Questões de Vestibular de Inglês - Interpretação de texto | Reading comprehension
Foram encontradas 4.863 questões
Read the text below and answer the following question based on it.
Yellow Fever — Once Again on the Radar Screen in the Americas
Over the past several weeks, a fifth arbovirus, yellow fever virus, has broken out in Brazil, with the majority of the infections occurring in rural areas of the country. These are referred to as sylvatic, or jungle, cases, since the typical transmission cycle occurs between forest mosquitoes and forest-dwelling nonhuman primates, with humans serving only as incidental hosts. In this ongoing outbreak, health authorities have reported 234 confirmed infections and 80 confirmed deaths as of February 2017. Confirmed infections have occurred in the Brazilian states of Minas Gerais, Espírito Santo, and São Paulo, and hundreds of additional cases remain under investigation. The high number of cases is out of proportion to the number reported in a typical year in these areas.
Although there is currently no evidence that human-tohuman transmission through Aedes aegypti mosquitoes (urban transmission) has occurred, the outbreak is affecting areas in close proximity to major urban centers where yellow fever vaccine is not routinely administered. This proximity raises concern that, for the first time in decades, urban transmission of yellow fever will occur in Brazil.
Yellow fever is the most severe arbovirus ever to circulate in the Americas, and although vaccination campaigns and vector-control efforts have eliminated it from many areas, sylvatic transmission cycles continue to occur in endemic tropical regions. The most recent outbreak in Brazil highlights this phenomenon. If the current outbreak leads to urban spread through A. aegypti mosquitoes, clinicians should adopt a high index of suspicion for yellow fever, particularly in travelers returning from affected regions. As with all potentially reemerging infectious diseases, public health awareness and preparedness are essential to prevent a resurgence of this historical threat.
Adaptado de:
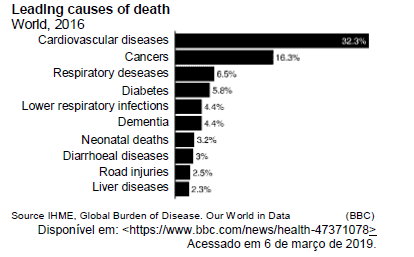
According to the graph above we can assert that
Read the cartoon below and answer the next questions based on it.

Disponível em: <https://www.greetingcarduniverse.com/holidaycards/nurses-day-cards/humor/greeting-card-607707> Acessado em 27 de fevereiro de 2019.
According to the cartoon above it is true to assert that the doctor
How Sleep Strengthens Your Immune System
Numerous studies have reported the benefits of a good night’s sleep, and now researchers from Germany have found that sound sleep improves immune cells known as T cells.
“T cells are a type of… immune cells that fight against intracellular pathogens, for example virus-infected cells such as flu, HIV, herpes, and cancer cells,” Stoyan Dimitrov, PhD, told Healthline.
The study found a new mechanism through which sleep can assist the immune system.
“We show that the stress hormones adrenaline and noradrenaline and pro-inflammatory molecules prostaglandins inhibit the stickiness of a class of adhesion molecules called integrins,” Dr. Dimitrov said. “Because the levels of adrenaline, noradrenaline, and prostaglandins are low during sleep time, the stickiness of the integrins is stronger. This stickiness is important because in order for T cells to kill virus-infected cells or cancer cells, they need to get in direct contact with them, and the integrin stickiness is known to promote this contact.”
When cells in the body recognize a virally infected cell, they activate integrins, a sticky type of protein, that then allows them to attach to and kill infected cells.
The researchers compared T cells from healthy volunteers who either slept or stayed awake all night.
They found that in the study participants who slept, their T cells showed higher levels of integrin activation than in the T cells of those who were awake.
The findings indicate that sleep has the potential to improve T cell functioning. For people who get poor sleep, stress hormones may inhibit the ability of T cells to function as effectively.
Less than five hours sleep per night on a regular basis is associated with higher mortality, and having less than seven hours sleep for three nights in a row has the same effect on the body as missing one full night of sleep.
Poor sleep can increase inflammation, blood pressure, insulin resistance, cortisol, weight gain, and cardiovascular disease, as well as decrease blood sugar regulation.
Despite numerous studies proving the negative health impacts of poor sleep, experts say many people still don’t prioritize getting enough sleep.
Adaptado de: <https://www.healthline.com/health-news/how-sleepbolsters-your-immune-system#The-bottom-line> Acessado em 21 de fevereiro de 2019.
How Sleep Strengthens Your Immune System
Numerous studies have reported the benefits of a good night’s sleep, and now researchers from Germany have found that sound sleep improves immune cells known as T cells.
“T cells are a type of… immune cells that fight against intracellular pathogens, for example virus-infected cells such as flu, HIV, herpes, and cancer cells,” Stoyan Dimitrov, PhD, told Healthline.
The study found a new mechanism through which sleep can assist the immune system.
“We show that the stress hormones adrenaline and noradrenaline and pro-inflammatory molecules prostaglandins inhibit the stickiness of a class of adhesion molecules called integrins,” Dr. Dimitrov said. “Because the levels of adrenaline, noradrenaline, and prostaglandins are low during sleep time, the stickiness of the integrins is stronger. This stickiness is important because in order for T cells to kill virus-infected cells or cancer cells, they need to get in direct contact with them, and the integrin stickiness is known to promote this contact.”
When cells in the body recognize a virally infected cell, they activate integrins, a sticky type of protein, that then allows them to attach to and kill infected cells.
The researchers compared T cells from healthy volunteers who either slept or stayed awake all night.
They found that in the study participants who slept, their T cells showed higher levels of integrin activation than in the T cells of those who were awake.
The findings indicate that sleep has the potential to improve T cell functioning. For people who get poor sleep, stress hormones may inhibit the ability of T cells to function as effectively.
Less than five hours sleep per night on a regular basis is associated with higher mortality, and having less than seven hours sleep for three nights in a row has the same effect on the body as missing one full night of sleep.
Poor sleep can increase inflammation, blood pressure, insulin resistance, cortisol, weight gain, and cardiovascular disease, as well as decrease blood sugar regulation.
Despite numerous studies proving the negative health impacts of poor sleep, experts say many people still don’t prioritize getting enough sleep.
Adaptado de: <https://www.healthline.com/health-news/how-sleepbolsters-your-immune-system#The-bottom-line> Acessado em 21 de fevereiro de 2019.
How Sleep Strengthens Your Immune System
Numerous studies have reported the benefits of a good night’s sleep, and now researchers from Germany have found that sound sleep improves immune cells known as T cells.
“T cells are a type of… immune cells that fight against intracellular pathogens, for example virus-infected cells such as flu, HIV, herpes, and cancer cells,” Stoyan Dimitrov, PhD, told Healthline.
The study found a new mechanism through which sleep can assist the immune system.
“We show that the stress hormones adrenaline and noradrenaline and pro-inflammatory molecules prostaglandins inhibit the stickiness of a class of adhesion molecules called integrins,” Dr. Dimitrov said. “Because the levels of adrenaline, noradrenaline, and prostaglandins are low during sleep time, the stickiness of the integrins is stronger. This stickiness is important because in order for T cells to kill virus-infected cells or cancer cells, they need to get in direct contact with them, and the integrin stickiness is known to promote this contact.”
When cells in the body recognize a virally infected cell, they activate integrins, a sticky type of protein, that then allows them to attach to and kill infected cells.
The researchers compared T cells from healthy volunteers who either slept or stayed awake all night.
They found that in the study participants who slept, their T cells showed higher levels of integrin activation than in the T cells of those who were awake.
The findings indicate that sleep has the potential to improve T cell functioning. For people who get poor sleep, stress hormones may inhibit the ability of T cells to function as effectively.
Less than five hours sleep per night on a regular basis is associated with higher mortality, and having less than seven hours sleep for three nights in a row has the same effect on the body as missing one full night of sleep.
Poor sleep can increase inflammation, blood pressure, insulin resistance, cortisol, weight gain, and cardiovascular disease, as well as decrease blood sugar regulation.
Despite numerous studies proving the negative health impacts of poor sleep, experts say many people still don’t prioritize getting enough sleep.
Adaptado de: <https://www.healthline.com/health-news/how-sleepbolsters-your-immune-system#The-bottom-line> Acessado em 21 de fevereiro de 2019.
New Parents Don’t Get Enough Sleep for Six Years After a Child Is Born
Those first three months with a newborn can be rough, but researchers say sleep deprivation is an issue with parents for years. New parents are sometimes shocked to discover how little sleep they get in the first six months after a baby is born. They might also be discouraged to learn that their sleep patterns might not return to normal until that newborn is ready for kindergarten.
A new study published in the journal Sleep found that both parental sleep satisfaction and sleep duration sharply declined after childbirth, hitting their lowest point when a baby is 3 months old.
Women’s sleep duration and quality were far more affected than men, whether or not they breastfed their child. Women lost an average of one hour of sleep nightly compared to what they got prior to pregnancy, while men lost about 15 minutes of sleep per night.
Even four to six years after childbirth, mothers were getting 20 minutes less sleep per night than before they became pregnant, while fathers were still getting 15 minutes less sleep.
“The short-term effects of childbirth on parental sleep is well known. Our study just confirmed these effects,” Lemola told Healthline. “However, it was largely unexpected to find decreased sleep duration and sleep satisfaction six years after birth.”
Sleep was more affected among first-time parents than among parents with more than one child.
The findings were based on interviews of 4,659 parents who had a child between 2008 and 2015.
“While having children is a major source of joy for most parents, it is possible that increased demands and responsibilities associated with the role as a parent lead to shorter sleep and decreased sleep quality even up to six years after birth of the first child,” said Lemola.
Lemola said that future research would be required to determine how parents can cope with sleep loss and regain their sleep patterns sooner.
Adaptado de: <https://www.healthline.com/health-news/newparents-dont-get-sound-sleep-for-6-years#The-bottom-line> Acessado em 04 de março de 2019
New Parents Don’t Get Enough Sleep for Six Years After a Child Is Born
Those first three months with a newborn can be rough, but researchers say sleep deprivation is an issue with parents for years. New parents are sometimes shocked to discover how little sleep they get in the first six months after a baby is born. They might also be discouraged to learn that their sleep patterns might not return to normal until that newborn is ready for kindergarten.
A new study published in the journal Sleep found that both parental sleep satisfaction and sleep duration sharply declined after childbirth, hitting their lowest point when a baby is 3 months old.
Women’s sleep duration and quality were far more affected than men, whether or not they breastfed their child. Women lost an average of one hour of sleep nightly compared to what they got prior to pregnancy, while men lost about 15 minutes of sleep per night.
Even four to six years after childbirth, mothers were getting 20 minutes less sleep per night than before they became pregnant, while fathers were still getting 15 minutes less sleep.
“The short-term effects of childbirth on parental sleep is well known. Our study just confirmed these effects,” Lemola told Healthline. “However, it was largely unexpected to find decreased sleep duration and sleep satisfaction six years after birth.”
Sleep was more affected among first-time parents than among parents with more than one child.
The findings were based on interviews of 4,659 parents who had a child between 2008 and 2015.
“While having children is a major source of joy for most parents, it is possible that increased demands and responsibilities associated with the role as a parent lead to shorter sleep and decreased sleep quality even up to six years after birth of the first child,” said Lemola.
Lemola said that future research would be required to determine how parents can cope with sleep loss and regain their sleep patterns sooner.
Adaptado de: <https://www.healthline.com/health-news/newparents-dont-get-sound-sleep-for-6-years#The-bottom-line> Acessado em 04 de março de 2019
New Parents Don’t Get Enough Sleep for Six Years After a Child Is Born
Those first three months with a newborn can be rough, but researchers say sleep deprivation is an issue with parents for years. New parents are sometimes shocked to discover how little sleep they get in the first six months after a baby is born. They might also be discouraged to learn that their sleep patterns might not return to normal until that newborn is ready for kindergarten.
A new study published in the journal Sleep found that both parental sleep satisfaction and sleep duration sharply declined after childbirth, hitting their lowest point when a baby is 3 months old.
Women’s sleep duration and quality were far more affected than men, whether or not they breastfed their child. Women lost an average of one hour of sleep nightly compared to what they got prior to pregnancy, while men lost about 15 minutes of sleep per night.
Even four to six years after childbirth, mothers were getting 20 minutes less sleep per night than before they became pregnant, while fathers were still getting 15 minutes less sleep.
“The short-term effects of childbirth on parental sleep is well known. Our study just confirmed these effects,” Lemola told Healthline. “However, it was largely unexpected to find decreased sleep duration and sleep satisfaction six years after birth.”
Sleep was more affected among first-time parents than among parents with more than one child.
The findings were based on interviews of 4,659 parents who had a child between 2008 and 2015.
“While having children is a major source of joy for most parents, it is possible that increased demands and responsibilities associated with the role as a parent lead to shorter sleep and decreased sleep quality even up to six years after birth of the first child,” said Lemola.
Lemola said that future research would be required to determine how parents can cope with sleep loss and regain their sleep patterns sooner.
Adaptado de: <https://www.healthline.com/health-news/newparents-dont-get-sound-sleep-for-6-years#The-bottom-line> Acessado em 04 de março de 2019
Read the comic strip below and answer the following question based on it.

Disponível em:<http://www.docjokes.com/i/farcus-comic-strip-on-gocomics-com.html> Acessado em 25 de abril de 2016.
Read the comic strip below and answer the following
question based on it.
