Questões de Concurso
Comentadas para if-sp
Foram encontradas 842 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Bruno (2005) aborda el tema dei acusativo preposicional y su uso por parte de los estudiantes brasileiros de lengua española. Para la autora, la tesis de la individnalidad o individuación ofrece “al alumno la comprensión del uso de la preposición a partir de una perspectiva enunciativa” (ibid., p. 139).
Elija la opción que contenga un ejemplo sobre el uso del acusativo preposicional en español cuya individuación es compartida tanto por el hablante como para el oyente:

(Disponible en: http://www.quitoquito.com/ entretenimiento/deportes/salud/45-noticias/799- protex-presenta-campana-qespera-dale-una-mano-a- tu-saludq . Acesso en: 29 nov. 2018)

(Disponible en: http://jorgewerthein.blogspot. com/2013/Ol/quino-los-chicos-fiieron-mis-mejores.
html. Acceso en: 29 nov. 2018)
Después de leer la viñeta, podemos afirmar que:

En los fragmentos entresacados del texto Las bicicletas son para el verano, “lo de la bicicleta” y
“lo del verano”, se usa el artículo neutro para:

ESPANOL PARA IMIGRANTES. Disponible en: <https://espanolparainmigrantes.files.wordpress.eom/2010/07/
preterito-perfecto2.png>. Acceso en: 24 nov. 2018.
La expresión del pasado en lengua española se hace de diferentes formas, utilizándose de tiempos y modos diversos. Matte Bon (1995) advierte del peligro de caer en errores como creer que el pretérito perfecto se refiere a acciones más recientes. La oposición entre el pretérito indefinido y el pretérito perfecto, en lugar de buscarse en las acciones y acontecimientos extralingüísticos en si, se debería buscar, según el autor, en:
Read the excert from HUTCHINSON & WATERS (1987) about the ESP origin:
“As with most developments in human activity, ESP was not a planned and coherent movement, but rather a phenomenon that grew out of a number of converging trends. These trends have operated in a variety of ways around the world, but we can identify three main reasons common to the emerge of all ESP.”
Taking into consideration HUTCHINSON & WATERS assumptions, what are the three main reasons for ESP emergence?
According to BROWN (2007):
“As students work together in pairs and groups, they share information and come to each others’ aid. They are a ‘team’ whose players must work together in order to achieve goals successfully.”
Taking into consideration the above passage it is possible to state that the authors refer to
According to Anthony’s model, approach is the level at which assumptions and beliefs about language and language learning are specified; method is the level at which theory is put into practice and at which choices are made about the particular skills to be taught, the content to be taught, and the order in which the content will be presented; technique is the level at which classroom procedures are described (RICHARDS and RODGERS, 2001).
Richards and Rodgers (2001) criticism concerning Anthony’s (1963) definition of approach, method and technique which resulted in the authors new model resides in:
Read the excerpt from Anthony (1963) apud Richards and Rodgers (2001):
“…An approach is a set of correlative assumptions dealing with the nature of language teaching and learning. An approach is axiomatic. It describes the nature of the subject matter to be taught… …
... Method is an overall plan for the orderly presentation of language material, no part of which contradicts, and all of which is based upon, the selected approach. An approach is axiomatic, a method is procedural.
Within one approach, there can be many methods…”
Considering the excerpt and the nature of approaches and methods in English teaching, it is correct to say that:
Given that communicative competence is the goal of a language classroom, instruction needs to point toward all its components: organizational, pragmatic, strategic, and psychomotor. Communicative goals are best achieved by giving due attention to language use and not just usage, to fluency and not just accuracy, to authentic language and contexts, and to students’ eventual need to apply classroom learning to previously unrehearsed contexts in the real world (BROWN, 2007).
Considering Communicative Competence as a reference, it is correct to state that:
The aim of this particular model is to provide a coherent framework for the integration of the various aspects of learning, while at the same time allowing enough room for creativity and variety to florish. The model consists of four elements: input, content focus, language focus, task (HUTCHINSON and WATERS,1987).
Hutchinson and Waters (1987) present a material design model based on four elements: input, content, language and task. According to the authors, the primary focus of the unit is:
[this domain] deals with the way in which utterences are interpreted in context, and the ways in which the utterences of a particular sentence in a certain context may convey a message that is not actually expressed in the sentence and in other contexts might not have been conveyed. (HUDDLESTON and PULLUM, 2002).
The previous passage is a definition of:
Regarding to questioning strategies for interactive learning, there are many ways to classify what kind of questions are effective in the classroom, beginning with display questions to highly referential ones. Asking a lot of questions in classroom does not guarantee stimulation of interaction, for that reason, knowing how to apply the appropriate question in order to achieve a previous fixed objective is of great importance (BROWN, 2007).
Considering the statement above, choose the alternative that properly presents: (1) a question category (2) its explanation and (3) a correct example of it.
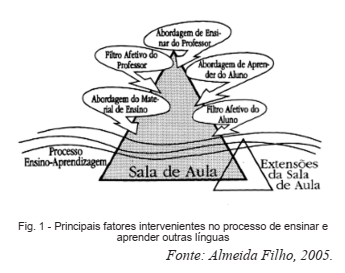
Almeida Filho (2005) illustrates in figure 1: