Questões de Concurso Militar EsFCEx 2021 para Magistério em Inglês
Foram encontradas 60 questões
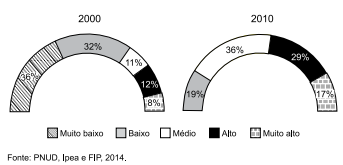
(Atlas do Desenvolvimento Humano nas Regiões Metropolitanas Brasileiras, 2014, p. 68)
A análise do gráfico e a comparação entre o período de 2000 a 2010 permitem afirmar que
“Não adianta uma residência combater o mosquito da dengue se o vizinho não colabora. A poluição de um córrego vai afetar toda a população que vive rio abaixo.” (DOWBOR, 2007, p. 79)
Assinale a alternativa que traz uma afirmação correta de acordo com a perspectiva do autor em relação à educação.
“A avaliação, enquanto ____________, vai conceber o conhecimento como apropriação do saber pelo aluno e também pelo professor, como ação-reflexão-ação que se passa na sala de aula em direção a um saber aprimorado, enriquecido, carregado de significados, de compreensão. Dessa forma, a avaliação passa a exigir do professor uma relação epistemológica com o aluno – uma conexão entendida como reflexão aprofundada a respeito das formas como se dá a compreensão do educando sobre o objeto do conhecimento.”
Assinale a alternativa que preenche corretamente a lacuna.
Leia o texto para responder à questão.
Because we all have different styles of teaching, and therefore planning, orientations about course planning and delivery should not be meant to be prescriptive. As Bailey (1996) points out, a lesson plan is like a road map “which describes where the teacher hopes to go in a lesson, presumably taking the students along”. It is the latter part of this quote that is important for teachers to remember, because they may need to make “in-flight” changes in response to the actuality of the classroom. As Bailey (1996) correctly points out, “In realizing lesson plans, part of a skilled teacher’s logic in use involves managing such departures to maximimize teaching and learning opportunities”. Clearly thought-out lesson plans will more likely maintain the attention of students and increase the likelihood that they will be interested.
(RICHARDS, Jack C.; RENANDYA, Willy A.(Ed.).
Methodology in language teaching: an anthology of current practice.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002. p. 36. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder à questão.
Because we all have different styles of teaching, and therefore planning, orientations about course planning and delivery should not be meant to be prescriptive. As Bailey (1996) points out, a lesson plan is like a road map “which describes where the teacher hopes to go in a lesson, presumably taking the students along”. It is the latter part of this quote that is important for teachers to remember, because they may need to make “in-flight” changes in response to the actuality of the classroom. As Bailey (1996) correctly points out, “In realizing lesson plans, part of a skilled teacher’s logic in use involves managing such departures to maximimize teaching and learning opportunities”. Clearly thought-out lesson plans will more likely maintain the attention of students and increase the likelihood that they will be interested.
(RICHARDS, Jack C.; RENANDYA, Willy A.(Ed.).
Methodology in language teaching: an anthology of current practice.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002. p. 36. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder à questão.
Because we all have different styles of teaching, and therefore planning, orientations about course planning and delivery should not be meant to be prescriptive. As Bailey (1996) points out, a lesson plan is like a road map “which describes where the teacher hopes to go in a lesson, presumably taking the students along”. It is the latter part of this quote that is important for teachers to remember, because they may need to make “in-flight” changes in response to the actuality of the classroom. As Bailey (1996) correctly points out, “In realizing lesson plans, part of a skilled teacher’s logic in use involves managing such departures to maximimize teaching and learning opportunities”. Clearly thought-out lesson plans will more likely maintain the attention of students and increase the likelihood that they will be interested.
(RICHARDS, Jack C.; RENANDYA, Willy A.(Ed.).
Methodology in language teaching: an anthology of current practice.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002. p. 36. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder à questão.
Because we all have different styles of teaching, and therefore planning, orientations about course planning and delivery should not be meant to be prescriptive. As Bailey (1996) points out, a lesson plan is like a road map “which describes where the teacher hopes to go in a lesson, presumably taking the students along”. It is the latter part of this quote that is important for teachers to remember, because they may need to make “in-flight” changes in response to the actuality of the classroom. As Bailey (1996) correctly points out, “In realizing lesson plans, part of a skilled teacher’s logic in use involves managing such departures to maximimize teaching and learning opportunities”. Clearly thought-out lesson plans will more likely maintain the attention of students and increase the likelihood that they will be interested.
(RICHARDS, Jack C.; RENANDYA, Willy A.(Ed.).
Methodology in language teaching: an anthology of current practice.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002. p. 36. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder à questão.
A number of writers in our field have criticized the concept of language teaching methods. Some say that methods are prescriptions for classroom behavior (Pennycook 1989); others that teachers do not think about methods when planning their lessons (Long 1991), and that methodological labels tell us little about what really occurs in classrooms (Katz 1996).
A particular method can be imposed on teachers by others. However, we also know that teaching is more than following a recipe. Any method is going to be shaped by a teacher’s own understanding, beliefs, style, and level of experience. After all, teachers are professionals who can, in the best of all worlds, make their own decisions. They are informed by their own experience, the findings from research, and the wisdom of practice accumulated by the profession (see, for example, Kumaravadivelu 1994).
Furthermore, a method is decontextualized. How a method is implemented in the classroom is going to be affected not only by who the teacher is, but also by who the students are, the institutional constraints and demands, and factors connected to the wider sociocultural context where the instruction takes place. In addition, decisions that teachers make are often affected by exigencies in the classroom rather than by methodological considerations. Saying that a particular method is practiced certainly does not give us the whole picture of what is happening in the classroom. Then, too, since a method is more abstract than a teaching activity, it is not surprising that teachers think in terms of activities rather than methodological choices when they plan their lessons.
[...] Some language teaching methods share the view that language can best be learned when it is taught through communication, rather than for it; and second, that language acquisition can be enhanced by working not only on language, but also on the process of learning (learnng strategies, cooperative learning and multiple intelligences).
(LARSEN FREEMAN, D. Techniques and principles in language
teaching. 2th ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000. pp. xi-xii. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder à questão.
A number of writers in our field have criticized the concept of language teaching methods. Some say that methods are prescriptions for classroom behavior (Pennycook 1989); others that teachers do not think about methods when planning their lessons (Long 1991), and that methodological labels tell us little about what really occurs in classrooms (Katz 1996).
A particular method can be imposed on teachers by others. However, we also know that teaching is more than following a recipe. Any method is going to be shaped by a teacher’s own understanding, beliefs, style, and level of experience. After all, teachers are professionals who can, in the best of all worlds, make their own decisions. They are informed by their own experience, the findings from research, and the wisdom of practice accumulated by the profession (see, for example, Kumaravadivelu 1994).
Furthermore, a method is decontextualized. How a method is implemented in the classroom is going to be affected not only by who the teacher is, but also by who the students are, the institutional constraints and demands, and factors connected to the wider sociocultural context where the instruction takes place. In addition, decisions that teachers make are often affected by exigencies in the classroom rather than by methodological considerations. Saying that a particular method is practiced certainly does not give us the whole picture of what is happening in the classroom. Then, too, since a method is more abstract than a teaching activity, it is not surprising that teachers think in terms of activities rather than methodological choices when they plan their lessons.
[...] Some language teaching methods share the view that language can best be learned when it is taught through communication, rather than for it; and second, that language acquisition can be enhanced by working not only on language, but also on the process of learning (learnng strategies, cooperative learning and multiple intelligences).
(LARSEN FREEMAN, D. Techniques and principles in language
teaching. 2th ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000. pp. xi-xii. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder à questão.
A number of writers in our field have criticized the concept of language teaching methods. Some say that methods are prescriptions for classroom behavior (Pennycook 1989); others that teachers do not think about methods when planning their lessons (Long 1991), and that methodological labels tell us little about what really occurs in classrooms (Katz 1996).
A particular method can be imposed on teachers by others. However, we also know that teaching is more than following a recipe. Any method is going to be shaped by a teacher’s own understanding, beliefs, style, and level of experience. After all, teachers are professionals who can, in the best of all worlds, make their own decisions. They are informed by their own experience, the findings from research, and the wisdom of practice accumulated by the profession (see, for example, Kumaravadivelu 1994).
Furthermore, a method is decontextualized. How a method is implemented in the classroom is going to be affected not only by who the teacher is, but also by who the students are, the institutional constraints and demands, and factors connected to the wider sociocultural context where the instruction takes place. In addition, decisions that teachers make are often affected by exigencies in the classroom rather than by methodological considerations. Saying that a particular method is practiced certainly does not give us the whole picture of what is happening in the classroom. Then, too, since a method is more abstract than a teaching activity, it is not surprising that teachers think in terms of activities rather than methodological choices when they plan their lessons.
[...] Some language teaching methods share the view that language can best be learned when it is taught through communication, rather than for it; and second, that language acquisition can be enhanced by working not only on language, but also on the process of learning (learnng strategies, cooperative learning and multiple intelligences).
(LARSEN FREEMAN, D. Techniques and principles in language
teaching. 2th ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000. pp. xi-xii. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder à questão.
A number of writers in our field have criticized the concept of language teaching methods. Some say that methods are prescriptions for classroom behavior (Pennycook 1989); others that teachers do not think about methods when planning their lessons (Long 1991), and that methodological labels tell us little about what really occurs in classrooms (Katz 1996).
A particular method can be imposed on teachers by others. However, we also know that teaching is more than following a recipe. Any method is going to be shaped by a teacher’s own understanding, beliefs, style, and level of experience. After all, teachers are professionals who can, in the best of all worlds, make their own decisions. They are informed by their own experience, the findings from research, and the wisdom of practice accumulated by the profession (see, for example, Kumaravadivelu 1994).
Furthermore, a method is decontextualized. How a method is implemented in the classroom is going to be affected not only by who the teacher is, but also by who the students are, the institutional constraints and demands, and factors connected to the wider sociocultural context where the instruction takes place. In addition, decisions that teachers make are often affected by exigencies in the classroom rather than by methodological considerations. Saying that a particular method is practiced certainly does not give us the whole picture of what is happening in the classroom. Then, too, since a method is more abstract than a teaching activity, it is not surprising that teachers think in terms of activities rather than methodological choices when they plan their lessons.
[...] Some language teaching methods share the view that language can best be learned when it is taught through communication, rather than for it; and second, that language acquisition can be enhanced by working not only on language, but also on the process of learning (learnng strategies, cooperative learning and multiple intelligences).
(LARSEN FREEMAN, D. Techniques and principles in language
teaching. 2th ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000. pp. xi-xii. Adaptado)