Questões de Vestibular FGV 2016 para Vestibular - Inglês, Física, Química e Língua Portuguesa
Foram encontradas 135 questões
Leia o texto para responder a questão.
Patience is needed for Brazil to come good again
Michael Hasenstab
Dr. Michael Hasenstab is executive
vice-president, portfolio manager
and chief investment officer of
Templeton Global Macro
The Olympic Games in Rio drew global interest to Brazil, but the country and the rest of South America has been in sharp focus for investors all year. They have flocked to the region as part of a broader migration into emerging market debt, following record low valuations and the hunt for yield in a low interest rate environment. While investors have been presented with a rarely seen buying opportunity in emerging markets like South America, it is a mistake to regard these countries as a homogenous group.
That leaves the challenge of working out which are the most attractive opportunities – some of our best known investments were not obvious choices.
We have devised a formula to help us evaluate the fundamental strength of different emerging market countries. It scores a country’s current and projected strength on five factors: how well it has learnt the lessons from past crises; the quality of its policy mix; the structural reform being undertaken to boost productivity; the level of domestic demand; and its ability to resist external shocks. The aim is to pick nations that are fundamentally strong but, for one reason or another, are out of favour with investors. It can take time for the market to catch up to reality. But if you are a long-term investor – and we are certainly in that camp – you have the luxury of being able to wait.
Brazil, for example, is known as a vulnerable market due to the commodities downturn, the ongoing corruption crisis and ensuing political turmoil, but our work suggests to us that it is poised for a potentially significant rebound in the long term. Its current score is low, but its projected future score tells a different story.
We believe the country has learnt the lessons from the most recent crisis, which brought home the importance of having a sustainable fiscal policy. It has already adopted a flexible exchange rate, has strong foreign exchange reserves and has limited short-term debt. This is also reflected in the country’s improving resilience to external shocks, with a reliance on commodities, at 60 per cent of exports, being the largest remaining negative.
It is perhaps no surprise, given Brazil’s deep recession and political instability, that there is much work required in terms of improving policy mix, making structural reforms and boosting domestic demand. However, there are signs things are being turned around, with monetary policy already being tightened aggressively to bring inflation expectations back under control, and the previously excessive levels of governmentsubsidised lending being cut. Once political stability returns, the government will be empowered to do even more.
Work on structural reform should accelerate too, as Brazil’s middle class has made it clear it wants greater transparency and an economic policy framework that can both boost living standards and improve the environment for businesses.
(www.ft.com. 01.09.2016. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder a questão.
Patience is needed for Brazil to come good again
Michael Hasenstab
Dr. Michael Hasenstab is executive
vice-president, portfolio manager
and chief investment officer of
Templeton Global Macro
The Olympic Games in Rio drew global interest to Brazil, but the country and the rest of South America has been in sharp focus for investors all year. They have flocked to the region as part of a broader migration into emerging market debt, following record low valuations and the hunt for yield in a low interest rate environment. While investors have been presented with a rarely seen buying opportunity in emerging markets like South America, it is a mistake to regard these countries as a homogenous group.
That leaves the challenge of working out which are the most attractive opportunities – some of our best known investments were not obvious choices.
We have devised a formula to help us evaluate the fundamental strength of different emerging market countries. It scores a country’s current and projected strength on five factors: how well it has learnt the lessons from past crises; the quality of its policy mix; the structural reform being undertaken to boost productivity; the level of domestic demand; and its ability to resist external shocks. The aim is to pick nations that are fundamentally strong but, for one reason or another, are out of favour with investors. It can take time for the market to catch up to reality. But if you are a long-term investor – and we are certainly in that camp – you have the luxury of being able to wait.
Brazil, for example, is known as a vulnerable market due to the commodities downturn, the ongoing corruption crisis and ensuing political turmoil, but our work suggests to us that it is poised for a potentially significant rebound in the long term. Its current score is low, but its projected future score tells a different story.
We believe the country has learnt the lessons from the most recent crisis, which brought home the importance of having a sustainable fiscal policy. It has already adopted a flexible exchange rate, has strong foreign exchange reserves and has limited short-term debt. This is also reflected in the country’s improving resilience to external shocks, with a reliance on commodities, at 60 per cent of exports, being the largest remaining negative.
It is perhaps no surprise, given Brazil’s deep recession and political instability, that there is much work required in terms of improving policy mix, making structural reforms and boosting domestic demand. However, there are signs things are being turned around, with monetary policy already being tightened aggressively to bring inflation expectations back under control, and the previously excessive levels of governmentsubsidised lending being cut. Once political stability returns, the government will be empowered to do even more.
Work on structural reform should accelerate too, as Brazil’s middle class has made it clear it wants greater transparency and an economic policy framework that can both boost living standards and improve the environment for businesses.
(www.ft.com. 01.09.2016. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder a questão.
Patience is needed for Brazil to come good again
Michael Hasenstab
Dr. Michael Hasenstab is executive
vice-president, portfolio manager
and chief investment officer of
Templeton Global Macro
The Olympic Games in Rio drew global interest to Brazil, but the country and the rest of South America has been in sharp focus for investors all year. They have flocked to the region as part of a broader migration into emerging market debt, following record low valuations and the hunt for yield in a low interest rate environment. While investors have been presented with a rarely seen buying opportunity in emerging markets like South America, it is a mistake to regard these countries as a homogenous group.
That leaves the challenge of working out which are the most attractive opportunities – some of our best known investments were not obvious choices.
We have devised a formula to help us evaluate the fundamental strength of different emerging market countries. It scores a country’s current and projected strength on five factors: how well it has learnt the lessons from past crises; the quality of its policy mix; the structural reform being undertaken to boost productivity; the level of domestic demand; and its ability to resist external shocks. The aim is to pick nations that are fundamentally strong but, for one reason or another, are out of favour with investors. It can take time for the market to catch up to reality. But if you are a long-term investor – and we are certainly in that camp – you have the luxury of being able to wait.
Brazil, for example, is known as a vulnerable market due to the commodities downturn, the ongoing corruption crisis and ensuing political turmoil, but our work suggests to us that it is poised for a potentially significant rebound in the long term. Its current score is low, but its projected future score tells a different story.
We believe the country has learnt the lessons from the most recent crisis, which brought home the importance of having a sustainable fiscal policy. It has already adopted a flexible exchange rate, has strong foreign exchange reserves and has limited short-term debt. This is also reflected in the country’s improving resilience to external shocks, with a reliance on commodities, at 60 per cent of exports, being the largest remaining negative.
It is perhaps no surprise, given Brazil’s deep recession and political instability, that there is much work required in terms of improving policy mix, making structural reforms and boosting domestic demand. However, there are signs things are being turned around, with monetary policy already being tightened aggressively to bring inflation expectations back under control, and the previously excessive levels of governmentsubsidised lending being cut. Once political stability returns, the government will be empowered to do even more.
Work on structural reform should accelerate too, as Brazil’s middle class has made it clear it wants greater transparency and an economic policy framework that can both boost living standards and improve the environment for businesses.
(www.ft.com. 01.09.2016. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder a questão.
Patience is needed for Brazil to come good again
Michael Hasenstab
Dr. Michael Hasenstab is executive
vice-president, portfolio manager
and chief investment officer of
Templeton Global Macro
The Olympic Games in Rio drew global interest to Brazil, but the country and the rest of South America has been in sharp focus for investors all year. They have flocked to the region as part of a broader migration into emerging market debt, following record low valuations and the hunt for yield in a low interest rate environment. While investors have been presented with a rarely seen buying opportunity in emerging markets like South America, it is a mistake to regard these countries as a homogenous group.
That leaves the challenge of working out which are the most attractive opportunities – some of our best known investments were not obvious choices.
We have devised a formula to help us evaluate the fundamental strength of different emerging market countries. It scores a country’s current and projected strength on five factors: how well it has learnt the lessons from past crises; the quality of its policy mix; the structural reform being undertaken to boost productivity; the level of domestic demand; and its ability to resist external shocks. The aim is to pick nations that are fundamentally strong but, for one reason or another, are out of favour with investors. It can take time for the market to catch up to reality. But if you are a long-term investor – and we are certainly in that camp – you have the luxury of being able to wait.
Brazil, for example, is known as a vulnerable market due to the commodities downturn, the ongoing corruption crisis and ensuing political turmoil, but our work suggests to us that it is poised for a potentially significant rebound in the long term. Its current score is low, but its projected future score tells a different story.
We believe the country has learnt the lessons from the most recent crisis, which brought home the importance of having a sustainable fiscal policy. It has already adopted a flexible exchange rate, has strong foreign exchange reserves and has limited short-term debt. This is also reflected in the country’s improving resilience to external shocks, with a reliance on commodities, at 60 per cent of exports, being the largest remaining negative.
It is perhaps no surprise, given Brazil’s deep recession and political instability, that there is much work required in terms of improving policy mix, making structural reforms and boosting domestic demand. However, there are signs things are being turned around, with monetary policy already being tightened aggressively to bring inflation expectations back under control, and the previously excessive levels of governmentsubsidised lending being cut. Once political stability returns, the government will be empowered to do even more.
Work on structural reform should accelerate too, as Brazil’s middle class has made it clear it wants greater transparency and an economic policy framework that can both boost living standards and improve the environment for businesses.
(www.ft.com. 01.09.2016. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder a questão.
Patience is needed for Brazil to come good again
Michael Hasenstab
Dr. Michael Hasenstab is executive
vice-president, portfolio manager
and chief investment officer of
Templeton Global Macro
The Olympic Games in Rio drew global interest to Brazil, but the country and the rest of South America has been in sharp focus for investors all year. They have flocked to the region as part of a broader migration into emerging market debt, following record low valuations and the hunt for yield in a low interest rate environment. While investors have been presented with a rarely seen buying opportunity in emerging markets like South America, it is a mistake to regard these countries as a homogenous group.
That leaves the challenge of working out which are the most attractive opportunities – some of our best known investments were not obvious choices.
We have devised a formula to help us evaluate the fundamental strength of different emerging market countries. It scores a country’s current and projected strength on five factors: how well it has learnt the lessons from past crises; the quality of its policy mix; the structural reform being undertaken to boost productivity; the level of domestic demand; and its ability to resist external shocks. The aim is to pick nations that are fundamentally strong but, for one reason or another, are out of favour with investors. It can take time for the market to catch up to reality. But if you are a long-term investor – and we are certainly in that camp – you have the luxury of being able to wait.
Brazil, for example, is known as a vulnerable market due to the commodities downturn, the ongoing corruption crisis and ensuing political turmoil, but our work suggests to us that it is poised for a potentially significant rebound in the long term. Its current score is low, but its projected future score tells a different story.
We believe the country has learnt the lessons from the most recent crisis, which brought home the importance of having a sustainable fiscal policy. It has already adopted a flexible exchange rate, has strong foreign exchange reserves and has limited short-term debt. This is also reflected in the country’s improving resilience to external shocks, with a reliance on commodities, at 60 per cent of exports, being the largest remaining negative.
It is perhaps no surprise, given Brazil’s deep recession and political instability, that there is much work required in terms of improving policy mix, making structural reforms and boosting domestic demand. However, there are signs things are being turned around, with monetary policy already being tightened aggressively to bring inflation expectations back under control, and the previously excessive levels of governmentsubsidised lending being cut. Once political stability returns, the government will be empowered to do even more.
Work on structural reform should accelerate too, as Brazil’s middle class has made it clear it wants greater transparency and an economic policy framework that can both boost living standards and improve the environment for businesses.
(www.ft.com. 01.09.2016. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder a questão.
Patience is needed for Brazil to come good again
Michael Hasenstab
Dr. Michael Hasenstab is executive
vice-president, portfolio manager
and chief investment officer of
Templeton Global Macro
The Olympic Games in Rio drew global interest to Brazil, but the country and the rest of South America has been in sharp focus for investors all year. They have flocked to the region as part of a broader migration into emerging market debt, following record low valuations and the hunt for yield in a low interest rate environment. While investors have been presented with a rarely seen buying opportunity in emerging markets like South America, it is a mistake to regard these countries as a homogenous group.
That leaves the challenge of working out which are the most attractive opportunities – some of our best known investments were not obvious choices.
We have devised a formula to help us evaluate the fundamental strength of different emerging market countries. It scores a country’s current and projected strength on five factors: how well it has learnt the lessons from past crises; the quality of its policy mix; the structural reform being undertaken to boost productivity; the level of domestic demand; and its ability to resist external shocks. The aim is to pick nations that are fundamentally strong but, for one reason or another, are out of favour with investors. It can take time for the market to catch up to reality. But if you are a long-term investor – and we are certainly in that camp – you have the luxury of being able to wait.
Brazil, for example, is known as a vulnerable market due to the commodities downturn, the ongoing corruption crisis and ensuing political turmoil, but our work suggests to us that it is poised for a potentially significant rebound in the long term. Its current score is low, but its projected future score tells a different story.
We believe the country has learnt the lessons from the most recent crisis, which brought home the importance of having a sustainable fiscal policy. It has already adopted a flexible exchange rate, has strong foreign exchange reserves and has limited short-term debt. This is also reflected in the country’s improving resilience to external shocks, with a reliance on commodities, at 60 per cent of exports, being the largest remaining negative.
It is perhaps no surprise, given Brazil’s deep recession and political instability, that there is much work required in terms of improving policy mix, making structural reforms and boosting domestic demand. However, there are signs things are being turned around, with monetary policy already being tightened aggressively to bring inflation expectations back under control, and the previously excessive levels of governmentsubsidised lending being cut. Once political stability returns, the government will be empowered to do even more.
Work on structural reform should accelerate too, as Brazil’s middle class has made it clear it wants greater transparency and an economic policy framework that can both boost living standards and improve the environment for businesses.
(www.ft.com. 01.09.2016. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder a questão.
Patience is needed for Brazil to come good again
Michael Hasenstab
Dr. Michael Hasenstab is executive
vice-president, portfolio manager
and chief investment officer of
Templeton Global Macro
The Olympic Games in Rio drew global interest to Brazil, but the country and the rest of South America has been in sharp focus for investors all year. They have flocked to the region as part of a broader migration into emerging market debt, following record low valuations and the hunt for yield in a low interest rate environment. While investors have been presented with a rarely seen buying opportunity in emerging markets like South America, it is a mistake to regard these countries as a homogenous group.
That leaves the challenge of working out which are the most attractive opportunities – some of our best known investments were not obvious choices.
We have devised a formula to help us evaluate the fundamental strength of different emerging market countries. It scores a country’s current and projected strength on five factors: how well it has learnt the lessons from past crises; the quality of its policy mix; the structural reform being undertaken to boost productivity; the level of domestic demand; and its ability to resist external shocks. The aim is to pick nations that are fundamentally strong but, for one reason or another, are out of favour with investors. It can take time for the market to catch up to reality. But if you are a long-term investor – and we are certainly in that camp – you have the luxury of being able to wait.
Brazil, for example, is known as a vulnerable market due to the commodities downturn, the ongoing corruption crisis and ensuing political turmoil, but our work suggests to us that it is poised for a potentially significant rebound in the long term. Its current score is low, but its projected future score tells a different story.
We believe the country has learnt the lessons from the most recent crisis, which brought home the importance of having a sustainable fiscal policy. It has already adopted a flexible exchange rate, has strong foreign exchange reserves and has limited short-term debt. This is also reflected in the country’s improving resilience to external shocks, with a reliance on commodities, at 60 per cent of exports, being the largest remaining negative.
It is perhaps no surprise, given Brazil’s deep recession and political instability, that there is much work required in terms of improving policy mix, making structural reforms and boosting domestic demand. However, there are signs things are being turned around, with monetary policy already being tightened aggressively to bring inflation expectations back under control, and the previously excessive levels of governmentsubsidised lending being cut. Once political stability returns, the government will be empowered to do even more.
Work on structural reform should accelerate too, as Brazil’s middle class has made it clear it wants greater transparency and an economic policy framework that can both boost living standards and improve the environment for businesses.
(www.ft.com. 01.09.2016. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder a questão.
Patience is needed for Brazil to come good again
Michael Hasenstab
Dr. Michael Hasenstab is executive
vice-president, portfolio manager
and chief investment officer of
Templeton Global Macro
The Olympic Games in Rio drew global interest to Brazil, but the country and the rest of South America has been in sharp focus for investors all year. They have flocked to the region as part of a broader migration into emerging market debt, following record low valuations and the hunt for yield in a low interest rate environment. While investors have been presented with a rarely seen buying opportunity in emerging markets like South America, it is a mistake to regard these countries as a homogenous group.
That leaves the challenge of working out which are the most attractive opportunities – some of our best known investments were not obvious choices.
We have devised a formula to help us evaluate the fundamental strength of different emerging market countries. It scores a country’s current and projected strength on five factors: how well it has learnt the lessons from past crises; the quality of its policy mix; the structural reform being undertaken to boost productivity; the level of domestic demand; and its ability to resist external shocks. The aim is to pick nations that are fundamentally strong but, for one reason or another, are out of favour with investors. It can take time for the market to catch up to reality. But if you are a long-term investor – and we are certainly in that camp – you have the luxury of being able to wait.
Brazil, for example, is known as a vulnerable market due to the commodities downturn, the ongoing corruption crisis and ensuing political turmoil, but our work suggests to us that it is poised for a potentially significant rebound in the long term. Its current score is low, but its projected future score tells a different story.
We believe the country has learnt the lessons from the most recent crisis, which brought home the importance of having a sustainable fiscal policy. It has already adopted a flexible exchange rate, has strong foreign exchange reserves and has limited short-term debt. This is also reflected in the country’s improving resilience to external shocks, with a reliance on commodities, at 60 per cent of exports, being the largest remaining negative.
It is perhaps no surprise, given Brazil’s deep recession and political instability, that there is much work required in terms of improving policy mix, making structural reforms and boosting domestic demand. However, there are signs things are being turned around, with monetary policy already being tightened aggressively to bring inflation expectations back under control, and the previously excessive levels of governmentsubsidised lending being cut. Once political stability returns, the government will be empowered to do even more.
Work on structural reform should accelerate too, as Brazil’s middle class has made it clear it wants greater transparency and an economic policy framework that can both boost living standards and improve the environment for businesses.
(www.ft.com. 01.09.2016. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder a questão.
Economists Reduce Outlook for Brazil Inflation – Survey
By Rogerio Jelmayer – Dow Jones Business News

Shutterstock phot
Economists reduced their inflation estimate in Brazil for this year and next year, according to the central bank’s weekly survey of 100 economists published Monday. Economists now expect inflation, as measured by the consumer-price index, to be 7.25% this year, compared with last week’s estimate of 7.34%, the survey showed.
Economists estimate Brazil’s gross domestic product is
likely to contract 3.14% this year, compared with an expected
contraction of 3.15% in last week’s survey. Last year, Brazil’s
economy contracted 3.80%, according to the country’s
statistical bureau, IBGE. For 2017, economists reduced their
view of GDP growth to 1.30% from 1.36%.
(www.nasdaq.com. 26.06.2016. Adaptado)
Leia o texto para responder a questão.
Economists Reduce Outlook for Brazil Inflation – Survey
By Rogerio Jelmayer – Dow Jones Business News

Shutterstock phot
Economists reduced their inflation estimate in Brazil for this year and next year, according to the central bank’s weekly survey of 100 economists published Monday. Economists now expect inflation, as measured by the consumer-price index, to be 7.25% this year, compared with last week’s estimate of 7.34%, the survey showed.
Economists estimate Brazil’s gross domestic product is
likely to contract 3.14% this year, compared with an expected
contraction of 3.15% in last week’s survey. Last year, Brazil’s
economy contracted 3.80%, according to the country’s
statistical bureau, IBGE. For 2017, economists reduced their
view of GDP growth to 1.30% from 1.36%.
(www.nasdaq.com. 26.06.2016. Adaptado)
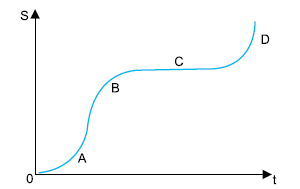
Analisando o gráfico, é correto concluir que
 (http://goo.gl/oeSWn)
(http://goo.gl/oeSWn) Considere uma nave que possa voar a uma velocidade igual a 80% da velocidade da luz e cuja viagem dure 9 anos para nós, observadores localizados na Terra. Para um astronauta no interior dessa nave, tal viagem duraria cerca de
 (Wikipedia)
(Wikipedia) Considere que, antes do salto, o centro de massa desse atleta estava a 1,0 m do solo; no ponto mais alto do salto, seu corpo estava totalmente na horizontal e ali sua velocidade era de 2 ·√5 m/s; a aceleração da gravidade é 10 m/s2; e não houve interferências passivas. Para atingir a altura recorde,ele deve ter partido do solo a uma velocidade inicial, em m/s, de
 (https://goo.gl/9aeM0K.com)
(https://goo.gl/9aeM0K.com) Se ela for acelerada por um piloto de 100 kg, à plena potência, a partir do repouso e por uma pista retilínea e horizontal, a velocidade de 144 km/h será atingida em, aproximadamente,
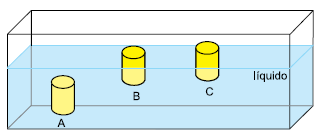
Sobre essa situação, é correto afirmar que