Questões Militares Comentadas sobre inglês
Foram encontradas 2.808 questões
Text II
Millions of people need homes. Millions of shipping containers are going unused. Could this be an answer to the global housing crisis? Cleveland Containers explore further.
England is facing a housing crisis. According to housing charity Shelter, more than 50,000 households a year are being forced out of their homes, and there are more than 9 million renters in unsecure rented accommodations.
The situation is shaky even for those who own their own homes. 28,900 homes were repossessed across the UK in 2013.
But this situation isn't unique to England. House prices are soaring across the world, which is placing home ownership out of reach for millions. And that's just in the developed world. Around 850 million people are currently living in “informal settlements”. In numerous rapidly urbanising cities, the average housing costs can be up to 200% of the net monthly income.
There is no single explanation as to why the world's facing a housing crisis, and there's no easy answer for how to solve it. But one major factor is a general dearth of good quality, affordable housing. Many developments in the housing market are focused on constructing high-end units that are expensive to build and out of the price range of most. This needs to change.
Desperate times often call for radical Solutions. One thing the world isn't lacking is shipping containers. There may be up to 40 million shipping containers in the world right now, and experts believe that only six million are currently in use.
Who'd live in a shipping Container?
Shipping containers are built to be strong, secure and practical. These are all sound benefits for storage and mass transit, but do they make for comfortable accommodation?
The idea of living in a shipping Container might strike some as odd, unfeasible, impractical and maybe even a little unappealing. But it's important to think of shipping containers not as finished products, but as raw materiais - as exoskeletons for future homes.
Because, really, there's no end to what you can do with a shipping Container. They can easily be insulated and fitted with Windows, doors, indoor partitions, electricity and running water - everything that's needed for human inhabitation. A single shipping Container can be transformed into a cosy dwelling in no time at all. But if more space is needed, you can just stack multiple containers on top of each other.
And if you're really wondering whether people would be comfortable living in converted shipping containers, just consider the great reaction that greets shipping containers converted for retail use. They're thought of as cool, hip and quirky. When used as affordable housing, it's no stretch to say that many won't think of shipping containers as a last resort, so much as actively desirable.
(Abridged and adapted from
https://www.openaccessgovemment.org)
Read the statements about the text and decide whether they are TRUE (T) or FALSE (F). Mark the correct option.
I - There is a surfeit of dwellings in England.
II - Housing is wobbly in England.
III - House prices are steep worldwide.
IV - Home ownership is attainable for many people.
V - Living in a shipping Container is alluring and ordinary throughout the world.
Text I
Read the text below and choose the correct option.
Buy a beach cruiser and help save sea turtles on Kiawah
Every spring, fierce female sea turtles-mostly loggerheads-make their way from the ocean to Kiawah Island during nesting season.
From May through October, Kiawah's beaches are home to 400 nests and thousands of baby loggerheads. But many of these endangered hatchlings would not survive without the island's hands-on nest protection program. Specifícally, the Kiawah Island Turtle Patrol efforts that help 75% of hatchlings make it from their nests to the ocean. Without these efforts: less than 10% have a chance.
Sea turtles are an endangered species and the loggerhead turtle has been on the threatened list since 1978. Over the years, the Kiawah Island Turtle Patrol has become one of the largest volunteer turtle efforts in the United States. From relocating nests to helping hatchlings find the sea, volunteering is open to island residents and guests, and the program relies on the community to help raise awareness about the importance of nesting season.
This May, you'11 see a custom fleet of beach cruisers with an original turtle print designed by Peter Millar at the new Timbers Kiawah Ocean Club and Residences.
“We approached Peter Millar, a favorite on Kiawah, to design a turtle-pattemed bike as a fun way to raise our owners' awareness about the turtles and show our commitment to protecting the wildlife on Kiawah”, says Chris Burden, managing director for Timbers Kiawah.
You don't have to be a Timbers' owner to help: the limited-edition beach cruisers are for sale to the public and 100% of the proceeds go to the turtle patrol. “Kiawah Island is one of the country's most vital nesting areas for loggerhead sea turtles and the turtle patrol is responsible for nesting patrols and monitoring efforts up and down the beach. The contributions will be used to fund their initiatives in whatever way they see fit”, Burden says. Anyone can volunteer in the nesting and hatching programs by contacting Kiawah Island Turtle Patrol.
(Abridged and adapted from https://www.newsweek.com/iawahsave-turtles-1412015)
It is possible to infer from the text that
What is Interpol?

Founded in 1923, Interpol is an international police organisation made up of 194 member countries. It is not a police force in the traditional sense – its agents are not able to arrest criminals. Instead, it is more of an informationsharing network, providing a way for national police forces to co-operate effectively and tackle international crime ranging from human trafficking and terrorism to money laundering and illegal art dealing.
The organisation, based in France, operates centralised criminal databases that contain fingerprint records, DNA samples and stolen documents: a treasure trove so valuable that police consulted it 146 times every second in 2017. Interpol’s other main function is to issue notices: alerts to member states for missing or wanted persons. The bestknown of these is the “Red Notice”, a notification that a member state would like someone arrested. States are not obliged to follow these notices, but will often treat them as a warrant for someone’s arrest and extradition. “Diffusions”, which can be issued with less bureaucracy, are another popular way of seeking arrests through Interpol.
Notices and diffusions lie at the heart of the organisation’s recent turmoil. Though Interpol’s constitution explicitly forbids any activities of a political character, activists accuse it of failing to enforce this rule.
(www.economist.com/the-economist-explains/2018/11/22/ what-is-interpol. Adaptado)
What is Interpol?

Founded in 1923, Interpol is an international police organisation made up of 194 member countries. It is not a police force in the traditional sense – its agents are not able to arrest criminals. Instead, it is more of an informationsharing network, providing a way for national police forces to co-operate effectively and tackle international crime ranging from human trafficking and terrorism to money laundering and illegal art dealing.
The organisation, based in France, operates centralised criminal databases that contain fingerprint records, DNA samples and stolen documents: a treasure trove so valuable that police consulted it 146 times every second in 2017. Interpol’s other main function is to issue notices: alerts to member states for missing or wanted persons. The bestknown of these is the “Red Notice”, a notification that a member state would like someone arrested. States are not obliged to follow these notices, but will often treat them as a warrant for someone’s arrest and extradition. “Diffusions”, which can be issued with less bureaucracy, are another popular way of seeking arrests through Interpol.
Notices and diffusions lie at the heart of the organisation’s recent turmoil. Though Interpol’s constitution explicitly forbids any activities of a political character, activists accuse it of failing to enforce this rule.
(www.economist.com/the-economist-explains/2018/11/22/ what-is-interpol. Adaptado)
What is Interpol?

Founded in 1923, Interpol is an international police organisation made up of 194 member countries. It is not a police force in the traditional sense – its agents are not able to arrest criminals. Instead, it is more of an informationsharing network, providing a way for national police forces to co-operate effectively and tackle international crime ranging from human trafficking and terrorism to money laundering and illegal art dealing.
The organisation, based in France, operates centralised criminal databases that contain fingerprint records, DNA samples and stolen documents: a treasure trove so valuable that police consulted it 146 times every second in 2017. Interpol’s other main function is to issue notices: alerts to member states for missing or wanted persons. The bestknown of these is the “Red Notice”, a notification that a member state would like someone arrested. States are not obliged to follow these notices, but will often treat them as a warrant for someone’s arrest and extradition. “Diffusions”, which can be issued with less bureaucracy, are another popular way of seeking arrests through Interpol.
Notices and diffusions lie at the heart of the organisation’s recent turmoil. Though Interpol’s constitution explicitly forbids any activities of a political character, activists accuse it of failing to enforce this rule.
(www.economist.com/the-economist-explains/2018/11/22/ what-is-interpol. Adaptado)
What is Interpol?

Founded in 1923, Interpol is an international police organisation made up of 194 member countries. It is not a police force in the traditional sense – its agents are not able to arrest criminals. Instead, it is more of an informationsharing network, providing a way for national police forces to co-operate effectively and tackle international crime ranging from human trafficking and terrorism to money laundering and illegal art dealing.
The organisation, based in France, operates centralised criminal databases that contain fingerprint records, DNA samples and stolen documents: a treasure trove so valuable that police consulted it 146 times every second in 2017. Interpol’s other main function is to issue notices: alerts to member states for missing or wanted persons. The bestknown of these is the “Red Notice”, a notification that a member state would like someone arrested. States are not obliged to follow these notices, but will often treat them as a warrant for someone’s arrest and extradition. “Diffusions”, which can be issued with less bureaucracy, are another popular way of seeking arrests through Interpol.
Notices and diffusions lie at the heart of the organisation’s recent turmoil. Though Interpol’s constitution explicitly forbids any activities of a political character, activists accuse it of failing to enforce this rule.
(www.economist.com/the-economist-explains/2018/11/22/ what-is-interpol. Adaptado)
What is Interpol?

Founded in 1923, Interpol is an international police organisation made up of 194 member countries. It is not a police force in the traditional sense – its agents are not able to arrest criminals. Instead, it is more of an informationsharing network, providing a way for national police forces to co-operate effectively and tackle international crime ranging from human trafficking and terrorism to money laundering and illegal art dealing.
The organisation, based in France, operates centralised criminal databases that contain fingerprint records, DNA samples and stolen documents: a treasure trove so valuable that police consulted it 146 times every second in 2017. Interpol’s other main function is to issue notices: alerts to member states for missing or wanted persons. The bestknown of these is the “Red Notice”, a notification that a member state would like someone arrested. States are not obliged to follow these notices, but will often treat them as a warrant for someone’s arrest and extradition. “Diffusions”, which can be issued with less bureaucracy, are another popular way of seeking arrests through Interpol.
Notices and diffusions lie at the heart of the organisation’s recent turmoil. Though Interpol’s constitution explicitly forbids any activities of a political character, activists accuse it of failing to enforce this rule.
(www.economist.com/the-economist-explains/2018/11/22/ what-is-interpol. Adaptado)
What is Interpol?

Founded in 1923, Interpol is an international police organisation made up of 194 member countries. It is not a police force in the traditional sense – its agents are not able to arrest criminals. Instead, it is more of an informationsharing network, providing a way for national police forces to co-operate effectively and tackle international crime ranging from human trafficking and terrorism to money laundering and illegal art dealing.
The organisation, based in France, operates centralised criminal databases that contain fingerprint records, DNA samples and stolen documents: a treasure trove so valuable that police consulted it 146 times every second in 2017. Interpol’s other main function is to issue notices: alerts to member states for missing or wanted persons. The bestknown of these is the “Red Notice”, a notification that a member state would like someone arrested. States are not obliged to follow these notices, but will often treat them as a warrant for someone’s arrest and extradition. “Diffusions”, which can be issued with less bureaucracy, are another popular way of seeking arrests through Interpol.
Notices and diffusions lie at the heart of the organisation’s recent turmoil. Though Interpol’s constitution explicitly forbids any activities of a political character, activists accuse it of failing to enforce this rule.
(www.economist.com/the-economist-explains/2018/11/22/ what-is-interpol. Adaptado)
Mark the right option to fill in the blanks in the cartoon, respectively.

Read and complete the sentence below.
I’m traveling to ,______ United States next month. I want to see _____ Hawaii and________ Rocky Mountains (depending on_______money and________time!).
Mark the option which best completes the blanks respectiveiy.
Complete the sentences using the correct verb tense for the verbs in brackets.
Hanna ______________ (drive) down the road when she ______________ (see)the perfect wedding dress on a shop window.
Mark usually ______________, (leave) for work early, but today he's a little late because he ______________ (have) problems with his car.
Jane ______________ (be)fifteen years old, so she _____________ (have) a driving license.
Mark the sentence that shows the correct use of verb tenses.
Match the questions and answers.
I- How’s Mary?
II- What does Cíndy do?
III- Whose daughter is Karen?
IV- How much meat does your sister have on a regular meal?
V- Hou many friends do Mark and Sue have on Facebook?
( ) A few.
( ) She’s hers.
( ) She’s all right.
( ) A little.
( ) She’s a shop manager.
Mark the option that shows the correct order of answers.
Read Garfield, a comic strip, by Jim Davis.

lt’s correct to say that Garfield
Observe the city map.
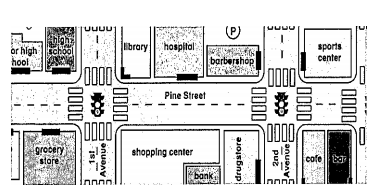
lt’s correct to say that the
Read the dialogue below.
A: Hi, Anna!
B: Good morning, Sue!
A: Tell me, dear,___________ you go to Theo's bday party last night?
B: oh, yes, I___________ . It was great! I ___________ so much fun! But I ___________ you there! ___________ you there, sweetie?
A: No, I ___________ . I ___________ at home. What time did you get home?
B: It___________ about 11 p.m. when I got there!
A: AII right then! See you around!
B See ya!
Mark the option that completes the dialogue correctly.
TEXT II
Passwords to be replaced by Web Authentication
It looks iike login usernames and passwords are on __(I)__ way out. No longer will we have to worry about the security of __(II)__ login credentiais. They are set to be replaced by an infinitely more secure login system known as Web Authentication. Web Authentication has become an official standard for logging in at the main Internet standards body, the World Wide Web Consortium (WWWC). It is a system that will be universally used by web browsers and platforms for simpier and stronger authentication processes. It will allow website users to iog in securely to their online accounts using a digital device, biometrics (such as fingerprints and facial recognition) or USB security keys.
The WWWC spoke about the days of passwords being numbered. A spokesperson said: "lt’s common knowledge that passwords have outlived their efficacy. Not only are stoien, weak or default passwords behind 81 per cent of data breaches, they are a drain of time and resources." It added: "Now is the time for web Services and businesses to adopt Web Authentication to move beyond vulnerable passwords and help web users improve the security of their online experiences," Web Authentication means users are at less risk of having their passwords and credentiais stoien. This is because login authentication is achieved via physicai vices or biometrics from our body.
<https://breakingnewsenglish.eom/1904/190401 -webauthentication.html>
TEXT II
Passwords to be replaced by Web Authentication
It looks iike login usernames and passwords are on __(I)__ way out. No longer will we have to worry about the security of __(II)__ login credentiais. They are set to be replaced by an infinitely more secure login system known as Web Authentication. Web Authentication has become an official standard for logging in at the main Internet standards body, the World Wide Web Consortium (WWWC). It is a system that will be universally used by web browsers and platforms for simpier and stronger authentication processes. It will allow website users to iog in securely to their online accounts using a digital device, biometrics (such as fingerprints and facial recognition) or USB security keys.
The WWWC spoke about the days of passwords being numbered. A spokesperson said: "lt’s common knowledge that passwords have outlived their efficacy. Not only are stoien, weak or default passwords behind 81 per cent of data breaches, they are a drain of time and resources." It added: "Now is the time for web Services and businesses to adopt Web Authentication to move beyond vulnerable passwords and help web users improve the security of their online experiences," Web Authentication means users are at less risk of having their passwords and credentiais stoien. This is because login authentication is achieved via physicai vices or biometrics from our body.
<https://breakingnewsenglish.eom/1904/190401 -webauthentication.html>
TEXT II
Passwords to be replaced by Web Authentication
It looks iike login usernames and passwords are on __(I)__ way out. No longer will we have to worry about the security of __(II)__ login credentiais. They are set to be replaced by an infinitely more secure login system known as Web Authentication. Web Authentication has become an official standard for logging in at the main Internet standards body, the World Wide Web Consortium (WWWC). It is a system that will be universally used by web browsers and platforms for simpier and stronger authentication processes. It will allow website users to iog in securely to their online accounts using a digital device, biometrics (such as fingerprints and facial recognition) or USB security keys.
The WWWC spoke about the days of passwords being numbered. A spokesperson said: "lt’s common knowledge that passwords have outlived their efficacy. Not only are stoien, weak or default passwords behind 81 per cent of data breaches, they are a drain of time and resources." It added: "Now is the time for web Services and businesses to adopt Web Authentication to move beyond vulnerable passwords and help web users improve the security of their online experiences," Web Authentication means users are at less risk of having their passwords and credentiais stoien. This is because login authentication is achieved via physicai vices or biometrics from our body.
<https://breakingnewsenglish.eom/1904/190401 -webauthentication.html>
TEXT I
Robotic Cars
The year is 2020, and it’s 7;45 on a rainy Monday morning, and you are in your car on your way to work. You turn right, and you turn left. A few minutes later, you stop at a traffic light. When the light turns green and there are no other cars in the intersection, you continue on your way. Ten minutes later you get to work and stop reading the morning paper. Then, you get out of your car and you say, “Thank you!". Your car replies, “You’re welcome!’’. This possibie future may sound unreai, but in fact many car companies are aiready testing robotic cars, or driverless cars, on the roads today, although the cars don't speak very much yet.
In the 1980s, Germany and the United States tested the first driverless cars, and by 2020 companies such as Volvo, GM, Nissan and BMW plan to seil driverless cars. Driverless cars are not really ‘driverless - the drivers are computers that use radar, Computer maps and other modern technology. They offer many advantages. Perhaps the most important of these is fewer deaths caused by road accidents. For example, in 1968 more than 53.000 people lost their lives in car accidents in the USA. This number has fallen to less than 33.000 but it’s still a high number. In addition, people will spend iess time stuck in traffic jams and there will be no need for people to have a driving license. One of the major disadvantages of this new technology, however, is the cost. It’s not free. U$5.000 to U$10.000 is added to the price of the new car. Nevertheless, at some time in your life, you will probably be sitting in a robotic, ;driverless car on your way to work or school. The future is almost here. Are you ready for it?
<https://www.aHthinastoDics.eom/uploads/2/3/2/9/23290220/lesson-drivina-robo ticcars2.pdf>