Questões de Concurso
Para policial legislativo federal
Foram encontradas 254 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
I. Convocar determinado ministro de Estado para prestar pessoalmente esclarecimentos.
II. Convocar o presidente do ente da Administração Pública indireta para prestar pessoalmente esclarecimentos. e
III. Quebrar o sigilo telefônico dessas autoridades.
Em relação às referidas medidas, à luz da sistemática constitucional, é correto afirmar que
O edital, logo após ser publicado, gerou grande insatisfação entre os candidatos em potencial, que argumentavam com a necessidade de as determinações acima referidas estarem disciplinadas em lei, não sendo admitido que constem apenas do edital.
Em relação às determinações acima, é correto afirmar que
Por essa razão, foi editada a Lei municipal nº XX, que limitou a exploração das jazidas às localidades indicadas no plano diretor do Município, com o que se buscava conciliar o interesse público com o interesse privado de natureza econômica.
Insatisfeita com o teor da Lei municipal nº XX, a associação das sociedades empresárias dedicadas à exploração de jazidas minerais solicitou que seu advogado analisasse a constitucionalidade desse diploma normativo.
Sobre a Lei municipal nº XX, assinale a afirmativa correta.
Irresignado com o desfecho do processo administrativo disciplinar, no qual não fora defendido por advogado, e mais ainda com a informação recebida do colega, Pedro procurou um renomado administrativista e o consultou a respeito da compatibilidade desses acontecimentos com a ordem constitucional.
Foi-lhe corretamente informado que o processo administrativo disciplinar
Na ocasião, foi requerida a declaração de inconstitucionalidade da Lei federal nº XX e do Decreto nº YY, que a regulamentou, detalhando a forma como seria aplicada.
Considerando a sistemática vigente, assinale a afirmativa correta.
Considerando os termos da narrativa, a providência passível de ser decretada pelo Presidente da República, acompanhada de certas medidas coercitivas, restringindo alguns direitos fundamentais, seria
Read Text II and answer the question that follow it.
Text II

From: https://aghlc.com/resources/articles/2016/how-to-prevent-phishing-attacks160812.aspx?hss_channel=tw-2432542152
Read Text II and answer the question that follow it.
Text II

From: https://aghlc.com/resources/articles/2016/how-to-prevent-phishing-attacks160812.aspx?hss_channel=tw-2432542152
Read Text II and answer the question that follow it.
Text II

From: https://aghlc.com/resources/articles/2016/how-to-prevent-phishing-attacks160812.aspx?hss_channel=tw-2432542152
( ) The “spray-and-pray” business model belongs to a late period in the history of ransomware.
( ) The analysis indicates that cybercrime is far from mushrooming.
( ) The text argues that solutions to cybercrime can be reached in a jiffy.
The statements are, respectively
Sendo assim, é correto afirmar que
Para que os dois candidatos fiquem empatados, a fração de eleitores de A que deve migrar para a candidatura de B, é:
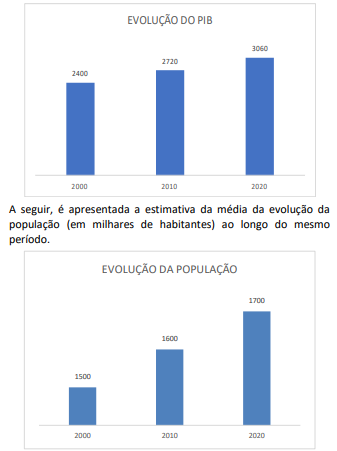
O PIB per capita médio estimado do país nesse período é igual a
O tigre corre a 30m/s, e o javali tenta escapar a uma velocidade de 10m/s.
A distância percorrida pelo javali até ser alcançado pelo tigre é igual a
(1) “Se tudo der certo, eu viajo amanhã.”
Avalie se as três frases a seguir são negações dessa afirmativa:
I. Se tudo der certo, eu não viajo amanhã.
II. Se tudo der errado, eu viajo amanhã.
III. Se algo der errado, eu não viajo amanhã.
Assim, é correto concluir que: