computed and what rate of tax they pay.
− The complex code makes tax fraud ..B.. to detect.
− Because the code is so complicated, it creates an impression that many taxpayers are not paying their fair share. This reduces trust
in the system and perhaps leads some people to cheat. Who wants to be the sucker in this game? So someone might not declare
all of his income, rationalizing that millionaires get to use the convoluted code to greatly reduce their tax liability.
− In fiscal year 2012, the IRS received around 125 million calls. But the agency answered only about two out of three calls from
people trying to reach a live person, and those taxpayers had to wait, on average, about 17 minutes to get through.
“I hope 2013 brings about fundamental tax simplification,” Olson pleaded in her report. She urged Congress to reassess the need for
the tax breaks we know as income exclusions, exemptions, deductions and credits. It’s all these tax advantage breaks that complicate the
code. If done right, and without reducing revenue, tax rates could be substantially lowered in exchange for ending tax breaks, she said.
(Adapted from http://js.washingtonpost.com/business/economy/for-taxpayer-advocate-a-familiar-refrain/2013/01/15/a10327ce-5f59-
11e2-b05a-605528f6b712_story.html)
A alternativa que, no contexto, preenche adequadamente a lacuna ..B.. é
By Michelle Singletary, Published: January 15, 2013
It’s not nice to tell people “I told you so.” But if anybody has the right to say that, it’s Nina E. Olson, the national taxpayer advocate.
Olson recently submitted her annual report to Congress and top on her list of things that need to be fixed is the complexity of the tax
code, which she called the most serious problem facing taxpayers.
Let’s just look at the most recent evidence of complexity run amok. The Internal Revenue Service had to delay the tax-filing season so it
could update forms and its programming to accommodate recent changes made under the American Taxpayer Relief Act. The IRS won’t start
processing individual income tax returns until Jan. 30. Yet one thing remains unchanged − the April 15 tax deadline.
Because of the new tax laws, the IRS also had to release updated income-tax withholding tables for 2013. These replace the tables
issued Dec. 31. Yes, let’s just keep making more work for the agency that is already overburdened. Not to mention the extra work for
employers, who have to use the revised information to correct the amount of Social Security tax withheld in 2013. And they have to make that
correction in order to withhold a larger Social Security tax of 6.2 percent on wages, following the expiration of the payroll tax cut in effect for
2011 and 2012.
Oh, and there was the near miss with the alternative minimum tax that could have delayed the tax filing season to late March. The AMT
was created to target high-income taxpayers who were claiming so many deductions that they owed little or no income tax. Olson and many
others have complained for years that the AMT wasn’t indexed for inflation.
“Many middle- and upper-middle-class taxpayers pay the AMT, while most wealthy taxpayers do not, and thousands of millionaires pay
..A.. income tax at all,” Olson said.
As part of the recent “fiscal cliff” deal, the AMT is now fixed, a move that the IRS was anticipating. It had already decided to program its
systems on the assumption that an AMT patch would be passed, Olson said. Had the agency not taken the risk, the time it would have taken to
update the systems “would have brought about the most chaotic filing season in memory,” she said in her report.
The tax code contains almost 4 million words. Since 2001, there have been about 4,680 changes, or an average of more than one
change a day. What else troubles Olson? Here’s what:
− Nearly 60 percent of taxpayers hire paid preparers, and another 30 percent rely on commercial software to prepare their returns.
− Many taxpayers don’t really know how their taxes are computed and what rate of tax they pay.
− The complex code makes tax fraud ..B.. to detect.
− Because the code is so complicated, it creates an impression that many taxpayers are not paying their fair share. This reduces trust
in the system and perhaps leads some people to cheat. Who wants to be the sucker in this game? So someone might not declare
all of his income, rationalizing that millionaires get to use the convoluted code to greatly reduce their tax liability.
− In fiscal year 2012, the IRS received around 125 million calls. But the agency answered only about two out of three calls from
people trying to reach a live person, and those taxpayers had to wait, on average, about 17 minutes to get through.
“I hope 2013 brings about fundamental tax simplification,” Olson pleaded in her report. She urged Congress to reassess the need for
the tax breaks we know as income exclusions, exemptions, deductions and credits. It’s all these tax advantage breaks that complicate the
code. If done right, and without reducing revenue, tax rates could be substantially lowered in exchange for ending tax breaks, she said.
(Adapted from http://js.washingtonpost.com/business/economy/for-taxpayer-advocate-a-familiar-refrain/2013/01/15/a10327ce-5f59-
11e2-b05a-605528f6b712_story.html)
A alternativa que preenche corretamente a lacuna ..A.. é
I. A crise internacional e as desonerações tributárias promovidas pelo governo para estimular a economia contribuíram para o baixo índice de crescimento da arrecadação, em 2012.
II. A manutenção, em 2012, da contratação de trabalhadores com carteira assinada permitiu que as contribuições para a Previdência Social tivessem papel significativo para o crescimento da arrecadação.
III. A arrecadação de impostos vinculados à importação aumentou, mas a do IPI sobre produtos nacionais caiu, pois a indústria teve fraco desempenho, em 2012.
Está correto o que se afirma em
I. A data do meu aniversário é mais próxima do primeiro dia de fevereiro do que de hoje.
II. Neste ano, meu aniversário não cairá em um final de semana.
Para deduzir a data exata do aniversário de Carlos,
Para que a conclusão acima seja verdadeira, qual das premissas a seguir deve ser verificada?
Qual dos fatos a seguir, se for verdadeiro, enfraquecerá consideravelmente o argumento apresentado?
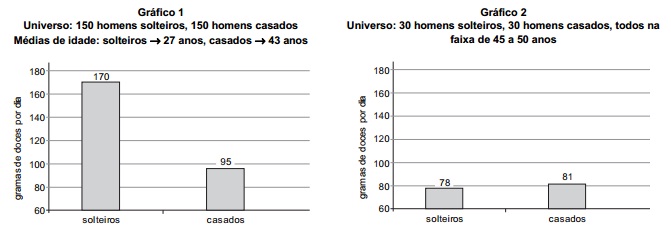
Os gráficos mostram que
O argumento do pesquisador a respeito do risco de lesões em jogadores de futebol
A causa mais provável para o aumento de 70% nas notas é
Cientistas do CENA (Centro de Energia Nuclear na Agricultura) da USP de Piracicaba desenvolveram uma técnica que usa radiação para tornar o Aedes aegypti estéril.
Usando uma fonte de Cobalto-60, os pesquisadores fazem uma espécie de "bombardeio" de raios gama no inseto. A técnica, chamada de irradiação, já tem uso consagrado em várias outras aplicações, inclusive na indústria de alimentos.
A dose de radiação usada é considerada baixa e não mata o mosquito, mas é suficiente para torná-lo estéril.
"A técnica é perfeitamente segura. Não há risco para o ambiente, porque a radiação não deixa nenhum tipo de resíduo perigoso",explica Valter Arthur, coordenador do estudo.
A irradiação é feita só nos mosquitos machos, quando eles atingem a chamada fase pupa, em que já estão com todos os órgãos formados, mas ainda não são adultos. (...)
Depois do processo, os mosquitos irradiados são soltos no ambiente, onde competirão com os machos normais pela cópula com as fêmeas. As relações chegam a acontecer, mas os ovos decorrentes delas não eclodem, o que ajuda a controlar a população dos insetos.
Cientistas do CENA (Centro de Energia Nuclear na Agricultura) da USP de Piracicaba desenvolveram uma técnica que usa radiação para tornar o Aedes aegypti estéril.
Usando uma fonte de Cobalto-60, os pesquisadores fazem uma espécie de "bombardeio" de raios gama no inseto. A técnica, chamada de irradiação, já tem uso consagrado em várias outras aplicações, inclusive na indústria de alimentos.
A dose de radiação usada é considerada baixa e não mata o mosquito, mas é suficiente para torná-lo estéril.
"A técnica é perfeitamente segura. Não há risco para o ambiente, porque a radiação não deixa nenhum tipo de resíduo perigoso",explica Valter Arthur, coordenador do estudo.
A irradiação é feita só nos mosquitos machos, quando eles atingem a chamada fase pupa, em que já estão com todos os órgãos formados, mas ainda não são adultos. (...)
Depois do processo, os mosquitos irradiados são soltos no ambiente, onde competirão com os machos normais pela cópula com as fêmeas. As relações chegam a acontecer, mas os ovos decorrentes delas não eclodem, o que ajuda a controlar a população dos insetos.
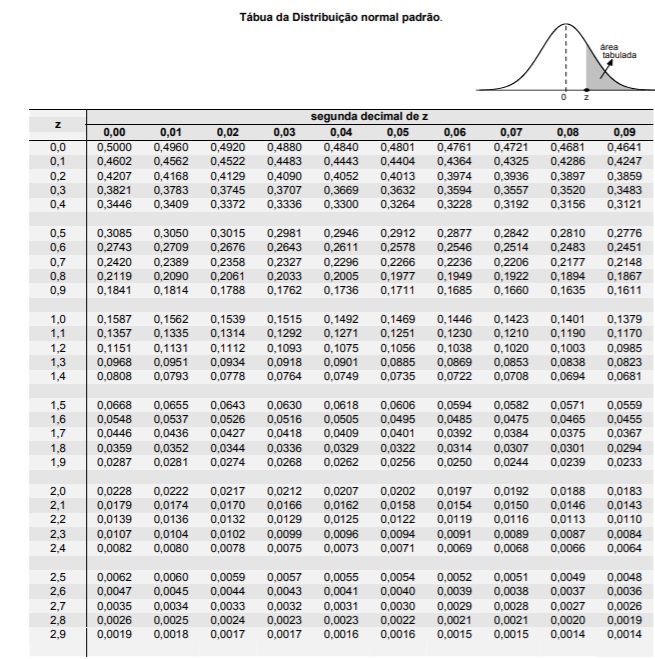
Atenção: Para resolver às questões de números 38 a 40, utilize os valores que julgar mais apropriados (observar sempre a melhor aproximação) da tábua da distribuição normal padrão.