Questões de Concurso Sobre inglês
Foram encontradas 17.638 questões
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Provas:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Analista Judiciário - Área Judiciária
|
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Analista Judiciário - Área Administrativa |
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Todos os Cargos - Conhecimentos Básicos - Cargos 3 e 5 |
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Analista Judiciário - Revisor de Texto |
Q352000
Inglês
Texto associado
The aging process affects us all at different rates. Some people of fifty-three, like the esteemed author, look a mere thirty-five, with sparkling brown eyes, a handsome gait and the virility of a steam train. Others, like the author’s friend Colin, look like little middle-aged men at twenty-one with middle-aged outlooks of set ways and planned futures. In women the former condition is common but women rarely suffer from the latter, being fired with the insatiable drive of ambition for either an independent and distinguished career in a still male-dominated world, or a home and seven children by the time they are thirty followed by an independent and distinguished career as a Cheltenham councillor or a public relations agent for Jonathan Cape, in later life.
No such luck for Charles Charlesworth, who was born on the 14th of March, 1829, in Stafford. At the age of four Charles had a beard and was sexually active.
In the final three years of his life his skin wrinkled, he developed varicose veins, shortness of breath, grey hair, senile dementia and incontinence. Some time in his seventh year he fainted and never gained consciousness
The coroner returned a verdict of natural causes due to old age.
Hugh Cory. Advanced writing with english in use. Oxford University Press, p. 34.
No such luck for Charles Charlesworth, who was born on the 14th of March, 1829, in Stafford. At the age of four Charles had a beard and was sexually active.
In the final three years of his life his skin wrinkled, he developed varicose veins, shortness of breath, grey hair, senile dementia and incontinence. Some time in his seventh year he fainted and never gained consciousness
The coroner returned a verdict of natural causes due to old age.
Hugh Cory. Advanced writing with english in use. Oxford University Press, p. 34.
According to the text above,
t is rather common for women to look older than they really are.
t is rather common for women to look older than they really are.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Prova:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Analista Judiciário - Área Judiciária |
Q351999
Inglês
Texto associado
The aging process affects us all at different rates. Some people of fifty-three, like the esteemed author, look a mere thirty-five, with sparkling brown eyes, a handsome gait and the virility of a steam train. Others, like the author’s friend Colin, look like little middle-aged men at twenty-one with middle-aged outlooks of set ways and planned futures. In women the former condition is common but women rarely suffer from the latter, being fired with the insatiable drive of ambition for either an independent and distinguished career in a still male-dominated world, or a home and seven children by the time they are thirty followed by an independent and distinguished career as a Cheltenham councillor or a public relations agent for Jonathan Cape, in later life.
No such luck for Charles Charlesworth, who was born on the 14th of March, 1829, in Stafford. At the age of four Charles had a beard and was sexually active.
In the final three years of his life his skin wrinkled, he developed varicose veins, shortness of breath, grey hair, senile dementia and incontinence. Some time in his seventh year he fainted and never gained consciousness
The coroner returned a verdict of natural causes due to old age.
Hugh Cory. Advanced writing with english in use. Oxford University Press, p. 34.
No such luck for Charles Charlesworth, who was born on the 14th of March, 1829, in Stafford. At the age of four Charles had a beard and was sexually active.
In the final three years of his life his skin wrinkled, he developed varicose veins, shortness of breath, grey hair, senile dementia and incontinence. Some time in his seventh year he fainted and never gained consciousness
The coroner returned a verdict of natural causes due to old age.
Hugh Cory. Advanced writing with english in use. Oxford University Press, p. 34.
According to the text above,
Charles Charlesworth’s cause of death was old age although he was only seven.
Charles Charlesworth’s cause of death was old age although he was only seven.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Provas:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Analista Judiciário - Área Judiciária
|
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Analista Judiciário - Área Administrativa |
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Todos os Cargos - Conhecimentos Básicos - Cargos 3 e 5 |
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Analista Judiciário - Revisor de Texto |
Q351998
Inglês
Texto associado
The aging process affects us all at different rates. Some people of fifty-three, like the esteemed author, look a mere thirty-five, with sparkling brown eyes, a handsome gait and the virility of a steam train. Others, like the author’s friend Colin, look like little middle-aged men at twenty-one with middle-aged outlooks of set ways and planned futures. In women the former condition is common but women rarely suffer from the latter, being fired with the insatiable drive of ambition for either an independent and distinguished career in a still male-dominated world, or a home and seven children by the time they are thirty followed by an independent and distinguished career as a Cheltenham councillor or a public relations agent for Jonathan Cape, in later life.
No such luck for Charles Charlesworth, who was born on the 14th of March, 1829, in Stafford. At the age of four Charles had a beard and was sexually active.
In the final three years of his life his skin wrinkled, he developed varicose veins, shortness of breath, grey hair, senile dementia and incontinence. Some time in his seventh year he fainted and never gained consciousness
The coroner returned a verdict of natural causes due to old age.
Hugh Cory. Advanced writing with english in use. Oxford University Press, p. 34.
No such luck for Charles Charlesworth, who was born on the 14th of March, 1829, in Stafford. At the age of four Charles had a beard and was sexually active.
In the final three years of his life his skin wrinkled, he developed varicose veins, shortness of breath, grey hair, senile dementia and incontinence. Some time in his seventh year he fainted and never gained consciousness
The coroner returned a verdict of natural causes due to old age.
Hugh Cory. Advanced writing with english in use. Oxford University Press, p. 34.
According to the text above,
Colin looks and behaves as if he were much older than he actually is.
Colin looks and behaves as if he were much older than he actually is.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Provas:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Analista Judiciário - Área Judiciária
|
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Analista Judiciário - Área Administrativa |
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Todos os Cargos - Conhecimentos Básicos - Cargos 3 e 5 |
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Analista Judiciário - Revisor de Texto |
Q351997
Inglês
Texto associado
The aging process affects us all at different rates. Some people of fifty-three, like the esteemed author, look a mere thirty-five, with sparkling brown eyes, a handsome gait and the virility of a steam train. Others, like the author’s friend Colin, look like little middle-aged men at twenty-one with middle-aged outlooks of set ways and planned futures. In women the former condition is common but women rarely suffer from the latter, being fired with the insatiable drive of ambition for either an independent and distinguished career in a still male-dominated world, or a home and seven children by the time they are thirty followed by an independent and distinguished career as a Cheltenham councillor or a public relations agent for Jonathan Cape, in later life.
No such luck for Charles Charlesworth, who was born on the 14th of March, 1829, in Stafford. At the age of four Charles had a beard and was sexually active.
In the final three years of his life his skin wrinkled, he developed varicose veins, shortness of breath, grey hair, senile dementia and incontinence. Some time in his seventh year he fainted and never gained consciousness
The coroner returned a verdict of natural causes due to old age.
Hugh Cory. Advanced writing with english in use. Oxford University Press, p. 34.
No such luck for Charles Charlesworth, who was born on the 14th of March, 1829, in Stafford. At the age of four Charles had a beard and was sexually active.
In the final three years of his life his skin wrinkled, he developed varicose veins, shortness of breath, grey hair, senile dementia and incontinence. Some time in his seventh year he fainted and never gained consciousness
The coroner returned a verdict of natural causes due to old age.
Hugh Cory. Advanced writing with english in use. Oxford University Press, p. 34.
According to the text above,
women around 30 have had distinguished careers in spite of living in a male-dominated world.
women around 30 have had distinguished careers in spite of living in a male-dominated world.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Prova:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Técnico Judiciário - Tecnologia da Informação |
Q351836
Inglês
Texto associado
Repeaters and hubs
A repeater is an electronic device that receives a network signal, cleans it of unnecessary noise, and regenerates it. The signal is retransmitted at a higher power level, or to the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances without degradation. In most twisted pair Ethernet configurations, repeaters are required for cable that runs longer than 100 meters. A repeater with multiple ports is known as a hub. Repeaters work on the physical layer of the OSI model. Repeaters require a small amount of time to regenerate the signal. This can cause a propagation delay which can affect network performance. As a result, many network architectures limit the number of repeaters that can be used in a row, e.g., the Ethernet 5-4-3 rule.
Hubs have been mostly obsoleted by modern switches; but repeaters are used for long distance links, notably undersea cabling.
Bridges
A network bridge connects multiple network segments at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model to form a single network. Bridges broadcast to all ports except the port on which the broadcast was received. However, bridges do not promiscuously copy traffic to all ports, as hubs do. Instead, bridges learn which MAC addresses are reachable through specific ports. Once the bridge associates a port with an address, it will send traffic for that address to that port only.
Bridges learn the association of ports and addresses by examining the source address of frames that it sees on various ports. Once a frame arrives through a port, the bridge assumes that the MAC address is associated with that port and stores its source address.
The first time a bridge sees a previously unknown destination address, the bridge will forward the frame to all ports other than the one on which the frame arrived.
Bridges come in three basic types:
Local bridges: Directly connect LANs
Remote bridges: Can be used to create a wide area network (WAN) link between LANs. Remote bridges, where the connecting link is slower than the end networks, largely have been replaced with routers. Wireless bridges: Can be used to join LANs or connect remote devices to LANs.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted).
A repeater is an electronic device that receives a network signal, cleans it of unnecessary noise, and regenerates it. The signal is retransmitted at a higher power level, or to the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances without degradation. In most twisted pair Ethernet configurations, repeaters are required for cable that runs longer than 100 meters. A repeater with multiple ports is known as a hub. Repeaters work on the physical layer of the OSI model. Repeaters require a small amount of time to regenerate the signal. This can cause a propagation delay which can affect network performance. As a result, many network architectures limit the number of repeaters that can be used in a row, e.g., the Ethernet 5-4-3 rule.
Hubs have been mostly obsoleted by modern switches; but repeaters are used for long distance links, notably undersea cabling.
Bridges
A network bridge connects multiple network segments at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model to form a single network. Bridges broadcast to all ports except the port on which the broadcast was received. However, bridges do not promiscuously copy traffic to all ports, as hubs do. Instead, bridges learn which MAC addresses are reachable through specific ports. Once the bridge associates a port with an address, it will send traffic for that address to that port only.
Bridges learn the association of ports and addresses by examining the source address of frames that it sees on various ports. Once a frame arrives through a port, the bridge assumes that the MAC address is associated with that port and stores its source address.
The first time a bridge sees a previously unknown destination address, the bridge will forward the frame to all ports other than the one on which the frame arrived.
Bridges come in three basic types:
Local bridges: Directly connect LANs
Remote bridges: Can be used to create a wide area network (WAN) link between LANs. Remote bridges, where the connecting link is slower than the end networks, largely have been replaced with routers. Wireless bridges: Can be used to join LANs or connect remote devices to LANs.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted).
According to the text above, judge the following items.
Remote devices can be connected to LANs with the use of wireless bridges.
Remote devices can be connected to LANs with the use of wireless bridges.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Prova:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Técnico Judiciário - Tecnologia da Informação |
Q351835
Inglês
Texto associado
Repeaters and hubs
A repeater is an electronic device that receives a network signal, cleans it of unnecessary noise, and regenerates it. The signal is retransmitted at a higher power level, or to the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances without degradation. In most twisted pair Ethernet configurations, repeaters are required for cable that runs longer than 100 meters. A repeater with multiple ports is known as a hub. Repeaters work on the physical layer of the OSI model. Repeaters require a small amount of time to regenerate the signal. This can cause a propagation delay which can affect network performance. As a result, many network architectures limit the number of repeaters that can be used in a row, e.g., the Ethernet 5-4-3 rule.
Hubs have been mostly obsoleted by modern switches; but repeaters are used for long distance links, notably undersea cabling.
Bridges
A network bridge connects multiple network segments at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model to form a single network. Bridges broadcast to all ports except the port on which the broadcast was received. However, bridges do not promiscuously copy traffic to all ports, as hubs do. Instead, bridges learn which MAC addresses are reachable through specific ports. Once the bridge associates a port with an address, it will send traffic for that address to that port only.
Bridges learn the association of ports and addresses by examining the source address of frames that it sees on various ports. Once a frame arrives through a port, the bridge assumes that the MAC address is associated with that port and stores its source address.
The first time a bridge sees a previously unknown destination address, the bridge will forward the frame to all ports other than the one on which the frame arrived.
Bridges come in three basic types:
Local bridges: Directly connect LANs
Remote bridges: Can be used to create a wide area network (WAN) link between LANs. Remote bridges, where the connecting link is slower than the end networks, largely have been replaced with routers. Wireless bridges: Can be used to join LANs or connect remote devices to LANs.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted).
A repeater is an electronic device that receives a network signal, cleans it of unnecessary noise, and regenerates it. The signal is retransmitted at a higher power level, or to the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances without degradation. In most twisted pair Ethernet configurations, repeaters are required for cable that runs longer than 100 meters. A repeater with multiple ports is known as a hub. Repeaters work on the physical layer of the OSI model. Repeaters require a small amount of time to regenerate the signal. This can cause a propagation delay which can affect network performance. As a result, many network architectures limit the number of repeaters that can be used in a row, e.g., the Ethernet 5-4-3 rule.
Hubs have been mostly obsoleted by modern switches; but repeaters are used for long distance links, notably undersea cabling.
Bridges
A network bridge connects multiple network segments at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model to form a single network. Bridges broadcast to all ports except the port on which the broadcast was received. However, bridges do not promiscuously copy traffic to all ports, as hubs do. Instead, bridges learn which MAC addresses are reachable through specific ports. Once the bridge associates a port with an address, it will send traffic for that address to that port only.
Bridges learn the association of ports and addresses by examining the source address of frames that it sees on various ports. Once a frame arrives through a port, the bridge assumes that the MAC address is associated with that port and stores its source address.
The first time a bridge sees a previously unknown destination address, the bridge will forward the frame to all ports other than the one on which the frame arrived.
Bridges come in three basic types:
Local bridges: Directly connect LANs
Remote bridges: Can be used to create a wide area network (WAN) link between LANs. Remote bridges, where the connecting link is slower than the end networks, largely have been replaced with routers. Wireless bridges: Can be used to join LANs or connect remote devices to LANs.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted).
According to the text above, judge the following items.
The signal regeneration that is performed by repeaters can cause small propagation delays that can affect the performance of a computer network.
The signal regeneration that is performed by repeaters can cause small propagation delays that can affect the performance of a computer network.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Prova:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Técnico Judiciário - Tecnologia da Informação |
Q351834
Inglês
Texto associado
Repeaters and hubs
A repeater is an electronic device that receives a network signal, cleans it of unnecessary noise, and regenerates it. The signal is retransmitted at a higher power level, or to the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances without degradation. In most twisted pair Ethernet configurations, repeaters are required for cable that runs longer than 100 meters. A repeater with multiple ports is known as a hub. Repeaters work on the physical layer of the OSI model. Repeaters require a small amount of time to regenerate the signal. This can cause a propagation delay which can affect network performance. As a result, many network architectures limit the number of repeaters that can be used in a row, e.g., the Ethernet 5-4-3 rule.
Hubs have been mostly obsoleted by modern switches; but repeaters are used for long distance links, notably undersea cabling.
Bridges
A network bridge connects multiple network segments at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model to form a single network. Bridges broadcast to all ports except the port on which the broadcast was received. However, bridges do not promiscuously copy traffic to all ports, as hubs do. Instead, bridges learn which MAC addresses are reachable through specific ports. Once the bridge associates a port with an address, it will send traffic for that address to that port only.
Bridges learn the association of ports and addresses by examining the source address of frames that it sees on various ports. Once a frame arrives through a port, the bridge assumes that the MAC address is associated with that port and stores its source address.
The first time a bridge sees a previously unknown destination address, the bridge will forward the frame to all ports other than the one on which the frame arrived.
Bridges come in three basic types:
Local bridges: Directly connect LANs
Remote bridges: Can be used to create a wide area network (WAN) link between LANs. Remote bridges, where the connecting link is slower than the end networks, largely have been replaced with routers. Wireless bridges: Can be used to join LANs or connect remote devices to LANs.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted).
A repeater is an electronic device that receives a network signal, cleans it of unnecessary noise, and regenerates it. The signal is retransmitted at a higher power level, or to the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances without degradation. In most twisted pair Ethernet configurations, repeaters are required for cable that runs longer than 100 meters. A repeater with multiple ports is known as a hub. Repeaters work on the physical layer of the OSI model. Repeaters require a small amount of time to regenerate the signal. This can cause a propagation delay which can affect network performance. As a result, many network architectures limit the number of repeaters that can be used in a row, e.g., the Ethernet 5-4-3 rule.
Hubs have been mostly obsoleted by modern switches; but repeaters are used for long distance links, notably undersea cabling.
Bridges
A network bridge connects multiple network segments at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model to form a single network. Bridges broadcast to all ports except the port on which the broadcast was received. However, bridges do not promiscuously copy traffic to all ports, as hubs do. Instead, bridges learn which MAC addresses are reachable through specific ports. Once the bridge associates a port with an address, it will send traffic for that address to that port only.
Bridges learn the association of ports and addresses by examining the source address of frames that it sees on various ports. Once a frame arrives through a port, the bridge assumes that the MAC address is associated with that port and stores its source address.
The first time a bridge sees a previously unknown destination address, the bridge will forward the frame to all ports other than the one on which the frame arrived.
Bridges come in three basic types:
Local bridges: Directly connect LANs
Remote bridges: Can be used to create a wide area network (WAN) link between LANs. Remote bridges, where the connecting link is slower than the end networks, largely have been replaced with routers. Wireless bridges: Can be used to join LANs or connect remote devices to LANs.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted).
According to the text above, judge the following items.
Multiple network segments at the layer 2 of the OSI model can be connected by a network bridge, in order to form a single network.
Multiple network segments at the layer 2 of the OSI model can be connected by a network bridge, in order to form a single network.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Prova:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Técnico Judiciário - Tecnologia da Informação |
Q351833
Inglês
Texto associado
Repeaters and hubs
A repeater is an electronic device that receives a network signal, cleans it of unnecessary noise, and regenerates it. The signal is retransmitted at a higher power level, or to the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances without degradation. In most twisted pair Ethernet configurations, repeaters are required for cable that runs longer than 100 meters. A repeater with multiple ports is known as a hub. Repeaters work on the physical layer of the OSI model. Repeaters require a small amount of time to regenerate the signal. This can cause a propagation delay which can affect network performance. As a result, many network architectures limit the number of repeaters that can be used in a row, e.g., the Ethernet 5-4-3 rule.
Hubs have been mostly obsoleted by modern switches; but repeaters are used for long distance links, notably undersea cabling.
Bridges
A network bridge connects multiple network segments at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model to form a single network. Bridges broadcast to all ports except the port on which the broadcast was received. However, bridges do not promiscuously copy traffic to all ports, as hubs do. Instead, bridges learn which MAC addresses are reachable through specific ports. Once the bridge associates a port with an address, it will send traffic for that address to that port only.
Bridges learn the association of ports and addresses by examining the source address of frames that it sees on various ports. Once a frame arrives through a port, the bridge assumes that the MAC address is associated with that port and stores its source address.
The first time a bridge sees a previously unknown destination address, the bridge will forward the frame to all ports other than the one on which the frame arrived.
Bridges come in three basic types:
Local bridges: Directly connect LANs
Remote bridges: Can be used to create a wide area network (WAN) link between LANs. Remote bridges, where the connecting link is slower than the end networks, largely have been replaced with routers. Wireless bridges: Can be used to join LANs or connect remote devices to LANs.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted).
A repeater is an electronic device that receives a network signal, cleans it of unnecessary noise, and regenerates it. The signal is retransmitted at a higher power level, or to the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances without degradation. In most twisted pair Ethernet configurations, repeaters are required for cable that runs longer than 100 meters. A repeater with multiple ports is known as a hub. Repeaters work on the physical layer of the OSI model. Repeaters require a small amount of time to regenerate the signal. This can cause a propagation delay which can affect network performance. As a result, many network architectures limit the number of repeaters that can be used in a row, e.g., the Ethernet 5-4-3 rule.
Hubs have been mostly obsoleted by modern switches; but repeaters are used for long distance links, notably undersea cabling.
Bridges
A network bridge connects multiple network segments at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model to form a single network. Bridges broadcast to all ports except the port on which the broadcast was received. However, bridges do not promiscuously copy traffic to all ports, as hubs do. Instead, bridges learn which MAC addresses are reachable through specific ports. Once the bridge associates a port with an address, it will send traffic for that address to that port only.
Bridges learn the association of ports and addresses by examining the source address of frames that it sees on various ports. Once a frame arrives through a port, the bridge assumes that the MAC address is associated with that port and stores its source address.
The first time a bridge sees a previously unknown destination address, the bridge will forward the frame to all ports other than the one on which the frame arrived.
Bridges come in three basic types:
Local bridges: Directly connect LANs
Remote bridges: Can be used to create a wide area network (WAN) link between LANs. Remote bridges, where the connecting link is slower than the end networks, largely have been replaced with routers. Wireless bridges: Can be used to join LANs or connect remote devices to LANs.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted).
According to the text above, judge the following items.
Since the invention of the hubs, the switches became obsolete.
Since the invention of the hubs, the switches became obsolete.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Prova:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Técnico Judiciário - Tecnologia da Informação |
Q351832
Inglês
Texto associado
Types of operating systems
Real-time
A real-time operating system is a multitasking operating system that aims at executing real-time applications. Real-time operating systems often use specialized scheduling algorithms so that they can achieve a deterministic nature of behavior. The main objective of real-time operating systems is their quick and predictable response to events. They have an event-driven or time-sharing design and often aspects of both. An event-driven system switches between tasks based on their priorities or external events while time-sharing operating systems switch tasks based on clock interrupts.
Multi-user
A multi-user operating system allows multiple users to access a computer system at the same time. Time-sharing systems and Internet servers can be classified as multi-user systems as they enable multiple-user access to a computer through the sharing of time. Single-user operating systems have only one user but may allow multiple programs to run at the same time.
Multi-tasking vs. single-tasking
A multi-tasking operating system allows more than one program to be running at the same time, from the point of view of human time scales. A single-tasking system has only one running program. Multi-tasking can be of two types: pre-emptive and co-operative. In pre-emptive multitasking, the operating system slices the CPU time and dedicates one slot to each of the programs. Unix-like operating systems such as Solaris and Linux support pre-emptive multitasking, as does AmigaOS. Cooperative multitasking is achieved by relying on each process to give time to the other processes in a defined manner. 16-bit versions of Microsoft Windows used cooperative multi-tasking. 32-bit versions of both Windows NT and Win9x, used pre-emptive multi-tasking. Mac OS prior to OS X used to support cooperative multitasking.
Distributed
A distributed operating system manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer. The development of networked computers that could be linked and communicate with each other gave rise to distributed computing. Distributed computations are carried out on more than one machine. When computers in a group work in cooperation, they make a distributed system.
Embedded
Embedded operating systems are designed to be used in embedded computer systems. They are designed to operate on small machines like PDAs with less autonomy. They are able to operate with a limited number of resources. They are very compact and extremely efficient by design. Windows CE and Minix 3 are some examples of embedded operating systems.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted)
Real-time
A real-time operating system is a multitasking operating system that aims at executing real-time applications. Real-time operating systems often use specialized scheduling algorithms so that they can achieve a deterministic nature of behavior. The main objective of real-time operating systems is their quick and predictable response to events. They have an event-driven or time-sharing design and often aspects of both. An event-driven system switches between tasks based on their priorities or external events while time-sharing operating systems switch tasks based on clock interrupts.
Multi-user
A multi-user operating system allows multiple users to access a computer system at the same time. Time-sharing systems and Internet servers can be classified as multi-user systems as they enable multiple-user access to a computer through the sharing of time. Single-user operating systems have only one user but may allow multiple programs to run at the same time.
Multi-tasking vs. single-tasking
A multi-tasking operating system allows more than one program to be running at the same time, from the point of view of human time scales. A single-tasking system has only one running program. Multi-tasking can be of two types: pre-emptive and co-operative. In pre-emptive multitasking, the operating system slices the CPU time and dedicates one slot to each of the programs. Unix-like operating systems such as Solaris and Linux support pre-emptive multitasking, as does AmigaOS. Cooperative multitasking is achieved by relying on each process to give time to the other processes in a defined manner. 16-bit versions of Microsoft Windows used cooperative multi-tasking. 32-bit versions of both Windows NT and Win9x, used pre-emptive multi-tasking. Mac OS prior to OS X used to support cooperative multitasking.
Distributed
A distributed operating system manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer. The development of networked computers that could be linked and communicate with each other gave rise to distributed computing. Distributed computations are carried out on more than one machine. When computers in a group work in cooperation, they make a distributed system.
Embedded
Embedded operating systems are designed to be used in embedded computer systems. They are designed to operate on small machines like PDAs with less autonomy. They are able to operate with a limited number of resources. They are very compact and extremely efficient by design. Windows CE and Minix 3 are some examples of embedded operating systems.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted)
Based on the text above, judge the following items from 111 through 116.
When a distributed operating system is used for managing several independent computers, this group of computers appears to behave like a single computer.
When a distributed operating system is used for managing several independent computers, this group of computers appears to behave like a single computer.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Prova:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Técnico Judiciário - Tecnologia da Informação |
Q351831
Inglês
Texto associado
Types of operating systems
Real-time
A real-time operating system is a multitasking operating system that aims at executing real-time applications. Real-time operating systems often use specialized scheduling algorithms so that they can achieve a deterministic nature of behavior. The main objective of real-time operating systems is their quick and predictable response to events. They have an event-driven or time-sharing design and often aspects of both. An event-driven system switches between tasks based on their priorities or external events while time-sharing operating systems switch tasks based on clock interrupts.
Multi-user
A multi-user operating system allows multiple users to access a computer system at the same time. Time-sharing systems and Internet servers can be classified as multi-user systems as they enable multiple-user access to a computer through the sharing of time. Single-user operating systems have only one user but may allow multiple programs to run at the same time.
Multi-tasking vs. single-tasking
A multi-tasking operating system allows more than one program to be running at the same time, from the point of view of human time scales. A single-tasking system has only one running program. Multi-tasking can be of two types: pre-emptive and co-operative. In pre-emptive multitasking, the operating system slices the CPU time and dedicates one slot to each of the programs. Unix-like operating systems such as Solaris and Linux support pre-emptive multitasking, as does AmigaOS. Cooperative multitasking is achieved by relying on each process to give time to the other processes in a defined manner. 16-bit versions of Microsoft Windows used cooperative multi-tasking. 32-bit versions of both Windows NT and Win9x, used pre-emptive multi-tasking. Mac OS prior to OS X used to support cooperative multitasking.
Distributed
A distributed operating system manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer. The development of networked computers that could be linked and communicate with each other gave rise to distributed computing. Distributed computations are carried out on more than one machine. When computers in a group work in cooperation, they make a distributed system.
Embedded
Embedded operating systems are designed to be used in embedded computer systems. They are designed to operate on small machines like PDAs with less autonomy. They are able to operate with a limited number of resources. They are very compact and extremely efficient by design. Windows CE and Minix 3 are some examples of embedded operating systems.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted)
Real-time
A real-time operating system is a multitasking operating system that aims at executing real-time applications. Real-time operating systems often use specialized scheduling algorithms so that they can achieve a deterministic nature of behavior. The main objective of real-time operating systems is their quick and predictable response to events. They have an event-driven or time-sharing design and often aspects of both. An event-driven system switches between tasks based on their priorities or external events while time-sharing operating systems switch tasks based on clock interrupts.
Multi-user
A multi-user operating system allows multiple users to access a computer system at the same time. Time-sharing systems and Internet servers can be classified as multi-user systems as they enable multiple-user access to a computer through the sharing of time. Single-user operating systems have only one user but may allow multiple programs to run at the same time.
Multi-tasking vs. single-tasking
A multi-tasking operating system allows more than one program to be running at the same time, from the point of view of human time scales. A single-tasking system has only one running program. Multi-tasking can be of two types: pre-emptive and co-operative. In pre-emptive multitasking, the operating system slices the CPU time and dedicates one slot to each of the programs. Unix-like operating systems such as Solaris and Linux support pre-emptive multitasking, as does AmigaOS. Cooperative multitasking is achieved by relying on each process to give time to the other processes in a defined manner. 16-bit versions of Microsoft Windows used cooperative multi-tasking. 32-bit versions of both Windows NT and Win9x, used pre-emptive multi-tasking. Mac OS prior to OS X used to support cooperative multitasking.
Distributed
A distributed operating system manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer. The development of networked computers that could be linked and communicate with each other gave rise to distributed computing. Distributed computations are carried out on more than one machine. When computers in a group work in cooperation, they make a distributed system.
Embedded
Embedded operating systems are designed to be used in embedded computer systems. They are designed to operate on small machines like PDAs with less autonomy. They are able to operate with a limited number of resources. They are very compact and extremely efficient by design. Windows CE and Minix 3 are some examples of embedded operating systems.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted)
Based on the text above, judge the following items from 111 through 116.
Systems that use time-sharing are not considered to be multi- user systems, since they do not allow the simultaneous access of several users to a computer.
Systems that use time-sharing are not considered to be multi- user systems, since they do not allow the simultaneous access of several users to a computer.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Prova:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Técnico Judiciário - Tecnologia da Informação |
Q351830
Inglês
Texto associado
Types of operating systems
Real-time
A real-time operating system is a multitasking operating system that aims at executing real-time applications. Real-time operating systems often use specialized scheduling algorithms so that they can achieve a deterministic nature of behavior. The main objective of real-time operating systems is their quick and predictable response to events. They have an event-driven or time-sharing design and often aspects of both. An event-driven system switches between tasks based on their priorities or external events while time-sharing operating systems switch tasks based on clock interrupts.
Multi-user
A multi-user operating system allows multiple users to access a computer system at the same time. Time-sharing systems and Internet servers can be classified as multi-user systems as they enable multiple-user access to a computer through the sharing of time. Single-user operating systems have only one user but may allow multiple programs to run at the same time.
Multi-tasking vs. single-tasking
A multi-tasking operating system allows more than one program to be running at the same time, from the point of view of human time scales. A single-tasking system has only one running program. Multi-tasking can be of two types: pre-emptive and co-operative. In pre-emptive multitasking, the operating system slices the CPU time and dedicates one slot to each of the programs. Unix-like operating systems such as Solaris and Linux support pre-emptive multitasking, as does AmigaOS. Cooperative multitasking is achieved by relying on each process to give time to the other processes in a defined manner. 16-bit versions of Microsoft Windows used cooperative multi-tasking. 32-bit versions of both Windows NT and Win9x, used pre-emptive multi-tasking. Mac OS prior to OS X used to support cooperative multitasking.
Distributed
A distributed operating system manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer. The development of networked computers that could be linked and communicate with each other gave rise to distributed computing. Distributed computations are carried out on more than one machine. When computers in a group work in cooperation, they make a distributed system.
Embedded
Embedded operating systems are designed to be used in embedded computer systems. They are designed to operate on small machines like PDAs with less autonomy. They are able to operate with a limited number of resources. They are very compact and extremely efficient by design. Windows CE and Minix 3 are some examples of embedded operating systems.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted)
Real-time
A real-time operating system is a multitasking operating system that aims at executing real-time applications. Real-time operating systems often use specialized scheduling algorithms so that they can achieve a deterministic nature of behavior. The main objective of real-time operating systems is their quick and predictable response to events. They have an event-driven or time-sharing design and often aspects of both. An event-driven system switches between tasks based on their priorities or external events while time-sharing operating systems switch tasks based on clock interrupts.
Multi-user
A multi-user operating system allows multiple users to access a computer system at the same time. Time-sharing systems and Internet servers can be classified as multi-user systems as they enable multiple-user access to a computer through the sharing of time. Single-user operating systems have only one user but may allow multiple programs to run at the same time.
Multi-tasking vs. single-tasking
A multi-tasking operating system allows more than one program to be running at the same time, from the point of view of human time scales. A single-tasking system has only one running program. Multi-tasking can be of two types: pre-emptive and co-operative. In pre-emptive multitasking, the operating system slices the CPU time and dedicates one slot to each of the programs. Unix-like operating systems such as Solaris and Linux support pre-emptive multitasking, as does AmigaOS. Cooperative multitasking is achieved by relying on each process to give time to the other processes in a defined manner. 16-bit versions of Microsoft Windows used cooperative multi-tasking. 32-bit versions of both Windows NT and Win9x, used pre-emptive multi-tasking. Mac OS prior to OS X used to support cooperative multitasking.
Distributed
A distributed operating system manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer. The development of networked computers that could be linked and communicate with each other gave rise to distributed computing. Distributed computations are carried out on more than one machine. When computers in a group work in cooperation, they make a distributed system.
Embedded
Embedded operating systems are designed to be used in embedded computer systems. They are designed to operate on small machines like PDAs with less autonomy. They are able to operate with a limited number of resources. They are very compact and extremely efficient by design. Windows CE and Minix 3 are some examples of embedded operating systems.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted)
Based on the text above, judge the following items from 111 through 116.
Since the first release of Windows NT, no version of Windows used cooperative multi-tasking.
Since the first release of Windows NT, no version of Windows used cooperative multi-tasking.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Prova:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Técnico Judiciário - Tecnologia da Informação |
Q351829
Inglês
Texto associado
Types of operating systems
Real-time
A real-time operating system is a multitasking operating system that aims at executing real-time applications. Real-time operating systems often use specialized scheduling algorithms so that they can achieve a deterministic nature of behavior. The main objective of real-time operating systems is their quick and predictable response to events. They have an event-driven or time-sharing design and often aspects of both. An event-driven system switches between tasks based on their priorities or external events while time-sharing operating systems switch tasks based on clock interrupts.
Multi-user
A multi-user operating system allows multiple users to access a computer system at the same time. Time-sharing systems and Internet servers can be classified as multi-user systems as they enable multiple-user access to a computer through the sharing of time. Single-user operating systems have only one user but may allow multiple programs to run at the same time.
Multi-tasking vs. single-tasking
A multi-tasking operating system allows more than one program to be running at the same time, from the point of view of human time scales. A single-tasking system has only one running program. Multi-tasking can be of two types: pre-emptive and co-operative. In pre-emptive multitasking, the operating system slices the CPU time and dedicates one slot to each of the programs. Unix-like operating systems such as Solaris and Linux support pre-emptive multitasking, as does AmigaOS. Cooperative multitasking is achieved by relying on each process to give time to the other processes in a defined manner. 16-bit versions of Microsoft Windows used cooperative multi-tasking. 32-bit versions of both Windows NT and Win9x, used pre-emptive multi-tasking. Mac OS prior to OS X used to support cooperative multitasking.
Distributed
A distributed operating system manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer. The development of networked computers that could be linked and communicate with each other gave rise to distributed computing. Distributed computations are carried out on more than one machine. When computers in a group work in cooperation, they make a distributed system.
Embedded
Embedded operating systems are designed to be used in embedded computer systems. They are designed to operate on small machines like PDAs with less autonomy. They are able to operate with a limited number of resources. They are very compact and extremely efficient by design. Windows CE and Minix 3 are some examples of embedded operating systems.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted)
Real-time
A real-time operating system is a multitasking operating system that aims at executing real-time applications. Real-time operating systems often use specialized scheduling algorithms so that they can achieve a deterministic nature of behavior. The main objective of real-time operating systems is their quick and predictable response to events. They have an event-driven or time-sharing design and often aspects of both. An event-driven system switches between tasks based on their priorities or external events while time-sharing operating systems switch tasks based on clock interrupts.
Multi-user
A multi-user operating system allows multiple users to access a computer system at the same time. Time-sharing systems and Internet servers can be classified as multi-user systems as they enable multiple-user access to a computer through the sharing of time. Single-user operating systems have only one user but may allow multiple programs to run at the same time.
Multi-tasking vs. single-tasking
A multi-tasking operating system allows more than one program to be running at the same time, from the point of view of human time scales. A single-tasking system has only one running program. Multi-tasking can be of two types: pre-emptive and co-operative. In pre-emptive multitasking, the operating system slices the CPU time and dedicates one slot to each of the programs. Unix-like operating systems such as Solaris and Linux support pre-emptive multitasking, as does AmigaOS. Cooperative multitasking is achieved by relying on each process to give time to the other processes in a defined manner. 16-bit versions of Microsoft Windows used cooperative multi-tasking. 32-bit versions of both Windows NT and Win9x, used pre-emptive multi-tasking. Mac OS prior to OS X used to support cooperative multitasking.
Distributed
A distributed operating system manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer. The development of networked computers that could be linked and communicate with each other gave rise to distributed computing. Distributed computations are carried out on more than one machine. When computers in a group work in cooperation, they make a distributed system.
Embedded
Embedded operating systems are designed to be used in embedded computer systems. They are designed to operate on small machines like PDAs with less autonomy. They are able to operate with a limited number of resources. They are very compact and extremely efficient by design. Windows CE and Minix 3 are some examples of embedded operating systems.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted)
Based on the text above, judge the following items from 111 through 116.
Only rarely, operating systems use specific scheduling algorithms that make sure that the programs behave in a deterministic way.
Only rarely, operating systems use specific scheduling algorithms that make sure that the programs behave in a deterministic way.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Prova:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Técnico Judiciário - Tecnologia da Informação |
Q351828
Inglês
Texto associado
Types of operating systems
Real-time
A real-time operating system is a multitasking operating system that aims at executing real-time applications. Real-time operating systems often use specialized scheduling algorithms so that they can achieve a deterministic nature of behavior. The main objective of real-time operating systems is their quick and predictable response to events. They have an event-driven or time-sharing design and often aspects of both. An event-driven system switches between tasks based on their priorities or external events while time-sharing operating systems switch tasks based on clock interrupts.
Multi-user
A multi-user operating system allows multiple users to access a computer system at the same time. Time-sharing systems and Internet servers can be classified as multi-user systems as they enable multiple-user access to a computer through the sharing of time. Single-user operating systems have only one user but may allow multiple programs to run at the same time.
Multi-tasking vs. single-tasking
A multi-tasking operating system allows more than one program to be running at the same time, from the point of view of human time scales. A single-tasking system has only one running program. Multi-tasking can be of two types: pre-emptive and co-operative. In pre-emptive multitasking, the operating system slices the CPU time and dedicates one slot to each of the programs. Unix-like operating systems such as Solaris and Linux support pre-emptive multitasking, as does AmigaOS. Cooperative multitasking is achieved by relying on each process to give time to the other processes in a defined manner. 16-bit versions of Microsoft Windows used cooperative multi-tasking. 32-bit versions of both Windows NT and Win9x, used pre-emptive multi-tasking. Mac OS prior to OS X used to support cooperative multitasking.
Distributed
A distributed operating system manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer. The development of networked computers that could be linked and communicate with each other gave rise to distributed computing. Distributed computations are carried out on more than one machine. When computers in a group work in cooperation, they make a distributed system.
Embedded
Embedded operating systems are designed to be used in embedded computer systems. They are designed to operate on small machines like PDAs with less autonomy. They are able to operate with a limited number of resources. They are very compact and extremely efficient by design. Windows CE and Minix 3 are some examples of embedded operating systems.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted)
Real-time
A real-time operating system is a multitasking operating system that aims at executing real-time applications. Real-time operating systems often use specialized scheduling algorithms so that they can achieve a deterministic nature of behavior. The main objective of real-time operating systems is their quick and predictable response to events. They have an event-driven or time-sharing design and often aspects of both. An event-driven system switches between tasks based on their priorities or external events while time-sharing operating systems switch tasks based on clock interrupts.
Multi-user
A multi-user operating system allows multiple users to access a computer system at the same time. Time-sharing systems and Internet servers can be classified as multi-user systems as they enable multiple-user access to a computer through the sharing of time. Single-user operating systems have only one user but may allow multiple programs to run at the same time.
Multi-tasking vs. single-tasking
A multi-tasking operating system allows more than one program to be running at the same time, from the point of view of human time scales. A single-tasking system has only one running program. Multi-tasking can be of two types: pre-emptive and co-operative. In pre-emptive multitasking, the operating system slices the CPU time and dedicates one slot to each of the programs. Unix-like operating systems such as Solaris and Linux support pre-emptive multitasking, as does AmigaOS. Cooperative multitasking is achieved by relying on each process to give time to the other processes in a defined manner. 16-bit versions of Microsoft Windows used cooperative multi-tasking. 32-bit versions of both Windows NT and Win9x, used pre-emptive multi-tasking. Mac OS prior to OS X used to support cooperative multitasking.
Distributed
A distributed operating system manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer. The development of networked computers that could be linked and communicate with each other gave rise to distributed computing. Distributed computations are carried out on more than one machine. When computers in a group work in cooperation, they make a distributed system.
Embedded
Embedded operating systems are designed to be used in embedded computer systems. They are designed to operate on small machines like PDAs with less autonomy. They are able to operate with a limited number of resources. They are very compact and extremely efficient by design. Windows CE and Minix 3 are some examples of embedded operating systems.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted)
Based on the text above, judge the following items from 111 through 116.
Single-user operating systems do not allow the use of a computer by multiple users. Moreover, they do not allow more than one program to run at the same time.
Single-user operating systems do not allow the use of a computer by multiple users. Moreover, they do not allow more than one program to run at the same time.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
STF
Prova:
CESPE - 2013 - STF - Técnico Judiciário - Tecnologia da Informação |
Q351827
Inglês
Texto associado
Types of operating systems
Real-time
A real-time operating system is a multitasking operating system that aims at executing real-time applications. Real-time operating systems often use specialized scheduling algorithms so that they can achieve a deterministic nature of behavior. The main objective of real-time operating systems is their quick and predictable response to events. They have an event-driven or time-sharing design and often aspects of both. An event-driven system switches between tasks based on their priorities or external events while time-sharing operating systems switch tasks based on clock interrupts.
Multi-user
A multi-user operating system allows multiple users to access a computer system at the same time. Time-sharing systems and Internet servers can be classified as multi-user systems as they enable multiple-user access to a computer through the sharing of time. Single-user operating systems have only one user but may allow multiple programs to run at the same time.
Multi-tasking vs. single-tasking
A multi-tasking operating system allows more than one program to be running at the same time, from the point of view of human time scales. A single-tasking system has only one running program. Multi-tasking can be of two types: pre-emptive and co-operative. In pre-emptive multitasking, the operating system slices the CPU time and dedicates one slot to each of the programs. Unix-like operating systems such as Solaris and Linux support pre-emptive multitasking, as does AmigaOS. Cooperative multitasking is achieved by relying on each process to give time to the other processes in a defined manner. 16-bit versions of Microsoft Windows used cooperative multi-tasking. 32-bit versions of both Windows NT and Win9x, used pre-emptive multi-tasking. Mac OS prior to OS X used to support cooperative multitasking.
Distributed
A distributed operating system manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer. The development of networked computers that could be linked and communicate with each other gave rise to distributed computing. Distributed computations are carried out on more than one machine. When computers in a group work in cooperation, they make a distributed system.
Embedded
Embedded operating systems are designed to be used in embedded computer systems. They are designed to operate on small machines like PDAs with less autonomy. They are able to operate with a limited number of resources. They are very compact and extremely efficient by design. Windows CE and Minix 3 are some examples of embedded operating systems.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted)
Real-time
A real-time operating system is a multitasking operating system that aims at executing real-time applications. Real-time operating systems often use specialized scheduling algorithms so that they can achieve a deterministic nature of behavior. The main objective of real-time operating systems is their quick and predictable response to events. They have an event-driven or time-sharing design and often aspects of both. An event-driven system switches between tasks based on their priorities or external events while time-sharing operating systems switch tasks based on clock interrupts.
Multi-user
A multi-user operating system allows multiple users to access a computer system at the same time. Time-sharing systems and Internet servers can be classified as multi-user systems as they enable multiple-user access to a computer through the sharing of time. Single-user operating systems have only one user but may allow multiple programs to run at the same time.
Multi-tasking vs. single-tasking
A multi-tasking operating system allows more than one program to be running at the same time, from the point of view of human time scales. A single-tasking system has only one running program. Multi-tasking can be of two types: pre-emptive and co-operative. In pre-emptive multitasking, the operating system slices the CPU time and dedicates one slot to each of the programs. Unix-like operating systems such as Solaris and Linux support pre-emptive multitasking, as does AmigaOS. Cooperative multitasking is achieved by relying on each process to give time to the other processes in a defined manner. 16-bit versions of Microsoft Windows used cooperative multi-tasking. 32-bit versions of both Windows NT and Win9x, used pre-emptive multi-tasking. Mac OS prior to OS X used to support cooperative multitasking.
Distributed
A distributed operating system manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer. The development of networked computers that could be linked and communicate with each other gave rise to distributed computing. Distributed computations are carried out on more than one machine. When computers in a group work in cooperation, they make a distributed system.
Embedded
Embedded operating systems are designed to be used in embedded computer systems. They are designed to operate on small machines like PDAs with less autonomy. They are able to operate with a limited number of resources. They are very compact and extremely efficient by design. Windows CE and Minix 3 are some examples of embedded operating systems.
Internet: http://en.wikipedia.org (adapted)
Based on the text above, judge the following items from 111 through 116.
In an event-driven system, the switching between tasks is triggered by clock interrupts, and the duration of each time slice is always the same.
In an event-driven system, the switching between tasks is triggered by clock interrupts, and the duration of each time slice is always the same.
Ano: 2013
Banca:
CESPE / CEBRASPE
Órgão:
BACEN
Prova:
CESPE - 2013 - BACEN - Analista - Gestão e Análise Processual |
Q351546
Inglês
Texto associado

Internet: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com (adapted).

Internet: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com (adapted).
Based on the text above, judge the following items.
Internal control is a central issue on corporate governance.
Internal control is a central issue on corporate governance.
Ano: 2014
Banca:
FCC
Órgão:
SEFAZ-RJ
Prova:
FCC - 2014 - SEFAZ-RJ - Auditor Fiscal da Receita Estadual - Prova 1 |
Q351457
Inglês
Texto associado
Why Is Spain Really Taking Lionel Messi to Tax Court?
By Jonathan Mahler Sep 27, 2013
So Spain has decided to haul Lionel Messi into court for tax evasion, which strikes me as completely insane on pretty much every level.
You may remember the story from a few months back: The greatest soccer player in the world and his father were accused of setting up
a bunch of shell companies in Belize and Uruguay to avoid paying taxes on royalties and other licensing income.
Messi - who makes an estimated $41 million a year, about half from sponsors - reached a settlement with Spain’s tax authorities earlier
this summer, agreeing to pay the amount he apparently owed, plus interest. The matter was settled, or so it seemed. Messi could go
back to dazzling the world with his athleticism and creativity.
Only it turns out that Spain wasn’t quite done with Messi. His adopted country - Messi is Argentine but became a Spanish citizen in 2005
- is now considering pressing criminal charges against him.
Cracking down on tax-evading footballers has become something of a trend in Europe, where players and clubs have been known to
launder money through “image-rights companies” often set up in tax havens. When you need money - and Europe needs money - go to
the people who have it, or something like that. Over the summer, dozens of Italian soccer clubs were raided as part of an investigation
into a tax-fraud conspiracy. A number of English Premier League clubs were forced last year to pay millions of pounds in back taxes.
No one likes a tax cheat, and there’s little doubt that widespread tax fraud has helped eat away at the social safety net in Spain and
elsewhere, depriving schools, hospitals and other institutions of badly needed funds. But Europe is not going to find the answers to its
financial problems in the pockets of some professional soccer players and clubs.
Messi’s defense, delivered by his father, seems credible enough to me. “He is a footballer and that’s it,” Messi’s father Jorge said of his
soccer-prodigy son. “If there was an error, it was by our financial adviser. He created the company. My mistake was to have trusted the
adviser.” Even if Messi is legally responsible for the intricate tax dodge he is accused of having participated in, it’s pretty hard to believe
that he knew much about it.
More to the point, Lionel Messi is probably Spain’s most valuable global asset. What could possibly motivate the Spanish government to
want to tarnish his reputation, especially after he’s paid off his alleged debt? After four years of Great-Depression level unemployment,
have anxiety and despair curdled into vindictiveness?
Here’s another explanation: Maybe this whole case has less to do with money than it does with history. Maybe it’s no coincidence that
the target of the Spanish government’s weird wrath happens to play for FC Barcelona, which is, after all, "mes que un club." It's a symbol
of Catalan nationalism - and a bitter, longtime rival of Spain’s establishment team, Real Madrid.
Too conspiratorial? Prove it, Spain. Release Cristiano Ronaldo’s tax return.
(Adapted form http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2013-09-27/why-is-spain-really-taking-lionel-messi-to-tax-court-.html)
By Jonathan Mahler Sep 27, 2013
So Spain has decided to haul Lionel Messi into court for tax evasion, which strikes me as completely insane on pretty much every level.
You may remember the story from a few months back: The greatest soccer player in the world and his father were accused of setting up
a bunch of shell companies in Belize and Uruguay to avoid paying taxes on royalties and other licensing income.
Messi - who makes an estimated $41 million a year, about half from sponsors - reached a settlement with Spain’s tax authorities earlier
this summer, agreeing to pay the amount he apparently owed, plus interest. The matter was settled, or so it seemed. Messi could go
back to dazzling the world with his athleticism and creativity.
Only it turns out that Spain wasn’t quite done with Messi. His adopted country - Messi is Argentine but became a Spanish citizen in 2005
- is now considering pressing criminal charges against him.
Cracking down on tax-evading footballers has become something of a trend in Europe, where players and clubs have been known to
launder money through “image-rights companies” often set up in tax havens. When you need money - and Europe needs money - go to
the people who have it, or something like that. Over the summer, dozens of Italian soccer clubs were raided as part of an investigation
into a tax-fraud conspiracy. A number of English Premier League clubs were forced last year to pay millions of pounds in back taxes.
No one likes a tax cheat, and there’s little doubt that widespread tax fraud has helped eat away at the social safety net in Spain and
elsewhere, depriving schools, hospitals and other institutions of badly needed funds. But Europe is not going to find the answers to its
financial problems in the pockets of some professional soccer players and clubs.
Messi’s defense, delivered by his father, seems credible enough to me. “He is a footballer and that’s it,” Messi’s father Jorge said of his
soccer-prodigy son. “If there was an error, it was by our financial adviser. He created the company. My mistake was to have trusted the
adviser.” Even if Messi is legally responsible for the intricate tax dodge he is accused of having participated in, it’s pretty hard to believe
that he knew much about it.
More to the point, Lionel Messi is probably Spain’s most valuable global asset. What could possibly motivate the Spanish government to
want to tarnish his reputation, especially after he’s paid off his alleged debt? After four years of Great-Depression level unemployment,
have anxiety and despair curdled into vindictiveness?
Here’s another explanation: Maybe this whole case has less to do with money than it does with history. Maybe it’s no coincidence that
the target of the Spanish government’s weird wrath happens to play for FC Barcelona, which is, after all, "mes que un club." It's a symbol
of Catalan nationalism - and a bitter, longtime rival of Spain’s establishment team, Real Madrid.
Too conspiratorial? Prove it, Spain. Release Cristiano Ronaldo’s tax return.
(Adapted form http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2013-09-27/why-is-spain-really-taking-lionel-messi-to-tax-court-.html)
O autor do texto
Ano: 2014
Banca:
FCC
Órgão:
SEFAZ-RJ
Prova:
FCC - 2014 - SEFAZ-RJ - Auditor Fiscal da Receita Estadual - Prova 1 |
Q351456
Inglês
Texto associado
Why Is Spain Really Taking Lionel Messi to Tax Court?
By Jonathan Mahler Sep 27, 2013
So Spain has decided to haul Lionel Messi into court for tax evasion, which strikes me as completely insane on pretty much every level.
You may remember the story from a few months back: The greatest soccer player in the world and his father were accused of setting up
a bunch of shell companies in Belize and Uruguay to avoid paying taxes on royalties and other licensing income.
Messi - who makes an estimated $41 million a year, about half from sponsors - reached a settlement with Spain’s tax authorities earlier
this summer, agreeing to pay the amount he apparently owed, plus interest. The matter was settled, or so it seemed. Messi could go
back to dazzling the world with his athleticism and creativity.
Only it turns out that Spain wasn’t quite done with Messi. His adopted country - Messi is Argentine but became a Spanish citizen in 2005
- is now considering pressing criminal charges against him.
Cracking down on tax-evading footballers has become something of a trend in Europe, where players and clubs have been known to
launder money through “image-rights companies” often set up in tax havens. When you need money - and Europe needs money - go to
the people who have it, or something like that. Over the summer, dozens of Italian soccer clubs were raided as part of an investigation
into a tax-fraud conspiracy. A number of English Premier League clubs were forced last year to pay millions of pounds in back taxes.
No one likes a tax cheat, and there’s little doubt that widespread tax fraud has helped eat away at the social safety net in Spain and
elsewhere, depriving schools, hospitals and other institutions of badly needed funds. But Europe is not going to find the answers to its
financial problems in the pockets of some professional soccer players and clubs.
Messi’s defense, delivered by his father, seems credible enough to me. “He is a footballer and that’s it,” Messi’s father Jorge said of his
soccer-prodigy son. “If there was an error, it was by our financial adviser. He created the company. My mistake was to have trusted the
adviser.” Even if Messi is legally responsible for the intricate tax dodge he is accused of having participated in, it’s pretty hard to believe
that he knew much about it.
More to the point, Lionel Messi is probably Spain’s most valuable global asset. What could possibly motivate the Spanish government to
want to tarnish his reputation, especially after he’s paid off his alleged debt? After four years of Great-Depression level unemployment,
have anxiety and despair curdled into vindictiveness?
Here’s another explanation: Maybe this whole case has less to do with money than it does with history. Maybe it’s no coincidence that
the target of the Spanish government’s weird wrath happens to play for FC Barcelona, which is, after all, "mes que un club." It's a symbol
of Catalan nationalism - and a bitter, longtime rival of Spain’s establishment team, Real Madrid.
Too conspiratorial? Prove it, Spain. Release Cristiano Ronaldo’s tax return.
(Adapted form http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2013-09-27/why-is-spain-really-taking-lionel-messi-to-tax-court-.html)
By Jonathan Mahler Sep 27, 2013
So Spain has decided to haul Lionel Messi into court for tax evasion, which strikes me as completely insane on pretty much every level.
You may remember the story from a few months back: The greatest soccer player in the world and his father were accused of setting up
a bunch of shell companies in Belize and Uruguay to avoid paying taxes on royalties and other licensing income.
Messi - who makes an estimated $41 million a year, about half from sponsors - reached a settlement with Spain’s tax authorities earlier
this summer, agreeing to pay the amount he apparently owed, plus interest. The matter was settled, or so it seemed. Messi could go
back to dazzling the world with his athleticism and creativity.
Only it turns out that Spain wasn’t quite done with Messi. His adopted country - Messi is Argentine but became a Spanish citizen in 2005
- is now considering pressing criminal charges against him.
Cracking down on tax-evading footballers has become something of a trend in Europe, where players and clubs have been known to
launder money through “image-rights companies” often set up in tax havens. When you need money - and Europe needs money - go to
the people who have it, or something like that. Over the summer, dozens of Italian soccer clubs were raided as part of an investigation
into a tax-fraud conspiracy. A number of English Premier League clubs were forced last year to pay millions of pounds in back taxes.
No one likes a tax cheat, and there’s little doubt that widespread tax fraud has helped eat away at the social safety net in Spain and
elsewhere, depriving schools, hospitals and other institutions of badly needed funds. But Europe is not going to find the answers to its
financial problems in the pockets of some professional soccer players and clubs.
Messi’s defense, delivered by his father, seems credible enough to me. “He is a footballer and that’s it,” Messi’s father Jorge said of his
soccer-prodigy son. “If there was an error, it was by our financial adviser. He created the company. My mistake was to have trusted the
adviser.” Even if Messi is legally responsible for the intricate tax dodge he is accused of having participated in, it’s pretty hard to believe
that he knew much about it.
More to the point, Lionel Messi is probably Spain’s most valuable global asset. What could possibly motivate the Spanish government to
want to tarnish his reputation, especially after he’s paid off his alleged debt? After four years of Great-Depression level unemployment,
have anxiety and despair curdled into vindictiveness?
Here’s another explanation: Maybe this whole case has less to do with money than it does with history. Maybe it’s no coincidence that
the target of the Spanish government’s weird wrath happens to play for FC Barcelona, which is, after all, "mes que un club." It's a symbol
of Catalan nationalism - and a bitter, longtime rival of Spain’s establishment team, Real Madrid.
Too conspiratorial? Prove it, Spain. Release Cristiano Ronaldo’s tax return.
(Adapted form http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2013-09-27/why-is-spain-really-taking-lionel-messi-to-tax-court-.html)
Segundo o texto,
Ano: 2014
Banca:
FCC
Órgão:
SEFAZ-RJ
Prova:
FCC - 2014 - SEFAZ-RJ - Auditor Fiscal da Receita Estadual - Prova 1 |
Q351455
Inglês
Texto associado
Why Is Spain Really Taking Lionel Messi to Tax Court?
By Jonathan Mahler Sep 27, 2013
So Spain has decided to haul Lionel Messi into court for tax evasion, which strikes me as completely insane on pretty much every level.
You may remember the story from a few months back: The greatest soccer player in the world and his father were accused of setting up
a bunch of shell companies in Belize and Uruguay to avoid paying taxes on royalties and other licensing income.
Messi - who makes an estimated $41 million a year, about half from sponsors - reached a settlement with Spain’s tax authorities earlier
this summer, agreeing to pay the amount he apparently owed, plus interest. The matter was settled, or so it seemed. Messi could go
back to dazzling the world with his athleticism and creativity.
Only it turns out that Spain wasn’t quite done with Messi. His adopted country - Messi is Argentine but became a Spanish citizen in 2005
- is now considering pressing criminal charges against him.
Cracking down on tax-evading footballers has become something of a trend in Europe, where players and clubs have been known to
launder money through “image-rights companies” often set up in tax havens. When you need money - and Europe needs money - go to
the people who have it, or something like that. Over the summer, dozens of Italian soccer clubs were raided as part of an investigation
into a tax-fraud conspiracy. A number of English Premier League clubs were forced last year to pay millions of pounds in back taxes.
No one likes a tax cheat, and there’s little doubt that widespread tax fraud has helped eat away at the social safety net in Spain and
elsewhere, depriving schools, hospitals and other institutions of badly needed funds. But Europe is not going to find the answers to its
financial problems in the pockets of some professional soccer players and clubs.
Messi’s defense, delivered by his father, seems credible enough to me. “He is a footballer and that’s it,” Messi’s father Jorge said of his
soccer-prodigy son. “If there was an error, it was by our financial adviser. He created the company. My mistake was to have trusted the
adviser.” Even if Messi is legally responsible for the intricate tax dodge he is accused of having participated in, it’s pretty hard to believe
that he knew much about it.
More to the point, Lionel Messi is probably Spain’s most valuable global asset. What could possibly motivate the Spanish government to
want to tarnish his reputation, especially after he’s paid off his alleged debt? After four years of Great-Depression level unemployment,
have anxiety and despair curdled into vindictiveness?
Here’s another explanation: Maybe this whole case has less to do with money than it does with history. Maybe it’s no coincidence that
the target of the Spanish government’s weird wrath happens to play for FC Barcelona, which is, after all, "mes que un club." It's a symbol
of Catalan nationalism - and a bitter, longtime rival of Spain’s establishment team, Real Madrid.
Too conspiratorial? Prove it, Spain. Release Cristiano Ronaldo’s tax return.
(Adapted form http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2013-09-27/why-is-spain-really-taking-lionel-messi-to-tax-court-.html)
By Jonathan Mahler Sep 27, 2013
So Spain has decided to haul Lionel Messi into court for tax evasion, which strikes me as completely insane on pretty much every level.
You may remember the story from a few months back: The greatest soccer player in the world and his father were accused of setting up
a bunch of shell companies in Belize and Uruguay to avoid paying taxes on royalties and other licensing income.
Messi - who makes an estimated $41 million a year, about half from sponsors - reached a settlement with Spain’s tax authorities earlier
this summer, agreeing to pay the amount he apparently owed, plus interest. The matter was settled, or so it seemed. Messi could go
back to dazzling the world with his athleticism and creativity.
Only it turns out that Spain wasn’t quite done with Messi. His adopted country - Messi is Argentine but became a Spanish citizen in 2005
- is now considering pressing criminal charges against him.
Cracking down on tax-evading footballers has become something of a trend in Europe, where players and clubs have been known to
launder money through “image-rights companies” often set up in tax havens. When you need money - and Europe needs money - go to
the people who have it, or something like that. Over the summer, dozens of Italian soccer clubs were raided as part of an investigation
into a tax-fraud conspiracy. A number of English Premier League clubs were forced last year to pay millions of pounds in back taxes.
No one likes a tax cheat, and there’s little doubt that widespread tax fraud has helped eat away at the social safety net in Spain and
elsewhere, depriving schools, hospitals and other institutions of badly needed funds. But Europe is not going to find the answers to its
financial problems in the pockets of some professional soccer players and clubs.
Messi’s defense, delivered by his father, seems credible enough to me. “He is a footballer and that’s it,” Messi’s father Jorge said of his
soccer-prodigy son. “If there was an error, it was by our financial adviser. He created the company. My mistake was to have trusted the
adviser.” Even if Messi is legally responsible for the intricate tax dodge he is accused of having participated in, it’s pretty hard to believe
that he knew much about it.
More to the point, Lionel Messi is probably Spain’s most valuable global asset. What could possibly motivate the Spanish government to
want to tarnish his reputation, especially after he’s paid off his alleged debt? After four years of Great-Depression level unemployment,
have anxiety and despair curdled into vindictiveness?
Here’s another explanation: Maybe this whole case has less to do with money than it does with history. Maybe it’s no coincidence that
the target of the Spanish government’s weird wrath happens to play for FC Barcelona, which is, after all, "mes que un club." It's a symbol
of Catalan nationalism - and a bitter, longtime rival of Spain’s establishment team, Real Madrid.
Too conspiratorial? Prove it, Spain. Release Cristiano Ronaldo’s tax return.
(Adapted form http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2013-09-27/why-is-spain-really-taking-lionel-messi-to-tax-court-.html)
A synonym for badly, as it is used in the text, is
Ano: 2014
Banca:
FCC
Órgão:
SEFAZ-RJ
Prova:
FCC - 2014 - SEFAZ-RJ - Auditor Fiscal da Receita Estadual - Prova 1 |
Q351454
Inglês
Texto associado
Why Is Spain Really Taking Lionel Messi to Tax Court?
By Jonathan Mahler Sep 27, 2013
So Spain has decided to haul Lionel Messi into court for tax evasion, which strikes me as completely insane on pretty much every level.
You may remember the story from a few months back: The greatest soccer player in the world and his father were accused of setting up
a bunch of shell companies in Belize and Uruguay to avoid paying taxes on royalties and other licensing income.
Messi - who makes an estimated $41 million a year, about half from sponsors - reached a settlement with Spain’s tax authorities earlier
this summer, agreeing to pay the amount he apparently owed, plus interest. The matter was settled, or so it seemed. Messi could go
back to dazzling the world with his athleticism and creativity.
Only it turns out that Spain wasn’t quite done with Messi. His adopted country - Messi is Argentine but became a Spanish citizen in 2005
- is now considering pressing criminal charges against him.
Cracking down on tax-evading footballers has become something of a trend in Europe, where players and clubs have been known to
launder money through “image-rights companies” often set up in tax havens. When you need money - and Europe needs money - go to
the people who have it, or something like that. Over the summer, dozens of Italian soccer clubs were raided as part of an investigation
into a tax-fraud conspiracy. A number of English Premier League clubs were forced last year to pay millions of pounds in back taxes.
No one likes a tax cheat, and there’s little doubt that widespread tax fraud has helped eat away at the social safety net in Spain and
elsewhere, depriving schools, hospitals and other institutions of badly needed funds. But Europe is not going to find the answers to its
financial problems in the pockets of some professional soccer players and clubs.
Messi’s defense, delivered by his father, seems credible enough to me. “He is a footballer and that’s it,” Messi’s father Jorge said of his
soccer-prodigy son. “If there was an error, it was by our financial adviser. He created the company. My mistake was to have trusted the
adviser.” Even if Messi is legally responsible for the intricate tax dodge he is accused of having participated in, it’s pretty hard to believe
that he knew much about it.
More to the point, Lionel Messi is probably Spain’s most valuable global asset. What could possibly motivate the Spanish government to
want to tarnish his reputation, especially after he’s paid off his alleged debt? After four years of Great-Depression level unemployment,
have anxiety and despair curdled into vindictiveness?
Here’s another explanation: Maybe this whole case has less to do with money than it does with history. Maybe it’s no coincidence that
the target of the Spanish government’s weird wrath happens to play for FC Barcelona, which is, after all, "mes que un club." It's a symbol
of Catalan nationalism - and a bitter, longtime rival of Spain’s establishment team, Real Madrid.
Too conspiratorial? Prove it, Spain. Release Cristiano Ronaldo’s tax return.
(Adapted form http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2013-09-27/why-is-spain-really-taking-lionel-messi-to-tax-court-.html)
By Jonathan Mahler Sep 27, 2013
So Spain has decided to haul Lionel Messi into court for tax evasion, which strikes me as completely insane on pretty much every level.
You may remember the story from a few months back: The greatest soccer player in the world and his father were accused of setting up
a bunch of shell companies in Belize and Uruguay to avoid paying taxes on royalties and other licensing income.
Messi - who makes an estimated $41 million a year, about half from sponsors - reached a settlement with Spain’s tax authorities earlier
this summer, agreeing to pay the amount he apparently owed, plus interest. The matter was settled, or so it seemed. Messi could go
back to dazzling the world with his athleticism and creativity.
Only it turns out that Spain wasn’t quite done with Messi. His adopted country - Messi is Argentine but became a Spanish citizen in 2005
- is now considering pressing criminal charges against him.
Cracking down on tax-evading footballers has become something of a trend in Europe, where players and clubs have been known to
launder money through “image-rights companies” often set up in tax havens. When you need money - and Europe needs money - go to
the people who have it, or something like that. Over the summer, dozens of Italian soccer clubs were raided as part of an investigation
into a tax-fraud conspiracy. A number of English Premier League clubs were forced last year to pay millions of pounds in back taxes.
No one likes a tax cheat, and there’s little doubt that widespread tax fraud has helped eat away at the social safety net in Spain and
elsewhere, depriving schools, hospitals and other institutions of badly needed funds. But Europe is not going to find the answers to its
financial problems in the pockets of some professional soccer players and clubs.
Messi’s defense, delivered by his father, seems credible enough to me. “He is a footballer and that’s it,” Messi’s father Jorge said of his
soccer-prodigy son. “If there was an error, it was by our financial adviser. He created the company. My mistake was to have trusted the
adviser.” Even if Messi is legally responsible for the intricate tax dodge he is accused of having participated in, it’s pretty hard to believe
that he knew much about it.
More to the point, Lionel Messi is probably Spain’s most valuable global asset. What could possibly motivate the Spanish government to
want to tarnish his reputation, especially after he’s paid off his alleged debt? After four years of Great-Depression level unemployment,
have anxiety and despair curdled into vindictiveness?
Here’s another explanation: Maybe this whole case has less to do with money than it does with history. Maybe it’s no coincidence that
the target of the Spanish government’s weird wrath happens to play for FC Barcelona, which is, after all, "mes que un club." It's a symbol
of Catalan nationalism - and a bitter, longtime rival of Spain’s establishment team, Real Madrid.
Too conspiratorial? Prove it, Spain. Release Cristiano Ronaldo’s tax return.
(Adapted form http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2013-09-27/why-is-spain-really-taking-lionel-messi-to-tax-court-.html)
Which of the following alternatives is the “odd man out”?
Ano: 2014
Banca:
FCC
Órgão:
SEFAZ-RJ
Prova:
FCC - 2014 - SEFAZ-RJ - Auditor Fiscal da Receita Estadual - Prova 1 |
Q351453
Inglês
2012 Federal Individual Income Tax Rates
These are the tax rates for the 2012 tax year, if your filing status is “single”.
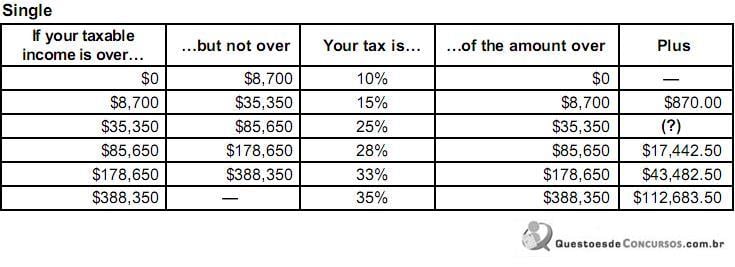
De acordo com o que é explicado no texto a respeito da tabela progressiva, o valor correto que preenche a célula (?) é
These are the tax rates for the 2012 tax year, if your filing status is “single”.

De acordo com o que é explicado no texto a respeito da tabela progressiva, o valor correto que preenche a célula (?) é