Questões de Vestibular
Sobre interpretação de texto | reading comprehension em inglês
Foram encontradas 4.926 questões
Games have been used as a learning tool for centuries. Chess was used to teach strategic (1) as far back as the Middle Ages, and the game of Kreigsspiel was invented in 1812 specifically to teach Prussian officers strategy. Beyond military strategy, the genesis of Kindergarten in the mid-1800s was Friedrich Fröbel’s ideas of learning through play.
The core concept behind game-based learning is teaching through repetition, failure and the accomplishment of goals. Video games are built on this principle. The player starts off slow and gains in skill until they’re able to skillfully navigate the most (2) levels. Games that are planned and designed well will offer enough difficulty to keep it (3) while still being easy enough for the player to win.
Game-based learning takes this same concept and applies it to teaching a curriculum. Students work toward a goal, choosing actions and experiencing the consequences of those actions. They (4) learn and practice the right way to do things. The result is active learning instead of passive learning.
Flight simulators are a perfect example of the (5) of game-based learning. Pilots commonly use flight simulators during their training. They’re given very specific goals and practice until they can accomplish them. The result is much more effective than sitting through lectures and theory.
CAHILL, Gavin. Why Game-Based Learning? The learning counsel: research and context on the digital education experience. Available in: https:// thelearningcounsel.com/article/why-game-based-learning. Access in: 29 oct. 2021 (adapted).
Cinco termos foram retirados desse excerto. Assinale a alternativa que apresenta as palavras que completam, correta e respectivamente, as lacunas numeradas nele.
TAYLOR, A. What is the strategic planning process? Available in: https://www.smestrategy.net/blog/ what-is-the-strategic-planning-process. Access in: 28 jul. 2018 (adapted).
Consider the text information to evaluate the following statements.
I. The strategic planning process must be individual so that diverse opinions do not hinder the good organizational progress of the company.
II. The strategic planning well-designed gives greater productivity, training and overall effectiveness in the execution of executive secretary's activities.
III. The strategic planning needs to disclose the steps to the company's employees, emphasizing their contribution to the success of the plan.
It is correct what is stated in
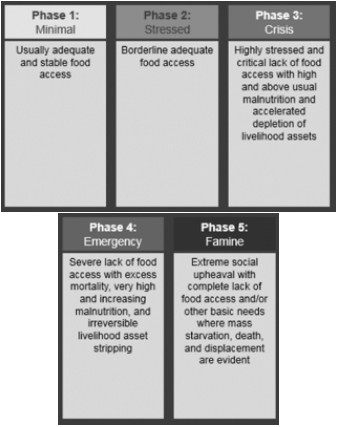

This text refers to question
How to Stop Eating Sugar
By David Leonhardt
If you’re like most Americans, you eat more sugar than is good for you. But it’s entirely possible to eat less sugar without sacrificing much — if any — of the pleasures of eating. Surprising as it may sound, many people who have cut back on sugar say they find their new eating habits more pleasurable than their old ones. This guide will walk you through why sugar matters, how you can make smart food choices to reduce sugar consumption, and how you can keep your life sweet, even without so many sweets.
Here's why you eat more sugar than you realize, and why it's a problem. The first thing to know: Added sugars, of one kind or another, are almost everywhere in the modern diet. They’re in sandwich bread, chicken stock, pickles, salad dressing, crackers, yogurt and cereal, as well as in the obvious foods and drinks, like soda and desserts.
The biggest problem with added sweeteners is that they make it easy to overeat. They’re tasty and highly caloric but they often don’t make you feel full. Instead, they can trick you into wanting even more food. Because we’re surrounded by added sweeteners — in our kitchens, in restaurants, at schools and offices — most of us will eat too much of them unless we consciously set out to do otherwise.
It’s not an accident. The sugar industry has conducted an aggressive, decades-long campaign to blame the obesity epidemic on fats, not sugars. Fats, after all, seem as if they should cause obesity. Thanks partly to that campaign, sugar consumption soared in the United States even as people were trying to lose weight. But research increasingly indicates that an overabundance of simple carbohydrates, and sugar in particular, is the No. 1 problem in modern diets. Sugar is the driving force behind the diabetes and obesity epidemics. Fortunately, more people are realizing the harms of sugar and cutting back.
[...]
Changing your diet is hard. If your strategy involves thinking about sugar all the time — whenever you’re shopping or eating — you’ll likely fail. You’ll also be miserable in the process. It’s much more effective to come up with a few simple rules and habits that then become second nature. (One strategy to consider: Eliminate all added sugars for one month, and then add back only the ones you miss. It’s easier than it sounds.)
Above all, most people’s goal should be to find a few simple, lasting ways to cut back on sugar. Once you’re done reading this guide, we suggest you choose two or three of our ideas and try them for a few weeks.
https://www.nytimes.com/guides/smarterliving/how-to-stop-eating-sugar (text adapted)
This text refers to question
How to Stop Eating Sugar
By David Leonhardt
If you’re like most Americans, you eat more sugar than is good for you. But it’s entirely possible to eat less sugar without sacrificing much — if any — of the pleasures of eating. Surprising as it may sound, many people who have cut back on sugar say they find their new eating habits more pleasurable than their old ones. This guide will walk you through why sugar matters, how you can make smart food choices to reduce sugar consumption, and how you can keep your life sweet, even without so many sweets.
Here's why you eat more sugar than you realize, and why it's a problem. The first thing to know: Added sugars, of one kind or another, are almost everywhere in the modern diet. They’re in sandwich bread, chicken stock, pickles, salad dressing, crackers, yogurt and cereal, as well as in the obvious foods and drinks, like soda and desserts.
The biggest problem with added sweeteners is that they make it easy to overeat. They’re tasty and highly caloric but they often don’t make you feel full. Instead, they can trick you into wanting even more food. Because we’re surrounded by added sweeteners — in our kitchens, in restaurants, at schools and offices — most of us will eat too much of them unless we consciously set out to do otherwise.
It’s not an accident. The sugar industry has conducted an aggressive, decades-long campaign to blame the obesity epidemic on fats, not sugars. Fats, after all, seem as if they should cause obesity. Thanks partly to that campaign, sugar consumption soared in the United States even as people were trying to lose weight. But research increasingly indicates that an overabundance of simple carbohydrates, and sugar in particular, is the No. 1 problem in modern diets. Sugar is the driving force behind the diabetes and obesity epidemics. Fortunately, more people are realizing the harms of sugar and cutting back.
[...]
Changing your diet is hard. If your strategy involves thinking about sugar all the time — whenever you’re shopping or eating — you’ll likely fail. You’ll also be miserable in the process. It’s much more effective to come up with a few simple rules and habits that then become second nature. (One strategy to consider: Eliminate all added sugars for one month, and then add back only the ones you miss. It’s easier than it sounds.)
Above all, most people’s goal should be to find a few simple, lasting ways to cut back on sugar. Once you’re done reading this guide, we suggest you choose two or three of our ideas and try them for a few weeks.
https://www.nytimes.com/guides/smarterliving/how-to-stop-eating-sugar (text adapted)
This text refers to question
How to Stop Eating Sugar
By David Leonhardt
If you’re like most Americans, you eat more sugar than is good for you. But it’s entirely possible to eat less sugar without sacrificing much — if any — of the pleasures of eating. Surprising as it may sound, many people who have cut back on sugar say they find their new eating habits more pleasurable than their old ones. This guide will walk you through why sugar matters, how you can make smart food choices to reduce sugar consumption, and how you can keep your life sweet, even without so many sweets.
Here's why you eat more sugar than you realize, and why it's a problem. The first thing to know: Added sugars, of one kind or another, are almost everywhere in the modern diet. They’re in sandwich bread, chicken stock, pickles, salad dressing, crackers, yogurt and cereal, as well as in the obvious foods and drinks, like soda and desserts.
The biggest problem with added sweeteners is that they make it easy to overeat. They’re tasty and highly caloric but they often don’t make you feel full. Instead, they can trick you into wanting even more food. Because we’re surrounded by added sweeteners — in our kitchens, in restaurants, at schools and offices — most of us will eat too much of them unless we consciously set out to do otherwise.
It’s not an accident. The sugar industry has conducted an aggressive, decades-long campaign to blame the obesity epidemic on fats, not sugars. Fats, after all, seem as if they should cause obesity. Thanks partly to that campaign, sugar consumption soared in the United States even as people were trying to lose weight. But research increasingly indicates that an overabundance of simple carbohydrates, and sugar in particular, is the No. 1 problem in modern diets. Sugar is the driving force behind the diabetes and obesity epidemics. Fortunately, more people are realizing the harms of sugar and cutting back.
[...]
Changing your diet is hard. If your strategy involves thinking about sugar all the time — whenever you’re shopping or eating — you’ll likely fail. You’ll also be miserable in the process. It’s much more effective to come up with a few simple rules and habits that then become second nature. (One strategy to consider: Eliminate all added sugars for one month, and then add back only the ones you miss. It’s easier than it sounds.)
Above all, most people’s goal should be to find a few simple, lasting ways to cut back on sugar. Once you’re done reading this guide, we suggest you choose two or three of our ideas and try them for a few weeks.
https://www.nytimes.com/guides/smarterliving/how-to-stop-eating-sugar (text adapted)