Questões de Vestibular
Comentadas sobre interpretação de texto | reading comprehension em inglês
Foram encontradas 680 questões
the question is not if another outbreak will happen, but when, (l. 28-29)
The underlined words present the health community’s opinion concerning new outbreaks of epidemics.
According to their opinion, future outbreaks are seen as:
The texts “Três teses sobre o avanço da febre amarela” and “The effect of climate change on epidemic risk” mention possible reasons for disease outbreaks.
The reason which is presented in both texts is:

In today’s political climate, it sometimes feels like we can’t even agree on basic facts. We bombard each other with statistics and figures, hoping that more data will make a difference. A progressive person might show you the same climate change graphs over and over while a conservative person might point to the trillions of dollars of growing national debt. We’re left wondering, “Why can’t they just see? It’s so obvious!”
Certain myths are so pervasive that no matter how many experts disprove them, they only seem to grow in popularity. There’s no shortage of serious studies showing no link between autism and vaccines, for example, but these are no match for an emotional appeal to parents worried for their young children.
Tali Sharot, a cognitive neuroscientist at University College London, studies how our minds work and how we process new information. In her upcoming book, The Influential Mind, she explores why we ignore facts and how we can get people to actually listen to the truth. Tali shows that we’re open to new information – but only if it confirms our existing beliefs. We find ways to ignore facts that challenge our ideals. And as neuroscientist Bahador Bahrami and colleagues have found, we weigh all opinions as equally valid, regardless of expertise.
So, having the data on your side is not always enough. For better or for worse, Sharot says, emotions may be the key to changing minds.
(Shankar Vedantam. www.npr.org. Adaptado.)

In today’s political climate, it sometimes feels like we can’t even agree on basic facts. We bombard each other with statistics and figures, hoping that more data will make a difference. A progressive person might show you the same climate change graphs over and over while a conservative person might point to the trillions of dollars of growing national debt. We’re left wondering, “Why can’t they just see? It’s so obvious!”
Certain myths are so pervasive that no matter how many experts disprove them, they only seem to grow in popularity. There’s no shortage of serious studies showing no link between autism and vaccines, for example, but these are no match for an emotional appeal to parents worried for their young children.
Tali Sharot, a cognitive neuroscientist at University College London, studies how our minds work and how we process new information. In her upcoming book, The Influential Mind, she explores why we ignore facts and how we can get people to actually listen to the truth. Tali shows that we’re open to new information – but only if it confirms our existing beliefs. We find ways to ignore facts that challenge our ideals. And as neuroscientist Bahador Bahrami and colleagues have found, we weigh all opinions as equally valid, regardless of expertise.
So, having the data on your side is not always enough. For better or for worse, Sharot says, emotions may be the key to changing minds.
(Shankar Vedantam. www.npr.org. Adaptado.)

In today’s political climate, it sometimes feels like we can’t even agree on basic facts. We bombard each other with statistics and figures, hoping that more data will make a difference. A progressive person might show you the same climate change graphs over and over while a conservative person might point to the trillions of dollars of growing national debt. We’re left wondering, “Why can’t they just see? It’s so obvious!”
Certain myths are so pervasive that no matter how many experts disprove them, they only seem to grow in popularity. There’s no shortage of serious studies showing no link between autism and vaccines, for example, but these are no match for an emotional appeal to parents worried for their young children.
Tali Sharot, a cognitive neuroscientist at University College London, studies how our minds work and how we process new information. In her upcoming book, The Influential Mind, she explores why we ignore facts and how we can get people to actually listen to the truth. Tali shows that we’re open to new information – but only if it confirms our existing beliefs. We find ways to ignore facts that challenge our ideals. And as neuroscientist Bahador Bahrami and colleagues have found, we weigh all opinions as equally valid, regardless of expertise.
So, having the data on your side is not always enough. For better or for worse, Sharot says, emotions may be the key to changing minds.
(Shankar Vedantam. www.npr.org. Adaptado.)

In today’s political climate, it sometimes feels like we can’t even agree on basic facts. We bombard each other with statistics and figures, hoping that more data will make a difference. A progressive person might show you the same climate change graphs over and over while a conservative person might point to the trillions of dollars of growing national debt. We’re left wondering, “Why can’t they just see? It’s so obvious!”
Certain myths are so pervasive that no matter how many experts disprove them, they only seem to grow in popularity. There’s no shortage of serious studies showing no link between autism and vaccines, for example, but these are no match for an emotional appeal to parents worried for their young children.
Tali Sharot, a cognitive neuroscientist at University College London, studies how our minds work and how we process new information. In her upcoming book, The Influential Mind, she explores why we ignore facts and how we can get people to actually listen to the truth. Tali shows that we’re open to new information – but only if it confirms our existing beliefs. We find ways to ignore facts that challenge our ideals. And as neuroscientist Bahador Bahrami and colleagues have found, we weigh all opinions as equally valid, regardless of expertise.
So, having the data on your side is not always enough. For better or for worse, Sharot says, emotions may be the key to changing minds.
(Shankar Vedantam. www.npr.org. Adaptado.)
Leia os cartuns 1 e 2 para responder à questão.

Leia os cartuns 1 e 2 para responder à questão.

Leia os cartuns 1 e 2 para responder à questão.

The modern F=ma form of Newton's second law occurs nowhere in any edition of the Principia even though he had seen his second law formulated in this way in print during the interval between the second and third editions in Jacob Hermann's Phoronomia of 1716. Instead, it has the following formulation in all three editions: A change in (1) ________ is proportional to the motive (2) ________ impressed and takes place along the (3) _________ line in which that force is (4)________. In the body of the Principia this law is applied both to (5) _______ cases, in which an instantaneous impulse such as from impact is effecting the change in motion, and to cases of (6) _______ action, such as the change in motion in the continuous deceleration of a body moving in a resisting medium. Newton thus appears to have intended his second law to be neutral between discrete forces (that is, what we now call impulses) and Hermann's Phoronomia of 1716. Instead, it has the following formulation in all three editions: A change in (1) ________ is proportional to the motive (2) ________ impressed and takes place along the (3) _________ line in which that force is (4)________. In the body of the Principia this law is applied both to (5) _______ cases, in which an instantaneous impulse such as from impact is effecting the change in motion, and to cases of (6) _______ action, such as the change in motion in the continuous deceleration of a body moving in a resisting medium. Newton thus appears to have intended his second law to be neutral between discrete forces (that is, what we now call impulses) and continuous forces.
(Adaptado de George Smith, "Newton's Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica", em Edward N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Winter 2008 Edition). Disponível em https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/win2008/entries/newton-principia/. Acessado em 24/10/2017.)
Assinale a alternativa que apresenta a sequência
adequada de palavras que preenchem as lacunas do texto
acima, para que os conceitos utilizados estejam corretos.
Coral reefs are colorful underwater forests which teem with life and act as a natural protective barrier for coastal regions. The fishes and plants which call them home belong to some of the most diverse ― and fragile ― ecosystems on the planet. Higher sea temperatures from global warming have already caused major coral bleaching events. Bleaching occurs when corals respond to the stress of warmer temperatures by expelling the colorful algae that live within them. Increased levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide result in higher levels of CO² in the water, leading to ocean acidification, which is also a threat to coral. As the oceans become more acidic, the corals' ability to form skeletons through calcification is inhibited, causing their growth to slow. Increasing sea levels caused by melting sea ice could also cause problems for some reefs by making them too deep to receive adequate sunlight, another factor important for survival.
(Adaptado de Coral Reefs, The National Wildlife Federation. Disponível em https://www.nwf.org/Wildlife/Threats-to-Wildlife/GlobalWarming/Effects-on-Wildlife-and-Habitat/Coral-Reefs.aspx. Acessado em 26/07/2017.)
Considerando o texto e seus conhecimentos, assinale a alternativa correta.
Os recifes de corais estão seriamente ameaçados pela combinação dos seguintes fatores:
Comedian Janey Godley's tweets of a couple's train-bound row raise questions of how to protect our privacy in public places.
If the troubles of the two travellers had made it on to a newspaper first rather than a comedian's Twitter feed, would we be so relaxed about loss of privacy? I think perhaps not. Social media has done so much for freedom of expression, it would be cruel if it actually leads to less social freedom for fear of having our every misstep, angry word or misbehaviour broadcast there for all to see.
(Adaptado de David Banks, Should Twitter entertain millions with public rows? The Guardian, 13/07/2012. Disponível em https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2012/jul/13/twittermillions-public-rows. Acessado em 10/07/2017.)
No artigo de opinião acima, o autor

Segundo o testemunho de Olaudah Equiano,
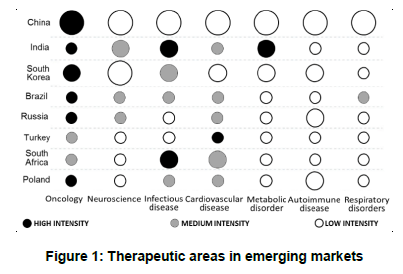

(Adaptado de Ajay Gautam, Lily Li e Kumar Srinivasan, Market watch: Therapeutic area ‘heat map’ for emerging markets. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 14, p. 518, jul. 2015.)
De acordo com o gráfico apresentado,
ZOMBIE NEUROSCIENCE
I don’t know if cockroaches dream, but I imagine if they do, jewel wasps feature prominently in their nightmares. These small, solitary tropical wasps are of little concern to us humans; after all, they don’t manipulate our minds so that they can serve us up as willing, living meals to their newborns, as they do to unsuspecting cockroaches. The story is simple, if grotesque: the female wasp controls the minds of the cockroaches she feeds to her offspring, taking away their sense of fear or will to escape their fate. What turns a once healthy cockroach into a mindless zombie it’s venom. Not just any venom, either: a specific venom that acts like a drug, targeting the cockroach's brain.
(Adaptado de Christie Wilcox, Zombie Neuroscience. Scientific American, New York, v. 315, n. 2, p. 70–73, 2016.)
De acordo com o autor,

