Questões de Vestibular Sobre inglês
Foram encontradas 6.020 questões
I. In 1946, a group of national governments formed the IWC in order to collaborate with the killing and hunting of whales for commercial purposes. II. The original regulations of IWC were not really helpful. III. The IWC does not make any exception for whaling. IV. The IWC requested a moratorium on commercial whaling in 1982. V. Japan and Norway completely agreed with the policy proposed by IWC.
Mark the correct option.
The phrase “long in the tooth” comes from the practice of gauging a horse’s age by the length of its teeth. Nineteenth century horse-traders were not a particularly trustworthy bunch, so a wise buyer would often check inside the animal’s mouth. If the teeth looked long it meant its gums had already receded, suggesting the potential purchase might be older than claimed. This might have served people well when it came to buying horses, but what about humans? Gingival recession, as it’s formally known, is more common amongst the elderly. A US study of almost 10,000 people found that 38% of people aged 30-39 had some degree of the condition, compared with 71% in the 50-59 age group, and 90% for those aged between 80-90. However that doesn’t mean ageing in itself is the cause. It’s a long process that can start in your teens, and one that can be triggered by various factors. In some cases, there is nothing people can do to reduce their chances of developing the condition. Some people inherit thin and fragile gums which recede more easily. Others have teeth which are overcrowded or stick out, meaning that there’s not enough jawbone to cover the root of the tooth. Dental hygiene also plays a big role. Plaque, consisting of a sticky film of bacteria, is constantly forming on our teeth. Failure to clear the build ups through brushing and flossing can lead to gum disease. If left untreated, one possible complication is the destruction of the bone around the teeth and the gum tissue in which they sit. As the tissue recedes, the root of the tooth is exposed, making it appear longer. Then there’s the way you brush your teeth. If you use a sawing action with a hard brush, there’s a danger of gradually wearing away the gum. For this reason dentists tend to advise brushing in small circles with a soft brush or using an electric toothbrush to prevent you from pressing so hard. The damage accumulates over time, causing the gums to recede imperceptibly, until one day you look in the mirror and realise you’ve changed. As this transformation can take decades, many people assume it’s a natural part of the ageing process. Research on receding gums often relies on asking people what kind of toothbrush they use, the brushing motions they use and how hard they brush. Some argue that due to a lack of controlled studies, there’s no definitive evidence that hard brushing does anything more than cause temporary abrasions, but many dentists do consider there to be a link. The condition is also more common in smokers. With so many different factors involved, controlled studies are difficult to do. Many are cross-sectional, meaning they take a snapshot in time. So if you’re looking to buy a horse it might be worth their checking their teeth, but ageing is not a direct cause of receding gums. It’s simply that the damage accumulates and becomes more obvious over time. Source: http://www.bbc.com (Adapted) According to the text, it is INCORRECT to say
The phrase “long in the tooth” comes from the practice of gauging a horse’s age by the length of its teeth. Nineteenth century horse-traders were not a particularly trustworthy bunch, so a wise buyer would often check inside the animal’s mouth. If the teeth looked long it meant its gums had already receded, suggesting the potential purchase might be older than claimed. This might have served people well when it came to buying horses, but what about humans? Gingival recession, as it’s formally known, is more common amongst the elderly. A US study of almost 10,000 people found that 38% of people aged 30-39 had some degree of the condition, compared with 71% in the 50-59 age group, and 90% for those aged between 80-90. However that doesn’t mean ageing in itself is the cause. It’s a long process that can start in your teens, and one that can be triggered by various factors. In some cases, there is nothing people can do to reduce their chances of developing the condition. Some people inherit thin and fragile gums which recede more easily. Others have teeth which are overcrowded or stick out, meaning that there’s not enough jawbone to cover the root of the tooth. Dental hygiene also plays a big role. Plaque, consisting of a sticky film of bacteria, is constantly forming on our teeth. Failure to clear the build ups through brushing and flossing can lead to gum disease. If left untreated, one possible complication is the destruction of the bone around the teeth and the gum tissue in which they sit. As the tissue recedes, the root of the tooth is exposed, making it appear longer. Then there’s the way you brush your teeth. If you use a sawing action with a hard brush, there’s a danger of gradually wearing away the gum. For this reason dentists tend to advise brushing in small circles with a soft brush or using an electric toothbrush to prevent you from pressing so hard. The damage accumulates over time, causing the gums to recede imperceptibly, until one day you look in the mirror and realise you’ve changed. As this transformation can take decades, many people assume it’s a natural part of the ageing process. Research on receding gums often relies on asking people what kind of toothbrush they use, the brushing motions they use and how hard they brush. Some argue that due to a lack of controlled studies, there’s no definitive evidence that hard brushing does anything more than cause temporary abrasions, but many dentists do consider there to be a link. The condition is also more common in smokers. With so many different factors involved, controlled studies are difficult to do. Many are cross-sectional, meaning they take a snapshot in time. So if you’re looking to buy a horse it might be worth their checking their teeth, but ageing is not a direct cause of receding gums. It’s simply that the damage accumulates and becomes more obvious over time. Source: http://www.bbc.com (Adapted)
According to the text, judge the items below as true (T) or false (F).
I. Nineteenth century horse-traders were reliable people. II. A buyer who would check the horse's gums before buying it, was not considered a clever person. III. Although it is more observed amongst the elderly, gingival recession can begin during youth. IV. The phrase “long in the tooth” is related to the practice of determining a horse's age, and therefore its value, by examining its teeth. V. People can always prevent the development of gingival recession, once it is never possible for them to inherited sensitive gums.
Mark the correct option:

Source: www.glasbergen.com
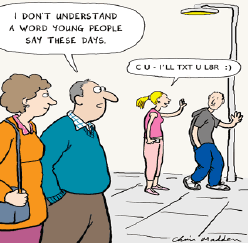
Source: http://eoienglishclub.wikispaces.com/ENGLISH+B1/unit3
I. The girl’s sentence can be transcript as “See you. I'll text you later”. II. Young people do not make difference between spoken and written speech. III. The old man can’t realize young people play with the sound of the words. IV. Young people text so much, they adequate their speech according to the facilities of keyboards. V. Language changes from one generation to another.
Choose the CORRECT alternative.
Choose the CORRECT alternative.
The correct form that completes the ifclause “If students had to learn to communicate their findings,” is “they __________________.”
The sentence “There will be almost half a million jobs in five years.” in the conditional form would be
The sentences “…they know it will make them employable.” and “…Amazon tells them what books they should read” contain, respectively, a/an
The sentences “Ethics classes address these questions.” and “The United States will need a great number of graduates with skills handling large amounts of data.” contain, respectively, a/an