Questões de Concurso
Sobre interpretação de texto | reading comprehension em inglês
Foram encontradas 9.532 questões
Ano: 2010
Banca:
FCC
Órgão:
METRÔ-SP
Provas:
FCC - 2010 - METRÔ-SP - Engenheiro Júnior - Engenharia Elétrica
|
FCC - 2010 - METRÔ-SP - Engenheiro Eletrônico |
Q74912
Inglês
Texto associado
Subways: The New Urban Status Symbol
Business Week - December 5, 2007
by Jennifer Fishbein
It seems like everywhere you turn these days, a new
high-speed train is whisking more passengers across longer
distances faster than ever before. A [NOUN] to Paris from
London is quicker than flying; Japanese bullet trains traverse the
320 miles from Tokyo to Osaka in two and a half hours; and
magnetic levitating trains in Shanghai cut through the city at 268
miles per hour. But while high-speed trains may grab all the
glamour, the more mundane business of subway construction is
what's driving the biggest growth for transportation companies.
Indeed, the world is seeing an unprecedented boom in new
subways and expansion to existing systems. Thanks to surging
economic growth and urban populations, demand for subways is
soaring in China and India. Lots of other places around the
world also are building new lines, from Dubai to Santo Domingo,
capital of the Dominican Republic. And many European and
American cities ? including even such improbable locales as Los
Angeles and Phoenix ? have caught the transit bug.
Problem-Solving and Prestige
Some cities build out of necessity. Rising prosperity
prompted Dubai residents to buy so many cars that they realized
they could [ADVERB] longer drive these cars because they
were stuck in traffic. Others are keen on the environmental
benefits of metros, which produce far less pollution and
encourage drivers to leave cars at home. Some places, mainly
in the Middle East, are looking to diversify their oil-dependent
economies. And others, to be honest, are chasing an urban
status symbol. Building a metro won't turn any old town into
Paris or London, but it does tell the world that you've arrived.
"You have in some cases a prestige issue, which is more
the case in young cities in need of an image," says Jean-Noël
Debroise, vice-president for product and strategy at Alstom
(ALSO.PA), the French transport company that has built a
quarter of the world's metros.
Rennes is an example of the new trend. The city of about
212,000 people in northwestern France was looking to raise its profile when it installed a metro in 2002. It raised the bar by
opting for a driverless system made by Siemens ? just like the
shiny new No. 14 line in Paris ? protecting passengers from the
French penchant for transit strikes. Turin, Italy, did the same to
help win its bid for the 2006 Winter Olympics; its driverless
system opened just before the games. Even the Spanish island
of Mallorca inaugurated a short metro line in April in hopes of
luring even more tourists to its capital, Palma. Alas, it closed
indefinitely in September due to flooding, amid charges of
mismanagement.
A Boon for Transit Builders
The world's three largest metro manufacturers, Montrealbased
Bombardier (BBDB.TO), Alstom, and Munich-based
Siemens (SI) report high demand for mass transit, including
tramways and light-rail systems that run both under and
[PREPOSITION] ground. The global subway market was worth
9.3 billion dollars in 2005 and is projected to grow at a rate of
2.7% per year until 2015, according to a 2007 study by the
European Railway Industry Assn. Subway lines [TO BUILD] or
extended in 20 European cities and five Middle Eastern ones,
and dozens of towns are constructing light-rail systems, reports
the Brussels-based International Association of Public
Transport.
The size of a city determines its need for a metro system.
Cities of a few million people ? or those anticipating huge
population growth ? really can't do without a mass transit
system. But cities of one or two million inhabitants can choose
between a subway and a surface tramway, which costs far less
but also runs more slowly. [CONJUNCTION] funding is an issue,
cities usually will spring for a subway, says Debroise. "The
tramway has a very old image of the 19th century, with horses in
the streets," he says.
(Adapted from http://www.businessweek.com/globalbiz/
content/dec2007/gb2007125_600001.htm?chan=top+news_
top+news+index_global+business)
Business Week - December 5, 2007
by Jennifer Fishbein
It seems like everywhere you turn these days, a new
high-speed train is whisking more passengers across longer
distances faster than ever before. A [NOUN] to Paris from
London is quicker than flying; Japanese bullet trains traverse the
320 miles from Tokyo to Osaka in two and a half hours; and
magnetic levitating trains in Shanghai cut through the city at 268
miles per hour. But while high-speed trains may grab all the
glamour, the more mundane business of subway construction is
what's driving the biggest growth for transportation companies.
Indeed, the world is seeing an unprecedented boom in new
subways and expansion to existing systems. Thanks to surging
economic growth and urban populations, demand for subways is
soaring in China and India. Lots of other places around the
world also are building new lines, from Dubai to Santo Domingo,
capital of the Dominican Republic. And many European and
American cities ? including even such improbable locales as Los
Angeles and Phoenix ? have caught the transit bug.
Problem-Solving and Prestige
Some cities build out of necessity. Rising prosperity
prompted Dubai residents to buy so many cars that they realized
they could [ADVERB] longer drive these cars because they
were stuck in traffic. Others are keen on the environmental
benefits of metros, which produce far less pollution and
encourage drivers to leave cars at home. Some places, mainly
in the Middle East, are looking to diversify their oil-dependent
economies. And others, to be honest, are chasing an urban
status symbol. Building a metro won't turn any old town into
Paris or London, but it does tell the world that you've arrived.
"You have in some cases a prestige issue, which is more
the case in young cities in need of an image," says Jean-Noël
Debroise, vice-president for product and strategy at Alstom
(ALSO.PA), the French transport company that has built a
quarter of the world's metros.
Rennes is an example of the new trend. The city of about
212,000 people in northwestern France was looking to raise its profile when it installed a metro in 2002. It raised the bar by
opting for a driverless system made by Siemens ? just like the
shiny new No. 14 line in Paris ? protecting passengers from the
French penchant for transit strikes. Turin, Italy, did the same to
help win its bid for the 2006 Winter Olympics; its driverless
system opened just before the games. Even the Spanish island
of Mallorca inaugurated a short metro line in April in hopes of
luring even more tourists to its capital, Palma. Alas, it closed
indefinitely in September due to flooding, amid charges of
mismanagement.
A Boon for Transit Builders
The world's three largest metro manufacturers, Montrealbased
Bombardier (BBDB.TO), Alstom, and Munich-based
Siemens (SI) report high demand for mass transit, including
tramways and light-rail systems that run both under and
[PREPOSITION] ground. The global subway market was worth
9.3 billion dollars in 2005 and is projected to grow at a rate of
2.7% per year until 2015, according to a 2007 study by the
European Railway Industry Assn. Subway lines [TO BUILD] or
extended in 20 European cities and five Middle Eastern ones,
and dozens of towns are constructing light-rail systems, reports
the Brussels-based International Association of Public
Transport.
The size of a city determines its need for a metro system.
Cities of a few million people ? or those anticipating huge
population growth ? really can't do without a mass transit
system. But cities of one or two million inhabitants can choose
between a subway and a surface tramway, which costs far less
but also runs more slowly. [CONJUNCTION] funding is an issue,
cities usually will spring for a subway, says Debroise. "The
tramway has a very old image of the 19th century, with horses in
the streets," he says.
(Adapted from http://www.businessweek.com/globalbiz/
content/dec2007/gb2007125_600001.htm?chan=top+news_
top+news+index_global+business)
Which one of the following is made NO reference to in the text as a reason for building a subway system?
Ano: 2010
Banca:
FCC
Órgão:
METRÔ-SP
Provas:
FCC - 2010 - METRÔ-SP - Engenheiro Júnior - Engenharia Elétrica
|
FCC - 2010 - METRÔ-SP - Engenheiro Eletrônico |
Q74911
Inglês
Texto associado
Subways: The New Urban Status Symbol
Business Week - December 5, 2007
by Jennifer Fishbein
It seems like everywhere you turn these days, a new
high-speed train is whisking more passengers across longer
distances faster than ever before. A [NOUN] to Paris from
London is quicker than flying; Japanese bullet trains traverse the
320 miles from Tokyo to Osaka in two and a half hours; and
magnetic levitating trains in Shanghai cut through the city at 268
miles per hour. But while high-speed trains may grab all the
glamour, the more mundane business of subway construction is
what's driving the biggest growth for transportation companies.
Indeed, the world is seeing an unprecedented boom in new
subways and expansion to existing systems. Thanks to surging
economic growth and urban populations, demand for subways is
soaring in China and India. Lots of other places around the
world also are building new lines, from Dubai to Santo Domingo,
capital of the Dominican Republic. And many European and
American cities ? including even such improbable locales as Los
Angeles and Phoenix ? have caught the transit bug.
Problem-Solving and Prestige
Some cities build out of necessity. Rising prosperity
prompted Dubai residents to buy so many cars that they realized
they could [ADVERB] longer drive these cars because they
were stuck in traffic. Others are keen on the environmental
benefits of metros, which produce far less pollution and
encourage drivers to leave cars at home. Some places, mainly
in the Middle East, are looking to diversify their oil-dependent
economies. And others, to be honest, are chasing an urban
status symbol. Building a metro won't turn any old town into
Paris or London, but it does tell the world that you've arrived.
"You have in some cases a prestige issue, which is more
the case in young cities in need of an image," says Jean-Noël
Debroise, vice-president for product and strategy at Alstom
(ALSO.PA), the French transport company that has built a
quarter of the world's metros.
Rennes is an example of the new trend. The city of about
212,000 people in northwestern France was looking to raise its profile when it installed a metro in 2002. It raised the bar by
opting for a driverless system made by Siemens ? just like the
shiny new No. 14 line in Paris ? protecting passengers from the
French penchant for transit strikes. Turin, Italy, did the same to
help win its bid for the 2006 Winter Olympics; its driverless
system opened just before the games. Even the Spanish island
of Mallorca inaugurated a short metro line in April in hopes of
luring even more tourists to its capital, Palma. Alas, it closed
indefinitely in September due to flooding, amid charges of
mismanagement.
A Boon for Transit Builders
The world's three largest metro manufacturers, Montrealbased
Bombardier (BBDB.TO), Alstom, and Munich-based
Siemens (SI) report high demand for mass transit, including
tramways and light-rail systems that run both under and
[PREPOSITION] ground. The global subway market was worth
9.3 billion dollars in 2005 and is projected to grow at a rate of
2.7% per year until 2015, according to a 2007 study by the
European Railway Industry Assn. Subway lines [TO BUILD] or
extended in 20 European cities and five Middle Eastern ones,
and dozens of towns are constructing light-rail systems, reports
the Brussels-based International Association of Public
Transport.
The size of a city determines its need for a metro system.
Cities of a few million people ? or those anticipating huge
population growth ? really can't do without a mass transit
system. But cities of one or two million inhabitants can choose
between a subway and a surface tramway, which costs far less
but also runs more slowly. [CONJUNCTION] funding is an issue,
cities usually will spring for a subway, says Debroise. "The
tramway has a very old image of the 19th century, with horses in
the streets," he says.
(Adapted from http://www.businessweek.com/globalbiz/
content/dec2007/gb2007125_600001.htm?chan=top+news_
top+news+index_global+business)
Business Week - December 5, 2007
by Jennifer Fishbein
It seems like everywhere you turn these days, a new
high-speed train is whisking more passengers across longer
distances faster than ever before. A [NOUN] to Paris from
London is quicker than flying; Japanese bullet trains traverse the
320 miles from Tokyo to Osaka in two and a half hours; and
magnetic levitating trains in Shanghai cut through the city at 268
miles per hour. But while high-speed trains may grab all the
glamour, the more mundane business of subway construction is
what's driving the biggest growth for transportation companies.
Indeed, the world is seeing an unprecedented boom in new
subways and expansion to existing systems. Thanks to surging
economic growth and urban populations, demand for subways is
soaring in China and India. Lots of other places around the
world also are building new lines, from Dubai to Santo Domingo,
capital of the Dominican Republic. And many European and
American cities ? including even such improbable locales as Los
Angeles and Phoenix ? have caught the transit bug.
Problem-Solving and Prestige
Some cities build out of necessity. Rising prosperity
prompted Dubai residents to buy so many cars that they realized
they could [ADVERB] longer drive these cars because they
were stuck in traffic. Others are keen on the environmental
benefits of metros, which produce far less pollution and
encourage drivers to leave cars at home. Some places, mainly
in the Middle East, are looking to diversify their oil-dependent
economies. And others, to be honest, are chasing an urban
status symbol. Building a metro won't turn any old town into
Paris or London, but it does tell the world that you've arrived.
"You have in some cases a prestige issue, which is more
the case in young cities in need of an image," says Jean-Noël
Debroise, vice-president for product and strategy at Alstom
(ALSO.PA), the French transport company that has built a
quarter of the world's metros.
Rennes is an example of the new trend. The city of about
212,000 people in northwestern France was looking to raise its profile when it installed a metro in 2002. It raised the bar by
opting for a driverless system made by Siemens ? just like the
shiny new No. 14 line in Paris ? protecting passengers from the
French penchant for transit strikes. Turin, Italy, did the same to
help win its bid for the 2006 Winter Olympics; its driverless
system opened just before the games. Even the Spanish island
of Mallorca inaugurated a short metro line in April in hopes of
luring even more tourists to its capital, Palma. Alas, it closed
indefinitely in September due to flooding, amid charges of
mismanagement.
A Boon for Transit Builders
The world's three largest metro manufacturers, Montrealbased
Bombardier (BBDB.TO), Alstom, and Munich-based
Siemens (SI) report high demand for mass transit, including
tramways and light-rail systems that run both under and
[PREPOSITION] ground. The global subway market was worth
9.3 billion dollars in 2005 and is projected to grow at a rate of
2.7% per year until 2015, according to a 2007 study by the
European Railway Industry Assn. Subway lines [TO BUILD] or
extended in 20 European cities and five Middle Eastern ones,
and dozens of towns are constructing light-rail systems, reports
the Brussels-based International Association of Public
Transport.
The size of a city determines its need for a metro system.
Cities of a few million people ? or those anticipating huge
population growth ? really can't do without a mass transit
system. But cities of one or two million inhabitants can choose
between a subway and a surface tramway, which costs far less
but also runs more slowly. [CONJUNCTION] funding is an issue,
cities usually will spring for a subway, says Debroise. "The
tramway has a very old image of the 19th century, with horses in
the streets," he says.
(Adapted from http://www.businessweek.com/globalbiz/
content/dec2007/gb2007125_600001.htm?chan=top+news_
top+news+index_global+business)
According to the text,
Ano: 2010
Banca:
FCC
Órgão:
METRÔ-SP
Provas:
FCC - 2010 - METRÔ-SP - Engenheiro Júnior - Engenharia Elétrica
|
FCC - 2010 - METRÔ-SP - Engenheiro Eletrônico |
Q74910
Inglês
Texto associado
Subways: The New Urban Status Symbol
Business Week - December 5, 2007
by Jennifer Fishbein
It seems like everywhere you turn these days, a new
high-speed train is whisking more passengers across longer
distances faster than ever before. A [NOUN] to Paris from
London is quicker than flying; Japanese bullet trains traverse the
320 miles from Tokyo to Osaka in two and a half hours; and
magnetic levitating trains in Shanghai cut through the city at 268
miles per hour. But while high-speed trains may grab all the
glamour, the more mundane business of subway construction is
what's driving the biggest growth for transportation companies.
Indeed, the world is seeing an unprecedented boom in new
subways and expansion to existing systems. Thanks to surging
economic growth and urban populations, demand for subways is
soaring in China and India. Lots of other places around the
world also are building new lines, from Dubai to Santo Domingo,
capital of the Dominican Republic. And many European and
American cities ? including even such improbable locales as Los
Angeles and Phoenix ? have caught the transit bug.
Problem-Solving and Prestige
Some cities build out of necessity. Rising prosperity
prompted Dubai residents to buy so many cars that they realized
they could [ADVERB] longer drive these cars because they
were stuck in traffic. Others are keen on the environmental
benefits of metros, which produce far less pollution and
encourage drivers to leave cars at home. Some places, mainly
in the Middle East, are looking to diversify their oil-dependent
economies. And others, to be honest, are chasing an urban
status symbol. Building a metro won't turn any old town into
Paris or London, but it does tell the world that you've arrived.
"You have in some cases a prestige issue, which is more
the case in young cities in need of an image," says Jean-Noël
Debroise, vice-president for product and strategy at Alstom
(ALSO.PA), the French transport company that has built a
quarter of the world's metros.
Rennes is an example of the new trend. The city of about
212,000 people in northwestern France was looking to raise its profile when it installed a metro in 2002. It raised the bar by
opting for a driverless system made by Siemens ? just like the
shiny new No. 14 line in Paris ? protecting passengers from the
French penchant for transit strikes. Turin, Italy, did the same to
help win its bid for the 2006 Winter Olympics; its driverless
system opened just before the games. Even the Spanish island
of Mallorca inaugurated a short metro line in April in hopes of
luring even more tourists to its capital, Palma. Alas, it closed
indefinitely in September due to flooding, amid charges of
mismanagement.
A Boon for Transit Builders
The world's three largest metro manufacturers, Montrealbased
Bombardier (BBDB.TO), Alstom, and Munich-based
Siemens (SI) report high demand for mass transit, including
tramways and light-rail systems that run both under and
[PREPOSITION] ground. The global subway market was worth
9.3 billion dollars in 2005 and is projected to grow at a rate of
2.7% per year until 2015, according to a 2007 study by the
European Railway Industry Assn. Subway lines [TO BUILD] or
extended in 20 European cities and five Middle Eastern ones,
and dozens of towns are constructing light-rail systems, reports
the Brussels-based International Association of Public
Transport.
The size of a city determines its need for a metro system.
Cities of a few million people ? or those anticipating huge
population growth ? really can't do without a mass transit
system. But cities of one or two million inhabitants can choose
between a subway and a surface tramway, which costs far less
but also runs more slowly. [CONJUNCTION] funding is an issue,
cities usually will spring for a subway, says Debroise. "The
tramway has a very old image of the 19th century, with horses in
the streets," he says.
(Adapted from http://www.businessweek.com/globalbiz/
content/dec2007/gb2007125_600001.htm?chan=top+news_
top+news+index_global+business)
Business Week - December 5, 2007
by Jennifer Fishbein
It seems like everywhere you turn these days, a new
high-speed train is whisking more passengers across longer
distances faster than ever before. A [NOUN] to Paris from
London is quicker than flying; Japanese bullet trains traverse the
320 miles from Tokyo to Osaka in two and a half hours; and
magnetic levitating trains in Shanghai cut through the city at 268
miles per hour. But while high-speed trains may grab all the
glamour, the more mundane business of subway construction is
what's driving the biggest growth for transportation companies.
Indeed, the world is seeing an unprecedented boom in new
subways and expansion to existing systems. Thanks to surging
economic growth and urban populations, demand for subways is
soaring in China and India. Lots of other places around the
world also are building new lines, from Dubai to Santo Domingo,
capital of the Dominican Republic. And many European and
American cities ? including even such improbable locales as Los
Angeles and Phoenix ? have caught the transit bug.
Problem-Solving and Prestige
Some cities build out of necessity. Rising prosperity
prompted Dubai residents to buy so many cars that they realized
they could [ADVERB] longer drive these cars because they
were stuck in traffic. Others are keen on the environmental
benefits of metros, which produce far less pollution and
encourage drivers to leave cars at home. Some places, mainly
in the Middle East, are looking to diversify their oil-dependent
economies. And others, to be honest, are chasing an urban
status symbol. Building a metro won't turn any old town into
Paris or London, but it does tell the world that you've arrived.
"You have in some cases a prestige issue, which is more
the case in young cities in need of an image," says Jean-Noël
Debroise, vice-president for product and strategy at Alstom
(ALSO.PA), the French transport company that has built a
quarter of the world's metros.
Rennes is an example of the new trend. The city of about
212,000 people in northwestern France was looking to raise its profile when it installed a metro in 2002. It raised the bar by
opting for a driverless system made by Siemens ? just like the
shiny new No. 14 line in Paris ? protecting passengers from the
French penchant for transit strikes. Turin, Italy, did the same to
help win its bid for the 2006 Winter Olympics; its driverless
system opened just before the games. Even the Spanish island
of Mallorca inaugurated a short metro line in April in hopes of
luring even more tourists to its capital, Palma. Alas, it closed
indefinitely in September due to flooding, amid charges of
mismanagement.
A Boon for Transit Builders
The world's three largest metro manufacturers, Montrealbased
Bombardier (BBDB.TO), Alstom, and Munich-based
Siemens (SI) report high demand for mass transit, including
tramways and light-rail systems that run both under and
[PREPOSITION] ground. The global subway market was worth
9.3 billion dollars in 2005 and is projected to grow at a rate of
2.7% per year until 2015, according to a 2007 study by the
European Railway Industry Assn. Subway lines [TO BUILD] or
extended in 20 European cities and five Middle Eastern ones,
and dozens of towns are constructing light-rail systems, reports
the Brussels-based International Association of Public
Transport.
The size of a city determines its need for a metro system.
Cities of a few million people ? or those anticipating huge
population growth ? really can't do without a mass transit
system. But cities of one or two million inhabitants can choose
between a subway and a surface tramway, which costs far less
but also runs more slowly. [CONJUNCTION] funding is an issue,
cities usually will spring for a subway, says Debroise. "The
tramway has a very old image of the 19th century, with horses in
the streets," he says.
(Adapted from http://www.businessweek.com/globalbiz/
content/dec2007/gb2007125_600001.htm?chan=top+news_
top+news+index_global+business)
In the text, you've arrived means
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESGRANRIO
Órgão:
BNDES
Prova:
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Técnico Administrativo |
Q73967
Inglês
The fragment "to the advantage of both." (line 72) indicates that there will be
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESGRANRIO
Órgão:
BNDES
Prova:
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Técnico Administrativo |
Q73965
Inglês
According to the text, ".the inclusion of local growers in big chain grocery stores," (lines 55-56) is seen as a(n)
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESGRANRIO
Órgão:
BNDES
Prova:
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Técnico Administrativo |
Q73964
Inglês
According to paragraphs 7 and 8 (lines 38-49), educating customers to become green is beneficial to green businesses because customers
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESGRANRIO
Órgão:
BNDES
Prova:
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Técnico Administrativo |
Q73962
Inglês
According to the text, all the examples below are definable trends that will dictate the future of green business, EXCEPT
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESGRANRIO
Órgão:
BNDES
Prova:
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Técnico Administrativo |
Q73961
Inglês
The main purpose of the article is to
Ano: 2010
Banca:
FCC
Órgão:
AL-SP
Prova:
FCC - 2010 - AL-SP - Agente Legislativo de Serviços Técnicos e Administrativos - Processamento de Dados |
Q71784
Inglês
Texto associado
Security: UAC Gets Tolerable
Let's talk about User Account Control ? the Windows
Vista security element that was a prominent example for
everything that bothered people about that OS. UAC aimed to
prevent rogue software from tampering with your PC by
endlessly prompting you to approve running applications or
changing settings. The experience was so grating that many
users preferred to turn UAC [PARTICLE] and [VERB] their
chances with Internet attackers. Those who left it active risked
slipping into the habit of incautiously clicking through every
prompt, defeating whatever value the feature might have had.
Whereas Vista's notorious User Account Control gave
users no control over the feature other than to turn it off,
Windows 7's version of UAC lets users choose from two
intermediate notification levels between 'Always notify' and
'Never notify'.
Windows 7 gives you control over UAC, in the form of a
slider containing four security settings. As before, you can
accept the full-blown UAC or elect to disable it. But you can also
tell UAC to notify you only when software changes Windows
settings, not when you're tweaking them yourself. And you can
instruct it not to perform the abrupt screen-dimming effect that
Vista's version uses to grab your attention.
If Microsoft had its druthers, all Windows 7 users [TO
USE] UAC in full-tilt mode: The slider that you use to ratchet
back its severity advises you not to do so if you routinely install
new software or visit unfamiliar sites, and it warns that disabling
the dimming effect is "Not recommended." , Redmond: I
, Redmond: I
have every intention of recommending the intermediate settings
to most people who ask me for advice, since those settings
retain most of UAC's theoretical value without driving users
bonkers.
(Adapted from
http://www.pcworld.com/article/172602/windows_7_review.html)
Let's talk about User Account Control ? the Windows
Vista security element that was a prominent example for
everything that bothered people about that OS. UAC aimed to
prevent rogue software from tampering with your PC by
endlessly prompting you to approve running applications or
changing settings. The experience was so grating that many
users preferred to turn UAC [PARTICLE] and [VERB] their
chances with Internet attackers. Those who left it active risked
slipping into the habit of incautiously clicking through every
prompt, defeating whatever value the feature might have had.
Whereas Vista's notorious User Account Control gave
users no control over the feature other than to turn it off,
Windows 7's version of UAC lets users choose from two
intermediate notification levels between 'Always notify' and
'Never notify'.
Windows 7 gives you control over UAC, in the form of a
slider containing four security settings. As before, you can
accept the full-blown UAC or elect to disable it. But you can also
tell UAC to notify you only when software changes Windows
settings, not when you're tweaking them yourself. And you can
instruct it not to perform the abrupt screen-dimming effect that
Vista's version uses to grab your attention.
If Microsoft had its druthers, all Windows 7 users [TO
USE] UAC in full-tilt mode: The slider that you use to ratchet
back its severity advises you not to do so if you routinely install
new software or visit unfamiliar sites, and it warns that disabling
the dimming effect is "Not recommended."
 , Redmond: I
, Redmond: Ihave every intention of recommending the intermediate settings
to most people who ask me for advice, since those settings
retain most of UAC's theoretical value without driving users
bonkers.
(Adapted from
http://www.pcworld.com/article/172602/windows_7_review.html)
De acordo com o texto, no Windows 7,
Ano: 2010
Banca:
FCC
Órgão:
AL-SP
Prova:
FCC - 2010 - AL-SP - Agente Legislativo de Serviços Técnicos e Administrativos - Processamento de Dados |
Q71783
Inglês
Texto associado
Security: UAC Gets Tolerable
Let's talk about User Account Control ? the Windows
Vista security element that was a prominent example for
everything that bothered people about that OS. UAC aimed to
prevent rogue software from tampering with your PC by
endlessly prompting you to approve running applications or
changing settings. The experience was so grating that many
users preferred to turn UAC [PARTICLE] and [VERB] their
chances with Internet attackers. Those who left it active risked
slipping into the habit of incautiously clicking through every
prompt, defeating whatever value the feature might have had.
Whereas Vista's notorious User Account Control gave
users no control over the feature other than to turn it off,
Windows 7's version of UAC lets users choose from two
intermediate notification levels between 'Always notify' and
'Never notify'.
Windows 7 gives you control over UAC, in the form of a
slider containing four security settings. As before, you can
accept the full-blown UAC or elect to disable it. But you can also
tell UAC to notify you only when software changes Windows
settings, not when you're tweaking them yourself. And you can
instruct it not to perform the abrupt screen-dimming effect that
Vista's version uses to grab your attention.
If Microsoft had its druthers, all Windows 7 users [TO
USE] UAC in full-tilt mode: The slider that you use to ratchet
back its severity advises you not to do so if you routinely install
new software or visit unfamiliar sites, and it warns that disabling
the dimming effect is "Not recommended." , Redmond: I
, Redmond: I
have every intention of recommending the intermediate settings
to most people who ask me for advice, since those settings
retain most of UAC's theoretical value without driving users
bonkers.
(Adapted from
http://www.pcworld.com/article/172602/windows_7_review.html)
Let's talk about User Account Control ? the Windows
Vista security element that was a prominent example for
everything that bothered people about that OS. UAC aimed to
prevent rogue software from tampering with your PC by
endlessly prompting you to approve running applications or
changing settings. The experience was so grating that many
users preferred to turn UAC [PARTICLE] and [VERB] their
chances with Internet attackers. Those who left it active risked
slipping into the habit of incautiously clicking through every
prompt, defeating whatever value the feature might have had.
Whereas Vista's notorious User Account Control gave
users no control over the feature other than to turn it off,
Windows 7's version of UAC lets users choose from two
intermediate notification levels between 'Always notify' and
'Never notify'.
Windows 7 gives you control over UAC, in the form of a
slider containing four security settings. As before, you can
accept the full-blown UAC or elect to disable it. But you can also
tell UAC to notify you only when software changes Windows
settings, not when you're tweaking them yourself. And you can
instruct it not to perform the abrupt screen-dimming effect that
Vista's version uses to grab your attention.
If Microsoft had its druthers, all Windows 7 users [TO
USE] UAC in full-tilt mode: The slider that you use to ratchet
back its severity advises you not to do so if you routinely install
new software or visit unfamiliar sites, and it warns that disabling
the dimming effect is "Not recommended."
 , Redmond: I
, Redmond: Ihave every intention of recommending the intermediate settings
to most people who ask me for advice, since those settings
retain most of UAC's theoretical value without driving users
bonkers.
(Adapted from
http://www.pcworld.com/article/172602/windows_7_review.html)
Segundo o texto,
Ano: 2010
Banca:
FCC
Órgão:
AL-SP
Prova:
FCC - 2010 - AL-SP - Agente Legislativo de Serviços Técnicos e Administrativos - Processamento de Dados |
Q71782
Inglês
Texto associado
Security: UAC Gets Tolerable
Let's talk about User Account Control ? the Windows
Vista security element that was a prominent example for
everything that bothered people about that OS. UAC aimed to
prevent rogue software from tampering with your PC by
endlessly prompting you to approve running applications or
changing settings. The experience was so grating that many
users preferred to turn UAC [PARTICLE] and [VERB] their
chances with Internet attackers. Those who left it active risked
slipping into the habit of incautiously clicking through every
prompt, defeating whatever value the feature might have had.
Whereas Vista's notorious User Account Control gave
users no control over the feature other than to turn it off,
Windows 7's version of UAC lets users choose from two
intermediate notification levels between 'Always notify' and
'Never notify'.
Windows 7 gives you control over UAC, in the form of a
slider containing four security settings. As before, you can
accept the full-blown UAC or elect to disable it. But you can also
tell UAC to notify you only when software changes Windows
settings, not when you're tweaking them yourself. And you can
instruct it not to perform the abrupt screen-dimming effect that
Vista's version uses to grab your attention.
If Microsoft had its druthers, all Windows 7 users [TO
USE] UAC in full-tilt mode: The slider that you use to ratchet
back its severity advises you not to do so if you routinely install
new software or visit unfamiliar sites, and it warns that disabling
the dimming effect is "Not recommended." , Redmond: I
, Redmond: I
have every intention of recommending the intermediate settings
to most people who ask me for advice, since those settings
retain most of UAC's theoretical value without driving users
bonkers.
(Adapted from
http://www.pcworld.com/article/172602/windows_7_review.html)
Let's talk about User Account Control ? the Windows
Vista security element that was a prominent example for
everything that bothered people about that OS. UAC aimed to
prevent rogue software from tampering with your PC by
endlessly prompting you to approve running applications or
changing settings. The experience was so grating that many
users preferred to turn UAC [PARTICLE] and [VERB] their
chances with Internet attackers. Those who left it active risked
slipping into the habit of incautiously clicking through every
prompt, defeating whatever value the feature might have had.
Whereas Vista's notorious User Account Control gave
users no control over the feature other than to turn it off,
Windows 7's version of UAC lets users choose from two
intermediate notification levels between 'Always notify' and
'Never notify'.
Windows 7 gives you control over UAC, in the form of a
slider containing four security settings. As before, you can
accept the full-blown UAC or elect to disable it. But you can also
tell UAC to notify you only when software changes Windows
settings, not when you're tweaking them yourself. And you can
instruct it not to perform the abrupt screen-dimming effect that
Vista's version uses to grab your attention.
If Microsoft had its druthers, all Windows 7 users [TO
USE] UAC in full-tilt mode: The slider that you use to ratchet
back its severity advises you not to do so if you routinely install
new software or visit unfamiliar sites, and it warns that disabling
the dimming effect is "Not recommended."
 , Redmond: I
, Redmond: Ihave every intention of recommending the intermediate settings
to most people who ask me for advice, since those settings
retain most of UAC's theoretical value without driving users
bonkers.
(Adapted from
http://www.pcworld.com/article/172602/windows_7_review.html)
Qual a alternativa que melhor preenche a lacuna 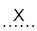 ?
?
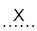 ?
?
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESGRANRIO
Órgão:
BNDES
Provas:
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Analista de Sistemas - Suporte
|
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Arquiteto |
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Arquivista |
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Advogado |
Q71387
Inglês
The sentence "It may mean trying different prices for your newly developed gadget to see which price makes sales pop." (lines 72-74) implies that
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESGRANRIO
Órgão:
BNDES
Provas:
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Analista de Sistemas - Suporte
|
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Arquiteto |
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Arquivista |
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Advogado |
Q71384
Inglês
The expression "...leaps of faith" (line 64) refers to
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESGRANRIO
Órgão:
BNDES
Provas:
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Analista de Sistemas - Suporte
|
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Arquiteto |
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Arquivista |
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Advogado |
Q71381
Inglês
Max Levchin, mentioned in paragraph 4 (lines 34-39), can be considered a(an)
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESGRANRIO
Órgão:
BNDES
Provas:
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Analista de Sistemas - Suporte
|
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Arquiteto |
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Arquivista |
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Advogado |
Q71380
Inglês
Mulins and Komisar, in paragraph 3 (lines 21-33), state that the typical business startup process is usually unsuccessful because it
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESGRANRIO
Órgão:
BNDES
Provas:
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Analista de Sistemas - Suporte
|
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Arquiteto |
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Arquivista |
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Advogado |
Q71379
Inglês
Google, Starbucks and PayPal are mentioned in paragraph 1 (lines 1-8) since they
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESGRANRIO
Órgão:
BNDES
Provas:
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Analista de Sistemas - Suporte
|
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Arquiteto |
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Arquivista |
CESGRANRIO - 2010 - BNDES - Advogado |
Q71378
Inglês
According to the authors,
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
ANEEL
Provas:
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Todos os Cargos - Nível Superior
|
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 1 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 2 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 3 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 4 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 5 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Analista Administrativo - Área 2 |
Q70801
Inglês
Texto associado
Europe and North Africa could be powered solely by
renewable electricity by 2050 through the implementation of a
"SuperSmart Grid", according to a report issued this week by global
advisory firm PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC).
According to Energy Source, the achievement of 100 per
cent renewable electricity would address energy security and supply
concerns, while decarbonizing electricity generation and reducing
energy poverty, according to the study.
The proposed SuperSmart Grid would allow load and
demand management for power independently of where and when
the electricity is generated.
The system would capitalize on natural resources and
established weather patterns and would incorporate: southern
Europe and North Africa's solar power potential; the hydro
capability of Scandinavia and the European Alps; onshore and
offshore wind farms in the Baltic and the North Sea; Europe's
potential for tidal and wave power; and biomass generation across
the continent.
According to Gus Schellekens, director of sustainability
and climate change at PricewaterhouseCoopers, Europe is now at
a crossroads, where the choice and ability to achieve renewable
power at scale is evident. "Opportunities to use clean and affordable
natural sources of electricity have been flirted with over the past
150 years. This study lays out a clear framework of how this time
could be different", he says.
The dominant source of European power is fossil fuels (55
per cent), while nuclear power provides 30 per cent and 15 per cent
is derived from renewable sources. According to the PwC study, a
renewables-powered Europe would change the landscape for
consumers and business. Electro-mobility could be introduced on
a mass scale, eliminating the carbon costs of day-to-day transport
for people and goods.

renewable electricity by 2050 through the implementation of a
"SuperSmart Grid", according to a report issued this week by global
advisory firm PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC).
According to Energy Source, the achievement of 100 per
cent renewable electricity would address energy security and supply
concerns, while decarbonizing electricity generation and reducing
energy poverty, according to the study.
The proposed SuperSmart Grid would allow load and
demand management for power independently of where and when
the electricity is generated.
The system would capitalize on natural resources and
established weather patterns and would incorporate: southern
Europe and North Africa's solar power potential; the hydro
capability of Scandinavia and the European Alps; onshore and
offshore wind farms in the Baltic and the North Sea; Europe's
potential for tidal and wave power; and biomass generation across
the continent.
According to Gus Schellekens, director of sustainability
and climate change at PricewaterhouseCoopers, Europe is now at
a crossroads, where the choice and ability to achieve renewable
power at scale is evident. "Opportunities to use clean and affordable
natural sources of electricity have been flirted with over the past
150 years. This study lays out a clear framework of how this time
could be different", he says.
The dominant source of European power is fossil fuels (55
per cent), while nuclear power provides 30 per cent and 15 per cent
is derived from renewable sources. According to the PwC study, a
renewables-powered Europe would change the landscape for
consumers and business. Electro-mobility could be introduced on
a mass scale, eliminating the carbon costs of day-to-day transport
for people and goods.

It is possible to infer from the text that
electro-mobility introduced on a mass scale can make everyday transport for people and goods cheaper.
electro-mobility introduced on a mass scale can make everyday transport for people and goods cheaper.
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
ANEEL
Provas:
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Todos os Cargos - Nível Superior
|
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 1 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 2 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 3 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 4 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 5 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Analista Administrativo - Área 2 |
Q70800
Inglês
Texto associado
Europe and North Africa could be powered solely by
renewable electricity by 2050 through the implementation of a
"SuperSmart Grid", according to a report issued this week by global
advisory firm PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC).
According to Energy Source, the achievement of 100 per
cent renewable electricity would address energy security and supply
concerns, while decarbonizing electricity generation and reducing
energy poverty, according to the study.
The proposed SuperSmart Grid would allow load and
demand management for power independently of where and when
the electricity is generated.
The system would capitalize on natural resources and
established weather patterns and would incorporate: southern
Europe and North Africa's solar power potential; the hydro
capability of Scandinavia and the European Alps; onshore and
offshore wind farms in the Baltic and the North Sea; Europe's
potential for tidal and wave power; and biomass generation across
the continent.
According to Gus Schellekens, director of sustainability
and climate change at PricewaterhouseCoopers, Europe is now at
a crossroads, where the choice and ability to achieve renewable
power at scale is evident. "Opportunities to use clean and affordable
natural sources of electricity have been flirted with over the past
150 years. This study lays out a clear framework of how this time
could be different", he says.
The dominant source of European power is fossil fuels (55
per cent), while nuclear power provides 30 per cent and 15 per cent
is derived from renewable sources. According to the PwC study, a
renewables-powered Europe would change the landscape for
consumers and business. Electro-mobility could be introduced on
a mass scale, eliminating the carbon costs of day-to-day transport
for people and goods.

renewable electricity by 2050 through the implementation of a
"SuperSmart Grid", according to a report issued this week by global
advisory firm PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC).
According to Energy Source, the achievement of 100 per
cent renewable electricity would address energy security and supply
concerns, while decarbonizing electricity generation and reducing
energy poverty, according to the study.
The proposed SuperSmart Grid would allow load and
demand management for power independently of where and when
the electricity is generated.
The system would capitalize on natural resources and
established weather patterns and would incorporate: southern
Europe and North Africa's solar power potential; the hydro
capability of Scandinavia and the European Alps; onshore and
offshore wind farms in the Baltic and the North Sea; Europe's
potential for tidal and wave power; and biomass generation across
the continent.
According to Gus Schellekens, director of sustainability
and climate change at PricewaterhouseCoopers, Europe is now at
a crossroads, where the choice and ability to achieve renewable
power at scale is evident. "Opportunities to use clean and affordable
natural sources of electricity have been flirted with over the past
150 years. This study lays out a clear framework of how this time
could be different", he says.
The dominant source of European power is fossil fuels (55
per cent), while nuclear power provides 30 per cent and 15 per cent
is derived from renewable sources. According to the PwC study, a
renewables-powered Europe would change the landscape for
consumers and business. Electro-mobility could be introduced on
a mass scale, eliminating the carbon costs of day-to-day transport
for people and goods.

It is possible to infer from the text that
the use of not dirty and inexpensive natural sources of electricity has been considered during the last 150 years.
the use of not dirty and inexpensive natural sources of electricity has been considered during the last 150 years.
Ano: 2010
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
ANEEL
Provas:
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Todos os Cargos - Nível Superior
|
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 1 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 2 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 3 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 4 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Especialista em Regulação de Serviços Públicos de Energia - Área 5 |
CESPE / CEBRASPE - 2010 - ANEEL - Analista Administrativo - Área 2 |
Q70799
Inglês
Texto associado
Europe and North Africa could be powered solely by
renewable electricity by 2050 through the implementation of a
"SuperSmart Grid", according to a report issued this week by global
advisory firm PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC).
According to Energy Source, the achievement of 100 per
cent renewable electricity would address energy security and supply
concerns, while decarbonizing electricity generation and reducing
energy poverty, according to the study.
The proposed SuperSmart Grid would allow load and
demand management for power independently of where and when
the electricity is generated.
The system would capitalize on natural resources and
established weather patterns and would incorporate: southern
Europe and North Africa's solar power potential; the hydro
capability of Scandinavia and the European Alps; onshore and
offshore wind farms in the Baltic and the North Sea; Europe's
potential for tidal and wave power; and biomass generation across
the continent.
According to Gus Schellekens, director of sustainability
and climate change at PricewaterhouseCoopers, Europe is now at
a crossroads, where the choice and ability to achieve renewable
power at scale is evident. "Opportunities to use clean and affordable
natural sources of electricity have been flirted with over the past
150 years. This study lays out a clear framework of how this time
could be different", he says.
The dominant source of European power is fossil fuels (55
per cent), while nuclear power provides 30 per cent and 15 per cent
is derived from renewable sources. According to the PwC study, a
renewables-powered Europe would change the landscape for
consumers and business. Electro-mobility could be introduced on
a mass scale, eliminating the carbon costs of day-to-day transport
for people and goods.

renewable electricity by 2050 through the implementation of a
"SuperSmart Grid", according to a report issued this week by global
advisory firm PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC).
According to Energy Source, the achievement of 100 per
cent renewable electricity would address energy security and supply
concerns, while decarbonizing electricity generation and reducing
energy poverty, according to the study.
The proposed SuperSmart Grid would allow load and
demand management for power independently of where and when
the electricity is generated.
The system would capitalize on natural resources and
established weather patterns and would incorporate: southern
Europe and North Africa's solar power potential; the hydro
capability of Scandinavia and the European Alps; onshore and
offshore wind farms in the Baltic and the North Sea; Europe's
potential for tidal and wave power; and biomass generation across
the continent.
According to Gus Schellekens, director of sustainability
and climate change at PricewaterhouseCoopers, Europe is now at
a crossroads, where the choice and ability to achieve renewable
power at scale is evident. "Opportunities to use clean and affordable
natural sources of electricity have been flirted with over the past
150 years. This study lays out a clear framework of how this time
could be different", he says.
The dominant source of European power is fossil fuels (55
per cent), while nuclear power provides 30 per cent and 15 per cent
is derived from renewable sources. According to the PwC study, a
renewables-powered Europe would change the landscape for
consumers and business. Electro-mobility could be introduced on
a mass scale, eliminating the carbon costs of day-to-day transport
for people and goods.

Based on the text, judge the items below.
Wind farms located far away from the coast are also supposed to take part in the project.
Wind farms located far away from the coast are also supposed to take part in the project.



