Questões de Concurso
Sobre interpretação de texto | reading comprehension em inglês
Foram encontradas 10.012 questões


I. But why are people so obsessed about it? II. But why are people obsessed by it? III. But why people obsess over it?
Which ones are correct?


What is blended learning and how does it work?
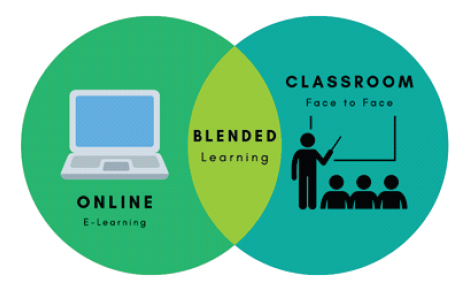

What is blended learning and how does it work?


TEXT IV

(Available at: https://www.teachthought.com/learning/what-is-competency-based-learning/ Accessed on October 22 , 2019).
TEXT IV

(Available at: https://www.teachthought.com/learning/what-is-competency-based-learning/ Accessed on October 22 , 2019).
TEXT III

(Available at: https://www.glasbergen.com/gallery-search/?tag=learning. Accessed on October 26 , 2019)
TEXT II
Another Brick In The Wall (Pink Floyd)
We don't need no education
We don't need no thought control
No dark sarcasm in the classroom
Teachers, leave them kids alone
Hey! Teacher! Leave them kids alone!
All in all, it's just another brick in the wall
All in all, you're just another brick in the wall
(Adapted from: https://www.letras.mus.br/pink-floyd/64541/. Accessed on October 31 , 2019).
TEXT I-
ENEM and the Language Policy forEnglish in the Brazilian Context
Andrea Barros Carvalho de Oliveira
1.INTRODUCTION
In the present article, I report the results of a doctoral research that focused on the language policy for English in Brazil, considering specifically the role of Exame Nacional do Ensino Médio (hereinafter ENEM) in this policy. Thus, taking into account the sociopolitical aspects of the teaching processes, learning, and use of English as a foreign language, we sought to identify the possible impact of ENEM on the status of English language as a school subject.
ENEM was initially conceived as a final exam to evaluate students at the end of basic education. However, it has been modified over the last few years to work as an entrance examination for public and private universities. In addition, the use of this exam in several governmental programs aimed at higher education access was preponderant to make it a high stakes exam in the educational scenario.
According to the literature on language examination exams, especially those considered to be high stakes, are seen as an intrinsically political activity (ALDERSON; BANERJEE, 2001). These exams can be used as educational policy tools as well as to promote a specific language related to local language policy objectives.
The theoretical conception of Language Policy (hereinafter LP) adopted in this investigation refers to Shohamy (2006). This author postulates that, although there is an official LP established in legislation and official documents, it is also necessary to consider the existence of a “real” LP, or “de facto” LP, which is put into practice through mechanisms, resources such as traffic signs, rules and laws related to official bodies, language exams, among others. Besides mechanisms, the beliefs or representations about the language that are shared in the community ought to be considered as well. The importance of mechanisms is that they reveal the true aims of LPas established by the government for a specific language, which are not always explicit in Brazilian law.
The research, the results of which are presented in this article, covered the three components of Shohamy’s theoretical model, namely: legislation, mechanisms (in this case, an exam, ENEM), and representations or beliefs about language. To obtain a sample of representations about English language, interviews were conducted with the students from an ENEM preparatory course for university entrance, with two teachers of English and two coordinators from public schools.
In the present article, I begin with a review of the expanded conception of LPelaborated by Shohamy, as it is the theoretical basis of this research. Second, I analyze some documents and laws regarding English teaching in Brazil. In addition to these documents, the English questions of ENEM (2016) were taken in consideration. Finally, I present an overview of the representations about English language that emerged from the interviews which constituted the empirical data of my doctoral thesis.
ALDERSON, J. C; BANERJEE, J. Language Testing and Assessment. Language Testing, [S.l.], n. 34, 2001, p. 213-236.
SHOHAMY, E. Language Policy: Hidden Agendas and New Approaches. London; New York: Routledge, 2006. (Adapted from: OLIVEIRA, A.B.C. ENEM and the Language Policy for English in the Brazilian Context. In.: Revista Brasileira de Linguística Aplicada. vol.19 no.2 th Belo Horizonte Apr./June 2019 Available at: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1984-63982019000200361 Accessed on October 20 , 2019)
TEXT I-
ENEM and the Language Policy forEnglish in the Brazilian Context
Andrea Barros Carvalho de Oliveira
1.INTRODUCTION
In the present article, I report the results of a doctoral research that focused on the language policy for English in Brazil, considering specifically the role of Exame Nacional do Ensino Médio (hereinafter ENEM) in this policy. Thus, taking into account the sociopolitical aspects of the teaching processes, learning, and use of English as a foreign language, we sought to identify the possible impact of ENEM on the status of English language as a school subject.
ENEM was initially conceived as a final exam to evaluate students at the end of basic education. However, it has been modified over the last few years to work as an entrance examination for public and private universities. In addition, the use of this exam in several governmental programs aimed at higher education access was preponderant to make it a high stakes exam in the educational scenario.
According to the literature on language examination exams, especially those considered to be high stakes, are seen as an intrinsically political activity (ALDERSON; BANERJEE, 2001). These exams can be used as educational policy tools as well as to promote a specific language related to local language policy objectives.
The theoretical conception of Language Policy (hereinafter LP) adopted in this investigation refers to Shohamy (2006). This author postulates that, although there is an official LP established in legislation and official documents, it is also necessary to consider the existence of a “real” LP, or “de facto” LP, which is put into practice through mechanisms, resources such as traffic signs, rules and laws related to official bodies, language exams, among others. Besides mechanisms, the beliefs or representations about the language that are shared in the community ought to be considered as well. The importance of mechanisms is that they reveal the true aims of LPas established by the government for a specific language, which are not always explicit in Brazilian law.
The research, the results of which are presented in this article, covered the three components of Shohamy’s theoretical model, namely: legislation, mechanisms (in this case, an exam, ENEM), and representations or beliefs about language. To obtain a sample of representations about English language, interviews were conducted with the students from an ENEM preparatory course for university entrance, with two teachers of English and two coordinators from public schools.
In the present article, I begin with a review of the expanded conception of LPelaborated by Shohamy, as it is the theoretical basis of this research. Second, I analyze some documents and laws regarding English teaching in Brazil. In addition to these documents, the English questions of ENEM (2016) were taken in consideration. Finally, I present an overview of the representations about English language that emerged from the interviews which constituted the empirical data of my doctoral thesis.
ALDERSON, J. C; BANERJEE, J. Language Testing and Assessment. Language Testing, [S.l.], n. 34, 2001, p. 213-236.
SHOHAMY, E. Language Policy: Hidden Agendas and New Approaches. London; New York: Routledge, 2006. (Adapted from: OLIVEIRA, A.B.C. ENEM and the Language Policy for English in the Brazilian Context. In.: Revista Brasileira de Linguística Aplicada. vol.19 no.2 th Belo Horizonte Apr./June 2019 Available at: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1984-63982019000200361 Accessed on October 20 , 2019)
CRIMINALS HAVE SMALLER BRAIN SIZE, SAYS STUDY
A new study has found that antisocial people are more likely to have smaller areas of their brain. Researchers said criminals' brains had a different structure to the brains of people who followed the law. The study is published in the journal "Lancet Psychiatry". Researchers used data from 672 people born in 1972-73. They looked at records of the people's antisocial behaviour between the ages of seven and 26. At the age of 45, the researchers scanned the people's brains. Eighty of the people had a history of criminal and antisocial behaviour from being early teenagers. Researchers found that the areas of the brain linked to emotions, motivation and behaviour control were smaller in the long-term criminals' brains.
Professor Terrie Moffitt, a co-author of the research, said the research could help doctors understand what is behind long-term antisocial behaviour. She said the antisocial people in the study may have behaved badly because of their brain structure. She said: "They are actually operating under some [disability] at the level of the brain." She added that because of this, we needed to care for these people in a kinder way. Lead author Dr Christina Carlisi said: "Differences in brain structure might make it difficult for people to develop social skills. This may prevent them from engaging in antisocial behaviour. These people could benefit from more support throughout their lives."
Available on: https://breakingnewsenglish.com/2002/200221-brain-size.html Accessed on: March, 20th 2020.
For the question use the poem below:
Eating Poetry
(Mark Strand)
Available at: https://www.poetryfoundation.org/poems/52959/eating-poetry Accessed on December 30th, 2019.
About the poem use TRUE (T) or FALSE (F):
( ) Describes a speaker who is literally eating poetry.
( )The most important aspect to consider in understanding this poem is the metaphor behind the act of eating a poem.
( ) The action of eating poetry is for the poet something that makes him happy.
( ) Strand uses short sentences and highlights one of the most common types of simple English sentences: subject, verb, object.
Respectively, the order is:
“...Australia amid a heatwave...” The underlined word means:
The correct sentences are:
The text below is the introduction from a book on sports.
SPORTSWRITING
Offices and bars are full of casual obscenity, but most British newspapers are ... well, not necessarily careful about language, but careful about bad words anyway. The phrase 'family newspaper' is an ineluctable part of our lives. Newspapers are not in the business of giving gratuitous offence. It is a limitation of newspaper writing, and one everybody in the business, whether writing or reading, understands and accepts. There are many other necessary limitations, and most of these concern time and space.
Newspapers have dominated sportswriting in Britain for years, and have produced their own totem figures and doyens. But ten years ago, a new player entered the game. This was the phenomenon of men's magazines; monthly magazines for men that had actual words in them - words for actually reading. GQ was the pioneer and, in my totally unbiased opinion as the long-term author of the magazine's sports column, it leads the way still, leaving the rest panting distantly in its wake.
Sport, is of course, a blindingly obvious subject for a men's magazine - but it could not be tacked in a blindingly obvious way. Certainly, one of the first things GQ was able to offer was a new way of writing about sport, but this was not so much a cunning plan as a necessity. The magazine was doomed, as it were, to offer a whole new range of freedoms to its sportwriters. Heady and rather alarming freedoms. Freedom of vocabulary was simply the most obvious one and, inevitably, it appealed to the schoolboy within us. But space and time were the others, and these possibilities meant that the craft of sportswriting had to be reinvented.
Unlike newspapers, a magazine can offer a decent length of time to research and to write. These are, you would think, luxuries - especially to those of us who are often required to read an 800-word match report over the telephone the instant the final whistle has gone. Such a discipline is nerve-racking, but as long as you can get it done at all, you have done a good job. No one expects a masterpiece under such circumstances. In some ways the ferocious restrictions make the job easier. But a long magazine deadline gives you the disconcerting and agoraphobic freedom to research, to write, to think.
To write a piece for a newspaper, at about a quarter of the massive GQ length, you require a single thought. The best method is to find a really good idea, and then to pursue it remorselessly to the end, where ideally you make a nice joke and bale out stylishly. If it is an interview piece, you look for a few good quotes, and if you get them, that's your piece written for you. For a longer piece, you must seek the non-obvious. This is a good quality in the best of newspaper writing, but an absolute essential for any writer who hopes to complete the terrifying amount of words that GQ requires. If you write for GQ you are condemned to try and join the best. There is no other way.
GQ is not restricted by the same conventions of reader expectation as a newspaper. You need not worry about offending people or alienating them; the whole ethos of the magazine is that readers are there to be challenged. There will be readers who would find some of its pieces offensive or even impossible in a newspaper, or even in a different magazine. But the same readers will read the piece in GQ and find it enthralling.
That is because the magazine is always slightly uncomfortable to be with. It is not like a cosy member of the family, nor even like a friend. It is the strong, self-opinionated person that you can never quite make up your mind whether you like or not. You admire him, but you are slightly uneasy with him. The people around him might not altogether approve of everything he says; some might not care for him at all. But they feel compelled to listen. The self-confidence is too compelling. And just when you think he is beginning to become rather a bore, he surprises you with his genuine intelligence. He makes a broad joke, and then suddenly he is demanding you follow him in the turning of an intellectual somersault.
Source: Adapted from (Pre-2013 Revision) CPE Handbook.
Choose the correct alternative that provides the correct answer for the question: Why were sportswriters for
GQ given new freedoms?
( ) According to Mikhail Bakhtin, textual genres are defined mainly by their social function. ( ) Textual genres are texts that are used for a particular reason in a communicative situation to promote a specific interaction. ( ) As they serve the need to communicate, textual genres are transmuted by presenting new forms from existing ones. The email address, for example, is a variation of the letter's communicative function. ( ) Textual genres define what kind of literature will be read by men and what type will be read by women. ( ) A textual genre is any one of the several linear sequences of elements of some specific kind whose combination constitutes a phonological representation.
Choose the alternative with the correct sequence:


