Questões de Vestibular Sobre inglês
Foram encontradas 5.992 questões
Fill in the parentheses with True or False.
According to the text, it’s correct to say:
( ) Concentrating Solar Power (CSP) is a great achievement in energy production.
( ) Most of the European countries are already importing electricity from the plants in the Sahara desert.
( ) Only one CSP factory is enough to provide all the energy needed by a modern city.
( ) An advantage of CSP towers is that they can work with just one large mirror.
The correct sequence, from top to bottom, is
Tate Modern – London
Hélio Oiticica
Until Summer 2019

Tropicália
Tropicália is used to describe the explosion of cultural creativity in Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo in 1968 as Brazil’s military regime tightened its grip on power.
Many of the artists, writers and musicians associated with Tropicália came of age during the 1950s in a time of intense optimism when the cultural world had been encouraged to play a central role in the creation of a democratic, socially just and modern Brazil. Nevertheless, a military coup in 1964 had brought to power a right-wing regime at odds with the concerns of left-wing artists. Tropicália became a way of exposing the contradictions of modernisation under such an authoritarian rule.
The word Tropicália comes from an installation by the artist Hélio Oiticica, who created environments that were designed to encourage the viewer’s emotional and intellectual participation. Oiticica called them “penetrables” because people were originally encouraged to enter them. They mimic the improvised, colourful dwellings in Rio de Janeiro’s favelas, or shanty towns. The lush plants and sand help to convey a sense of the tropical character of the city. When Oiticica exhibited the work, he also included live parrots.
From its beginning, Tropicália was seen as a re-articulation of Anthropophagia (“cannibalism”), an artistic ideology promoted by Oswald de Andrade.
(www.tate.org.uk. Adaptado.)
Tate Modern – London
Hélio Oiticica
Until Summer 2019

Tropicália
Tropicália is used to describe the explosion of cultural creativity in Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo in 1968 as Brazil’s military regime tightened its grip on power.
Many of the artists, writers and musicians associated with Tropicália came of age during the 1950s in a time of intense optimism when the cultural world had been encouraged to play a central role in the creation of a democratic, socially just and modern Brazil. Nevertheless, a military coup in 1964 had brought to power a right-wing regime at odds with the concerns of left-wing artists. Tropicália became a way of exposing the contradictions of modernisation under such an authoritarian rule.
The word Tropicália comes from an installation by the artist Hélio Oiticica, who created environments that were designed to encourage the viewer’s emotional and intellectual participation. Oiticica called them “penetrables” because people were originally encouraged to enter them. They mimic the improvised, colourful dwellings in Rio de Janeiro’s favelas, or shanty towns. The lush plants and sand help to convey a sense of the tropical character of the city. When Oiticica exhibited the work, he also included live parrots.
From its beginning, Tropicália was seen as a re-articulation of Anthropophagia (“cannibalism”), an artistic ideology promoted by Oswald de Andrade.
(www.tate.org.uk. Adaptado.)
Tate Modern – London
Hélio Oiticica
Until Summer 2019

Tropicália
Tropicália is used to describe the explosion of cultural creativity in Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo in 1968 as Brazil’s military regime tightened its grip on power.
Many of the artists, writers and musicians associated with Tropicália came of age during the 1950s in a time of intense optimism when the cultural world had been encouraged to play a central role in the creation of a democratic, socially just and modern Brazil. Nevertheless, a military coup in 1964 had brought to power a right-wing regime at odds with the concerns of left-wing artists. Tropicália became a way of exposing the contradictions of modernisation under such an authoritarian rule.
The word Tropicália comes from an installation by the artist Hélio Oiticica, who created environments that were designed to encourage the viewer’s emotional and intellectual participation. Oiticica called them “penetrables” because people were originally encouraged to enter them. They mimic the improvised, colourful dwellings in Rio de Janeiro’s favelas, or shanty towns. The lush plants and sand help to convey a sense of the tropical character of the city. When Oiticica exhibited the work, he also included live parrots.
From its beginning, Tropicália was seen as a re-articulation of Anthropophagia (“cannibalism”), an artistic ideology promoted by Oswald de Andrade.
(www.tate.org.uk. Adaptado.)
Tate Modern – London
Hélio Oiticica
Until Summer 2019

Tropicália
Tropicália is used to describe the explosion of cultural creativity in Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo in 1968 as Brazil’s military regime tightened its grip on power.
Many of the artists, writers and musicians associated with Tropicália came of age during the 1950s in a time of intense optimism when the cultural world had been encouraged to play a central role in the creation of a democratic, socially just and modern Brazil. Nevertheless, a military coup in 1964 had brought to power a right-wing regime at odds with the concerns of left-wing artists. Tropicália became a way of exposing the contradictions of modernisation under such an authoritarian rule.
The word Tropicália comes from an installation by the artist Hélio Oiticica, who created environments that were designed to encourage the viewer’s emotional and intellectual participation. Oiticica called them “penetrables” because people were originally encouraged to enter them. They mimic the improvised, colourful dwellings in Rio de Janeiro’s favelas, or shanty towns. The lush plants and sand help to convey a sense of the tropical character of the city. When Oiticica exhibited the work, he also included live parrots.
From its beginning, Tropicália was seen as a re-articulation of Anthropophagia (“cannibalism”), an artistic ideology promoted by Oswald de Andrade.
(www.tate.org.uk. Adaptado.)
Analyse the following comic.

(http://iniscommunication.com)
The objective of the comic is to
The future is largely urban
By 2030, there will be 5 billion people living in
urban areas (61% of the estimated world
population of 8.2 billion)
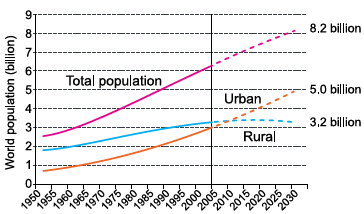
(http://esa.un.org. Adaptado.)
The chart shows that the approximate period of time when both urban and rural estimated populations were equal was
Cerrado

Located between the Amazon, Atlantic Forests and Pantanal, the Cerrado is the largest savanna region in South America.
The Cerrado is one of the most threatened and overexploited regions in Brazil, second only to the Atlantic Forests in vegetation loss and deforestation. Unsustainable agricultural activities, particularly soy production and cattle ranching, as well as burning of vegetation for charcoal, continue to pose a major threat to the Cerrado’s biodiversity. Despite its environmental importance, it is one of the least protected regions in Brazil.
Facts & Figures
• Covering 2 million km2 , or 21% of the country’s territory, the Cerrado is the second largest vegetation type in Brazil.
• The area is equivalent to the size of England, France, Germany, Italy and Spain combined.
• More than 1,600 species of mammals, birds and reptiles have been identified in the Cerrado.
• Annual rainfall is around 800 to 1600 mm.
• The capital of Brazil, Brasilia, is located in the heart of the Cerrado. • Only 20% of the Cerrado’s original vegetation remains intact; less than 3% of the area is currently guarded by law.
(http://wwf.panda.org. Adaptado.)

Cerrado

Located between the Amazon, Atlantic Forests and Pantanal, the Cerrado is the largest savanna region in South America.
The Cerrado is one of the most threatened and overexploited regions in Brazil, second only to the Atlantic Forests in vegetation loss and deforestation. Unsustainable agricultural activities, particularly soy production and cattle ranching, as well as burning of vegetation for charcoal, continue to pose a major threat to the Cerrado’s biodiversity. Despite its environmental importance, it is one of the least protected regions in Brazil.
Facts & Figures
• Covering 2 million km2 , or 21% of the country’s territory, the Cerrado is the second largest vegetation type in Brazil.
• The area is equivalent to the size of England, France, Germany, Italy and Spain combined.
• More than 1,600 species of mammals, birds and reptiles have been identified in the Cerrado.
• Annual rainfall is around 800 to 1600 mm.
• The capital of Brazil, Brasilia, is located in the heart of the Cerrado. • Only 20% of the Cerrado’s original vegetation remains intact; less than 3% of the area is currently guarded by law.
(http://wwf.panda.org. Adaptado.)

Cerrado

Located between the Amazon, Atlantic Forests and Pantanal, the Cerrado is the largest savanna region in South America.
The Cerrado is one of the most threatened and overexploited regions in Brazil, second only to the Atlantic Forests in vegetation loss and deforestation. Unsustainable agricultural activities, particularly soy production and cattle ranching, as well as burning of vegetation for charcoal, continue to pose a major threat to the Cerrado’s biodiversity. Despite its environmental importance, it is one of the least protected regions in Brazil.
Facts & Figures
• Covering 2 million km2 , or 21% of the country’s territory, the Cerrado is the second largest vegetation type in Brazil.
• The area is equivalent to the size of England, France, Germany, Italy and Spain combined.
• More than 1,600 species of mammals, birds and reptiles have been identified in the Cerrado.
• Annual rainfall is around 800 to 1600 mm.
• The capital of Brazil, Brasilia, is located in the heart of the Cerrado. • Only 20% of the Cerrado’s original vegetation remains intact; less than 3% of the area is currently guarded by law.
(http://wwf.panda.org. Adaptado.)

Cerrado

Located between the Amazon, Atlantic Forests and Pantanal, the Cerrado is the largest savanna region in South America.
The Cerrado is one of the most threatened and overexploited regions in Brazil, second only to the Atlantic Forests in vegetation loss and deforestation. Unsustainable agricultural activities, particularly soy production and cattle ranching, as well as burning of vegetation for charcoal, continue to pose a major threat to the Cerrado’s biodiversity. Despite its environmental importance, it is one of the least protected regions in Brazil.
Facts & Figures
• Covering 2 million km2 , or 21% of the country’s territory, the Cerrado is the second largest vegetation type in Brazil.
• The area is equivalent to the size of England, France, Germany, Italy and Spain combined.
• More than 1,600 species of mammals, birds and reptiles have been identified in the Cerrado.
• Annual rainfall is around 800 to 1600 mm.
• The capital of Brazil, Brasilia, is located in the heart of the Cerrado. • Only 20% of the Cerrado’s original vegetation remains intact; less than 3% of the area is currently guarded by law.
(http://wwf.panda.org. Adaptado.)

Examine o cartum de Pia Guerra, publicado no Instagram da revista The New Yorker em 13.11.2018.
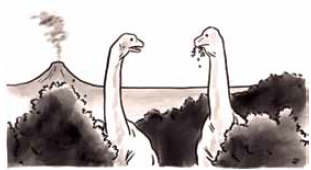
“I had that dream again where the small hairy creatures were selling my body for three dollars a gallon.”
A mercadoria a que o cartum faz alusão está diretamente relacionada ao seguinte problema ambiental:
Examine o cartum de Steinberg, publicado em seu Instagram em 06.04.2019.

Para o cartunista, a diferença entre estar ou não estar de
dieta limita-se a um sentimento de
