Questões de Concurso
Sobre inglês
Foram encontradas 17.476 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
INSTRUÇÃO: O texto a seguir refere-se à questão. Leia-o atentamente.
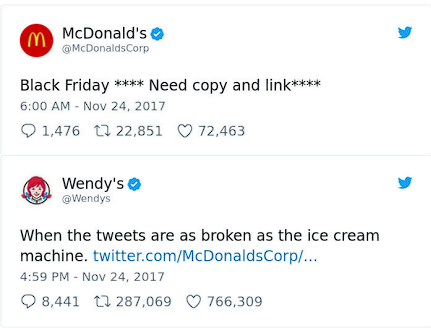
Disponível em: https://alidropship.com/funny-tweets-for-brand-engagement/. Acesso em: 23 set. 2023.
Tanto o Wendy’s quanto o McDonald’s são redes de restaurantes de “fast food” que oferecem refeições preparadas
rapidamente para consumo no local, para viagem ou por meio de serviços de entrega. Em 24 de novembro de 2017,
a rede McDonald's realizou uma postagem na sua conta, em uma rede social, e foi prontamente respondida pela
franquia concorrente, Wendy’s. Baseando-se na imagem, qual foi a intenção da rede Wendy’s?
INSTRUÇÃO: Leia o texto a seguir para responder à questão.
The counteroffensive may be flagging, but Crimea attack shows Ukraine can still inflict serious damage on the Russian military
On Wednesday, a large plume of smoke rose from a naval base near Sevastopol. Local authorities played down the incident, saying that a number of drones were brought down. But the Ukrainian military says it successfully hit a Russian command post near Verkhniosadove, a few kilometers from Sevastopol.
The Institute for the Study of War (ISW) noted that satellite imagery confirmed that Ukrainian forces “struck the 744th Communications Center of the Command of the Black Sea FleetD as part of an apparent Ukrainian effort to target Black Sea Fleet facilities.”
Fonte: LISTER, T. Disponível em: https://edition.cnn.com/2023/09/22/europe/ukraine-crimea-russia-black-sea-intl-cmd/index.html. Acesso em: 23
set. 2023. Adaptado.
( ) Many believe AI will eventually make jobs redundant.
( ) The conclusion of the text is that the current outlook regarding employment is rather bleak.
( ) The authors prefer to probe forthcoming evidence before issuing unequivocal accounts.
The statements are, respectively,
Text I
Text I
Text I
( ) The dawning of generative art has given rise to a quandary.
( ) The winner mentioned was thrilled with the prize he was awarded.
( ) The organization responsible for the award stood by their earlier statement that AI yields finer art than that of humans.
The statements are, respectively,